International Business Conference (IBC) 2015
College of Business Administration
International Business Conference
(IBC) 2015
Diversity and Sustainability: Challenges
and Opportunities of Global Business
12 – 14 May 2015
Ajman University of Science & Technology
United Arab Emirates
PROCEEDINGS
Edited By:
Dr. Lilian Gheyathaldin Taher, Dean
Dr. Mohamed Naim Chaker, Head - Dept. of Finance
Dr. Akinola Olatunde Fadahunsi, Professor of Marketing
Dr. Mohd Ariff Bin Kasim, Assistant Professor of Accounting
His Highness Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan
President of the United Arab Emirates
His Highness Sheikh Humaid Bin Rashid Al Nuaimi
Member of the Supreme Council – Ruler of Ajman
Chairman of Ajman University Board of Trustees
Dean Welcome Note
Dear Respected Scholars:
It is my great pleasure to welcome you to the International Business Conference
(IBC) 2015 at Ajman University of Science and Technology (AUST).
I am honored today to express, on behalf of the all colleagues and students, great
heartfelt gratitude to His Highness Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the UAE
President, for his wise leadership and support to higher education which makes UAE
a special place for young people to live in.
I also wish to express my utmost appreciation to His Highness Sheikh Humaid
bin Rashid Al-Nuaimi, Member of the Supreme Council of United Arab Emirates,
Ruler of Ajman and the Chairman of AUST Board of Trustees, thanking him for his
keenness to support Ajman University of Science and Technology and his patronage
to the IBC 2015.
On behalf of my colleagues, I would like to express my deepest gratitude to Mr.
Osama Salman, Vice President of AUST for his enthusiasm and incontrovertible
support.
I further would like to extend my appreciation to Professor Norman Wright, Dean-Woodbury School of
Business at Utah Valley University, Mr. IVano Iannelli, CEO of Dubai Carbon Centre of Excellence Dubai, UAE,
Mr. Burke Franklin, Founder, and CEO of JIAN and Inventor of BizPlanBuilder, and Mr. Christian Farioli,
Sales and Marketing Director of Al Habtoor in Dubai for their unprecedented and novel contributions.
I also should acknowledge the arduous work and assiduous efforts of the Business Administration College
faculty, staff and Heads of Departments for organizing this conference. I am truly humbled and thrilled for
their exuberance, academic contribution, and ineffable cooperation.
Ajman University of Science and Technology is committed to diversity in all its forms. Diversity in general
creates bridges for the community posterity. The bridges between determinative past and pursuing prospect
of the people’s pellucid future. It is overwhelming to see the diversity of age, race, education, nationality
and life experience that coexist at Ajman University of Science and Technology.
We have probed diversity on the university campus, and it has unequivocally divulged the sumptuousness
and splendiferous of its promise. For instance, the College of Business Administration has attracted welldiversified and qualified academic staff from around the world, and they have obtained their doctorate
degrees from reputable institutions in the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Western
Europe and Asia. Furthermore, we have built a diverse student body that genuinely reflects the inhabitant
community of the United Arab Emirates. In essence, diversity leads to diffusion of new ideas, innovations,
and ex novo methodologies.
Recent research has indicated that greater degrees of difference in social settings correlate with creativity,
and groups that demonstrate a multifarious range of perspectives and notions usually outperform groups
of homogeneous--minded experts at solving challenging and fuzzy problems by imperishable margins. On
the other hand, sustainability is about self-preservation, understanding, and basically doing more with less.
We also have an ever growing population and, people demand the same quality of life as some of us have
experienced. Hence, we ought to be able to do more with less vis-a-vis managing the existing resources
more efficiently, and certainly embrace the opportunity that sustainability presents. All in all, it can be
concluded that sustainability coupled with diversity is the most astonishing catalyst for innovation and
economic prosperity of all nations.
Last but not least, I wish to express my felicitations and commendations for your continued prosperity and
prodigious progress. I am confident that with our collegial and variegated academic engagements we can meet
the high expectations of the citizens we serve in our respective communities.
Dr. Lilian Gheyathaldin Salih
Dean and Associate Professor of Accounting
College of Business Administration
Ajman University of Science and Technology
Ajman, United Arab Emirates
IBC2015
Proceedings
i
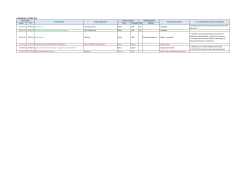
List of Abstracts
No.
1
2
Title
Author (s)
A Comparative Study of Diversity Policies and Practices in UAE Public
and Private Sector Organizations
A Study on Information & Communication Technology (ICT) Externalities
With Reference to India
Page
Samia Kargwell
Akin Fadahunsi
Sujata Rao
Lakshmikanth Hari
Abdulhaq. A.
Suliman
Raghad Hashim
Godwin Fancis
Tamer Elewa2
Hanan Taleb
Noorah Tayab
Tariq Bhatti
1
2
3
A Survey of Dental Students on Quality of Preclinical Operative Dentistry
Course at College of Dentistry Ajman University, UAE
4
Achieving Green Organization Practices: Case Study of Product
Packaging Factory in the UAE
5
An Empirical Analysis of Adopters of social Technologies in the UAE
6
An Evaluation of Industry Expectations from Academia: An Empirical
Study in the Context of Contemporary Post-Graduate Graduate
Management Education in Kolkata, India
Indranil Bose
Sredharran Sampath
6
7
Assessing the Entrepreneurial Attitude and Intentions of the Newly
Enrolled University Students in the UAE. – The Case of Ajman University
of Science & Technology
Abdullah Ismail
7
8
Awareness about Ergonomics among Human Resource Professionals
Lakshmikanth Hari
Wricha Mishra
Sujata Rao
8
9
Capital Formation in India- Why Are We Lagging Behind?
Charles Suresh David
10
Change Continuum - From a Discrete Perspective
Shanthi Rajan
10
11
College Student Retention in the Southern Region of the United States:
An Institutional Perspective
Joseph G.M. Lutta
11
12
Consumers' Perceptions of Banks Country of Origins in the UAE
13
Corporate Governance and Financing Decision of Small Growing Firms in
Sudan
14
Cultural Drivers of Family Business Succession
15
Data Integrity Between Government and Non-Government Schools in
the UAE: Findings and Issues
16
Determinants of the Adoption of Transactional E-Governmental for
Public Service Provision
17
Determining the Relationship between Strategic Thinking and Brand
Orientation among Sales and Business Managers
18
Digital Culture in a High Political Risk Environment: Cross Cultural
Studies in Middle Eastern Countries
ii
Mohammad Naim
Chaker
Sayed Abbas Ahmed
Neimat Abdalla
Ibrahim
3
4
5
9
12
13
Rima Bizri
14
Rima Shishakly
Mervyn Misajon
15
AbdelRahman A.
AbdelRahman
Hosein Vazifehdust
Ali Sadeghi
Ahmad Motaghi Rad
Tarek Taha Kandil
Emadeddin Ahmed
Abu El Enain
16
17
18
No.
19
20
Title
Author (s)
Does Positive Relationship Exist Between Bank Mergers and Asset
Turnover? Facts From Nigeria
Electricity Consumption and Growth in the UAE, Estimation and
Forecast, 1990 – 2025
Page
Hassan Yusuf
19
Abdulkarim Ali
Dahan
20
21
Emotional Intelligence as a predictor of Job Performance – A Study
Among the Sales Persons of the UAE
Rhoda Alexander
Aneesa Ahmed
21
22
Entrepreneurial Orientation and Firm Performance: The Mediating
Effect of the Leadership Style
Ali Yassin Sheikh
22
23
Evaluation of Sudanese Telecommunication Companies in Corporate
Social Responsibility (CSR) Performance: Case Study of Sudatel Company
(CSR) Performance
Ahmed Zain Elabdin
Ahmed
23
24
Growth Strategies of Gruma
José G. VargasHernández
Tarek Taha Kandil
Madiha Hamed
Elmohhamadi Ali
24
25
Higher Educational Electronic Leadership's Impacts on Transforming
Mobile Learning
26
How Diversity Stimulates Organizational Learning in a Complex
Environment
27
Impact of Advertisement on Consumers in Mobile and Laptop Industry
28
Importance of Factors Affecting Destination Image; In the Context of
Dubai Tourism
29
Interest Rate Risk Measurement and Management: An Application of
Income Gap
30
Internationalization of Family Business: A Readiness Scale
Mazen Jaber
30
31
Is Financing Structure of Islamic Financial Institutions Different? A Case
of Modarba Companies of Pakistan
Zulfiqar Ahmed
Bowra
Sarfraz Khan
Ossama Fazal
31
32
Islamic Modes of Finance and its Impact on Reducing Poverty in The
Islamic World: Malaysian Experience Model
Bouhezam Sidahmed
32
33
Knowledge Intensity of Innovation Project: Measurement and
Management Features
Aibek Galymkair
Aziza Zhuparova
33
34
35
Main Challenges of Big Data on Firm Accountancy: New Applications for
Cost and Benefit Analysis
Mediating the Role of Virtual Supply Chain Integration in the Effect of
Traceability on Responsible Automotive Recall
Bocanet, Anca
Anirudh Jhavar
Lajwanti Kishnani
Akshey Aggarwal
Sunitha K Haneef
Aftab Rizvi
Ibrahim Elsiddig
Ahmad
Suja Sarah Thomas
Nancy Ibrahim
Tarek Taha Kandil
Shereen Hassan
Nassar
José G. VargasHernández
MC. César Francisco
Cárdenas Dávila
25
26
27
28
29
34
35
36
Methodological Proposal for the Study of the Impact of Globalization on
Business Strategy of Mexican International Enterprises
37
Observing Coworkers’ Violations and Managers’ Discipline: The Effect of
Violation and Punishment Severity on Coworker Attitudes
Jeff Peterson
37
38
Optimal Control Fuzzy Logic Controller Makes a Naked Vanilla Call
Option Half Naked
Mohd Khoshnevisan
38
iii
36
No.
39
40
41
Title
Author (s)
Quantitative Analysis of Managerial Capabilities and Internationalization
of Manufacturing SMEs – Empirical Evidence from Developing Countries
Social Media Technology Management: Digital Marketing
Communication as A Sustainable Competitive Adv. for Business
Stock Market Reaction to the Political Terrorism: An Event Study
Approach
Page
Nana Osei-Bonsu
39
Nouri beyrouti
40
Sarfraz Khan
Zafar Ahmed
Farah Liyana
Bustaman
Abdul Razak Ibrahim
Fakhrul Zaman
Abdullah
Joseph Affholter
George Puia
Mark Potts
Mazen Jaber
Anthony Bowrin
41
42
Stress as a Mediating Effects of Personality and Job Satisfaction: Service
Experience in Malaysia
43
Sustainable Governance and Internationalization in Family Enterprises
44
Sustainable Urbanization through Information Systems: Establishing
Holistic Frameworks
Chadi Aoun
44
45
Testing the Micro Structure Theory of Liquidity: A Case of Karachi Stock
Exchange (KSE) of Pakistan
Safdar Husain Tahir
Hazoor Muhammad
Sabir
Nadeem Nazir
45
46
The Applications of the Economics of New & Renewable Energy: A Case
Study of Egypt
Karim Badr El-Din
Attia Hassanien
46
47
The Dilemma of Markets and Resources Paradox : The Way Forward
Gulzar A AkoorShahul
47
48
The Effective Adoption of ICT-Enabled Services in Educational
Institutions – Key Issues and Policy Implications
Abdullah Ismail
48
49
The Evaluation of Talent Management Practices in Software Industry
AbdulQuddus
Mohammed
49
50
The Impact of Job Stress on Job Satisfaction and Organizational
Commitment In the Banking Sector In Pakistan
Masood Ahmed
50
51
The Impact of Social Media on Brand loyalty: Implications for Hospitality
Industry in the UAE.
Samia Kargwell
Mohammad Q.
Siddiqui
51
52
The Impact of Social Media Marketing on Customer Loyalty
Abdullah AlSagheer
52
53
The Influence of Entrepreneurial Leadership Style on Human Resources
Training Quality
Basma Waleed
Kashmoola
Tarek Taha Kandil
53
Azeemuddin Subhani
54
Tarek El Kassar
55
Mohd Ariff Bin Kasim
Siti Rosmaini Binti
Mohd Hanafi
56
54
55
56
The Islamic Financial System
-Foundations and Viability
The Learning Organization Concept: A Study on Private Companies in
Dubai
The Outlook of the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Roles of
Internal Auditors: A Critical Review
iv
42
43
No.
Title
Author (s)
Rizwan Ahmad
Divakaran Liginlal
Robert Meeds
Kashif Saleem
Monika Shrestha
Kichan Nam
Sojung Lucia Kim
Thompson S.H. Teo
Page
57
The Richness of Metaphor and the Metaphor of Richness In Arabic
Ecommerce
58
Time Varying Conditional correlation Between Stock and Bond Returns:
Evidence From Civets Nations
59
Understanding of IS Audit Process
with Success Factors
60
Writing Effective Business E-mail
Amany Al Sabbagh
61
أثر التطور التكنولوجي على االقتصاد األردني
)2013-1980( دراسة حالة
Samer Abdelhadi
Ali Al Assaf
61
62
التدابير غير الجمركية وأثرها على نمو وتطور صادرات الدول النامية
Salim Moualdi
62
63
ذكـــاء األعمــال و هندســة
القـــرار في المنظــمة
Hamidouche
M'hamed
63
v
57
58
59
60
A Comparative Study of Diversity Policies and Practices in UAE Public and Private Sector
Organizations.
Samia Kargwell
Akin Fadahunsi
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE.
Abstract
Organizational effectiveness is typically a function of a rational utilization of human
resources, the levels of motivation and the degree of job satisfaction that employees
experience in the organization. One outcome of deficiencies in any of these listed areas
relates to challenges with employee recruitment and retention. Prior studies have identified
recruitment and retention of skilled staff as an area of growing concern for organizations in
the UAE due in part to employee dissatisfaction with the management of diversity-related
issues. As such, the present study seeks to examine the policies and practices through which
UAE managers deal with diversity issues, especially in the prevailing context in which the
UAE is evidently a high net-migration country, with organizations that therefore operate in
an environment in which they are continually brought into contact with an array of facets of
diversity. Specifically, the study examines key points of parity and difference between UAE
public and private sector organizations with a view to making more focused analysis and
recommendations to policy planners on the management of workplace diversity matters.
The field methodology includes the administration of 150 self-completion questionnaires to
a sample of HR managers in the public sector, and a further 150 self-completion
questionnaires to HR managers in the private sector. The preliminary conclusions support
the relative lack of awareness of several diversity matters and suggest a link to subsequent
performance inefficiencies in those organizations.
1
A Study on Information & Communication Technology (ICT) Externalities with Reference
to India
Sujata Rao
Lakshmikanth Hari
K.J. Somaiya Institute of Management Studies and Research (SIMSR), Mumbai, India.
Abstract
Successful adoption and utilization of ICTs in various sectors is crucial for development of
countries. For a developing country like India, adopting ICTs provides huge benefits as well
as challenges. Interestingly, IT sector contributes more than 7% of India’s GDP. The growth
of IT sector combined with increasing population & GDP may become burden on
environment. In view of above, the present study aims to study the externalities of ICTs with
respect to India. It mainly concentrates on negative externalities on environment and
provides measures for reducing these externalities.
2
A Survey of Dental Students on Quality of Preclinical Operative
Abdulhaq.A. Suliman
Raghad Hashim
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
Course evaluations are an integral part of course development in dental education. Purpose:
The purpose of the survey was to investigate the students’ satisfaction with respect to
various aspects of the pre-clinical operative dentistry course at Ajman University of Science
and Technology – College of Dentistry in United Arab Emirates. A questionnaire was
distributed among 148 dental students in the third year. The questions were in respect to
quality of the course, facility and materials provided, staff evaluation and self-assessment of
competence by the students. Results: The response rate for this survey was 83.1%. Among
the participating students 76.4% thought that the duration of the lab component of the
course was just right while 19.5% of the students felt that it was too short, still some
student thought it is too long (4.1%). As part of the evaluation, the students were asked if
they thought the faculty members were well prepared regarding the course content for
each session, 89.4% of the students answered ‘Yes’ while 4.9% of the students said ‘No’ and
the remaining were not sure. 30.9% of the students reported that they found the
information given to them by different faculty members were inconsistent while 49.9% of
the students did not share this opinion. The study shows that course evaluations may prove
useful to improving the quality of education provided to the students. Taking the current
finding in consideration might have a positive impact on preclinical-operative course in the
future.
3
Achieving Green Organization Practices: Case Study of Product Packaging Factory in the
UAE
Godwin Fancis
Tamer Elewa
Hanan Taleb
British University in Dubai, UAE
Abstract
With the growing evidence that the phenomenon of climate change is caused by
greenhouse gas emissions it has become necessary to take some immediate action to avoid
dangerous consequences for future generations. Green business organizations are growing
in UAE market and the country witnesses many green shifting especially after realizing the
huge energy consumption in the region. Consequently, the aim of this paper is to achieve
green organization practices in the UAE. Questionnaire was distributed among many
stakeholders including the employees, managers and consumers. Open-ended questions
were also included to identify barriers and discuss potential enablers to implement green
organizational practices. After carrying out in-depth qualitative and quantitative analysis,
the research revealed many interesting findings including that there is a strong potential of
shifting to green business not only in the packaging organizations but many organizations in
the UAE market. As a final remark, whilst this paper mainly focuses on UAE business
practice, it could be argued that many of the research outcomes are relevant to several
countries especially those with similar social and extreme environmental and organizational
behavior conditions as United Arab Emirates.
4
An Empirical Analysis of Adopters of Social Technologies in the UAE
Noorah Tayab
Tariq Bhatti
College of Business Sciences, Zayed University, Dubai, UAE.
Abstract
This article presents a study on adoption of social technologies by teenagers in the UAE.
Most Emiratis have adopted new technologies such as computer, Internet mobile phone
and smart phone are nearly heading towards 100% or more penetration rate. The number
of Internet users in MENA grew from 16.0 million in 2003 to 85.5 million in 2008. Their share
of the world's total users rose from 2.0% to 5.2% over the same period. In the last decade
(2000-2010), the number of Internet users in MENA increased by 1,800%, which is four
times greater than the rest of the world. (Internet World Statistics, 2010) Of that, the United
Arab Emirates accounts for 6% of the Middle East's internet users. With over 3.7 million
users in the country, internet penetration is at 75%, the second highest in the region to
Bahrain. Middle Eastern internet users spend more time online than watching television,
where email and social networking remain the most popular activities. Still when looking
into more detail, there are notable differences in the adoption rate of social technologies.
We develop and test an extended version of the technology acceptance model (TAM) to
explain these differences. We found that age, education, income and race are associated
differentially with beliefs about the social technologies, and that these beliefs influence a
consumer's attitude toward and use of the social technologies. We also provide key insights
for both managers and policymakers.
5
An Evaluation of Industry Expectations from Academia: An Empirical Study in the Context
of Contemporary Post-Graduate Management Education in Kolkata, India
Indranil Bose
Sredharran Sampath
Westford School of Management, Sharjah, UAE
Abstract
The study attempts to explore gap between industry expectations and quality of recent
management graduates. The main objective of the study is to create an active interface
between industry and academia. This paper also studies the gap between academic output
and industrial requirement in current scenario. It seeks to find out the relevance of
academic output (from higher academic institutions, named as Recent Management
Graduates-REGs) to the industry and its underlying determinants. Quantitative and
descriptive research has been done, based on data collected through structured
questionnaire, from recently passed 70 management post-graduates based in Kolkata, India.
Standard statistical tools have been adopted at different stages of research. The study
reveals the 12 factors which directly contribute in maintaining the quality of RMGs. The
study also suggests some recommendations which may be helpful to find out the solution of
this problem.
6
Assessing the Entrepreneurial Attitude and Intentions of Newly Enrolled University
Students in the UAE
Abdullah Ismail
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
The amount of entrepreneurial activities carried out by individuals is related to the presence
of a supporting entrepreneurial context, and with having a positive entrepreneurial attitude
and intention. The subject of entrepreneurial attitude and intention has been widely
researched previously within various contexts using different analytical frameworks. This
study aims at inquiring about those stimulating factors that may potentially trigger the
entrepreneurial drive, attitude and intention. The study also discusses those major
challenges and risks which are perceived by the respondents as bottlenecks and barriers to
their entrepreneurial journey i.e. in their efforts to turn their entrepreneurial intentions into
actions, and thus to move ahead from being a “latent entrepreneur” to a “nascent
entrepreneur”. The newly enrolled university students in the college of business
administration at Ajman University of Science & Technology have been chosen as a case
study. Mixed method research has been employed to conduct this study on the selected
sample size of 121 students that include both males and females almost in equal proportion.
This research offers some interesting results and findings thought to be informative and
relevant for young entrepreneurs, policymakers, universities, financial institutions, industrial
players and academic researchers alike.
7
Awareness about Ergonomics among Human Resource Professionals
Lakshmikanth Hari
Wricha Mishra
Sujata Rao
K.J. Somaiya Inst. of Mgt. Studies and Research (SIMSR), Mumbai,
National Institute of Industrial Engineering (NITIE), Mumbai, India.
Abstract
Ergonomics aims to fit the task to the person. Human resource (HR) professionals are often
recruited with an intention to recruit other professionals for the organizations who best fit
to the task. It is essential for HR professionals to take into account ergonomic considerations
in the organization. In view of the above, a study was conducted on thirty one HR
professionals. The objective of the study was to assess the levels of awareness of
ergonomics among HR professionals. Only HR Professionals having a minimum work
experience of two years were included in the study. A questionnaire was administered to
them which comprised questions on demographic details, knowledge about work station
design, safety considerations and occupational disorders.
8
Capital Formation in India – Why Are We Lagging Behind?
Charles Suresh David
Madras Christian College, Chennai, India.
Abstract
Capital Formation is the back-bone of development of a country. It is very difficult to ensure
a steady and sustainable growth of an economy without well developed and structured
norms of capital formation. Capital formation is defined as “transfer of savings from
individuals or households to the business sector; directly through investments or indirectly
through bank deposits which are loaned out to the firms”. The conceptual aspect of this
definition categorically mentions that the entire edifice of economic development of a
country rests upon the strong foundation of capital formation. The term ‘Capital’ means
‘Gross Capital’ or ‘Gross Fixed Capital’. Gross fixed capital formation (formerly known as
gross domestic fixed investment) includes land improvements (fences, ditches, drains, and
so on); plant, machinery, and equipment purchases; and the construction of roads, railways,
and the like, including schools, offices, hospitals, private residential dwellings, and
commercial and industrial buildings. India had been showing steady increase in the process
of capital formation since independence. But of late, India has shown downward trend in
capital formation, notwithstanding the sustainable growth of capital formation by her
neighbouring countries like China, Pakistan and Bangladesh. The researcher, based on the
empirical evidence of factorial influence, will summarize the findings and highlight the
suggestions for growth of capital formation.
9
Change Continuum – From a Discrete Perspective
Shanthi Rajan
University of Bolton, Ras Al Khaimah, UAE
Abstract
Organizations grapple with change and growth in a highly competitive and customer driven
globalised environment. If organizations want to create and sustain a competitive
advantage, it is insufficient to have just the ability and flexibility to compete globally, but
also have a self reliant workforce with a vision of inventing new markets and an inside
outside focus approach as well. This can be attained only with a radical shift of focus
coupled with an organization’s ability to develop and explore the skills of its employees by
continuous innovation and improvement. Leaders, therefore, before setting out any change
initiative, should understand the emotional vulnerability of individuals. The nature of
organizational change has to be understood as a stream of process in terms of recognizing
the need for change, the forces that lead and resist change, change readiness state and
most importantly managing change. This report has 2 parts: the first part focuses on the
conceptual aspects of change and the second part gives a perspective on how British
Airways (BA) over a span of 2 decades (two phases) under the supervision of strong leaders
with good leadership skills and vision transformed the company from a state of slumber to
the world’s most favorite and profitable airline. Surveying what caused the dent from the
state of inertia to surviving the damage by means of a radical transformation and
modification of its deep structure is the focus of this report.
10
College Student Retention in the Southern Region of the United States: An Institutional
Perspective
Joseph G.M. Lutta
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
The primary purpose of this study was to find out factors affecting college student retention
in the United States. Higher education institutions all over the world are under pressure to
reduce the rates of students dropping out of college (Crosling, Thomas, & Heagney, 2008;
Thomas & Quinn, 2003). In this study, a total of 16 independent variables were collected
from admissions and student aid databases of a research-extensive university in the
Southern region of the United States of America and transferred to a computerized,
recording form that served as the research instrument. Using stepwise multiple discriminant
analysis, a significant model was identified which accurately explained the college retention
status. The model correctly classified 86.7% of the cases, which was a 39.3% improvement
over chance. The results of the study showed that many non-retained students entered the
study institution with very good high school academic records. Further studies are
recommended to increase the percentage of correctly classified cases by integrating these
variables with others to further explain retention status. Additional research is also required
to determine why students with strong academic credentials leave college before their third
year. It was also recommended that more funding be sought to increase the number of
scholarships for incoming students.
11
Consumers' Perceptions of Banks Country of Origins in the UAE
Mohammad Naim Chaker
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
The overarching objective of this research paper is to undertake an analysis of the Country
of Origin (COO) influence on banking services. The paper assesses consumers’ perceptions
and selection of banking services in the UAE. This study is based on a survey exercise
conducted across UAE. This study is important as it has great implications for decision
making and the literature focusing on banking services in the Middle East. In recent years,
however, there have been a number of changes in the global banking industry which have
had significant effects on the development of this rapidly growing sector of the economy in
most countries of the world (Pustay 1992). The continuous relationship between banks and
their customers has become the benchmark for banking industry standard. Despite the
importance of the research findings of the present study, the study has some limitations. A
quantitative technique was used in this research, limiting the richness of information that
could have been obtained from some qualitative methods of data collection. This might
have reduced the validity of some of the questions. Due to financial and time limitations,
the sample was drawn from only UAE consumers. If other states of the Gulf (Bahrain, Oman,
Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and Kuwait) had been included, the information gathered would have
been more comprehensive, and more generalizable. Another important limitation was
related to the length of the questionnaire. Finally, it may be observed that in a cross-cultural
environment, country of origin has an important role in influencing consumers’ decisions
about banking services.
12
Corporate Governance and Financing Decision of Small Growing Firms in Sudan
Sayed Abbas Ahmed
Neimat Abdalla Ibrahim
Al Ghurair University, UAE
Prince Sultan University, KSA
Abstract
Corporate governance issue has gained significant attention in management research
especially among large listed firms. However, research has seldom been conducted on small
and medium sized firms. Therefore, the objective of this paper is to investigate the link
between corporate governance and financing decision and its impact on firm performance
across a sample of 25 small growing firms operated in Sudan. Specifically, the paper
examines how ownership structure and corporate control affect financing decisions through
a theoretical framework that links owner profile, financial planning, control characteristics
and practice. The empirical findings show that managers are concerned with cash flow and
profitability to maintain high internal sourcing of finance, which ultimately, affects financing
decisions. The centralization of decision in the hand of the owners gives clear evidence that
financing decisions are influenced by their knowledge, experience and typology. The
existence of the family at the higher echelon of the hierarchy affects the way in which the
business is operated, managed and controlled. These empirical findings provide
confirmation that ownership structure and degree of financial control affect financing
decisions and have an impact on firm performance.
13
Cultural Drivers of Family Business Succession
Rima Bizri
Rafik Hariri University, Lebanon
Abstract
Despite the ever increasing research on this topic, succession in the family business remains
one of the hottest areas of study in this field. This paper explores the influence of
individualism as a cultural driver of succession in the family business. It seeks to explain how
individualism drives both incumbent and successors to engage in the succession process,
thus leading to interesting and thought-provoking findings. The qualitative approach was
used in this study where multiple-case analysis was performed. Semi-structured interviews
were conducted with successors of 12 family firms, following the purposive sampling
technique, and generating data that were recorded and appropriately analyzed. In a
collectivistic country like Lebanon, it was expected that the collectivistic cultural dimension
would have a significant influence on the succession decision in the family firm. Contrary to
expectations, the findings of this study suggest that though the collectivistic dimension was
the main driver behind the succession decision in larger formalized firms, the
“Individualistic” dimension had the greater influence on succession in family firms that were
small in size and low in formalization. Despite the magnitude of research on family firm
succession, this study is distinct as it seeks to offer a novel perspective of the influence of
individualism as a cultural driver of succession. This perspective contributes to a deeper
understanding of succession as related to size and degree of formalization of the family
business.
14
Data Integrity between Government and Non-Government Schools in the UAE: Findings
and Issues
Rima Shishakly
Mervyn Misajon
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
Education is similar to other different businesses and industries where achieving system and
data integrity is essential, in order to achieve automated management for the educational
sector, efficient data flow and processing management, and delivery of successful solutions
to the different stakeholders. The Ministry of Education (MOE) in United Arab Emirates
(UAE) has adopted “Education 2020,” a series of five-year plans designed to introduce
advanced education management information systems, improve data processing, data
quality and improve innovative skills. As part of this program, in 2010 the MOE implemented
several information systems in order to achieve a fully computerized educational
management. A student information system (SIS) was implemented by MOE to be used in
the private international schools in UAE to enter students’ data and students’ examination
marks. The authors in 2014 conducted a study focusing on the EMIS in the public sectors,
utilization, and data integrity. This paper will now focus on the private sectors specifically,
to investigate the data integrity problems and issues, between SIS the system implemented
by MOE, and the systems used by private international schools in UAE. Taking samples from
both public and private school systems, the study clarifies the possibility of data integrity
and makes recommendations regarding the challenges that private schools are confronted
with.
15
Determinants of the Adoption of Transactional E-Governmental for Public Service
Provision
AbdelRahman A. AbdelRahman
Al-Ghurair University, Dubai Academic City, Dubai, UAE
Abstract
The study examines the impact of bureaucratic corruption, economic freedom, and egovernment readiness on the probability of having in place transactional e-government or
Web-enabled transactions for public services. The study uses a logistic regression model and
aggregate data on a cross-section of countries to investigate this relationship. The principal
finding of the study is that a high level of a country’s corruption reduces the probability of
having transactional e-government whereas the presence of economic freedom and high
levels of e-government readiness enhance such probability.
16
Determining the Relationship between Strategic Thinking and Brand Orientation among
Sales and Business Managers
Hosein Vazifehdust
Ali Sadeghi
Ahmad Motaghi Rad
Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran.
Abstract
In today’s changing context, understanding the conditions and predicting the main
processes are the only ways through which the organizations can improve their
competitiveness. Such a thing can be achieved solely by managers with high levels of
strategic thinking. The purpose of the present research is Determining the Relationship
between Strategic Thinking and Brand Orientation. The research hypothesis was as follows:
There is a significant relationship between strategic thinking and brand orientation. The
findings of the study showed a significant relationship between strategic thinking and brand
orientation among Sales and Business Managers.
17
Digital Culture in a High Political Risk Environment: Cross Cultural Study in Middle Eastern
Countries
Tarek Taha Kandil
Emadeddin Ahmed Abu El Enain
The University of Modern Sciences, Dubai, UAE.
Abstract
The Arab Peoples’ revolutions crises that took place in the first quarter of 2011 in some Arab
countries have raised the challenges that Middle Eastern countries have in the last three
decades. Such a turbulent environment has revealed the curtain on the political and
enterprise environments. The importance of the present comes from the role of the
Electronic performance orientation leadership style that the research measures in the three
Arab countries: Egypt Iraq and Saudi Arabia. The political risk reports put the Arab countries
as high risk environment, which affect the Arabian decision makers in the private and public
sectors in those countries. The present research sheds light on the importance of Electronic
performance orientation leadership style that considers as the “future key of concept of a
better performing state” Ritz, 2008.P 1). The present research has carried out in three Arab
countries Egypt, Iraq and Saudi Arabia. The research takes all the Arabian Middle managers
of the public and private sectors’ companies in the main capitals and big cities of the
selected countries, those managers are the research sample. The research used a semi
structural questionnaire that has been used to measure the GLOBE leadership styles
designed by Hair et al., (1998) in the literature review. The questionnaires were distributed
in the three countries from December 2010 to May 2011. The research uses the structural
equation model analysis technique with Amos 18 in order to measuring the Multi-group
confirmatory factor analysis.
18
Does Positive Relationship Exist Between Bank Mergers and Asset Turnover? Facts from
Nigeria
Hassan Yusuf
American University of Nigeria, Yola, Nigeria.
Abstract
This study examines the nature of relationship that exists between merger and acquisition
(M&A) and banks’ Asset Turnover following M&As that took place during the 2004/2005
consolidation in the Nigerian banking industry. The study compared the mean Asset
Turnover (AT) ratios of the banks before and after M&A. Using data extracted from the
annual financial reports of the banks, mean AT ratios were computed. Chow Test for
Structural Break, paired sample and Independent sample t-tests were performed on the
mean AT ratios to gauge the impact of M&A. Our findings suggest that there is no positive
relationship between M&A and banks’ Asset Turnover as either the AT ratios of the banks
deteriorated or at best, did not improve significantly. Furthermore, we obtained evidence
that suggests that the stand-alone banks outperformed the merged banks in terms of AT
following M&As in Nigeria. Therefore the study concludes that bank M&As in Nigeria, as in
most parts of the world, have fallen short of the popular expectations and pre-merger
promises of improved performance. The study thus recommends that future restructuring
policy should not be prompted by the thinking that increment in sheer size will have
synergistic impact on banks’ financial performance, rather than this “one size fits all” policy
of consolidation by recapitalization, regulatory authorities may refocus attention on creating
banks that are geographically specialized based on their individual capital wherewithal, and
managerial acumen.
19
Electricity Consumption and Growth in the UAE, Estimation and Forecast, 1990 – 2025
Abdulkarim Ali Dahan
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE.
Abstract
This paper examines the essence of the distributed lag (stock of adjustment) hypotheses
both theoretically and empirically. As one of the main objectives of this study is to construct
and estimate a simple econometric model for electricity consumption in United Arab
Emirates, the model must be simple because of severe data limitations on useful economic
variables. The format of this paper is as follows : Section 2 is a historical review of electricity
consumption and growth in UAE. Section 3 reviews the theory of stock adjustment and
formulates a total aggregate electricity consumption function. Section 4 includes the
estimation of the total electricity function for the period 1990 – 2014, and empirical
estimates of elasticities. Finally, the estimated model will be used to forecast electricity in
the Emirates for the coming ten years, up to 2025, and the paper ends with a summary of
findings and conclusion.
20
Emotional Intelligence as a predictor of Job Performance – A Study among the Sales
Persons of the UAE
Rhoda Alexander
Aneesa Ahmed
BIT-Ranchi Offshore Campus, Ras Al Khaimah, UAE
Abstract
The main purpose of this study is to empirically test emotional intelligence as a predictor of
job performance among the sales persons in the automotive industry of UAE. Data was
collected from 200 sales persons using a questionnaire comprising standardized scales.
Emotional Intelligence is hypothesized as positively related to job performance. The effect
of demographic variables like age and total years of sales experience are also explored.
Simple linear regression is carried out to predict the relationship between Emotional
Intelligence and Job Performance. Multiple regressions are also carried out to find the
relationship between the various sub-dimensions of Emotional Intelligence and Job
Performance. Data analysis shows a statistically significant positive correlation between
emotional intelligence and sales performance. Hence it is concluded that emotional
intelligence is a predictor of sales performance.
21
Entrepreneurial Orientation and Firm Performance: The Mediating Effect of the
Leadership Style
Ali Yassin Sheikh
SIMAD University, Somalia
Abstract
This study investigates the mediating role of leadership style on entrepreneurial orientation
and firm performance relationship in telecommunication industry in Somalia. The objective
of the study was to explore the relationship between entrepreneurial orientation
dimensions and firm performance furthermore to identify the mediating effect of leadership
style. The data were collected in October 2014 and a total of 104 directors responded to the
study from four telecommunication in south central Somalia. The data was analyzed using
SPSS version 16.0 to answer research objectives and test its hypotheses. The findings
indicate that innovation (β=.228, p=.020), pro-activeness (=.232, p=.027) and risk taking
(β=.306, p=.001) were found to have statistically significant and positive effect on firm
performance. When the mediating variable was introduced; the standardized beta of the
relationship between innovation and firm performance was reduced from .228 to .191; and
between risk taking and firm performance however, it is still significant. It means that
leadership style partially mediates these relationships. On the other hand, the relationship
between pro-activeness and firm performance was fully mediated by leadership style since
the standardized beta was reduced from .232 to .117, which is not significant.
Research scope and implications are further discussed.
22
Future
Evaluation of Sudanese Telecommunication Companies in Corporate Social Responsibility
(CSR) Performance: Case Study of Sudatel Company (CSR) Performance
Ahmed Zain Elabdin Ahmed
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Fujairah, UAE.
Abstract
Corporate Social Responsibility has received a lot of debate in last decades, from the
economic responsibility to generate profits, to the discretionary responsibility to meet extra
activities that society finds desirable. Companies are under pressure from the stakeholders
to engage in the line of social, environmental, and economical responsibilities. To date, no
research has been conducted using a dataset from the telecommunication industry in the
developing countries. Hence the main purpose of this paper is to investigate the strategic
perspectives of CSR in Sudan Telecommunication Company (Sudatel). In doing so this paper
would seek to understand if the concept of CSR programs are featured in the company’s
culture and strategic plans or if the managements of the company are highly committed to
CSR programs. Telecommunication companies are expanding in economical size; considered
as the largest industry in the world in terms of employment, the fastest growth area in
business. There are many social and economic benefits and opportunities that can be
created through investment in the telecommunication infrastructure, which have the
potential to enhance sustainable development, especially for developing countries. To be
able to investigate this problem, qualitative case study methodology has been used to
collect and analyze the data.
23
Growth Strategies of Gruma
José G. Vargas-Hernández
Rosa Penélope Mares Galindo
Universidad de Guadalajara, Mexico.
Abstract
This article touches the strategy that has led the company Gruma to be one of the best in
Mexico and worldwide, currently their main strategies have made to reach new markets
across alliances, in 2012 and 2013 Gruma has been recognized by the Great place to Work
Institute as one of the best companies to work for, given that the aim of this article is to find
the reason why Gruma has been second consecutive first. Dare of theories explain the
results of Gruma, in order to achieve that other companies can learn the strategies currently
Gruma performed not only in Mexico, but also globally.
24
Higher Educational Electronic Leadership’s Impacts on Transforming Mobile Learning
Tarek Taha Kandil
Madiha Hamed Elmohhamadi Ali
The University of Modern Sciences, Dubai, UAE.
Abstract
The electronic leadership style is one of the most important changes in the higher education
system. In the Arab world, higher education institutions have begun to restructuring
improvement aimed at putting their universities in the world wide picture in terms of the
quality of educational services provided. However, students perceive services quality to still
need greater reliability. The present paper investigates the extent to which electronic
leadership styles enhance the reliability of the education services quality in three main
Arabian counties – Egypt, Iraq and Saudi Arabia – which witnessed in the last decade
reasonable improvement in the higher institutional structures and technology but they did
not raise their reliability level to consider their universities as one of the five hundred higher
institutions all over the world. The present research will use quantitative method for data
collection and analysis to answer the research question. Multi-group structure equation
model will be the research analysis technique that will be used in the data analysis. The
research sample size consists of two sample groups: University educators and students in
the three countries. Cross-validation test will be used in order to make the comparison
analysis between the three countries.
25
How Diversity Stimulates Organizational Learning in a Complex Environment
Bocanet, Anca
University of Modern Science, Dubai, UAE
Abstract
Employees’ diversity has been acknowledged as a key factor in individual and organizational
learning across the industries. This paper analyses the effect of diversity on organizational
learning by manipulating organizational turnover rates, introducing organizational change
and employees’ socialization methods. The organizational learning is happening by engaging
in both exploration and exploitation activities and diversity is a stimulator in this process.
While the theme of learning being influenced by diversity is a prominent subject in the
literature, how learning is being influenced by diversity in a complex environment it is still a
concept under investigation. The methodology used is agent-based model to investigate
interactions of different agents and NK modeling to represent the complexity of a business
environment. After simulating different levels of diversity in different organizational
contexts, it was found that complexity brings a constant negative impact on the
organizational learning and high rates of diversity are not efficient in uncertain
environments. Because of the uncertainty of the business environment, it is very difficult to
establish learning rules in order to cope with the constant increasing complexity. However,
by maintaining diversity via a prolonged socialization, individuals provide the exploration that
allows the knowledge found in the organization to improve, thereby increasing the potential
gains to other members (i.e., exploitation), result which is being constant with Tivnan, 2007,
p.98. Best performances are achieved when the organizational memory addapts very fast to
the best practices in organization and individuals are able to preserve some of their initial
diversity. So for low and moderate levels of complexity, a balance between exploration and
exploitation is possible to be determined. For high levels of complexity, system’s
performances are strongly affected by randomness.
26
Impact of Advertisement on Consumers in Mobile and Laptop Industry
Anirudh Jhavar
Lajwanti Kishnani
Akshey Aggarwal
BITS-Pilani, Dubai, UAE
Abstract
Advertising is a subset of marketing, a form of contact aimed to convince people to buy or
seize each deed alongside respect to the products or the services. In today's globe, firms
don't grasp back in paying millions of dollars on publicizing and marketing. The seeming
reason being that the contest is extremely elevated and every single stable wants to vend its
product and make it a brand. Competent publicizing methods utilized in advertisements
make a globe of difference in sales prospects of a product. Publicizing effectiveness is
measured by the act, the advertisement has frolicked in making the product a real
accomplishment and how well it has related alongside the customers. The intention of this
project is to scrutinize the encounter of brand image and advertisement on customer
behavior in the IT industry, in Dubai. Questionnaire survey was utilized to amass the data. A
sample of questionnaires were amassed and evaluated. Findings display that brand picture
and advertisement have forceful affirmative impact and momentous connection alongside
Customer buying behavior. People discern the brand picture alongside affirmative attitude.
Discovery delineated that teenagers/young adults in Dubai are extra cognizant concerning
their communal rank so they favor brands and advertisement affects their Customer Buying
Deeds positively.
27
Importance of Factors Affecting Destination Image in the Context of Dubai Tourism
Sunitha K Haneef
Aftab Rizvi
Manipal University, Dubai, UAE.
Abstract
One of the important concepts used in understanding tourists' behavior in the tourism
industry is the destination image tourists have towards destination. Developing a
competitive position among tourism destinations is usually accomplished by creating and
transmitting a favorable image to potential tourists in target markets. Destination Image is
formed by many factors. This study will carry out an in-depth literature review to explore
the factors affecting image of the tourism destination and also the study would take
destination image formation into consideration. The study has the following objectives, To
explore various destination image factors related to tourists' holiday experience; to review
tourists' pre visit & post visit destination image formation on these factors; to identify the
importance of factors affecting destination image; in the context of Dubai tourism. The
study will cover the entire Dubai. The study will adopt an approach of observation and
survey to meet the objectives. The method adopted in the study will be exploratory,
descriptive and analytical support with empirical data. This research will definitely be an
important contribution to destination pursuers, place marketers, government agencies and
other stakeholders.
28
Interest Rate Risk Measurement and Management: An Application of Income Gap
Ibrahim Elsiddig Ahmad
Suja Sarah Thomas
Al Ghurair University, Dubai Academic City, Dubai, UAE
Abstract
In an ever-changing environment, banks are exposed to different types of risks such as
market, operational and financial risks. Fluctuation in interest rate is one of the major
financial risks that the banking sector faces. This paper addresses the problem of measuring
and managing interest rate risk in UAE commercial banks. The main objective of the study is
to come up with a suitable measure of interest rate risk, to investigate variations in interest
rate risk prior to, during and subsequent to the financial crisis period, and to suggest
possible methods by which bank managers could manage interest rate risk. The application
of income gap analysis helps to forecast the banks’ financial position and performance. To
achieve the objectives of the study, secondary data have been collected from published
financial statements of the selected banks. Incomer gap analysis model is used to measure
the interest rate risk for the period 2005 to 2012 in order to test two hypotheses: H1: There
is a significant relationship between UAE banks’ profitability and interest rate risk measured
by the gap sensitivity. H2: There is a significant relationship between interest rate risk and
the profitability of banks in the context of the financial crisis. SPSS correlation and
regression techniques have been applied to test the hypotheses. It is found that there is a
significant correlation between income gap and net income of the UAE banking sector. Also
there is a positive and significant correlation between income gap and profitability prior,
during, and post to financial crisis.
29
Internationalization of Family Business: A Readiness Scale
Mazen Jaber
Saginaw Valley State University, Michigan, USA.
Abstract
International business has been dominated by large, multinational enterprises. However,
globalization, combined with advancing information and communications technologies, is
contributing to a growing role in international business for the small and medium
enterprise. First, we examine the role of specific organizational competences, intangible
resources that engender success in the international family businesses. In the literature,
research themes like family business motivation and innovation have been central in
relation to organizational strategy and performance. Current knowledge in this area,
however, is fragmented and incomplete, and what it takes to achieve global readiness, is
not yet clear. In this paper, we provide a new conceptual definition of international family
business readiness (IFBR), which incorporates key firm characteristics or factors expected to
collectively enhance international performance. We also develop a self-report measure of
IFBR and its underlying dimensions and extensively validate that scale. In the first phase, we
conduct in-depth interviews with senior managers at selected family businesses that derive
a substantial proportion of their revenues from international business, as well as firms that
have just started conducting international transactions. Data from these interviews
supplement our literature review and secondary data analysis, and help the authors develop
a number of scales to measure the latent constructs that IFBR includes.
30
Is Financing Structure of Islamic Financial Institutions Different? A Case of Modarba
Companies of Pakistan
Zulfiqar Ahmed Bowra
Sarfraz Khan
Ossama Fazal
University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan.
Abstract
Debate on the determinants of the capital structure has been raging since MM theorem was
proposed in 1958 and various theories and explanations have been proposed as to why
firms prefer certain financing policies over others but no conclusive explanation has been
offered to date. There is also indication that determinants of the capital structure may be
different from sector to sector and various researchers have provided evidence in this
regard even in Pakistan. This study investigates financing structure of Modarba companies
in Pakistan which are prime players in the Islamic financial sector. Specifically, the evidence
whether such companies avoid debt financing and whether determinants of leverage in
such companies are different from the organizations in conventional financial sector is
sought out in this study. Considering data of 28 Modarba companies for the period from
2008 to 2012, this study found that on average, Modarba companies are less levered than
other companies representing conventional financial sector of Pakistan. This is consistent
with the Pecking Order Theory of capital structure which proposed that firms use internal
financing as first choice of financing before debt and external financing options.
31
Islamic Modes of Finance and its Impact on Reducing Poverty in the Islamic World:
Malaysian Experience Model
Bouhezam Sidahmed
University of Mascara, Algeria
Abstract
The Islamic finance and economy is one of the most important themes that began to impose
its presence on both academic and professional domains, researchers and specialists in
economic and financial fields indicated, in particular, after the economic and financial
repeated crises at the beginning of the 21st century. The eradication and exclusion of
poverty is on the top of the list of Millennium objectives development. Moreover, many of
policies and strategies were set to combat this phenomenon to reduce the number of poor
people in the world by half by the year 2015. Through this study, the theoretical side was
tackled as a first step. In this part, we dealt with the main theories that explained the
phenomenon of poverty as well as the international and local policies and strategies in
Islamic countries that used to combat and minimize it. We then talk about Islamic finance
especially Islamic finance modes including old widespread versions the books of Fiqh and
Hadith as well as the new one that has been issuing fatwas on their availability by Fiqh
Councils and Centers for Research in Islamic Economics as an Islamic Fiqh. In addition, we
tried to link the application of Islamic finance modes within the framework of Islamic
finance and combat poverty in Islamic countries by demonstrating the scientific and
practical efficiency of Islamic finance to reducing poverty rates in the Islamic world.
32
Knowledge Intensity of Innovation Project: Measurement and Management Features
Aibek Galymkair
Aziza Zhuparova
Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, Almaty, Kazakhstan
Abstract
It is widely known that in a very general form any innovation project can be considered as a
complex system of interdependent and interrelated by resources, terms and performer
sections aimed at achieving specific goals (tasks) on the development of new technologies,
new product or service. In this case, the specific features of innovation are its length,
expensiveness and high uncertainty. This is due to the fact that any innovation project from
the creation of new ideas to its full completion passes through a certain number of
succeeding steps of its development, which forms the project life cycle. Length of the
project life cycle is significantly influenced by the innovation field, and also the adopted
system of work organization. As a rule, the life cycle of innovation project begins with basic
research and provides applied and development activities. It is followed by a stage of
mastering of a new product: testing and preparation of production, after which the next
steps are commercial production and realization of new products. Nature of innovation at
each stage has its own specific features, which are very important for the manager, as the
current stage determines tasks and activities of the manager, and also affects his methods
and tools.
33
Main Challenges of Big Data on Firm Accountancy: New Applications for Cost and Benefit
Analysis
Nancy Ibrahim
Tarek Taha Kandil
The University of Modern Sciences, Dubai, UAE.
Abstract
The big data trends issued new development in so many fields. In particular, for accountants
and financial professionals, new ways of thinking, application and collaboration techniques,
have been arranged for meet the new financial data quality requirements (Cooke, 2013;
Curtis, 2014; Karaki, 2014; Sari, Anugerah, & Herly, 2014; Tarling, 2013). The present research
raises the following key question for accounting firms and financial data analytics: “What are
the main challenging points need to be addressed in accounting and financial databases?”
Three main challenges are addressed in the present studies. They are: The sheer volumes of
accounting and financial data and data details speed accessing, interpreting data came from
different disciplines (social media channels sides, social networking and bulges webs, and
telecommunication services [Borio, 2014; Brigham & Daves, 2012; Brigham & Ehrhardt, 2013;
Schaltegger & Csutora, 2012]).
34
Mediating the Role of Virtual Supply Chain Integration in the Effect of Traceability on
Responsible Automotive Recall
Shereen Hassan Nassar
The University of Modern Sciences, Dubai, UAE.
Abstract
Globalization, incremental complexity of product design, rigid product safety legislations,
higher consumer demand are the main reasons for automotive recall that can be seen as the
most catastrophic event a firm would face. Complexity shapes supply chain activities has
resulted in a vulnerable automotive supply chain that are prone to errors. Product recall is
one of the major features of vulnerability in automotive supply chains. Automotive recalls
can constitute a significant crunch for manufacturers, and highly undesirable financial
consequences. Managing supply chain risk requires adopting appropriate traceability and
recall plans. Recalls can be seen as additional measure of performance with regard to
automotive design, supply and product chain. Traceability is critical for today’s automotive
supply chain. Traceability can eliminate business failure due to product recalls through
providing the manufacturer with the information about what, where, when, the product is,
within a specified time frame. Here, inter-organizational relationships supported by IT
infrastructure for achieving information visibility and physical traceability among value chain
partners are crucial. This study examines the impact of traceability practices in automotive
supply chain on achieving more responsible recall management through the mediation
effect of both virtual and process supply chain integration.
35
Methodological Proposal for the Study of the Impact of Globalization on Business Strategy
of Mexican International Enterprises
José G. Vargas-Hernández
MC. César Francisco Cárdenas Dávila
University of Guadalajara, Mexico.
Universidad Autónoma de Durango, Mexico.
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to support a methodology proposal for the analysis of the impact on
commercial globalization trend in relation to the internationalization of Mexicans firms. Also
this paper analyzes the advantage the Mexican firms took in the liberalization agenda of the
Mexican government with the multilateralism and regionalism policies. For this purpose, the
statistic descriptive modeling methodology is used to relate grow of the internationalization
of the Mexican firms and the impact in the foreign investment of the main multinationals in
Mexico, forcing them to centering in competitive productive processes and improving their
internal organization, innovation and development.
36
Observing Coworkers’ Violations and Managers’ Discipline: The Effect of Violation and
Punishment Severity on Coworker Attitudes
Jeff Peterson
Utah Valley University, USA.
Abstract
Study one was conducted to determine how a coworker’s perception of how severe a
violation is relates their desire for retributive justice and their attitude towards the violator
and to determine what coworkers feel is the appropriate discipline for a given violation.
Coworkers' desire for retribution and attitudes towards the violator and their assessment of
how severe a punishment should be imposed were found to be directly proportional the
how severe they assessed the violation to be. I also obtained information about what levels
of punishment for various violations are considered appropriate to serve as anchors for
study two. Study two examined how coworkers react when the punishments given by
managers are too mild, appropriate or too severe. A more complex relationship was found
where the severity of the violation interacted with severity of the punishment. One key
finding was that under punishing had a much more pronounced impact on coworkers than
did over punishing which was not significantly different than appropriate punishment.
37
Optimal Control Fuzzy Logic Controller Makes a Naked Vanilla Call Option Half Naked
Mohd Khoshnevisan
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE.
Abstract
Khoshnevisan et al. (2007) posited a fuzzy logic controller (FLC) to minimize the cumulative
hedging error based on the Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model. FLC process was utilized as
the optimum interface between man and machine allowing prioritization between
exploitation and exploration for long term options.
Shipley (2009) extended the FLC
proposed by Khoshnevisan et al. and offered a unique fuzzy controller approach that is
capable of evaluating potential financial losses before adjusting the portfolio of stocks.
However, her model does not address the stochastic nature of trade, and is unable to
minimize the target tracking error of a naked call option, and in particular these frailties are
further exacerbated when the underlying security becomes surpassingly volatile. In this
short paper, I will put forward a de facto relationship between the Canonical Fuzzy
Controller and the Optimal Control Model that is capable of handling fragile naked positions
over the length of the investment horizon with minimum error. The necessary condition for
the dynamic naked call option pay-off is derived from the following optimal control model,
𝜕
𝜕
Georgescu et.al. (1993) normalization tracking error €= (𝜕𝑟 {µRj (r)} = -𝜕𝑟 { µRj+1 (r)}, and the
1
expected payoff of a naked option µ= E [V (ST,T)]=𝜎√2𝜋𝑇
𝑇
Minimize J=∫0 𝑓 (𝑟, 𝑣, 𝑡)𝑑𝑡Subject to
𝑑𝑟
𝑑𝑡
= f(r,v,t)
38
∞
∫0 𝑉(𝑠)
𝑆
1
e {–[ln(s/so)-(r-2 σ2)T]2/2σ2T} ds.
Quantitative Analysis of Managerial Capabilities and Internationalization of
Manufacturing SMEs – Empirical Evidence from Developing Countries
Nana Osei-Bonsu
Ajman University of Science & Technology, Fujairah, UAE.
Abstract
In this study, managerial capabilities: management capacity or size; management expertise;
and management process were quantitatively analyzed through longitudinal methodology
to ascertain their importance as one of the key driving forces or factors of firm’s
international operations. The objective is to examine whether there is a significant
relationship between these factors and the firm’s degree of internationalization. The study
is based on a sample of 500 low, medium and highly-internationalized non-SMEs and SMEs
from five developing countries. The results indicate that there is a significant difference in
the managerial capabilities of SMEs and non-SMEs at all levels of internationalization. For
example, management capacity (size) of SMEs was significantly less than their non-SMEs
counterparts at the moderate and high levels of internationalization. SMEs were
significantly less likely to employ a qualified managers (expertise) or uses professional
training at the low, moderate and high levels of internationalization when compared to nonSMEs. SMEs were also found to be significantly less likely to develop management process,
(international expansion, export and strategic plans, TQM, JIT, QA) when compared to nonSMEs. Overall, the study results suggest that compared to non-SMEs, SMEs grow
internationally with less managerial capability.
39
Social Media Technology Management: Digital Marketing Communication as a Sustainable
Competitive Advantage for Business
Nouri Beyrouti
Lebanese American University, Beirut, Lebanon
Abstract
Social Media have revolutionized the way people communicate and share information
between each other. The consolidation of social media on a daily basis is increasingly
intense. The advantage of the competitiveness comes from a technological introduction and
the constant adaptation along the time to the technological evolution inserted in the
strategy of the organization (Hamel, 2007). But technology alone can hardly provide a
sustainable competitive advantage to business, the value comes from the sphere of
innovation and business structural changes (new business models, process changes…) and
the product / service (Peppard J. & Ward, J., 2004) “the phenomenon has changed social
behaviors and captivated new users, especially in female and senior citizens, who did not
use information technologies as much before pre social media when users were
overwhelming male.” This new century may still be young, but it has already spawned a
sizable brood of daunting manager’s challenges that are markedly different from the ones
that taxes our forebears; the new reality calls for new organizational and managerial
capabilities. Therefore, marketing in social media is not “speak loud” ads to people, but to
lead, to do something that captivate, connect people who are interested in a connection
with a mutual order. This work is a qualitative analysis about the behavior, reactions and
attitudes of individuals to organizations, in order to understand the social factors that
contribute to sustainable competitive advantages of organizations which can support
strategic and future actions.
40
Stock Market Reaction to the Political Terrorism: An Event Study Approach
M. Sarfraz Khan
Zafar Ahmad
University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
Abstract
Pakistan is a developing country which has suffered a lot due to ongoing terrorism over the
last decade. A series of terrorist attacks were also witnessed in Pakistan where main political
figures of Pakistan were targeted or assassinated. A total of 24 terrorism events from 2003
to 2013 were selected; where either political leaders or political parties were targeted.
Subsequent impact of such events was assessed on Karachi Stock Market using Event Study
approach. It was found that Karachi Stock Market responded to terrorist events targeting
main political figures of Pakistan i.e. Pervez Musharraf (President of country that time),
Shaukat Azia (Prime Minister of the county at that time) and Benazir Bhutto (Prime Minister
Candidate in an upcoming election). The study further found that stock markets in Pakistan
do not respond much to the terrorist attacks on political activities (rallies, meetings etc.).
Furthermore, stock markets in Pakistan showed the strongest negative response of
assassination of Benazir Bhutto and after assassination of Benazir Bhutto subsequent
terrorism events even on political leaders lost their significance in Pakistan. This implies that
extreme negative events increase the absorption capacity of stock markets and after a
strong negative event market may only respond to a stronger negative event than
previously witnessed by the market.
41
Stress as a Mediating Effects of Personality and Job Satisfaction: Service Experience in
Malaysia
Farah Liyana Bustaman
Abdul Razak Ibrahim
Fakhrul Zaman Abdullah
Asia e- University, Malaysia
Kolej Poly-Tech MARA, Malaysia
Fahad bin Sultan University, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
To remain competitive, hotels are keen to probe into factors which may result to the ups or
downs of an organization. Being part of the ‘people oriented’ industry, organizations are to
abide by the fact that their performances are measured through customers’ satisfaction.
Due to this, human capital has been identified to be one of the key factors in determining
the success or failure of a business. Hence, it is crucial for organizations to select the right
people with the right personality to represent the organizations. A total of 165 employees
participated in this study around Kuala Lumpur vicinity . Data were collected through selfadministered survey questionnaires. The regressions analyses of this study revealed that
stress mediated the relationship between personality and job satisfaction in which two out
of five personality traits used in this study were found to be partially mediated by stress;
Openness (β=.32, p<0.01) and extroversion (β=.23, p<0.05). Therefore, it could be concluded
that not all personality traits could be affected by stress. From the study, one can have a
greater understanding of to what extent personality types contribute to job stress and how
job satisfaction could also be affected. In addition, this study provides a basis especially for
the hospitality industry researcher to further test the relationships among these constructs.
42
Sustainable Governance and Internationalization in Family Enterprises
Joseph Affholter
George Puia
Mark Potts
Mazen Jaber
Anthony Bowrin
Saginaw Valley State University, Michigan, USA
Abstract
Corporate governance has attracted broad scholarly attention across academic disciplines.
More recently, scholars have begun to study the unique governance challenges of family
enterprises. Governance arrangements in family firms differ from their non-family corporate
counterparts in a variety of ways: family members own and control the firm’s resources,
control the firm’s decision making, have a longer term orientation, and typically exist within
a framework of providing economic opportunity to the next generation of family members.
Decisions within a family firm affect the well-being of the family. Environmental
sustainability has become a major theme in business. While some scholarship focuses upon
the importance of consumer responsibility of government intervention, there is a growing
focus upon the role of business in creating a framework for sustainability in business the
extent to which businesses can sustain their financial performance while also sustaining
environmental
performance.
Our
paper
explores
the
relationship
between
internationalization decisions and sustainable practices in family owned farms. From this,
we develop a generalized model of sustainable governance and decision making in family
enterprises. Implications for future research are explored, as are limitations to the model.
43
Sustainable Urbanization through Information Systems: Establishing Holistic Frameworks
Chadi Aoun
Carnegie Mellon University, Qatar.
Abstract
The rapid increase in global population has contributed to a massive strain on urban areas.
The United Nations estimates that the world will witness an increase in urban populations
from what is now 54% to 66% by 2050, an increase of 2.5 billion people to current
populations (UN 2014).While some antecedents of such strain could be attributed to
economic necessity, many social and environmental impacts have ensued. Concurrently,
advancements in Information Systems witnessed in recent history have provided for an
opportunity to create smarter cities and regions through transforming urban centers to
intelligent and interactive sustainable hubs. This research, currently in its inception, will
explore the potential for smarter cities in the Middle Eastern and Asian regions from a
Green Information Systems perceptive. It aims to extend the scholarly and public discourse
beyond the building of smart infrastructure, to also encompass the enablement of smart
communities, empowered through the use of Green Information Systems to develop
sustainable economic, social and environmental practice. The project also aims to influence
practice, particularly given the growing regional investments in smart city infrastructure.
The findings would contribute towards establishing holistic empirically grounded
frameworks for smarter cities, with knowledge-centric, sociocultural and sociomaterial
underpinnings.
44
Testing the Micro Structure Theory of Liquidity: A Case of Karachi Stock Exchange (KSE) of
Pakistan
Safdar Husain Tahir
Hazoor Muhammad Sabir
Nadeem Nazir
Government College University, Faisalabad, Pakistan.
Abstract
The microstructure theory uses bid-ask spread as strong measure of stock market liquidity.
This theory is based on two important theories (inventory cost and asymmetric information
cost) linked with liquidity. Inventory cost theory indicates cost of inventory as factor of
liquidity while asymmetric information cost theory shows information as strong
determinant of price. Others accepted measures of liquidity are Depth, the cost of trip
Trade, turnover and the Lambda etc. The study aims to estimate the effectiveness of each
liquidity measure by taking a sample of 50 companies for the period of 2009-2014 listed at
Karachi Stock Exchange (KSE) Pakistan. The existence of market model is concluded. Trading
volume, return and asymmetric information cost show strong linkage with stock liquidity.
But the relation between trade volume and stock liquidity is meaningless. Furthermore, the
study indicates no association between volatility and liquidity.
45
The Applications of the Economics of New & Renewable Energy: A Case Study of Egypt
Karim Badr El-Din Attia Hassanien
The British University in Egypt, Cairo, Egypt.
Abstract
This research paper focuses on the application of the environmental economics of new and
renewable energy in this respect in both the developed countries, and in the developing,
then applying this in the case of Egypt. This in fact deals with several pillars that provide for
studying the effect of the application of the environmental resource economics on key
macroeconomic variables related to development and growth. The common acceptable
measures of the impact of new and renewable energy on the process of development and
that of the growth are researched and analyzed. The analysis covers the effect on key
macroeconomic variables. The methodology used in this study provide for a comparative
analysis of the case of the developed countries versus that of the developing countries with
extended application on the case of Egypt. The research work is an original combination of
integrated framework of the analysis of the role of the environmental economics of new
and renewable energy in the process of economic development and growth. The findings of
econometric running of the Egypt’s data explored that there is a very strong correlation with
a Pearson correlation coefficient of degree one (r = 1) between the GDP and the “New &
Renewable Energy Consumption in '000 Current USD” in one hand, and between the GDP
per capita and the “New & Renewable Energy Consumption in '000 Current USD” in the
other hand. The study made set of recommendations concerning the possible means to help
the developing countries.
46
The Dilemma of Markets and Resources Paradox: The Way Forward
Gulzar A Akoor-Shahul
TRANSCO, Abu Dhabi, UAE
Abstract
This report analyses the paradox between markets and resources and suggests the way
forward for strategically challenged companies. When deep pocketed companies, such as
those backed by sovereign wealth funds from the Middle East, can procure almost any
resource, the question arises whether resource restrictions can be considered a hindrance
for success. Can resource rich companies diversify into any market they choose by buying
required resources? Newly procured talents and tangible resources often do not cohere to
form competencies. On the other hand, considering the resource based approach, though
distinct competencies lead to competitive advantages, unless these competencies are
constantly updated, the advantage will be lost. Thus, for an organisation to be successful, it
is not enough to be market driven or resource driven. It has to be 'competence adaptability'
driven.
47
The Effective Adoption of ICT-Enabled Services in Educational Institutions – Key Issues and
Policy Implications
Abdullah Ismail
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
Educational institutions are becoming increasingly aware of the need to fully integrate ICTenabled modern educational services in order to supplement the traditional paradigm of
teaching and learning with more efficient and effective practices. However in achieving their
urge for technology adoption at a quicker pace, they often get overwhelmingly obsessed
with the supply-side dynamics of technology diffusion; thus running a risk of ignoring the
demand-driven dimensions of technology adoption. Due to the poor understanding of the
user-context and not paying enough attention to the inherent challenges faced by the users
in the adoption of new technological services, these institutions may not achieve the
intended results in terms of the desired educational improvements. Such a linear or
“technology-push” approach may lead to a waste of organizational resources, as well as
causing an increasing frustration both among teachers and students. This paper investigates
the patterns of adoption for two ICT-enabled educational services: Learning Management
System and e-books. Mixed method research has been employed to study the adoption
experiences of 150 newly enrolled university students in the UAE. The research findings and
discussions are relevant and beneficial for students, teachers, researchers, administrators of
academic institutions, parents and policy makers.
48
The Evaluation of Talent Management Practices in Software Industry
AbdulQuddus Mohammed
Effat University, KSA
Abstract
Modern organizations are striving to remain competent in the dynamic business
environment (technology growth, increasing customer needs and high competition).
Talented Employee is accepted as a source of sustainable competitive advantage in high
performance organizations like IT Sector. The capability to attract and retain talent is
becoming a key challenge for HR Managers. Competitive market reduces the chance of
recruiting the top talent and increasing the risk of losing the talent to competitors. IT Sector
companies needs to remain market leaders, there is need of mechanism to reduce turnover
and retain the best talent. Managers needs to be competent to reduce increasing turnover
(as employees are leaving their managers, not companies). This research study tries to
investigate talent management practices in major IT companies and its relationship with
employee turnover. The aim of this study is to investigate the prevailing talent management
practices in software industry so that new model can be developed for effective talent
retention and organizational effectiveness. The researcher is planning to adopt qualitative
and quantitative approaches, the data was collected by using questionnaires. The
preliminary results from the study shows that the companies are finding difficulty in finding
the right talent and it’s challenging to retain the talented employees.
49
The Impact of Job Stress on Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment in the
Banking Sector in Pakistan
Masood Ahmed
Government College Township, Lahore, Pakistan.
Abstract
The banking sector plays a cardinal role in Pakistan’s economy. It is a major employer of the
educated workforce in Pakistan. However, employees in this sector undergo potential stress
which yields negative behavioural and work-related attitudes and causes mental and
physical illness. This study aims at investigating the levels of stress confronting the human
resource in banking sector vis-à-vis its impact on two major work-related attitudes i.e. job
satisfaction and organizational commitment. Survey methodology was employed in this
study to collect the data. Through multistage sampling, 300 potential respondents were
located and questionnaires were sent to them. Data collection yielded 225 valid responses
(Response rate: 83%) which were used for the subsequent analysis in the study. The study
found a negative impact of job stress on job satisfaction and on the core dimension of
organizational commitment i.e. affective commitment. However, a positive correlation was
also seen between job stress on the one hand and continuance and normative commitment
on the other. Negative impact of stress on job satisfaction and employee commitment was
also confirmed by some previous studies. The positive correlation between stress and the
two dimensions of organizational commitment (continuance and normative) could be
attributed to unemployment, economic issues and social issues.
50
The Impact of Social Media on Brand loyalty: Implications for Hospitality Industry in the
UAE
Samia Kargwell
Mohammad Q. Siddiqui
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE.
Abstract
The advent of social media and especially the development of web 2.0 has drastically
changed the way marketers approach target markets, influence brand perception, and
ultimately build brand equity. It has been observed that majority of the companies in UAE
are very skeptical about the effect of social media on business. The lack of research on
regional basis is the main motivation factor of this study. The aim of this study is to identify
the effect of this tool on brand loyalty. The scope of the study consists of marketers and
customers of hospitality industry in the UAE. The study further aims to identify current
practices and strategies of the major players of the industry towards social media and its
role in building brand loyalty. The analysis is based on data obtained from the
administration of structured self-completion questionnaire with a sample of 100
management position personnel from 25 chain hotels, and 250 customers of the same
organizations. The study will conceptualize the potential of social media for hospitality
industry to support decision-making and policymaking, for sustainable competitive
advantage through identification of major drivers of brand loyalty. The results will
contribute to the scarce literature on the subject matter.
51
The Impact of Social Media Marketing on Customer Loyalty
Abdullah AlSagheer
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE.
Abstract
The basic purpose of this paper is to research and analyze the impact of social media
marketing on brand loyalty. In this paper, a research study will be conducted in the context
of United States (US) to see whether social media marketing efforts of an organization
enhance its customer loyalty or not in case of premium brands. There are actually two views
regarding impact of social media marketing on customer loyalty. One group of researchers
argue that social media marketing has a positive impact on customer loyalty and it enhances
brand loyalty of an organization. Quantitative research methodology is adopted in this
research study and the researcher engaged 60 participants in a questionnaire survey. The
participants were customers that were active social media users and they were following at
least one premium clothing brands among all famous brands in US such as Ralph Lauren,
Versace, Armani, Dolce and Gabbana “D&G”, Dior, Fendi, Gucci, Hermès, and Louis Vuitton.
It is found that social media marketing efforts such as advantageous offers, relevant
content, brand updates, popular content, and using multiple social media platforms have a
positive impact on customer loyalty in case of premium brands. With social media marketing
efforts, word of mouth communication among the customers would increase who would
make intentional repeat purchases as well as recommend the brand to other customers. It is
concluded that social media marketing has a positive impact on customer loyalty in case of
premium brands. Therefore, those organizations that maximize their social media marketing
efforts are likely to enjoy high customer loyalty.
52
The Influence of Entrepreneurial Leadership Style on Human Resources Training Quality
Basma Waleed Kashmoola
Tarek Taha Kandil
Lily Julienti Abu Bakar
The University of Modern Sciences, Dubai, UAE
Universiti Utara Malaysia
Abstract
The present paper aims to investigate the impacts of the entrepreneurial leadership styles
and behaviours in the Arab world on the training programmes perceived service quality.
There was a gap among previous studies that reveals the impacts of such leadership
behaviours on the perceived services quality of the training programmes (POON , Alhudaithy
2015, Swart, Chisholm et al. 2015, Wang 2015). The present study carries on the field of
construction industry that witnessed a huge progress on technology, structures and human
resources development all over the world, especially in the Arab Gulf area. The research
sample was drawn from all parts of the labour force that had recently been involved in a
training programme. A pilot study was conducted in order to investigate the research
relationships and variables. The questionnaire was distributed in three Arab Gulf countries
between December 2010 and May 2011. The trainees that decide that they got high quality
perceived services quality have significantly agreed that the entrepreneurial leadership
plays a crucial role in delivering a useful message that let them get the most they can do in
the training programme.
53
The Islamic Financial System-Foundations and Viability
Azeemuddin Subhani
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
The Islamic Worldview governing all component systems, including the financial system,
displays a unique unity of the temporal and the spiritual that translates to a day-to-day
religious self-regulation of the financial market. This unique authority is vested in the Islamic
religious scholar, exercised classically from the masjid and contemporeously from the
Shari’ah Board room of the Islamic financial institution. The commercial potential of Islamic
finance has also been recognized by non-Islamic financial institutions in the form of Islamic
Banking Windows. In spite of the impressive strides on the practical front, Islamic
finance/economics is still beset with conceptual research problems typical of a new
academic discipline. Notwithstanding these academic issues, the Islamic financial system is
viable theoretically, operationally, and ethically. Operationally, the financial viability of the
presently employed Islamic financial modes is testified on a global historical basis as having
withstood the test of time. Ethically, the governing principle of Islamic banking is not a
reliance on the conventional exploitative ever-climbing interest rate differentials for
guaranteed profitability of operations, but on the just, fair and ethical principle of realized
profit-sharing both with the provider and the user of the funds. The former Pope had
publicly declared the ethical principles of Islamic banking as the solution of the present
financial crisis.
54
The Learning Organization Concept: A Study on Private Companies in Dubai
M. Tarek El Kassar
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Dubai, UAE.
Abstract
Organizational learning is a principal tool in achieving long-term survival and sustainable
competitive advantage of an enterprise. There is considerable debate regarding the
importance of organizational learning and its impact on the performance and competitive
advantage of the organization. The purpose of this research is to study to which extent the
concepts of the learning organization are present in private companies in Dubai, UAE. In this
study, we used a survey research design, with the organization as the unit of analysis. We
used a convenience sample of private companies based in the Emirate of Dubai, UAE. The
target population was managers at all levels: general management, operations,
administration, human resources, marketing sales, and technical head. We obtained 155 (N)
respondents in the final sample with complete data. Measuring learning orientation has
been framed in the literature by constructs described by Watkins and Marsick (1993; 1999),
Senge (1990) and Garvin (2000). Learning orientation was measured using the scale
originally constructed and validated by Watkins and Marsick (1999), the Dimensions of the
Learning Organization, and Yang, Watkins and Marsick (2004). The data gathered from the
survey was then organised in multiple ways for better analysis and entered into SPSS version
22.0. Based on the findings, we can conclude that Dubai Private Companies embrace to
some extent the Learning Organization Dimensions described by Watkins and Marsick which
we measured using the DLOQ (Dimensions of the Learning Organization Questionnaire).
55
The Outlook of the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Roles of Internal Auditors: A
Critical Review
Mohd Ariff Bin Kasim
Siti Rosmaini Binti Mohd Hanafi
Ajman University of Science and Technology, Ajman, UAE
Abstract
The lesson from corporate failure perhaps provides a new perspective in the new world of
risk faced by organisations. There are studies documenting the connection or links among
risk management, corporate governance and financial results. Empirical researches that
considered the impact of the integrated ERM implementation were very limited. Most
studies on the ERM in the finance literature focused on individual risks such as interest rate
risks, foreign exchange and commodities risks. Some claimed that the ERM should be
studied across a broad range of its activities to reflect the integrated approach of it. This
paper discuss critical issues concerning the ERM, internal auditors’ roles in the ERM’s
implementation, the challenges and the extent to which the ERM could enhance financial
performance. The paper also proposed various critical research questions aim to promote
new research in this area.
56
The Richness of Metaphor and the Metaphor of Richness in
Arabic e-commerce
Rizwan Ahmad
Divakaran Liginlal
Robert Meeds
Qatar University, Qatar.
Carnegie Melon University, Qatar.
Abstract
Until recently the use of metaphorical language was believed to be restricted to literary
genres such as poetry and novel. Many studies have however shown that metaphors are
used widely in businesses to persuade customers and clients in order to enhance sales. Most
of this line of research however is based on data from non-Arabic cultures. Based on a
corpus of Arabic e-commerce, which we created by analyzing data from websites spanning
across 22 Arabic speaking countries, this paper shows that the use of metaphors on Arabic
e-commerce websites is quite pervasive. We examine many different domains such as
fashion, airlines, e-government, and travel. In the domain of restaurant we find the use of
the metaphor in phrases such as “rich taste”, “burger rich in cheese”, “herbs rich in their
natural contents”, etc. The same metaphor is used in the domain of tourism to refer to the
richness of the old Arab tradition in the phrases “the rich Arab exotic tradition”, “rich
buffets”, and
‘rich history of the Arabic musical instrument “alqanoon”’. The use of
‘richness metaphor’ across a number of domains clearly suggests that the metaphor is quite
pervasive and simultaneously it also reflects the way richness metaphor structures the way
Arabs think about many different and often disparate-looking experiences.
57
Time Varying Conditional Correlation between Stock and Bond Returns: Evidence from
Civets Nations
Kashif Saleem
Monika Shrestha
Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland.
Abstract
“When investors are scared, they look for safety. They adjust their portfolios to include
more safe assets and fewer risky assets. As a result, even though there are just as many
stocks and bonds as before, bonds now make up a larger percentage of the value of the
nation’s investment portfolio.” The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, December 1987, No. 4.
Estimation of time varying conditional correlation between asset returns is one of the
essential concerns in financial econometrics in order to ensure a secure financial
environment. It helps to develop confidence in investment decisions, since broad financial
applications are based on it, such as risk management, portfolio diversification and asset
allocation. Keim and Stambaugh (1986) is the first study, which examined correlation
between stock-bond returns and succeed to draw attention towards this topic. After this
work, numerous studies were performed and came up with several outcomes. Further, the
results of empirical analysis in the sub-period reflect mixed (increase and decrease) changes
during crisis and pre crisis periods. Therefore, these results provide evidence for investment
in CIVETS capital market for maximum portfolio diversification benefits. Similarly, the
Asymmetric Dynamic Conditional Correlation (ADCC) GARCH model suggested by Cappiello,
Engle, and Sheppard (2006) discover strong presence of asymmetric volatility effect in the
stock market rather than the bond market.
58
Understanding of IS Audit Process with Success Factors
Kichan Nam
Sojung Lucia Kim
Thompson S.H. Teo
Al Yamamah University, KSA
Chung-Ang University, South Korea
National University of Singapore
Abstract
As the demand for information systems (IS) audit continues to grow, the academic literature has
lagged behind practice due to our inattention to the audit process, its antecedents, and its
outcomes. In light of this gap in the literature, this paper postulates a model of IS audit success by
drawing upon auditor characteristics, such as auditor expertise and auditor role clarity, whose
effects on audit success is mediated by audit process attributes, such as audit responsiveness and
audit compliance. The proposed model was empirically tested using survey data from 254 IS
projects in public sector firms in South Korea. Our results validates the importance of auditor
characteristics and audit process variables in shaping the outcomes of IS audits, while also
illustrating how academic research can contribute incrementally toward building a useful knowledge
base on IS audits and thereby advance future research and practice in this area.
59
Writing Effective Business Email
Amany Al Sabbagh
Emirates Canadian University College, Um al Qwain, UAE.
Abstract
Most of our day-to-day communication, both official and unofficial, is done by email. Email
has become so common and so easy to use that it is easy for us to become careless and to
fall into bad Email habits. This paper will provide some guidelines that will make you look
more professional, make it easier for your correspondents to understand and respond to
your Email, and keep you and your organization out of trouble.
60
أثر التطور التكنولوجي على االقتصاد األردني:
دراسة حالة ()2013-1980
سامر علي عبدالهادي
علي العساف
جامعة البترا ,األردن
الجامعة األردنية ,األردن
الملخص
يعتبر التقدم التكنولوجي ركن أساسي في التنمية االقتصادية ،حيث أن إدخال تكنولوجيا جديدة لن تقلل من تكاليف اإلنتاج
فحسب ،ولكن يمكن أيضا أن تؤدي إلى زيادة كفاءة عمليات اإلنتاج .واألردن يعتبر من تل الدول التي حقق
تقدما في
تكنولوجيا في مختلف القطاعات ،األمر الذي انعكس وبشكل إيجابي على االقتصاد األردني ،وتهدف هذه الدراسة إلى
التعرف على التطور التكنولوجي وأثره على االقتصاد األردني وذل للفترة ( )2013 – 1980والذي يساهم في حل العديد
من المشاكل االقتصادية ،ودوره في تنمية وزيادة حجم اإلنتاج الوطني ولتحقيق االكتفاء الذاتي وتوفير فرص العمل
للعاطلين عنه .وقد تم استخدام أسلوب تصحيح متجهات الخطأ () Vector Error Correction Model (VECMفي
تقدير دالة كوب دوغالس لإلنتاج ،وتوصل
الدراسة إلى ان التكنولوجيا تؤثر بشكل إيجابي على النمو االقتصادي في
األردن بمقدار ( ،)1.107802باإلضافة إلى أن التغير التكنولوجي يكون اكثر كثافة لرأس المال في المدى الطويل.
61
التدابير غير الجمركية وأثرها على نمو وتطور صادرات الدول النامية
موالدي سليم
جامعة الجياللي بونعامة بخميس مليانة ،الجزائر
الملخص
ستظل فكرة حماية السوق المحلي والحد من تدفق السلع والخدمات ألية دولة هي الشغل الشاغل للعديد من بلدان العالم على
اختالف مستويات نموها وتحضرها ،األمر الذي انعكس على اإلجراءات والسياسات التي تهدف إلى منع نفاذ المنتجات
إلى األسواق بالتنامي والتعدد والتغير ،ولعل من أبرز هذه السياسات والنظم الحواجز غير تعريفية التي أصبح شيئا فشيئا
تشكل شواغل رئيسية فيما يتعلق بدخول األسواق وأصبح
تستخدم بشكل كبير كأدوات تجارية تنظيمية خاصة في ظل
انخفاض التعريفات الجمركية ،ويشكل األثر التقييدي التي تمارسه الحواجز غير جمركية على نمو وتطور صادرات
الدول النامية أهم اآلثار التي يمكن أن يمارسها هذا النوع من القيود وهذا ما سنتطرق إليه في هذه الدراسة.
62
ذكـــاء األعمــال وهندســة
القـــرار في المنظــمة
الدكتور حميدوش أمحمد
جامعة الجياللي بونعامة بخميس مليانة (الجزائر)
الملخص
إنّ عملية توثيق المعطيات ينشأ ذاكرة للمنظمة بينما استغاللها ينشأ الذكاء؛ فمع التدفق المتزايد للمعلومات فإنّ سياق
معالجة وإستغالل المعطيات قد تغيّر بالكثير ألنه تم االنتقال من النمط العملياتي الذي يولي الحسابات اإلحصائية إلى نمط
يتطلب الحسابات السريعة التي ال تخص بعض أفراد و إنما متغيّرات و عيّنات عشوائية تظم الماليين من األفراد و التي
تظم كميات هائلة من المعلومات باإلضافة إلى المئات من المتغيّرات و المعطيات ت ّم جمعها بدون دراسة مسبقة تديرها
برمجيات مختلفة لنصبح أمام مشكل إدارة المعطيات الكبيرة حيث أصبح على المحللّين استخراج معلومات أصلية وذات
أهمية لم تكن معروفة سابقا انطالقا من حجم كبير من المعطيات وذلك للتوصل إلى الربط الجديد بين المعطيات
والتوجهات والنماذج .وبالتالي الهدف الجديد من هذه األبحاث هو التوصل إلى نماذج مفسرة للمعطيات والتي قد تم ّكن
من اتخاذ القرارات االستراتيجية بمساعدة تكنولوجيات األعمال.
63
Participants’ Index
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Title
A Comparative Study of Diversity Policies
and Practices in UAE Public and Private
Sector Organizations.
A Study on Information & Communication
Technology (ICT) Externalities With
Reference to India
A Survey of Dental Students on Quality of
Preclinical Operative Dentistry Course at
College of Dentistry Ajman University, UAE
Achieving Green Organization Practices:
Case Study of Product Packaging Factory in
the UAE
An Empirical Analysis of Adopters of Social
Tqechnologies in the UAE
An Evaluation of Industry Expectations from
Academia: An Empirical Study in the Context
of Contemporary Post-Graduate Graduate
Management Education in Kolkata, India
Assessing the Entrepreneurial Attitude and
Intentions of the Newly Enrolled University
Students in the UAE. – The Case of Ajman
University of Science & Technology
Awareness about Ergonomics among Human
Resource Professionals
Capital Formation in India - Why Are We
Lagging Behind?
Change Continuum - From a Discrete
Perspective
College Student Retention in the Southern
Region of the United States: An Institutional
Perspective
Consumers' Perceptions of Banks Country of
Origins in the UAE
Corporate Governance and Financing
Decision of Small Growing Firms in Sudan
Cultural Drivers of Family Business
Succession
Data Integrity Between Government and
Non-Government Schools in the UAE:
Findings and Issues
Determinants of the Adoption of
Transactional E-Governmental for Public
Service Provision
Determining the Relationship between
Strategic Thinking and Brand Orientation
among Sales and Business Managers
Digital Culture in a High Political Risk
Environment: Cross Cultural Studies in
Middle Eastern Countries
Does Positive Relationship Exist Between
Bank Mergers and Asset Turnover? Facts
Author (s)
Samia Kargwell
Akin Fadahunsi
Sujata Rao
Lakshmikanth Hari
Abdulhaq. A. Suliman
Raghad Hashim
Godwin Fancis
Tamer Elewa2
Hanan Taleb
Noorah Tayab
Tariq Bhatti
Email
a.kargewil@ajman.ac.ae
sujata_rao@somaiya.edu
a.suliman@ajman.ac.ae
hanan.taleb@buid.ac.ae
Tariq.Bhatti@zu.ac.ae
Indranil Bose
Sredharran Sampath
sentindranil@gmail.com
Abdullah Ismail
a.qazi@ajman.ac.ae
Lakshmikanth Hari
Wricha Mishra
Sujata Rao
hlkanth@yahoo.com
Charles Suresh David
dr_csd@rediffmail.com
Shanthi Rajan
shanthi_rajan@hotmail.com
Joseph G.M. Lutta
j.lutta@ajman.ac.ae
Mohammad Naim
Chaker
m.chaker@ajman.ac.ae
Sayed Abbas Ahmed
Neimat Abdalla Ibrahim
sayed@agu.ac.ae
Rima Bizri
bizrirm@rhu.edu.lb
Rima Shishakly
Mervyn Misajon
r.shishakly@ajman.ac.ae
AbdelRahman A.
AbdelRahman
abusitah29@yahoo.com
Hosein Vazifehdust
Ali Sadeghi
Ahmad Motaghi Rad
ALI.SADEGHI@srbiau.ac.ir
Tarek Taha Kandil
Emadeddin Ahmed Abu
El Enain
Hassan Yusuf
64
amdrhassanyusuf@gmail.com
No.
20
21
22
23
24
Title
From Nigeria
Electricity Consumption and Growth in the
UAE, Estimation and Forecast, 1990 – 2025
Emotional Intelligence as a predictor of Job
Performance – A Study Among the Sales
Persons of the UAE
Entrepreneurial Orientation and Firm
Performance: The Mediating Effect of the
Leadership Style
Evaluation of Sudanese Telecommunication
Companies in Corporate Social Responsibility
(CSR) Performance: Case Study of Sudatel
Company (CSR) Performance
Growth Strategies of Gruma
25
Higher Educational Electronic Leadership's
Impacts on Transforming Mobile Learning
26
How Diversity Stimulates Organizational
Learning in a Complex Environment
27
Impact of Advertisement on Consumers in
Mobile and Laptop Industry
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
Importance of Factors Affecting Destination
Image; In the Context of Dubai Tourism
Interest Rate Risk Measurement and
Management: An Application of Income Gap
Internationalization of Family Business: A
Readiness Scale
Is Financing Structure of Islamic Financial
Institutions Different? A Case of Modarba
Companies of Pakistan
Islamic Modes of Finance and its Impact on
Reducing Poverty in The Islamic World:
Malaysian Experience Model
Author (s)
Abdulkarim Ali Dahan
a.dahan@ajman.ac.ae
Rhoda Alexander
Aneesa Ahmed
rhoda.philip@biticrak.ae
Ali Yassin Sheikh
profali@simad.edu.so
Ahmed Zain Elabdin
Ahmed
fjac.zainelabdin.a@ajman.ac.ae
José G. VargasHernández
Tarek Taha Kandil
Madiha Hamed
Elmohhamadi Ali
Bocanet, Anca
Anirudh Jhavar
Lajwanti Kishnani
Akshey Aggarwal
Sunitha K Haneef
Aftab Rizvi
Jvargas2006@gmail.com
a.bocanet@ums.ae
anirudhjhavar07@gmail.com
sunia27@gmail.com
Ibrahim Elsiddig Ahmad
Suja Sarah Thomas
ibrahim_ahmed7@yahoo.com
Mazen Jaber
mjaber@svsu.edu
Zulfiqar Ahmed Bowra
Sarfraz Khan
Ossama Fazal
sarfrazkhalil@gmail.com
Bouhezam Sidahmed
Bouhezam29@yahoo.fr
Aibek Galymkair
Aziza Zhuparova
aziza_z@mail.ru
Knowledge Intensity of Innovation Project:
Measurement and Management Features
Main Challenges of Big Data on Firm
Accountancy: New Applications for Cost and
Benefit Analysis
Mediating the Role of Virtual Supply Chain
Integration in the Effect of Traceability on
Responsible Automotive Recall
Methodological Proposal for the Study of
the Impact of Globalization on Business
Strategy of Mexican International
Enterprises
Observing Coworkers’ Violations and
Managers’ Discipline: The Effect of Violation
and Punishment Severity on Coworker
Attitudes
Optimal Control Fuzzy Logic Controller
Makes a Naked Vanilla Call Option Half
Email
Nancy Ibrahim
Tarek Taha Kandil
Shereen Hassan Nassar
José G. VargasHernández
MC. César Francisco
Cárdenas Dávila
jvargas2006@gmail.com
Jeff Peterson
jeff.peterson@uvu.edu
Mohd Khoshnevisan
m.khoshnevisan@ajman.ac.ae
65
No.
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
Title
Naked
Quantitative Analysis of Managerial
Capabilities and Internationalization of
Manufacturing SMEs – Empirical Evidence
from Developing Countries
Social Media Technology Management:
Digital Marketing Communication as A
Sustainable Competitive Adv. for Business
Stock Market Reaction to the Political
Terrorism: An Event Study Approach
Stress as a Mediating Effects of Personality
and Job Satisfaction: Service Experience in
Malaysia
Sustainable Governance and
Internationalization in Family Enterprises
Sustainable Urbanization through
Information Systems: Establishing Holistic
Frameworks
Testing the Micro Structure Theory of
Liquidity: A Case of Karachi Stock Exchange
(KSE) of Pakistan
The Applications of the Economics of New &
Renewable Energy: A Case Study of Egypt
53
The Dilemma of Markets and Resources
Paradox : The Way Forward
The Effective Adoption of ICT-Enabled
Services in Educational Institutions – Key
Issues and Policy Implications
The Evaluation of Talent Management
Practices in Software Industry
The Impact of Job Stress on Job Satisfaction
and Organizational Commitment In the
Banking Sector In Pakistan
The Impact of Social Media on Brand loyalty:
Implications for Hospitality Industry in the
UAE.
The Impact of Social Media Marketing on
Customer Loyalty
The Influence of Entrepreneurial Leadership
Style on Human Resources Training Quality
54
The Islamic Financial System
-Foundations and Viability
55
The Learning Organization Concept: A Study
on Private Companies in Dubai
47
48
49
50
51
52
56
57
The Outlook of the Enterprise Risk
Management (ERM) and Roles of Internal
Auditors: A Critical Review
The Richness of Metaphor and the
Metaphor of Richness in Arabic Ecommerce
Author (s)
Email
Nana Osei-Bonsu
n.bonsu@ajman.ac.ae
Nouri beyrouti
nbeyruti@lau.edu.lb
Sarfraz Khan
Zafar Ahmed
Farah Liyana Bustaman
Abdul Razak Ibrahim
Fakhrul Zaman
Abdullah
Joseph Affholter
George Puia
Mark Potts
Mazen Jaber
Anthony Bowrin
sarfrazkhalil@gmail.com
Chadi Aoun
Safdar Husain Tahir
Hazoor Mohd Sabir
Nadeem Nazir
razak.om@gmail.com
mjaber@svsu.edu
chadi@cmu.edu
safdartahir@gmail.com
Karim Badr El-Din Attia
Hassanien
Karim.Hassanien@bue.edu.eg
Gulzar A Akoor-Shahul
gahmadh@me.com
Abdullah Ismail
a.qazi@ajman.ac.ae
AbdulQuddus
Mohammed
Masood Ahmed
masoodahmed748@hotmail.com
Samia Kargwell
Mohammad Q. Siddiqui
a.kargewil@ajman.ac.ae
Abdullah AlSagheer
a.abdalla@ajman.ac.ae
Basma Waleed
Kashmoola
Tarek Taha Kandil
basma_waleed_85@yahoo.com
Azeemuddin Subhani
a.subhani@ajman.ac.ae
Tarek El Kassar
tarek_kassar@yahoo.com
Mohd Ariff Bin Kasim
Siti Rosmaini Binti
Mohd Hanafi
Rizwan Ahmad
Divakaran Liginlal
66
m.ariff@ajman.ac.ae
rizwan.ahmad@qu.edu.qa
No.
58
59
Title
Time Varying Conditional correlation
Between Stock and Bond Returns: Evidence
From Civets Nations
Understanding of IS Audit Process
with Success Factors
62
Writing Effective Business E-mail
أثر التطور التكنولوجي على االقتصاد األردني
)2013-1980( دراسة حالة
التدابير غير الجمركية وأثرها على نمو وتطور صادرات
الدول النامية
63
ذكـــاء األعمــال و هندســة
القـــرار في المنظــمة
60
61
Author (s)
Robert Meeds
Kashif Saleem
Monika Shrestha
Kichan Nam
Sojung Lucia Kim
Thompson S.H. Teo
Amany Al Sabbagh
Samer Abdelhadi
Ali Al Assaf
Email
kashif.saleem@lut.fi
kchnam@gmail.com
dramany.abdelghany@ecuc.ac.ae
sabdelhadi@uop.edu.jo
Salim Moualdi
moualdis@yahoo.com
Hamidouche M'hamed
mah_hamdouche@yahoo.fr
67
© Copyright 2025