This photograph was taken 216 miles above Earth. From this altitude
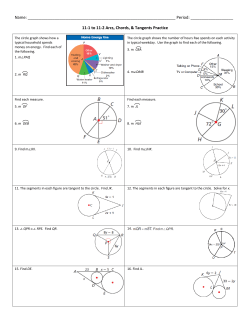
GEO: Sem 2 Unit 5 – Circles (1) 12.1 – Lines that Intersect Circles NAME _____________________________ Objectives: Identify tangents, secants, and chords. Use properties of tangents to solve problems. This photograph was taken 216 miles above Earth. From this altitude, it is easy to see the curvature of the horizon. Facts about circles can help us understand details about Earth. Recall that a circle is the set of all points in a plane that are ____________________ from a given point, called the ______________of the circle. A circle with center C is called circle C, or C. The of a circle is the set of all points inside the circle. The ______________ of a circle is the set of all points outside the circle. Identify each line or segment that intersects L. chords: tangent: secant: diameter: radii: Identify each line or segment that intersects P. chords: tangent: secant: diameter: radii: Find the length of each radius. Identify the point of tangency and write the equation of the tangent line at this point. Radius of S = Radius of R = Point of tangency = Equation of tangent line: A __________ ____________ is a line that is tangent to two circles. Early in its flight, the Apollo 11 spacecraft orbited Earth at an altitude of 120 miles. What was the distance from the spacecraft to Earth’s horizon rounded to the nearest mile? (It is 4000 miles from the center of the earth to the surface….radius.) Kilimanjaro, the tallest mountain in Africa, is 19,340 ft tall. What is the distance from the summit of Kilimanjaro to the horizon to the nearest mile? (Miles and feet…convert to miles. 5280 ft = 1 mile) RS and RT are tangent to Q. Find RS. COMP BOOK section 12.1: Define, draw and properly label a circle. Define, draw and properly label a chord, secant, tangent, diameter, radius and point of tangency. Define, draw and properly label congruent circles, concentric circles and tangent circles. List and draw an example of Theorem 11-1-1, 11-1-2, and 11-1-3. 12.1 HOMEWORK: page 797 #1-27, 31.
© Copyright 2025