What is microbiology? Study of organisms too small to
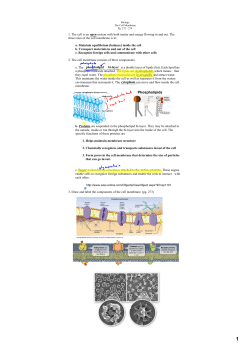
What is microbiology? Study of organisms too small to be seen without a microscope ARCHEABACTERIA BACTERIA PROTISTA (subject to change) FUNGI (MYCETEAE) PLANTAE ANIMALIAE Viruses are NOT living, but virology is part of microbiology. Classification • Domain – Kingdom • Phylum – Class » Order » Family » Genus + species Scientific names • Use italics • After first use, it is okay to use a letter to represent genus (unless you are beginning a sentence) • Escherichia coli • Staphylococcus aureus Why care about microbes? • • • • • • • First life Necessary for life on Earth Valuable tools for research and industry Food and drink preparation Disease in humans, plants, & other animals Increased knowledge bioremediation Areas of research/clinical application • • • • • • • • • Epidemiology Health Care Immunology Agricultural microbiology Biotech Industrial microbiology Genetic Engineering Environmental microbiology Pharmaceutical microbiology Scientific Method • Ask a question • Formulate hypotheses – null – alternative • • • • Test hypotheses (carefully) Statistics Interpretation Reporting • A LITTLE CHEMISTRY ELEMENTS TYPES OF BONDS Ionic bonds Covalent bonds Polar Covalent bonds Non Polar Hydrogen bonds pH • ORGANIC COMPOUNDS LIPIDS • Characteristics – Mostly C & H, not soluble in water, uses include storage (energy), support, part of cell membranes • Building blocks – Vary depending on type – Triglycerides have glycerol head + 3 fatty acids • Types – Triglycerides, phospholipids, steriods, waxes etc. CARBOHYDRATES General characteristics Composed mostly of C,H, and O, uses include energy storage and as parts of various structures (e.g. cell walls) Building blocks monosaccharides or simple sugars Types monosaccharides e.g., glucose disaccharides e.g., sucrose polysaccharides e.g., starch Disaccharides Polysaccharides PROTEINS • Characteristics- composed of C,H,O, N, and some with S, uses include as structures, recognition, endocrine, muscle contraction etc. • Building blocks amino acids • Structural levels – Primary – Secondary – Tertiary – Quaternary Structural levels NUCLEIC ACIDS • Characteristics: nucleic acids contain C,H, O, N, and P • Building blocksare nucleotides (composed of a nitrogenous base, sugar and phosphate group. • Types – DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid is the heritable material that codes for proteins. It exists as a double helix – RNA (ribonucleic acid) is the compound that takes the information from DNA for the formation of proteins. It is usually single stranded. DNA RNA Prokaryotes • • • • • • • • Archeabacteria and Bacteria Unicellular Smaller in general than eukaryotes Membrane bound organelles - absent Reproduction - asexual DNA - circular Proteins assoc. with DNA - Basic Ribosomes - 70S subunit Eukaryotes • • • • • • • • Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals Mostly Multicellular except protists Larger in general than prokaryotes Membrane bound organelles-present Reproduction – asexual & sexual DNA - linear Proteins assoc. with DNA - Histone Ribosomes - 80S subunit Eukaryotic Cell Cell Membrane Cell membrane Structure Components Arrangement Functions include Barrier Transport (know diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion and active transport) Recognition (e.g., self vs. non-self) Reception (for protein hormones) Adhesion Cell membrane Nucleus • Structure and Function – membrane similar to cell membrane (similar function) – Nucleolus (formation of ribosomes) – Chromosomes (gene expression) – Nucleoplasm (matrix) Ribosomes • Structure – rRNA – Proteins • Function – Site of protein formation (translation) • Found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes (different structurally) Endoplasmic Reticulum • Structure membranous system of tunnels and sacs – Rough – with ribosomes on surface – Smooth- no ribosomes on surface • Function – Rough – protein synthesis – Smooth- lipid synthesis Golgi Apparatus • Structure also membranous, kind of like a stack of pancakes • Function processing of lipids and proteins Lysosomes • Structure membrane bound sac containing hydrolytic enzymes • Function digestion Mitochondria • Structure – cigar-shaped, double membrane-bound organelle • Function – Energy transfer by ATP synthesis Chloroplast • Structure – Also cigar or spindle shaped, double membrane-bound, green • Function – Site of photosynthesis OTHER STUCTURES • • • • Cell walls, not in animal cells Vacuoles Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm PROKARYOTIC CELLS APPENDAGES • Flagellum • Arrangements of flagella • Fimbriae • Pili GRAM STAIN • A differential stain for most bacteria SPORES • Some bacteria produce spores that allow them to survive during adverse conditions SHAPES AND ARRANGEMENTS METABOLISM • FOR THIS SECTION I WILL BE USING THE OVERHEAD SO THAT I CAN GO OVER INFORMATION AS I WRITE IT DOWN
© Copyright 2025