Turbochargers and Superchargers Karl Lynch
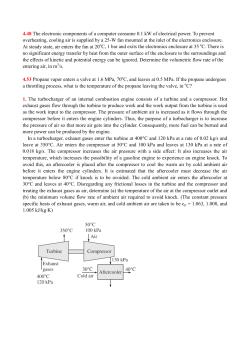
Turbochargers and Superchargers Karl Lynch Increasing Engine Power • There are a few ways to increase engine horsepower: ▫ Larger engine displacement But it’s costly and adds unwanted weight ▫ Nitrous oxide Short duration of increased power ▫ Turbochargers and Superchargers Lightweight, relatively cheap, continuous supply of power Turbocharger Brief History • 1st forced induction patent in 1885 to Gottlieb Daimler • 1st turbocharger patent given in 1905 to Alfred Büchi • Installed on French WW1 fighter planes to limited success • GE installed a turbocharger on a plane in 1918 • Began being used on diesels in the 1920s Forced Induction • All naturally aspirated engines use the down stroke of the piston to create a low pressure area, drawing in the air and fuel mixture into the cylinder • However, most engines cannot inhale the full displacement of the atmospheric-density fuel mixture ▫ This volumetric efficiency varies from engine to engine • Forced induction is when air is forced into the cylinder to increase the volumetric efficiency How turbochargers work • They are used to increase the volumetric efficiency of the engine by increasing the air-fuel mixture entering the cylinder • The turbocharger housing contains a turbine and centrifugal air compressor on the same shaft • The exhaust leaving cylinder spins turbine • The compressor forces more air into the cylinder ▫ Compressor typically increases pressure by 6-8 psi, but it can be greater • Increased air pressure allows more fuel to burn • The compressed air is usually cooled to allow more air in the cylinder and to prevent knocking • The increase of 6-8 psi increases horsepower by 3040% Turbocharger vs. Supercharger • Both operate on the same principle ▫ Both use forced induction to increase engine performance • Supercharger use belts and chains that are directly connected to the engine to drive the compressor ▫ Results in the engine needing to withstand the stresses of generating the increased power Supercharger • Turbochargers do not place a direct mechanical load on the engine ▫ Allows the turbocharger to produce more power that the supercharger without stronger hardware in the engine Turbocharger connected to engine • However, the increased power using a supercharger is immediate, while a turbocharger’s power increase contains a lag ▫ The lag is because the turbine in the turbocharger needs to increase in speed using the exhaust ▫ Lag can be reduced by reducing the moment of inertia of the turbine Cut-away view Turbine is on the left, compressor on the right Applications • High altitudes: ▫ Aircraft and automobiles ▫ Air pressure is less at high altitudes, so there is less air in naturally aspirated engines ▫ This leads to less power ▫ Turbochargers will increase the pressure, reducing altitude induced power loss • Increasing power ▫ Used on heavy trucks, ships, etc. ▫ Much better power:weight ratio than just putting in a larger engine Summary • Turbochargers are one of the best ways to increase power ▫ They’re lighter and cost less than a larger engine ▫ Do not place as much stress on the engine as a supercharger does ▫ They actually help to increase efficiency Twin turbochargers on an engine
© Copyright 2025