Fleas, Ticks, Intestinal Parasites, Oh My! Pembroke Animal Hospital
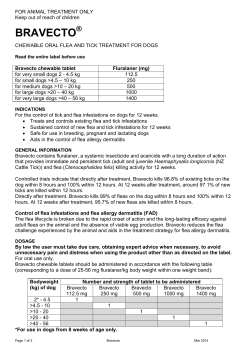
Fleas, Ticks, Intestinal Parasites, Oh My! Pembroke Animal Hospital Dr. Heidi Hemmett June 14, 2012 Flea Life Cycle Flea Facts • Adults = tip of iceberg of infestation • Egg, larvae, pupae, adult • Adult female = 40 eggs a day • Approx 3 weeks from egg to adult • Adults suck blood, leave “flea dirt”, eaten by larvae • Larvae killed at 95 F, tapeworm eggs • Pupa detect host by CO2, vibration, light and sound patterns • Prefer lower back of pets-itching, hair loss • “Fed flea” dies in weeks if no host Flea Myths • No fleas because -only indoor pets -humans not affected -hardwood floors -I don’t see them I can just treat one pet -must treat all pets -environment Flea Identification • Flea Comb • Flea Dirt The Evidence Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD) Flea Prevention • • • • Topical monthly preventative Part the hair between shoulders Apply directly to the skin Do NOT bathe/let swim for 48 hours BEFORE or AFTER application • Apply at night and don’t handle for 12 hours Flea Product Application Frontline Plus • Monthly product • Most effective 21 days • Pesticide • Does not repel (flea or tick must bite) Advantage • Monthly topical flea preventative • Doesn’t prevent ticks • Indoor cats that live with dogs Advantix • NO CATS • Stronger ingredient • Risk of reaction • Repellant action (ticks, fleas, mosquitoes • Can apply if coat is dry (swimmers) Flea Infestation • Pets: • Re-start monthly preventative ALL PETS • Capstar if lots of fleas, bathe if lots of flea dirt • • • • • • • Environment: Wash and dry bedding Twice weekly vacuuming, throw out bag Borax on carpets (information online) Flea bombs not that effective Flea collars and OTC products not reliable Takes AT LEAST 3 months to clear Source: animals in attic, rodents in basement Ticks • Early spring, fall • Bushes, leaf debris • Can’t jump • Heavy burden this year • Acorns 2010 and whitefooted mouse 2011 Tick Life Cycle • 4 stages: egg, larva, nymph, adult • Requires blood meal to molt to new stage • 2 year cycle: egg to adult, reproduce, die • Female lays 3000 eggs in spring, hatch to larvae, wait for animal • One mouse = 100s larvae Tick Life Cycle What to do if you find a tick • Don’t panic • Don’t use a match, petroleum jelly, alcohol or other substance to make it “back out” (regurgitation of gut contents) • Locate appropriate tool (pointed tweezers) • Don’t jerk or twist tick • Remember: Nymph = poppy seed size Adult = sesame seed size Tick Removal tools Removal of Ticks • How to Remove a Tick (U Tube) • Tweezers, grasp as close to skin as possible, pull upwards with slow, steady motion • Okay if piece left behind, body will push out • Clean wound with soap/water or alcohol • Monitor for redness, pus Tick-born diseases • Lyme Disease • Anaplasmosis • Ehrlichiosis Lyme Disease in Dogs • Transmission-deer tick, 36 hours • Nymph or Adult can transmit • Can take months for signs to develop • Clinical signs-poor appetite, lethargy, fever, lameness, reluctance to get up • Diagnosis-Heartworm 4DX • Treatment- antibiotics • Prevention: Lyme vaccine, monthly topical Lyme Disease in People • • • • Expanding rash near bite, 7-14 days Bull’s eye target sign Joint pain, chills, fever, fatigue Swollen lymph nodes near bite • CONTACT YOUR DOCTOR if bitten • Some false negative blood tests <30 days • No vaccine for people Increased risk Lyme Disease • Grassy or wooded areas • Intermediate hosts (deer, mice) • Time outdoors • Heavy tick population (eg 2012) • Other animals or people test positive in same area Other Tick-borne Diseases Disease Clinical signs Testing Therapy Anaplasmosis Fever, anorexia, lethargy, limping Heartworm 4DX CBC (platelets) Antibiotics Ehrlichiosis Fever, anorexia, weight loss, big lymph nodes Heartworm 4DX, CBC (anemia, white cells) Urine (protein) Antibiotics Protection against Ticks • PETS: • Monthly topical preventative • Consider Lyme vaccine for dogs • PEOPLE: • repellant with DEET or permethrin • Light colored clothing with tight weave, enclosed shoes, long pants/sleeves • Tuck in shirts and pants into boots/socks • Don’t sit on ground or rock walls Protection against Ticks • BOTH PEOPLE AND PETS: • Final full body tick check at end of the day, new freckle or dirt speck (36 hour window) • Remove ticks, call your doctor if bitten (+/- prophylactic antibiotic) • Monitor for rash near bite (PEOPLE) Intestinal Parasites • • • • Roundworms Hookworms Whipworms Tapeworms • Coccidia • Giardia Roundworms Roundworms Infection In utero, fecal-oral (soil), rodents Life cycle Intestines, migrate in tissues- lungs, cysts in tissues, eggs shed in stool Cysts activated during pregnancy NONE, cough, pneumonia, vomit, diarrhea Clinical signs Diagnosis Fecal exam, vomited worm (spaghetti) Roundworms Eggs VERY resistant in environment Infective-one month (soil, not stool) Adults Round, white, up to 7 inches, looks like spaghetti Treatment De-worm q two weeks- if high risk Adult-deworm twice 2-3 weeks apart Heartworm medication = 1 treatment RECHECK FECAL Public Health Eggs persists in soil (sandbox, park, gardeners, beach) Visceral Larval Migans (eye) Visceral Larval Migrans • • • • Children, hands in mouth (soil, sandbox, etc) Worm gets lost and dies in abnormal host (eye) Inflammatory reaction can lead to blindness Prevention: leash laws, restricted access public parks/playgrounds, Heartworm preventative monthly, annual fecal checks Heartworm Preventative • Monthly year-round • Prevents Heartworm • One treatment for roundworms and hookworms • Some also treat/control whipworms Hookworms Hookworms Infection Life cycle Penetrate skin, fecal-oral (soil), in utero and milk-dogs, rodents, cockroach-cat Intestines, lung, can ENCYST and remerge, suck blood in intestines Clinical signs NONE, weakness, anemia Diagnosis Fecal exam Hookworms Eggs Die within months, bleach will kill, can’t survive freezing Adults Have teeth, suck blood Treatment De-worm high risk groups frequently Two treatments, 2-3 weeks apart (P) Heartworm medication = 1 treatment Public Health Infected soil-gardeners, children Cutaneous Larval Migrans Cutaneous Larval Migrans • • • • Source: contaminated soil (park, beach) Signs: intensely itchy raised migration paths Usually treatable Prevention: leash laws, restricted access, prompt removal of stool, wear SHOES Parasite exposure Whipworms Whipworms Infection Fecal-oral (soil), normal grooming Life Cycle Large intestines Clinical Signs NONE, diarrhea with blood, mucus, straining to defecate Diagnosis Fecal Whipworms Eggs VERY RESISTANT, survive all conditions for YEARS Adult worms Whip shape, live in colon Treatment De-worm now, three weeks, three months, INTERCEPTOR Public Health Eggs very resistant in environment, prompt removal of stool, wash hands well Tapeworms Tapeworms Infection Flea ingestion (grooming) Life Cycle Egg sac breaks, flea larvae eats eggs, adult flea swallowed, tapeworm attaches to intestines, grows and sheds in 3 weeks (mobile egg sack) Clinical signs NONE, +/- weight loss, scooting Diagnosis Tapeworm segments on fur or feces, fleas present, fecal exam Tapeworms Eggs Live in fleas Adult worms Segmented, 4-28 inches long, looks like rice, mouth has 6 rows of teeth Treatment/ Special de-wormer, one treatment Re-infection if fleas present Prevention Monthly flea preventative product Public Health Children/people at risk if swallow flea (clean environment) Monthly flea preventative 3+ months Tapeworm Prevention Tapeworm Advertisement Coccidia Coccidia Infection/ Risk Fecal-oral (cysts in soil), rodents Young animals, groups (shelter, rescue, kennel) Life Cycle Oocyst passed in stool, matures to infective state, swallowed by mouse or pet, intestinal cell destruction Clinical Signs Watery diarrhea, +/- blood, dehydration, poor appetite Diagnosis Fecal test, may need to repeat Coccidia Organism Protozoan parasite, not a worm Treatment Special de-wormer RECHECK A FECAL Public Health Isospora species of cats and dogs is NOT infective to people Giardia Giardia Infection Fecal-oral (cysts in soil), higher risk in groups (shelter, rescue, kennel), rodents Clinical Signs Watery diarrhea, dehydration, poor appetite Diagnosis Fecal test, maybe repeat (shedding late or intermittently) Life Cycle Wet areas, cyst form-swallowed, shell is digested and 2 trophozoites enter intestines, both trophs and cysts shed in stool (up to 5-16 days after diarrhea) Giardia Organism Protozoal parasite, 2 forms-trophs and cysts, loves water, not a worm (CAN’T SEE IN STOOL) De-wormer, can require two courses of treatments, +/-probiotic RETEST FECAL SAMPLE Public Health WATER, Remove stool promptly, bleach 1:32, bathe pet if stool on fur, wash hands well after contact Treatment Protect your Pet • QUARANTINE new pets, separate bathroom area/litter box • Frequently de-worm puppies/kittens • Annual fecal exam or when diarrhea • Monthly heartworm preventative year-round • Recheck stool if negative/diarrhea persists • Twice annual de-worming in outdoor cats • Remove stool promptly, wash hands well Protect your Family • • • • Cover sandboxes Wear shoes in parks, public sandbox Wear gloves while gardening Wash hands well, especially before eating • Do NOT let pets lick you on the mouth • Wash or peel raw fruits and vegetables Public Health Reminders • Negative fecal doesn’t mean no parasites • RECHECK fecal after treatment • Most common clinical sign = NO SIGNS • Leash dogs and prompt removal of stool • Treat more often if higher risk: diarrhea, dog parks/day care, frequently kenneled, recent exposure Useful Websites • www.pembrokeanimalhosp.com (Trusted Pet Information) • www.veterinarypartner.com • www.cdc.gov • Companion Animal Parasite Council www.capcvet.org Sources • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • www.cdc.gov www.veterinarypartner.com http://blog.harvardvanguard.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/deer-vs-dogtick.jpg http://www.aldf.com/images/Iscapularisposter.JPG http://rianimalhospital.com/vet/wp-content/uploads/2011/05/tapeworm_dog.jpg foxvalleyvet.net bouldersnaturalanimal.com ticktwister.com capstarpet.com http://gravitygarden.com/happy-dog/?p=254 gettingridofthings.com http://forum.baby-gaga.com/about1946160.html ahsvet.com vhah.com gettingridoffleasondogs.com Questions?
© Copyright 2025