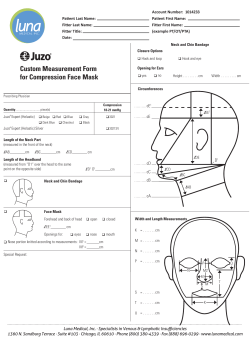
HPV and Head and Neck Cancer
Cancer Professional: Autumn 2013; Vol 7, (3) HPV and Head and Neck Cancer Clinical and Public Policy Updates from an international symposium held at NUI Galway on May 17th Prof. Ivan Keogh: Head of the Academic Department of Otorhinolaryngology, NUI Galway and Consultant Otolaryngologist, Galway University Hospitals. Mr. Tony O'Connor: Consultant Otolaryngologist, Bon Secours Hospital, Galway & Academic Department of Otorlaryngology, NUI Galway. Diarmuid Coughlan: HRB/NCI Health Economics Fellow in Cancer Prevention. School of Economics, NUI Galway. * Corresponding Author: Diarmuid Coughlan – diarmuid.coughlan@nuigalway.ie In June 2013, Hollywood actor Michael Douglas, in an interview with the Guardian newspaper, spoke frankly about a subset of head and neck cancers that has been branded as an ‘epidemic’ in the medical literature(1). These cancers are considered to be a distinct epidemiologic, clinical and molecular entity(2) and are linked to oral sex. A symposium on May 17th in NUI Galway was held to discuss the causal role of the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) in head and neck cancers. This was the first formal dialogue on this subject by Irish clinicians and public health professionals. The Health Research Board (HRB) sponsored this symposium as part of their Knowledge Exchange and Dissemination Scheme (KEDS) grant funding. A “NUI Galway Millennium Fund” was also awarded to support the symposium. Over 140 delegates listened attentively and debated with 13 national and international experts. A webinar and various social media components were utilised to disseminate information. Speakers’ video presentations and slides are available online via the following website: http://www.nuigalway.ie/health-economics/hpvsymposium/ Epidemiology on HPV-related Head and Neck Cancer: Head and neck Cancer is a heterogeneous group (17 different sites) of neoplasms that share a common anatomic origin. Research over the past 15 years has shown that HPV causes a subset of head and neck cancers, primarily oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (OPSCC). Although most head and neck cancers are still caused by excessive tobacco and alcohol use, the incidence of HPV-related OPSCC is increasing in the United States(3) and parts of Western Europe, most notable in Sweden(4). Greater than 90% are due to a single HPV type: HPV-16 (1). The increasing incidence of HPV-related OPSCC, particularly in men (3:1 vs. women), <50 years, with no history of alcohol or tobacco use, has been recorded over the past decade. These cancers have an improved prognosis and survival in comparison to other head and neck cancers (5) – see table 1 for comparison of general epidemiology. Table 1: Comparison of the general epidemiology of HPV related and unrelated head and neck cancers (HNC)(6) HPV-related HNC HPV-unrelated HNC Incidence trend Increasing Decreasing/stable Anatomic location Primarily tonsil and All head and neck sites base of tongue Median age (y) at diagnosis 54 60 Socioeconomic status Higher Lower Primary risk factors Sexual exposure to Tobacco oral HPV exposure Survival Better Worse 3-y oropharyngeal survival (%) 93% 57% and alcohol What are the risk factors for HPV-related Head and Neck Cancer? HPV is a family of more than 100 virus types that can live in the flat, thin cells on the surface of the skin, cervix, vagina, anus, vulva, penis, mouth, and throat. A lot remains unknown about the natural history of this viral infection that spreads through contact with infected skin, mucous membranes, and bodily fluids. Epidemiologic studies show that there are several notable differences in the demographics of patients who develop HPV-related head and neck cancers compared to traditional head and neck cancer patients. HPV-related patients tend to have had more active sex lives(7): • Earlier age of sexual debut • Higher number of lifetime vaginal sex partners • Higher number of lifetime oral sex partners As all sexual behaviours are colinear (people who have a higher number of partners for 1 sexual act tend to have a higher number of partners for other sexual acts as well), it is difficult to differentiate which sexual behaviours are associated with oral HPV transmission. It most be stressed that HPV is very common with 75% of the sexually active population in the US having the virus at some stage in their life. The vast, vast majority of infections (90-99%) are cleared without any problems. For some reason, possible linked to smoking and more probably linked to a deficiency in the immune system, people are not able to clear the virus in the oral cavity and develop cancer in the oropharynx region (it is thought that tonsillar crypts, the site of initial HPV infection, may be an immune privileged site). A review reported that higher oral HPV prevalence has been reported among select groups such as individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (33%), current smokers (10%) and people with >5 lifetime sexual partners (7.4%) (6). Signs and symptoms of HPV-related Head and Neck Cancer: Tobacco and alcohol related oral cancers, present with visible symptoms such as white lesions (leukoplakia), red plaques (erythroplakia) or persistent ulcers. HPV-related cancers are associated with lymph tissue in the oropharynx (palatine tonsils and lingual tonsils). The oropharynx is an anatomic site, which is difficult to visualise and palpate. Patients may present with difficulty swallowing, chronic hoarseness, persistent sore throat or painless swelling in the neck (usually an enlarged lymph gland). What is happening in HPV & Head and Neck Cancer in Ireland? Dr. Linda Sharp (Senior Epidemiologist, National Cancer Registry Ireland) set the scene at the symposium by stating that as a group, head and neck cancer were the 6th most common cancer in men and the 16th most common cancer in women on the island of Ireland. Each year, on average 438 men and 170 women are diagnosed with a head and neck cancer. The number that is truly HPV-related is currently unknown. However, in autumn 2013, the CERVIVA research collaboration funded by the HRB, in partnership with surgeons and pathologists around Ireland, will embark on a major investigation of HPV of the oropharynx, oral cavity and larynx diagnosed since 1994. This will provide the first population-based data on the epidemiology of HPV infection in head and neck cancer in Ireland. How to detect HPV-related Head and Neck Cancer? One of the evolving developments in characterising this cancer has been the indiscriminate and non-standardised testing of clinical samples. HPV infection is strongly correlated with the oropharynx region and in particular the base of tongue, palatine and lingual tonsils (See Figure 1). Professor William Westra (Johns Hopkins) stated at the symposium that no single test has been universally accepted as best practice. The crux of establishing gold standard HPV testing is to differentiate an incidental virus (e.g. passenger virus or vial contaminant) from an active oncologic agent. Evidence for transcriptional activation of the viral oncoproteins E6 and E7 is generally regarded as the gold standard for clinically relevant HPV. Most diagnostic laboratories that perform routine testing of clinical samples use 1 of the 2 methods for HPV detection: 1. PCR-based amplification. 2. DNA in situ hybridization. However, another detection method that is increasing in popularity is the immunohistochemical detection of the cellular protein p16 as a practical alternative or complimentary procedure for HPV testing (8). This is based on the high correlation between HPV detection and p16 overexpression(9). Figure 1: Anatomical distribution of HPV-related head and neck cancer (Taken with permission from Prof. Westra’s presentation on May 17th) Treatment of HPV-positive Head and Neck Cancer The common consensus among the experts at the symposium was that given the better survival (cure rate) of the HPV-positive patients; de-intensification treatment regimes (Radiotherapy, Chemotherapy), with the aim of maintaining current survival whilst mitigating long term adverse events is the goal. Keynote speaker from the US, Professor Sara Pai (Johns Hopkins) and from the UK, Professor Terry Jones (Liverpool), both pointed to randomised controlled trials that are ongoing in their jurisdictions that are focused on the reduction of morbidity including therapeutic vaccine. Current treatment strategies, typically involving concurrent cisplatin based chemoradiotherapy are associated with high rates of acute and long-term toxicity, particularly with respect to long-term swallowing function. What was evident from the case-studies discussion, led by Mr. Paul O’Neill & Ms Helena Rowley (Mater, Dublin) was that all treatment options: Surgery, radiation therapy, concurrent chemoradiotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, surgery followed by surgery radiotherapy followed and by induction chemotherapy with concurrent chemoradiotherapy all may have a place in treatment depending on the patient’s clinical, demographic and smoking status. Professor Pai elaborated on the multi-disciplinary management offered by the head and neck cancer clinic at Hopkins where patients meet with head and neck surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and speech and language pathologists in one clinic visit. After review of medical records, pathology, imaging studies and physical examination, a consensus opinion regarding management is given. This process allows patients to have open discussion of the pros and cons of various treatment options with all disciplines present. Implications for the spouse: What was unfortunate with the treatment of Michael Douglas’s comments about throat cancer in the social media era was the slanderous innuendo directed at his wife. There is still so much unknown about the natural history of oral HPV and it is likely that HPV-associated head and neck cancers are due to legacy infections that take 10-40 years to develop into a cancer tumour. Evidence from Sweden suggests that husbands’ of wives with invasive cervical cancer or in-situ cervical cancer had at least twice the expected rate of tonsil cancer(10). Preliminary US findings showed that spouses and long-term partners of patients diagnosed with HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer were no more likely to test positive for oral HPV infection than people in the general population and have a low risk of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer(11). Should boys be vaccinated against HPV? The last session at the symposium focused on the public policy implications of HPV-related head and neck cancer and in particular the case for vaccinating boys against HPV. The HPV-quadrivalent vaccine (Gardasil®) protects against HPV – type 6,11, 16 & 18 and is however only licensed for use for prevention of genital warts in men in Europe. It will take decades before we know whether the vaccine is effective against HPV-related cancers in men (HPV causes penile and anal cancer too at much lower rates than in the oropharynx). The benefit of adding boys to a school-wide program is dependent on coverage in girls. Consider that the 3-dose uptake of HPV vaccine of girls in the US is only 35% where as in Ireland it is 82%. Recently, in Australia, where the 3-dose vaccination uptake is 73% there was a 82% decline in genital warts in heterosexual men attributable to herd immunity with no genital warts in vaccinated women(12). Another consideration is that sexual networks are not bounded by jurisdiction and there will be plenty of females that are not vaccinated in the world. Moreover, there is an equity question, as homosexual men would not be protected against the virus. What is evident now in the US is that HPV-associated head and neck cancers have now surpassed cervical cancer in incidence cases (13). In France, the estimated annual costs of treating HPV-associated HNC in men (€94.6million) is greater than invasive cervical cancer (€83.9million) in women(14). This has implications for how HPV vaccination is portrayed to the public, as Gardasil is not a direct cervical cancer prevention vaccine; it is a quadrivalent HPV vaccine that hopefully prevents all HPV-related cancers and not just 70% of cervical cancer attributable to HPV-type 16. In essence, only time will tell, but for the next 30-40 years men will be disproportionately inflicted with the scourge of this virus. Ireland should see more cases given the changes in sexual norms over the past 20 years. Hopefully, trial results will help doctors prescribe safe and effective treatment that will reduce the debilitating adverse effects associated with treating this cancer. Finally, the intended consequence of the symposium was to foster and develop multidisciplinary and multi-centred research on the island of Ireland. As stated so eloquently by Professor Sara Pai that: “Within each patient there is an opportunity to learn more about the disease. We should not only treat the patient but advance the field by enrolling patients in studies, be they epidemiological or clinical trials”. References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Marur S, D’Souza G, Westra WH, Forastiere AA. HPV-associated head and neck cancer: a virus-related cancer epidemic. Lancet Oncol. 2010 Aug;11(8):781–9. Gillison ML. Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancer is a distinct epidemiologic, clinical, and molecular entity. Semin. Oncol. 2004 Dec;31(6):744–54. Chaturvedi AK, Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM, Hernandez BY, Xiao W, Kim E, et al. Human Papillomavirus and Rising Oropharyngeal Cancer Incidence in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011; 29(32): 4294-301 Attner P, Du J, Näsman A, Hammarstedt L, Ramqvist T, Lindholm J, et al. The role of human papillomavirus in the increased incidence of base of tongue cancer. Int. J. Cancer J. Int. Cancer. 2010; 126(12): 2879–84. O’Rorke MA, Ellison MV, Murray LJ, Moran M, James J, Anderson LA. Human papillomavirus related head and neck cancer survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2012; 48(12): 1191–201. Joseph AW, D’Souza G. Epidemiology of human papillomavirus-related head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2012; 45(4): 739–64. D’Souza G, Kreimer AR, Viscidi R, Pawlita M, Fakhry C, Koch WM, et al. Casecontrol study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007; 356(19): 1944–56. Westra WH. Detection of human papillomavirus in clinical samples. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2012; 45(4): 765–77. Hoffmann M, Ihloff AS, Görögh T, Weise JB, Fazel A, Krams M, et al. p16(INK4a) overexpression predicts translational active human papillomavirus infection in tonsillar cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010; 127(7): 1595–602. 10. Hemminki K, Dong C, Frisch M. Tonsillar and other upper aerodigestive tract cancers among cervical cancer patients and their husbands. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. Off. J. Eur. Cancer Prev. Organ. Ecp. 2000; 9(6):433–7. 11. D'Souza G. Pai SI, Hadddad RI. Gillison M, Posner R. Oral HPV infection in HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer cases and their spouses. J Clin Oncol, 2013 (suppl; abstr CRA6031) Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/111185-132 12. Ali H, Donovan B, Wand H, Read TRH, Regan DG, Grulich AE, et al. Genital warts in young Australians five years into national human papillomavirus vaccination programme: national surveillance data. BMJ. 2013; 346: 20-32. 13. Jemal A, Simard EP, Dorell C, Noone A-M, Markowitz LE, Kohler B, et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975–2009, Featuring the Burden and Trends in Human Papillomavirus (HPV)–Associated Cancers and HPV Vaccination Coverage Levels. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013; 105(3): 175-201 14. Borget I, Abramowitz L, Mathevet P. Economic burden of HPV-related cancers in France. Vaccine. 2011; 29(32):5 245–9. Pictures from Symposium: 1. Opening address - HPV and Head and Neck Cancer Symposium – May 17th 2012 Aula Maxima NUI Galway. 2. Prof. Ivan Keogh - Head of the Academic Department of Otorlaryngology, NUIG and Consultant Otolaryngologist, Galway University Hospitals 3. Prof. William Westra - Professor of Pathology, Oncology and Otolaryngology/ Head and Neck Surgery at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine 4. Prof. Sara Pai - Associate Professor of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
© Copyright 2025