Teacher Instructions - Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural
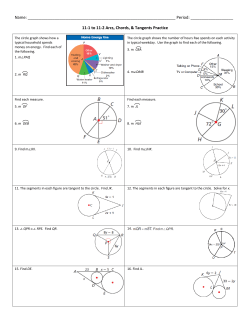
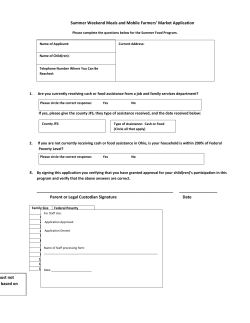
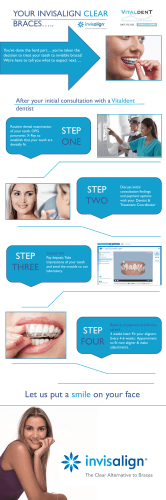
Teacher Instructions for Discovery Guide to Hall of Ancient Life for grades 3 through 5 Before Your Visit: • This activity was developed by the Education Department to help your students focus on learning while at the museum. • Please make copies of this activity and bring it with you to the museum. The museum does not provide copies for your students. • Please remind your students to use pencil, not pen, when completing this Discovery Guide. Encourage your students to fold this guide in half so it will be easier to write on. Students should not place their papers on exhibit walls, cases, or labels, as this can damage them. • Save paper! Print pages 2-3, and copy them one to two-sided, so that you have a one piece of paper with questions on both sides. While at the Museum: • These questions will encourage students to look closely at museum exhibits, think critically about what they are seeing, and discuss their findings with their classmates and chaperones. • Most of the questions can be answered by reading the labels, but there are several thought and open-ended questions, and students are encouraged to give an original answer. • Students may not always come up with the “right” answer, so if this activity is to be used for a graded assignment, we suggest that you grade more on participation and thoughtfulness than accuracy. • Volunteers are frequently available in the galleries to answer questions. Other Information: • This is one of three Discovery Guides for this grade range. Discovery Guides are available for three galleries, including the Halls of Ancient Life, People of Oklahoma, and Natural Wonders. • Have questions or suggestions? Send us your feedback at education@ snomnh.ou.edu, or Education Department, Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History, 2401 Chautauqua Ave., Norman, OK, 73072. Answers 1. circle all four 2. Stromatolites 3. body rolls up - protection, eyes - finding food, exoskeleton - molting 4. C. 5. lower 6. millipede and cockroach 7. mammals 8. Eoraptor, Eoraptor 9. C. 10. birds 11. 6 12. B. 13. Saurophaganax - predator, Apatosaurus - prey 14. water or ocean 15. Protostega - marine turtle, Platecarpus - swimming lizard, Pteranodon flying reptile, Hesperornis - flightless bird, Xiphactinus - bony fish 16. hunted in packs with other Deinonychus; wolves, lions 17. 10.5 18. B. 19. flowering plants; 85 millions years old 20. Mammals 21. grass 22. leaves - Mastodon, grass - Mammoth 23. Arctodus (bear) and Smilodon (cat) Discovery Guide Permian Period 6. Captorhinus is the most common fossil at the Fort Sill site in Lawton, Oklahoma. Its teeth are arranged in multiple rows and are just right for eating what kind of animals? (circle your answers) Hall of Ancient Life for grades 3 through 5 Directions: Questions begin at the entry of the Ancient Life gallery in the Paleozoic Era and go in sequence through the gallery. Finding the answers will be easier if you answer the questions in order. To answer the questions labeled Think, you have to use information on the label, common sense, and talk to your friends and to the volunteers to think of the answer. Paleozoic Gallery 1. What are some events caused by continental plates moving on the Earth’s surface? (circle your answers) volcanoes earthquakes larger oceans mountains forming 2. _______________________ are rocks built by bacteria. There are several in this gallery that you can sit on. millipede butterfly cockroach mouse 7. In the Permian Period, the top predator was sail-backed Dimetrodon. Dimetrodon was a synapsid. Synapsids are related to which modern group? (circle one) mammals reptiles Mesozoic Era: The Age of Dinosaurs Triassic Period 8. Find the Alligator, Marasuchus and Eoraptor skeletons and models. Think - which animal could run the fastest? ____________________ Which of the three was a dinosaur? ___________________________ Cambrian Period - look for the models hanging from the ceiling. 3. In the Cambrian exhibits, there are many trilobite fossils and models. Match the feature with the function: body rolls up molting eyes with many lenses protection exoskeleton finding food 9. Find the moving jaw models and compare the reptile and mammal teeth. Why can’t an alligator (or a dinosaur) chew gum? (circle one) Carboniferous Period- look for the tropical forest. 4. Insects like dragonflies were large because the level of ______ was very high in the atmosphere. Jurassic Period 10. Look for the gastroliths, “stomach stones” that helped sauropod (long-neck) dinosaurs grind their food.You can touch these stones, and you can see how they helped the dinosaur process its food. A. carbon B. nitrogen C. oxygen 5. If dragonflies today are smaller, the levels of this gas today are: (circle one) the same higher lower A. Alligators (and dinosaurs) have no teeth B. It’s not cool for an alligator (or a dinosaur) to chew gum C. Alligators (and dinosaurs) have teeth, but they don’t fit together What modern animals swallow sand and grit to help digest their food? ____________________________________________________ 11. Find the Saurophaganax foot in the case on the wall. Most of the bones are actual fossils, but some are casts, or carefully-sculpted replicas. How many foot bones are casts? 1 4 6 10 What modern animal hunts in a similar way? __________________________________________________ 17. The Pentaceratops record breaking skull is _________ feet tall. 12. Why are some bones casts instead of fossils? A. Paleontologists are lazy. B. Some bones were missing when the foot was excavated (dug up). C. The missing bones were used for book ends. 13. Find the two large dinosaurs on the Jurassic Island. Look for the huge mouth full of sharp teeth and the strong arms with curved claws. This is the Saurophaganax. Look for the long neck and large leg bones of the Apatosaurus. Match the dinosaur to its role. Saurophaganax Prey Apatosaurus Predator Cretaceous Period – Marine Community 14. Large swimming reptiles and other marine animals were able to live in Oklahoma during this period because a large portion of the state was covered by ______________. 15. Match the animal name with the type of animal. 18. Pentaceratops and other ceratopsians had specialized teeth for chewing: A. meat B. plants C. pizza 19. What kind of plants take over the world at the end of the Mesozoic Era (age of dinosaurs)? Circle your answer. flowering plants ferns How old are the flower specimens in the case? _______________ Cenozoic Era 20. The Cenozoic Era is called the Age of ______________________. 21. What new type of plant spreads out and changes Oklahoma’s landscape? ______________________ Protostega marine turtle Platecarpus flying reptile 22. Feel both the mammoth and mastodon teeth. Pteranodon flightless bird Which tooth would be better for crushing leaves? ________________ Hesperornis bony fish Which tooth would be better for grinding grass? _________________ Xiphactinus swimming lizard Cretaceous Period – Coastal Community 16. Look at the diorama with Deinonychus and Tenontosaurus. Deinonychus was a light weight but vicious predator. How did Deinonychus attack a large, heavy animal like Tenontosaurus? __________________________________________________ Pleistocene Community 23. Circle the animals that are predators. Arctodus Bison latifrons Mastodon Smilodon Created by Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History Education Department, 2011
© Copyright 2025