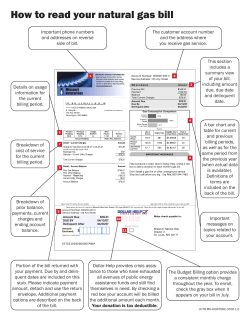
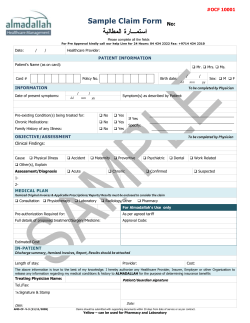
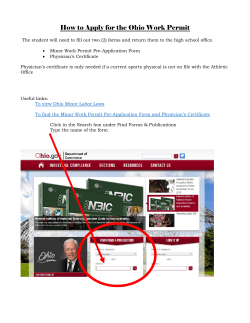
A manual for NEtwork BLUE Health Care Providers/Facilities
A manual for NEtwork BLUE Health Care Providers/Facilities Policies and Procedures Revised August 1, 2014 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Dear Health Care Provider: This manual is dedicated to keeping you and your staff informed regarding our operational policies and procedures at Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE). The contents of this manual are contractually binding for compliance, based on your provider agreement with BCBSNE. Providers will follow all applicable BCBSNE Policies and Procedures and those applicable to the Covered Person, and Provider agrees to provide appropriate information to Provider employees, agents and representatives consistent with this commitment. It is important to familiarize yourself with the information provided within this manual, and have it readily available as a reference. For your convenience, the manual is available for access online at www.nebraskablue.com by clicking “Providers” and then “Policies and Procedures” in the left column. The online version of the manual contains the most current and updated information. If you have any suggestions as to how we can improve this manual as a comprehensive resource for you, please let us know. Sincerely, Lee Handke, Senior Vice President Health Network Services 1 Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Preface Different needs created different Blues. Many “Blue” terms are used to describe the different programs and products of Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska designed to meet your needs and of our members. Each program/product is unique in its focus and because it carries the term “Blue,” you can be assured that it is supported by our mission to deliver the health and wellness solutions people value most. You are required to ensure that your subcontractors are subject to and comply with the terms of the provider contract, this manual and all applicable Federal and State statutes, laws and regulations. When there is a discrepancy between the terminology in this manual and provider contract language, the specific contract language will prevail. The information in this manual is subject to change. There may be deletions and additions published periodically, each with its own effective date. We encourage you to utilize the most current version of the manual by visiting www.nebraskablue.com and clicking on “Providers” and then “Policies and Procedures” in the left column. Revisions are often published in our UPDATE provider newsletter and in direct mailings to your office. Newsletters can also be viewed at www.nebraskablue.com by clicking on “Providers,” then “Newsletters” in the left column. To receive an e-mail each time we post a new issue of the newsletter on the provider website, click on “Sign up for our newsletters” on the Newsletter page. In addition, we encourage you to visit our website at www.nebraskablue.com and view our comprehensive online provider library. The information in this manual should not be considered all-inclusive. This is general information that applies to many but not all group endorsements. Groups can and do request variations of endorsements. Health care providers should take advantage of our online provider portal through NaviNet to verify member eligibility and benefits, verify claim status, or access a remittance advice. Go to our provider page on www.nebraskablue.com, or www.navinet.net/solutions/plans/bcbsne to register or log-in. This information has been made available for you free of charge by BCBSNE, and should be your primary source of verification. Call 800-635-0579, our toll-free voice response system, to research answers to questions about a claim or BCBSNE benefit coverage that may not be available on NaviNet. 2 Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents About Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska Who we are Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE) is a member of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, an association of independent Blue Cross and Blue Shield Plans. BCBSNE is an independent insurance company licensed by the State of Nebraska. BCBSNE has done business in Nebraska for over 70 years. We work jointly with network health care professionals in providing the best health care possible to our customers. Financial stability Although the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association does not act as a guarantor of each Plan’s financial obligations, all Plans are subject to uniform financial standards established by the Association. These standards are intended to foster a system in which each Plan maintains adequate resources to meet its obligations to its customers. BCBSNE monitors financial and operational performance in several ways. Business leaders, consumers and health care professionals across the state sit on our Board of Directors. The Board sets standards for operations and financial performance. Such standards include the amount of operating reserves we maintain. Reserves are funds that are set aside over and above dollars needed to pay claims and run the business. The Board also establishes and monitors all policies governing the conduct of our employees, officers and directors. These policies ensure that the corporation operates ethically and within the laws and regulations prescribed for us. Our mission BCBSNE exists to deliver the health and wellness solutions people value most. 3 Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Advertising Policy As a NEtwork Blue health care provider, you are permitted to mention your Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE) network affiliation(s) in any electronic or print advertising or promotional materials, such as telephone directories, websites, and brochures with prior approval. As a health care provider you are NOT permitted to use the Blue Cross and Blue Shield symbols at any time. You are required to submit your camera-ready copy for review and approval to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska Public Relations and Corporate Communications Department P.O. Box 3248 Omaha, NE 68180-0001 4 Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Table of Contents Section 1 NEtwork BLUE Section 2 What is the BlueCard® Program? Section 3 Federal Employee Health Benefits Program Section 4 Member ID Card Information Section 5 Member Cost-Share Information Section 6 Preventive Care Benefits Section 7 Routine Vision Services Section 8 Pharmacy Benefits Overview Section 9 Provider Responsibilities Section 10 Claims Submission and Provider Reimbursement Section 11 General Billing Guidelines – Professional Section 12 General Billing Guidelines – Hospital and Facility Section 13 Home Medical Equipment, Home Infusion, Home Health, and Hospice Section 14 Mental Health Section 15 Quality Management Section 16 Member Benefit Appeal, Network Termination and Appeal, and Provider Corrective Actions Section 17 Non-Covered Services Section 18 Definitions, Terms, and Abbreviations Section 19 How to Contact Us 5 Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 1 NEtwork BLUE What is NEtwork BLUE? NEtwork BLUE is Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska’s PPO network. This network serves as the foundation for all of our business. Claim Information NEtwork BLUE providers can access claim status information, as well as remittance advice information for a processed claim, by logging into NaviNet (www.navinet.net/solutions/plans/bcbsne). Information is also made available to providers through our telephone voice response system at 800-635-0579. Providers who have not signed an agreement with BCBSNE are not able to access claim information telephonically. Direct Payment As a Participating Provider in NEtwork BLUE, you will receive direct payment for covered services in accordance with your provider agreement. Claims from non-participating providers are paid to the member. Notification of Disposition You always know when a claim is paid, how much is paid and what the patient’s liability is because you receive our remittance advice. Patient Base We actively promote our health care professionals and facilities. Provider access information is continuously updated on local, national and group websites for customers to review when making a selection. Up-to-date provider directories are available to our customers at www.nebraskablue.com. Members who obtain covered services from network providers have lower out-of-pocket expenses and receive the highest level of benefits. You are responsible for your relationship with each patient and are solely responsible for the medical care provided, including the discussion of treatment alternatives. BCBSNE does not prohibit you from discussing treatment options or pricing with members or others as authorized by law, irrespective of BCBSNE’s position on the treatment options or from advocating on behalf of members within the utilization management program or grievance process established by the Policies and Procedures Manuals or a person contracting with BCBSNE. Provider Nondiscrimination BCBSNE will not discriminate with respect to plan participation or coverage against any health care provider acting within the scope of that provider’s license or certification under applicable state law, in accordance with ACA Section 1558 and PHSA Section 2706. 6 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Confidence You can rely on our excellent reputation in the industry and the community. We’ve done business in Nebraska for over half a century. Our network consultants and physician reviewers who help develop our policies are also BCBSNE network providers. We work jointly with our health care professionals in providing the best health care possible to our customers. How to Participate? To participate in NEtwork BLUE, complete the credentialing process and sign a NEtwork BLUE agreement. All NEtwork BLUE applicants must go through the credentialing process and satisfy all credentialing requirements prior to being accepted into the PPO network. Note: BCBSNE cannot credential a provider who holds a temporary Nebraska state license. BCBSNE entered into an arrangement with the Council of Affordable Quality Healthcare (CAQH), as part of an initiative to obtain professional credentialing information electronically. The Council offers an electronic application that can be completed online, and because CAQH is used by some other insurance companies, using CAQH will reduce some of the administrative duplication of efforts related to credentialing. Provider offices that have already been supplying information to CAQH will want to verify that BCBSNE has been granted access to the credentialing data and that the information stored by CAQH remains active and valid. New practitioners wishing to join BCBSNE can complete the CAQH application and authorization directly to BCBSNE. More details about CAQH and the process to join are available at www.caqh.org For more information regarding Credentialing and/or to request a Provider Agreement, please visit www.nebraskablue.com/providers/credentialing/ For questions pertaining to credentialing or to inquire about the status of an application, call or send an e-mail to: Phone: 402-982-8293 or 800-821-4787 (option 4) Fax: 402-392-4148 E-mail: credentialingrequests@nebraskablue.com How do I know if I’ve been accepted in NEtwork BLUE? Health Care Providers / Facilities whose applications have been approved for participation will be notified in writing. Adding or Changing Practice Locations If a Health Care Provider is already in our network and is adding a location with the same tax identification number, would like to extend their network status to an additional location with a different tax identification number while keeping the current/old location active, or is transferring 7 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents network status to a new location under a new tax identification number, they need to complete a Provider Add/Extend/Transfer form. The form requires the practitioner’s signature and is available at www.nebraskablue.com by clicking the “Providers” button and then on “Forms for Providers” in the left column. The Tax ID Number that should be listed at the top of the form is the one tied to the current practice location and existing BCBSNE Provider Agreement. All required fields must be completed prior to printing out and submitting the form to BCBSNE. Submitting a Facility/Clinic Name Change When a facility changes its name but keeps the same tax ID, ownership, location and providers, BCBSNE must be notified by letter or email (ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com) requesting the name be changed from [current name] to [new name] and include in the request the tax ID that the new name will appear under. If the facility has multiple NPI’s and lines of business (skilled nursing, home health, hospice, HME, etc.) those entities must also be listed in the request. The request needs to also include the effective date. Tax Identification Number - Multiple Locations As a network provider, you have agreed to file all claims to BCBSNE for any covered benefit provided to our members and to accept our payment as payment in full. If an office has multiple locations with multiple billing addresses, the provider will need to designate one payee location. BCBSNE policy is that all payment will go to one location since the offices share the same tax identification number. National Provider Identifier (NPI) The Administrative Simplification provisions of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) mandated the adoption of standard unique identifiers for health care providers. As a result, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) developed the National Plan and Provider Enumeration System (NPPES) to assign these unique identifiers. BCBSNE also requires providers to use an NPI number when submitting claims. Providers can apply for NPIs in one of three ways: For the fastest receipt of NPIs, use the web-based application process. Simply log onto the National Plan and Provider Enumeration System (NPPES) at https://nppes.cms.hhs.gov and apply on line. To complete the paper NPI Application/Update Form, providers may obtain a copy of the form in any of these ways: o Phone: 800-465-3203 or TTY 800-692-2326 o E-mail: customerservice@npienumerator.com o Mail: NPI Enumerator P.O. Box 6059 Fargo, ND 58108-6059 8 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Onsite Review BCBSNE may designate an Onsite Review Coordinator to examine quality of care at an office where any issues of safety, privacy or environment have been brought to our attention. An assessment will be made by the Coordinator and a summary of findings will be provided to the provider. If corrective action is deemed necessary, a repeat visit will be scheduled. Bill Audit This section includes information about the Bill Audit Program. Standard Review Policy BCBSNE reserves the right to perform a review or audit of any service provided to covered persons performed by physicians, hospitals, or other health care providers. BCBSNE can conduct reviews to assess medical record completeness, quality of care, billing practices, and management of other applicable areas of concern to BCBSNE. Reviews may also be conducted as a part of BCBSNE’s Utilization Review Program. For example, a review may be part of a continued stay review, case management review, medical necessity review, DRG validation review or other review of services provided to members. These reviews may be conducted onsite, or BCBSNE may request documents to review at the BCBSNE site. Health Care Providers agree to cooperate and assist with these efforts. BCBSNE agrees to abide by reasonable and non-obstructive practices. Reviews and audits will be conducted by BCBSNE staff or designated vendors acting on behalf of BCBSNE. The review may include inspection and duplication of any and all medical and other records applicable to treatment of a covered person necessary to determine liability and/or to verify performance. Only medical records of BCBSNE covered persons will be reviewed. Covered persons have consented to release medical records to us and an additional release is not required. All information resulting from a review is confidential. BCBSNE reserves the right to require a NEtwork Blue physician, facility or other health care provider to comply with recommendations resulting from reviews or audits when noncompliance with BCBSNE utilization review criteria is identified. Prepayment / Post-payment Review The purpose of these reviews is to monitor and assess the accuracy of diagnosis and procedure coding as well as the medical necessity of services provided. Claims subject to prepayment / post-payment reviews include, but are not limited to: 1) All inpatient claims indicating a readmission within seven (7) calendar days are subject to review. Each readmission is reviewed in conjunction with the previous admission. 9 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) All inpatient claims indicating a transfer to an inpatient facility. All outlier claims as identified by BCBSNE Bill Audit Department. All inpatient interim claims. Randomly selected outpatient claims. Medical/Surgical services performed in an office and/or patient’s home. DRG Category Assignment If the diagnosis/procedural code information submitted on an inpatient claim is determined to be incorrect following a review of pertinent parts of facility patient records, a DRG category regrouping will be made, and contract payment is adjusted. Notification of the regrouping is issued to the facility. DRG Assignment Appeal Facilities have the right to appeal the DRG regrouping assignment or associated payment. An appeal request must be submitted in writing. The appeal must include all documentation to support the request. Submit the appeal and all additional material to the following address: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska Special Investigations Unit Attention: Health Network Reimbursement, DRG Unit P.O. Box 3248 Omaha, NE 68180-0001 Appeal information is reviewed by the Institutional Reimbursement staff. The appeal will be processed after receipt of all necessary clinical information. A written response will be issued within 30 calendar days. Bill Audit Program Audit Process The audit process can be conducted as either a desk review of the pertinent records at BCBSNE or an onsite audit of the same records at the facility. If an onsite audit is performed, BCBSNE will contact the facility to schedule an appropriate audit date as soon as possible. BCBSNE will verify the mutually agreed upon audit date and time. An itemized statement and any applicable facility audit work papers are generally requested prior to scheduling the audit. Preliminary Report Sheet and the Final Summary of Adjustments When an audit has been completed, a Preliminary Report Sheet is provided to the facility outlining the audit findings. Either BCBSNE or the facility may request an onsite exit interview, if desired. Onsite Exit Interview: If an onsite exit interview is requested, audit results will be reviewed with the facility within 30 days of completion of the audit findings. 10 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Upon completion of the exit interview, BCBSNE has fourteen (14) calendar days to return the Final Summary of Adjustments back to the facility. After the receipt date of the Final Summary of Adjustments the facility has 14 calendar days to file a written appeal. If an appeal is not received by close of business on the 14th calendar day, the Final Summary of Adjustment will stand as final. Process to Appeal Bill Audit Findings 1) The facility is required to submit a written appeal to BCBSNE. The appeal must state the specific reason for the dispute. Send the appeal and all required supporting documentation to the following address: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska ATTN: Bill Audit/SIU P.O. Box 3248 Omaha, NE 68180-0001 2) Required supportive documentation: a. The appeal must be accompanied by any new or additional documentation from facility records to substantiate the facility’s position. This additional information must meet the following criteria: i. The information must be relevant to the disputed issue(s), and ii. it must have existed during the dates of stay for the record in question, and iii. provide evidence based supporting documentation. b. If the appeal contests the case review decision of the BCBSNE Medical Director or other BCBSNE physician consultant, the facility must provide its medical staff member or medical consultant written reply to BCBSNE for case review. c. Peer-reviewed medical literature and other expert opinion may be included. 3) Level II Appeal Process – Upon communication of the appeal results, the facility has an additional 14 calendar days to submit a written notice of second appeal with additional supportive documentation. The Bill Audit staff will review the additional documentation. If the dispute is still unresolved, Bill Audit staff will forward documentation to the BCBSNE Medical Director or other BCBSNE Physician Consultant. Once Physician/Medical Director decision is made, documentation for that decision will be returned to the Bill Audit Department to communicate the appeal results back to the facility. Bill Audit Provisions 1) All BCBSNE policies and procedures, medical policy, and Provider Agreements are considered while reviewing medical records. BCBSNE medical policy includes, but is not limited to: medical necessity policy and investigative policy. 11 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 2) In no case will an audit be scheduled beyond one year from the final payment date. 3) Once a claim has been selected for audit review, the facility should not submit a replacement or corrected electronic or paper claim nor should one be submitted at any time during or after the review process. 4) Standing orders or care protocols must be available for review. 5) Charges for nursing and/or ancillary personnel care that do not include supplies are not considered billable services and will be removed from the charges prior to calculation of negotiated reimbursement methodology. These services are not billable to the member. 6) Issues identifying lack of appropriate documentation to support billed charges may result in recommendations by our audit staff to address a corrective action plan. These recommendations are noted in the Final Report Letter. Effective for dates of services three (3) months after such recommendation, continued absence of appropriate documentation supporting billed charges will result in disallowance of those charges. 7) When BCBSNE medical policy determines an item or service to be investigative or experimental, the item(s) or service(s) considered noncovered services will be deducted from the total charges prior to calculation of reimbursement methodology. These noncovered services may or may not be billed directly to the member. Examples of Nonbillable Facility Charges The list below contains examples of nonbillable facility component charges. This list is NOT an all-inclusive list of nonbillable charges. Nonbillable charges are removed from the total charges before calculating reimbursement. Nonbillable services may not be billed to the member. Nonbillable Services • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Administration of blood products or medications After-hours, On-call, stand-by, emergency call or stat charges - e.g., Lab, EKG/EEGs, X-ray, CT Scan, U/S, Nuc. Med., O.R. Blood service charges Bone marrow collection or aspiration Bronchoscopy assist Catheterization technical services Charges for nursing and/or ancillary personnel care that do not include supplies Code 99, CPR, or unscheduled cardioversion E.R. patient assist or transport Extubation/intubation Insertion of catheters, i.e., arterial, Groschong, central line, PICC, IV, foley, nasogastric Incentive spirometry or MDI treatment Kinetic consult or monitoring Manual ventilation 12 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • • • • • • • • • • • Medication mixing fees Nasal tracheal, tracheal tube suction or aspiration, cough induction, suctioning, secretion induction Patient assessment Patient assistance Patient education or teaching Patient transportation Pathology tech assist or slide preparation Peritoneal lavage procedure Set-up charges e.g., ventilators, arterial lines, oximetry, etc. Swab specimen collection Therapist assist; PT/OT/Speech, Respiratory Therapist Vital sign monitoring Duplication of Therapeutic Services 13 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 2 What is the BlueCard® Program? Definition BlueCard® is a national program that enables members of one Blue Plan to obtain health care services while traveling or living in another Blue Plan’s service area. The program links participating health care providers with independent Blue Plans across the country, and in more than 200 countries and territories worldwide through a single electronic network for claims processing and reimbursement. The program allows you to submit claims for patients from other Blue Plans, domestic and international, to your local Blue Plan. Your local Blue Plan is your sole contact for claims payment, problem resolution and adjustments. BlueCard® Program Advantages to Providers The BlueCard® Program allows you to conveniently submit claims for members from other Blue Plans, including international Blue Plans, directly to Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE). BCBSNE will be your one point of contact for all of your claims-related questions. BCBSNE continues to experience growth in out-of-area membership because of our partnership with you. That is why we are committed to meeting your needs and expectations. In doing so, your patients will have a positive experience with each visit. Products Included in BlueCard A variety of products and claim types are eligible to be delivered via BlueCard; however, not all Blue Plans offer all of these products to their members: • • • • • • • • Traditional (Indemnity insurance) PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization) POS (Point of Service) HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) Medigap Medicaid (Payment is limited to the member’s Plan’s state Medicaid reimbursement rates.) These cards will not have a suitcase logo. SCHIP (State Children’s Health Insurance Plan) if administered as part of Medicaid: payment is limited to the member’s Plan’s state Medicaid reimbursement rates. These member ID cards also do not have a suitcase logo. Stand-alone SCHIP programs will have a suitcase logo. 14 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • Stand-alone vision Stand-alone prescription drugs Note: Stand-alone vision and stand- alone self-administered prescription drugs programs are eligible to be processed through BlueCard when such products are not delivered using a vendor. Refer to the claim filing instructions on the back of the ID cards. Products Excluded from the BlueCard Program The following claims are excluded from the BlueCard Program: • Stand-alone dental • Medicare Advantage • The Federal Employee Program (FEP) How does the BlueCard® Program work? How to Identify Members When a member of a Blue Plan arrives at your office or facility, be sure to ask them for their current Blue Plan membership identification (ID) card. The main identifier for out-of-area members is the alpha prefix. The ID cards also may have: PPO in a suitcase logo, for eligible PPO members Blank suitcase logo Important facts concerning member IDs: A correct member ID number includes the alpha prefix (first three positions) and all subsequent characters, up to 17 positions total. The alpha prefix on a member’s ID must be three characters. It is always located at the beginning of the member’s ID number. Some member ID numbers may include alphabetic characters in other positions following the alpha prefix. Others may be fewer than 17 positions. Do not add/delete characters or numbers within the member ID. Do not change the sequence of the characters following the alpha prefix. The alpha prefix is critical for the electronic routing of specific HIPAA transactions to the appropriate Blue Plan. Alpha Prefix The three-character alpha prefix, at the beginning of the member’s ID number, is the key element used to identify and correctly route claims. The alpha prefix identifies the Blue Plan or National 15 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Account to which the member belongs. It is critical for confirming a patient’s membership and coverage. To ensure accurate claim processing, it is critical to capture all ID card data. If the information is not captured correctly, you may experience a delay with the claim processing. Please make copies of the front and back of the ID card, and pass this key information to your billing staff. Do not make up alpha prefixes. Sample ID Cards The three-character alpha prefix. The “PPO in a suitcase” logo may appear in the lower right corner of the I.D. card. BlueCard ID cards have a suitcase logo, either as an empty suitcase or as a PPO in a suitcase. The PPO in a suitcase logo indicates that the member is enrolled in either a PPO product or an EPO product. In either case, you will be reimbursed according to your NEtwork BLUE provider agreement. Please note, however, that EPO products may have limited benefits out-of-area. The potential for such benefit limitations are indicated on the reverse side of an EPO ID card. The empty suitcase logo indicates that the member is enrolled in one of the following products: Traditional, HMO or POS. For members having traditional, HMO or POS coverage, you will be reimbursed for covered services according to your NEtwork BLUE provider agreement. Some Blue ID cards don’t have any suitcase logo on them. Those are the ID cards for Medicaid, State Children’s Health Insurance Programs (SCHIP) if administered as part of State’s Medicaid, and Medicare Complementary and Supplemental products, also known as Medigap. Government-determined reimbursement levels apply to these products. While BCBSNE routes all of these claims for out-of-area members to the member’s Blue Plan, most of the Medicare Complementary or Medigap claims are sent directly from the Medicare intermediary to the member’s Plan via the established electronic crossover process. 16 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents How to Identify International Members Occasionally, you may see ID cards from Blue members of international Blue Plans, which include: BCBS of U.S. Virgin Islands, BCBS of Uruguay and BCBS of Panama. These ID cards will also contain three-character alpha prefixes. Please treat these members the same as domestic Blue Plan members (e.g. do not collect any payment from the member beyond their cost-sharing amounts such as deductible, coinsurance, and copayment). Submit all claims for international Blue members to BCBSNE. NOTE: The Canadian Association of Blue Cross Plans and its members are separate and distinct from the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association and its members in the United States. Claims for members of the Canadian Blue Cross Plans are not processed through the BlueCard Program. Please follow the instructions of these Plans and those, if any, on their ID cards for servicing their members. The Blue Cross Plans in Canada are: Alberta Blue Cross Manitoba Blue Cross Atlantic Blue Cross Care Quebec Blue Cross Saskatchewan Blue Cross Pacific Blue Cross Consumer Directed Healthcare and Healthcare Debit Cards Consumer Directed Healthcare (CDHC) is a term that refers to a movement in the healthcare industry to empower members, reduce employer costs and change consumer healthcare purchasing behavior. 17 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Health plans that offer CDHC provide the member with additional information to make an informed and appropriate healthcare decision through the use of member support tools, provider and network information and financial incentives. Members who have CDHC plans often carry healthcare debit cards that allow them to pay for out-of-pocket costs using funds from their Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA), Health Savings Account (HSA) or Flexible Spending Account (FSA). All three are types of tax favored accounts offered by the member’s employer to pay for eligible expenses not covered by the health plan. Some cards are “stand-alone” debit cards that cover eligible out-of-pocket costs, while others also serve as a health plan member ID card. These debit cards can help you simplify your administration process and can potentially help: • • • • Reduce bad debt Reduce paper work for billing statements Minimize bookkeeping and patient-account functions for handling cash and checks Avoid unnecessary claim payment delays The card will have the nationally recognized Blue logos, along with the logo from a major debit card such as MasterCard® or Visa® Sample stand-alone Health Care Debit Card Sample combined Health Care Debit Card and Member ID Card 18 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The cards include a magnetic strip allowing providers to swipe the card at the point of service and collect the member cost sharing amount. With health debit cards, members can pay for copayments and other out-of-pocket expenses by swiping the card through any debit card swipe terminal. The funds will be deducted automatically from the appropriate member’s HRA, HSA or FSA account. Combining a health insurance ID card with a source of payment is an added convenience to members and providers. Members can use their cards to pay outstanding balances on billing statements. They can also use their cards via phone in order to process payments. In addition, members are more likely to carry their current ID cards because of the payment capabilities. If your office currently accepts credit card payments, there is no additional cost or equipment necessary. The cost to you is the same as what you pay to swipe any other signature debit card. Helpful tips: • Ask members for their current ID card and regularly obtain new photocopies (front and back) of the member ID card. Having the current card will enable you to submit claims with the appropriate member information (including alpha prefix) and avoid unnecessary claims payment delays. • Check eligibility and benefits by submitting an Eligibility and Benefits Inquiry through NaviNet, or by calling the BlueCard Eligibility line at 800-676-BLUE (2583). • If the member presents a debit card (stand-alone or combined), be sure to verify the copayment amounts before processing payment. • Remember, a deductible amount applicable to a service can change between the time of service and when the claim is actually processed. This can also affect the member coinsurance amount since the coinsurance amount is determined after applying any remaining deductible to the allowable charge. Therefore, we ask that at the time of service, the debit card only be used for the collection of “known” member copayments or “verified” non-covered services. • Please do not use the card to process full payment upfront. • For questions about the debit card processing instructions or payment issues, please contact the toll-free debit card administrator’s number on the back of the card. Note: All services, regardless of whether or not you’ve collected the member responsibility at the time of service, must be billed to BCBSNE for proper benefit determination, and to update the member’s claim history. 19 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Limited Benefits Products Verifying Blue patients’ benefits and eligibility is now more important than ever. In addition to patients who have traditional Blue PPO, HMO, POS or other coverage, typically with high lifetime coverage limits (i.e. $1million or more) you may now see patients whose annual benefits are limited to $50,000 or less. Currently, Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska does not offer such limited benefit plans to our members; however, you may see patients with limited benefits who are covered by another Blue Plan. How do I recognize members with limited benefits products? Patients who have Blue limited benefits coverage carry ID cards that have: • Either of two product names - InReach or MyBasic, • A tagline in a green stripe at the bottom of the card, and • A black cross and/or shield to help differentiate it from other identification cards. These ID cards may look like this: How do I know if the patient has limited benefit coverage? In addition to obtaining a copy of the patient’s ID card and regardless of the benefit product type, we recommend that you verify patient’s benefits and eligibility prior to rendering services, whenever possible. You may do so by submitting an Eligibility and Benefits inquiry through NaviNet, or you may call the BlueCard Eligibility Line at 800-676-BLUE (2583). Whether you access this information on the provider portal or by telephone, you will receive your patient’s accumulated benefits to help you understand the benefits remaining for the member. What should I do if the patient’s benefits are exhausted before the end of their treatment? Annual benefit limits should be handled in the same manner as any other limits on the medical coverage. We recommend that you inform the patient of any potential liability they might have as soon as possible. 20 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Coverage and Eligibility Verification To verify eligibility and benefits for other Blue Plan members, submit an Eligibility and Benefits request through NaviNet. You may also call the BlueCard Eligibility® line at 800-676-BLUE (2583). English and Spanish speaking phone operators are available to assist you. Submitting your inquiry through NaviNet is the most efficient method of verifying a Blue member’s eligibility and benefits. However, if you choose to call the BlueCard Eligibilility line, keep in mind that Blue Plans are located throughout the country and may operate on a different time schedule than BCBSNE. You may be transferred to a voice response system linked to customer enrollment and benefits or you may need to call back at a later time. Note: The BlueCard Eligibility® line is for eligibility, benefit and pre-certification/referral authorization inquiries only. It should not be used for claim status. Electronic Health ID Cards Some Blue Plans have implemented electronic health ID cards to facilitate a seamless coverage and eligibility verification process. Electronic health ID cards enable electronic transfer of core subscriber/member data from the ID card to the provider’s system. • A Blue electronic health ID card has a magnetic stripe on the back of the ID card, similar to what you can find on the back of a credit or debit card. • The subscriber/member electronic data is embedded on the third track of the three-track magnetic stripe, and includes subscriber/member name, subscriber/member ID, subscriber/member date of birth and Plan ID. • The PlanID data element identifies the health plan that issued the ID card. Plan ID will help providers facilitate health transactions among various payers in the marketplace. • Providers will need a track 3 card reader in order for the data on track 3 of the magnetic stripe to be read (the majority of card readers in provider offices only read tracks 1 and 2 of the magnetic stripe, tracks 1 and 2 are proprietary to the financial industry.). 21 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Sample of electronic health ID card Utilization Review You should remind patients that they are responsible for obtaining pre-certification/preauthorization for their services from their Blue Plan. You may also contact the member’s Plan on the member’s behalf. You can do so by: • Phone - Call the utilization management / pre-certification number on the back of the member’s ID card. • If the utilization management number is not listed on the back of the member’s ID card, call 800-676-BLUE (2583) and ask to be transferred to the utilization review area. • The member’s Blue Plan may contact you directly regarding clinical information and medical records prior to treatment or for concurrent review or disease management for a specific member. Medical Policy and Pre-cert Lists for all Blue Plans In one easy step, you can look up medical policy and precertification/preauthorization requirements applicable to your out-of-area Blue members. To access medical policy and precertification/preauthorization information, go to the “Provider” page at www.nebraskablue.com, and click on “Medical Policy and Pre-cert Lists for all Blue Plans”. Once you are on the page, choose “Medical Policy” or “General Precertification/Preauthorization Information”, enter the member’s three-character alpha prefix, and click “Submit”. The member’s Blue Plan site will be displayed. This is an excellent resource for the verification of medical policy applicable to a member’s benefit contract, and required precertification/preauthorization requirements. Claim Filing After the member of another Blue Plan receives services from you, you should file the claim with the local Blue Plan. Generally speaking, your local Blue Plan is BCBSNE. However, the determination 22 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents of “local” Blue Plan can differ for contiguous county providers, and ancillary providers. Refer to the subsections related to these topics for more information. When serving as your local Plan, we will work with the member’s Blue Plan to process the claim. Once the claim is adjudicated, the member’s Blue Plan will send the member an explanation of benefits (EOB). BCBSNE will send you the remittance advice (RA) and claim payment for covered services. • Benefits are determined by the Blue Plan that insures the member. • Payment for covered services is made to the provider in accordance to the terms of the provider agreement. Below is an example of how claims flow through BlueCard®: Following these helpful tips will improve your claim experience: • Ask members for their current member ID card and regularly obtain new photocopies of it (front and back). Having the current card enables you to submit claims with the appropriate member information (including alpha prefix) and avoid unnecessary claim payment delays. • Check eligibility and benefits online with NaviNet. You may also call BlueCard Eligibility® at 800-676-BLUE (2583). 23 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • Verify the member’s cost sharing amount before processing payment. Do not collect full payment upfront. • Be sure to include the members’ complete identification number, including alpha-prefix, when submitting the claim. Claims with incorrect or missing alpha prefixes and member identification numbers cannot be processed. • Do not send duplicate claims. Sending another claim, or having your billing agency resubmit claims automatically, actually slows down the claims payment process and creates confusion for the member. • Use NaviNet as your primary source of claim status verification. To verify claim status over the phone, call GABBI (800-635-0579) at BCBSNE. Do NOT contact the member’s out-of-area Blue Plan regarding a post-service claim. Contiguous Area Claim Filing A contiguous area is generally a border county in another Blue Plan’s service area one county over from the Plan’s own service area. Claim filing rules for contiguous area providers are based on the permitted terms of the contiguous area contract which may include: • • • • The provider’s physical location The providers contract status with the two contiguous states The member’s Plan and where the member works or resides The location where the member received services Scenario One 1. Provider is located in Nebraska and has a contract with BCBSNE. 2. Provider also has a contiguous area contract with the Iowa plan. 3. Provider files a claim to Iowa for an Iowa member who resides or works in Iowa. It is a local Iowa in-network claim. 4. Provider files a BCBSNE member’s claim to BCBSNE. It is a local Nebraska in-network claim. 5. Provider files claims for an Iowa member who does NOT reside or work in Iowa, or any other Plan’s member, to BCBSNE. BlueCard processing applies, and it is an in-network claim. Scenario Two 1. Provider is located in Nebraska and has a contract with BCBSNE. 2. Provider does not have a contiguous area contract with the Iowa plan. 3. Provider files a claim BCBSNE member’s claim to BCBSNE. It is a local Nebraska in-network claim. 4. Provider files claims for an Iowa member and any other Plan’s member to BCBSNE. BlueCard processing applies, and it is an in-network claim. 24 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Scenario Three 1. Provider is located in Nebraska and does not have a contract with BCBSNE. 2. Provider has a contiguous area contract with the Iowa plan. 3. Provider files a claim to Iowa for an Iowa member who resides or works in Iowa. It is a local Iowa in-network claim. 4. Provider files a claim for a BCBSNE member to BCBSNE. It is a local BCBSNE out-of-network claim. 5. Provider files claims to BCBSNE for an Iowa member who does NOT reside or work in Iowa, as well as any other Blue Plan out-of-area member. BlueCard processing applies, and it is an out-of-network claim. Scenario Four 1. Provider has an office in Nebraska in an area contiguous to Iowa, and an office in Iowa contiguous to Nebraska. 2. Provider has a contract with BCBSNE and the Iowa Plan. 3. Provider sees a Nebraska member in Nebraska. The claim is filed to BCBSNE and it is a local in-network claim. 4. Provider sees an Iowa member who works or resides in Iowa, in his/her Nebraska office. The claim is filed to the Iowa Plan. It is a local Iowa in-network claim. 5. Provider sees an Iowa member in Nebraska, who does not work or reside in Iowa. The claim is filed to BCBSNE. BlueCard processing applies, and it is an in-network claim. 6. Provider sees any other out-of-area Blue member in his/her Nebraska office. The claim is filed to BCBSNE. BlueCard processing applies, and it is an in-network claim. Scenario Five 1. Provider has an office in Nebraska in an area contiguous to Iowa, and an office in Iowa in an area contiguous to Nebraska. 2. Provider has a contract with BCBSNE but does not have a contract with Iowa. 3. Provider sees a BCBSNE member in Nebraska. The claim is filed to BCBSNE. It is a local in-network claim. 4. Provider sees any other Plan member in Nebraska. The claim is filed to BCBSNE. BlueCard processing applies, and it is an in-network claim. 5. Provider sees an Iowa member in Iowa. The claim is filed to the Iowa Plan. It is a local out-of-network claim. 6. Provider sees any other Plan member in Iowa. The claim is filed to the Iowa Plan. BlueCard processing applies, and it is an out-of-network claim. Scenario Six 1. Provider has an office in Nebraska in an area contiguous to Iowa, and an office in Iowa in an area contiguous to Nebraska. 2. Provider does not have a contract with Nebraska or Iowa. 3. Provider sees a Nebraska member in Nebraska. The claim is filed to BCBSNE. It is a local Nebraska out-of-network claim. 25 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 4. Provider sees any other Plan member in Nebraska. The claim is filed to BCBSNE. BlueCard processing applies. It is a BlueCard out-of-network claim. 5. Provider sees an Iowa member in Iowa. The claim is filed to the Iowa Plan. It is a local Iowa out-of-network claim. 6. Provider sees any other Plan member in Iowa. The claim is filed to the Iowa Plan. BlueCard processing applies. It is a BlueCard out-of-network claim. Ancillary Claim Filing (for BCBSNE and other Blue Plan members, but excluding FEP members) Ancillary providers are defined as Independent Clinical Laboratory, Durable/Home Medical Equipment and Supplies, and Specialty Pharmacy providers. These ancillary providers must file their claim to the local Blue Plan, regardless of their network status with that Plan. The local Blue Plan is determined as follows: Independent Clinical Laboratory (Lab) - The Plan in whose state the specimen was drawn. Durable/Home Medical Equipment and Supplies (DME) - The Plan in whose state the equipment was shipped to or purchased at a retail store. Specialty Pharmacy - The Plan in whose state the member resides. Note: If you contract with more than one Plan in a state for the same product type (i.e., PPO or Traditional), you may file the claim with either Plan. • The ancillary claim filing rules apply regardless of the provider’s contracting status with the Blue Plan where the claim is filed. Providers who do not currently have a contract with a Plan where claims will be filed should contact the out-of-state Plan directly for information. • Providers are encouraged to verify member eligibility and benefits using the provider portal on NaviNet, contacting the phone number on the back of the Member ID card or calling 800-676-BLUE (2583) prior to providing any ancillary service. • Members are financially liable for ancillary services not covered under their benefit plan. It is the provider’s responsibility to request payment directly from the member for non-covered services. • FEP member claims for DME, Home Infusion Therapy supplier, and independent laboratories must be filed to the Plan where the provider is located. 26 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Required fields as noted in the following chart must be populated on the claim. Claims that are missing required information will be returned to the provider. Provider Type Independent Clinical Laboratory (any type of non -hospital based laboratory) Types of Service include, but are not limited to: Blood, urine, samples, analysis, etc. Durable/Home Medical Equipment and Supplies (DME/HME) Types of Service include, but are not limited to: Hospital beds, oxygen tanks, crutches, etc. How to file (required fields) Where to file Referring Provider Name and Type I NPI Number: - Field 17B on CMS 1500 Health Insurance Claim Form or - Loop 2310A (claim level) on the 837 Professional Electronic File the claim to the Plan in whose state the specimen was drawn* * Where the specimen was drawn will be determined by which state the referring provider is located. Patient’s Address: - Field 5 on CMS 1500 Health Insurance Claim Form or - Loop 2010CA on the 837 Professional Electronic Submission. File the claim to the Plan in whose state the equipment was shipped to or purchased in a retail store. Ordering Provider Name and Type I NPI Number: - Field 17B on CMS 1500 Health Insurance Claim Form or - Loop 2420E (line level) on the 837 Professional Electronic Submission. Note: Items shipped to the patient should be submitted with a POS 12 (Home). Items purchased in the retail store should be submitted with a POS 17 (Retail Clinic). Place of Service: - Field 24B on the CMS 1500 Health Insurance Claim Form or - Loop 2300, CLM05-1 on the 837 Professional Electronic Submissions. Specialty Pharmacy Types of Service: Non-routine, biological therapeutics ordered by a healthcare professional as a covered medical benefit as defined by the member’s Plan’s Specialty Pharmacy formulary. Include, but are not limited to: injectable, infusion therapies, etc. 27 Service Facility Location Information: - Field 32 on CMS 1500 Health Insurance Form or - Loop 2310C (claim level) on the 837 Professional Electronic Submission. Referring Provider Name and Type I NPI Number: - Field 17B on CMS 1500 Health Insurance Claim Form or - Loop 2310A (claim level) on the 837 Professional Electronic Submission. File the claim to the Plan whose state the member resides. Example Blood is drawn* in lab or office setting located in Nebraska . Blood analysis done in Minnesota. File claim to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska. *Claims for the analysis of a lab must be filed to the Plan in whose state the specimen was drawn. A. Wheelchair is purchased at a retail store in Nebraska. File claim to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska. The physical location of the retail store must be populated in field 32 (Loop 2310C). B. Wheelchair is purchased on the internet from an online retail supplier in Nebraska and shipped to Minnesota.. File claim to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota. Field 32 (Loop 2310C) should be blank. C. Wheelchair is purchased at a retail store in [Nebraska and shipped to Minnesota. File claim to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota. Patient is seen by a physician in Nebraska who orders a specialty pharmacy injectable for this patient. Patient will receive the injections in Florida where the member lives for 6 months of the year. File to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska. Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Medicare Advantage Claims Overview “Medicare Advantage (MA) is the program alternative to standard Medicare Part A and Part B fee-for-service coverage, generally referred to as “traditional Medicare”. Members will not have a standard Medicare card; instead, a Blue logo will be visible on the ID card. The following examples illustrate how the different products associated with the Medicare Advantage Program will be designated on the front of the member’s ID card. MA offers Medicare beneficiaries several product options (similar to those available in the commercial market), including health maintenance organization (HMO), preferred provider organization (PPO), point-of-service (POS) and private fee-for-service (PFFS) plans. All Medicare Advantage plans must offer beneficiaries at least the standard Medicare Part A and B benefits, but many offer additional covered services as well (e.g., enhanced vision and dental benefits). In addition to these products, Medicare Advantage organizations may also offer a Special Needs Plan (SNP), which can limit enrollment to subgroups of the Medicare population in order to focus on ensuring that their special needs are met as effectively as possible. Medicare Advantage plans may allow in- and out-of-network benefits, depending on the type of product selected. Providers should confirm the level of coverage by calling 800.676.BLUE (2583) or submitting and Eligibility and Benefits inquiry through NaviNet. Medicare Advantage HMO A Medicare Advantage HMO is a Medicare managed care option in which members typically receive a set of predetermined and prepaid services provided by a network of physicians and hospitals. Generally (except in urgent or emergency care situations), medical services are only covered when provided by in-network providers. The level of benefits, and the coverage rules, may vary by Medicare Advantage plan. Medicare Advantage POS A Medicare Advantage POS program is an option available through some Medicare HMO programs. It allows members to determine – at the point of service – whether they want to receive certain designated services within the HMO system, or seek such services outside the HMO’s provider 28 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents network (usually at greater cost to the member). The Medicare Advantage POS plan may specify which services will be available outside of the HMO’s provider network. Medicare Advantage PPO A Medicare Advantage PPO is a plan that has a network of providers, but unlike traditional HMO products, it allows members who enroll access to services provided outside the contracted network of providers. Required member cost-sharing may be greater when covered services are obtained out-of-network. Medicare Advantage PPO plans may be offered on a local or regional (frequently multi-state) basis. Special payment and other rules apply to regional PPOs. Medicare Advantage PFFS A Medicare Advantage PFFS plan is a plan in which the member may go to any Medicare-approved doctor or hospital that accepts the plan’s terms and conditions of participation. Acceptance is “deemed” to occur where the provider is aware, in advance of furnishing services, that the member is enrolled in a PFFS product and where the provider has reasonable access to the terms and conditions of participation. The Medicare Advantage organization, rather than the Medicare program, pays providers on a fee-for-services basis for services rendered to such members. Members are responsible for cost-sharing, as specified in the plan, and balance billing may be permitted in limited instances where the provider is a network provider and the plan expressly allows for balance billing. Medicare Advantage PFFS varies from the other Blue products you might currently participate in: • You can see and treat any Medicare Advantage PFFS member without having a contract with BCBSNE. If you do provide services, you will do so under the Terms and Conditions of that member’s Blue Plan. MA PFFS Terms and Conditions might vary for each Blue Plan and we advise that you review them before servicing MA PFFS members. Refer to the back of the member’s ID card for information on accessing the Plan’s Terms and Conditions. You may choose to render services to a MA PFFS member on an episode of care (claim-by-claim) basis. For your convenience, you will find MA PFFS Terms and Conditions for all Blue Plan on our website (www.nebraskablue.com) by entering the member’s three-character alpha prefix. Submit your MA PFFS claims to BCBSNE. • • • • • Medicare Advantage Medical Savings Account (MSA) Medicare Advantage Medical Savings Account (MSA) is a Medicare health plan option made up of two parts. One part is a Medicare MSA Health Insurance Policy with a high deductible. The other part is a special savings account where Medicare deposits money to help members pay their medical bills. 29 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Medicare Advantage PPO Network Sharing Note: The MedicareBlue Regional PPO plan terminated on December 31, 2012. BCBSNE is exploring the idea of a local Medicare PPO and/or HMO. More information will be shared with the provider community as soon as it is available. We thank you for your service to our Medicare Blue PPO members and we hope to work with you again in the future. Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield Medicare Advantage (MA) PPO members will receive in-network benefits when traveling or living in the service areas of a Blue plan who is participating in Medicare Advantage PPO Network Sharing. Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE) opted not to participate in the Network Sharing program. What does this mean to you? There is no change from your current practice. You should continue to verify eligibility and bill for services as you currently do for any out-of-area Blue Medicare Advantage member you agree to treat. Benefits will be based on the Medicare allowed amount for covered services and be paid under the member’s out-of-network benefits unless the services are for urgent or emergency care. Once you submit the MA claim, BCBSNE will send you the payment. Does this affect my MedicareBlue PPO patient population? No. MedicareBlue PPO members will continue to receive in-network benefits for all covered services received from a MedicareBlue PPO network provider. How do I recognize an out-of-area member from one of these Plans? The “MA” in the suitcase on the member’s ID card indicates a member who is covered under the network sharing program. Do I have to provide services to these Medicare Advantage PPO network sharing members? You may see Medicare Advantage PPO members whose Blue plan participates in network sharing, but you are not required to provide services. Where do I submit the claim? You should submit the claim to BCBSNE as you do today. Do not bill Medicare directly for any services rendered to a Medicare Advantage member. What is the member cost sharing level and co-payments? Any MA PPO member not enrolled with MedicareBlue PPO will pay the out-of-network cost sharing amount. You may collect the co-payment amounts from the member at the time of service. 30 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents May I request full payment upfront? Generally, once the member receives care you should not ask for full payment upfront. • Under certain circumstances when the member has been notified in advance that a service will not be covered, you may request payment from the member before services are rendered or billed to the member. The member should sign an Advance Benefit Notification (ABN) form before services are rendered in these situations. May I balance bill the member the difference in my charge and the allowance? No, you may not balance bill the member for this difference. Members may be balance billed for any deductibles, co-insurance, and/or co-pays. Reimbursement for Medicare Advantage PPO, HMO, POS, PFFS The reimbursement information below applies when a provider treats a Blue Medicare Advantage member to whom the provider’s contract does NOT apply. Based upon the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) regulations, if you are a provider who accepts Medicare assignment and you render services to a Medicare Advantage member for whom you have no obligation to provide services under your contract with a Blue Plan, you will generally be considered a non-contracted provider and be reimbursed the equivalent of the current Medicare allowed amount for all covered services (i.e., the amount you would collect if the beneficiary were enrolled in traditional Medicare). Special payment rules apply to hospitals and certain other entities (e.g., skilled nursing facilities) that are non-contracted providers. Providers should make sure they understand the applicable Medicare Advantage reimbursement rules. Providers that are paid on a reasonable cost basis under Original Medicare should send their CMS Interim Payment Rate letter with their Medicare Advantage claim. This letter will be needed by the Plan to calculate the Medicare allowed amount. Other than the applicable member cost sharing amounts, reimbursement is made directly by a Blue Plan or its branded affiliate. In general, you may collect only the applicable cost sharing (e.g., co-payment) amounts from the member at the time of service, and may not otherwise charge or balance bill the member. Traditional Medicare-Related Claims The following are guidelines for the processing of traditional Medicare-related claims: When Medicare is primary payor, submit claims to your local Medicare intermediary. All Blue claims are set up to automatically cross-over to the member’s Blue Plan after being adjudicated by the Medicare intermediary. 31 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents How do I submit Medicare primary / Blue Plan secondary claims? For members with Medicare primary coverage and Blue Plan secondary coverage, submit claims to your Medicare intermediary and/or Medicare carrier. When submitting the claim, it is essential that you enter the correct Blue Plan name as the secondary carrier. This may be different from the local Blue Plan. Check the member’s ID card for additional verification. Include the alpha prefix as part of the member identification number. The member’s ID will include the alpha prefix in the first three positions. The alpha prefix is critical for confirming membership and coverage, and key to facilitating prompt payments. When you receive the remittance advice from the Medicare intermediary, look to see if the claim has been automatically forwarded (crossed over) to the Blue Plan: • If the remittance advice indicates that the claim was crossed over, Medicare has forwarded the claim on your behalf to the appropriate Blue Plan and the claim is in process. DO NOT file the claim to BCBSNE. • If the remittance advice indicates that the claim was not crossed over, submit the claim to BCBSNE with the Medicare remittance advice. • In some cases, the member identification card may contain a COBA ID number. If so, be sure to include that number on your claim. • Verify claim status by submitting a Claim Status Inquiry on NaviNet, or by calling GABBI (800-635-0579). When should I expect to receive payment? Claims submitted to the Medicare intermediary will be crossed over to the Blue Plan only after they have been processed. This process may take up to 14 business days. This means that the Medicare intermediary will be releasing the claim to the Blue Plan for processing about the same time you receive the Medicare remittance advice. As a result, it may take an additional 14-30 business days for you to receive payment from the Blue Plan. What should I do in the meantime? If you submitted the claim to the Medicare intermediary/carrier, and haven’t received a response to your initial claim submission, don’t automatically submit another claim. Rather, you should: • Review the automated resubmission cycle on your claim system. • Wait 30 days. • Check claims status before resubmitting. Sending another claim, or having your billing agency resubmit claims automatically, actually slows down the claim payment process and creates confusion for the member. Coding your BlueCard Claims Code your claims based upon the medical record and the BCBSNE billing/coding guidelines as noted herein. If the coding/billing guidelines differ between BCBSNE and the Blue plan that insures the member, ALWAYS follow BCBSNE guidelines. 32 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Medical Records Blue Plans around the country have made improvements to the medical records process to make it more efficient. Blue Plans now have the capability to send and receive medical records electronically among each other. This new method significantly reduces the time it takes to transmit supporting documentation for out-of-area claims, reduces the need to request records multiple times and significantly reduces the potential for lost or misrouted records. Under what circumstances may the provider get requests for medical records for out-of-area members? 1. As part of the pre-authorization process – If you receive requests for medical records from other Blue Plans prior to rendering services, as part of the pre-authorization process, you will be instructed to submit the records directly to the member’s Plan that requested them. This is the only circumstance where you would not submit the records to BCBSNE. 2. As part of claim review and adjudication – These requests will come from BCBSNE in the form of a letter requesting specific medical records and including instructions for submission. BlueCard Medical Record Process for Claim Review • An initial communication, generally in the form of a letter, should be received by your office requesting the needed information. • A remittance may be received by your office indicating the claim is being denied pending receipt and review of records. Occasionally, the medical records you submit might cross in the mail with the remittance advice for the claim indicating a need for medical records. A remittance advice is not a duplicate request for medical records. If you submitted medical records previously, but received a remittance advice indicating records were still needed, please contact BCBSNE Provider Service to ensure your original submission has been received and processed. This will prevent duplicate records being sent unnecessarily. • If you received only a remittance advice indicting records are needed, but you did not receive a medical records request letter, contact BCBSNE Provider Service to determine if the records are needed from your office. • Upon receipt of the information, the claim will be reviewed to determine the benefits. Helpful Ways you Can Assist in Timely Processing of Medical Records • If the records are requested following submission of the claim, forward all requested medical records to BCBSNE within ten (10) days, whenever possible. • Follow the submission instructions given on the request, using the specified address or fax number. The address or fax number for medical records may be different than the address you use to submit claims. • Only send the information specifically requested. Do not send “complete” medical records unless asked to do so. • Always include the cover letter you received with the request when submitting the medical records. • Do not write anywhere on the letter that might obstruct information necessary to match the medical records with the claim. 33 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • Do not use marker or highlighter anywhere on the letter or medical records. When the documents are scanned the highlighted portions shows as blacked out and therefore illegible. Do not submit medical records unless they have been requested. Unsolicited medical records will not be reviewed, and could further impede the claim review and adjustment process. Adjustments Claim adjustments must be submitted to BCBSNE. We will work with the member’s Blue Plan for adjustments; however, your workflow should not be different. Appeals Appeals for all claims are handled through BCBSNE. Submit the appeal using an Appeal/Reconsideration Request form, and attach all supportive documentation. BCBSNE will forward the appeal electronically to the member’s Blue Plan for their review. Coordination of Benefits (COB) Coordination of Benefits (COB) refers to how we ensure members receive full benefits and prevent double payment for services when a member has coverage from two or more sources. The member’s contract language explains the order for which entity has primary responsibility for payment and which entity has secondary responsibility for payment. If you discover the member is covered by more than one health plan, and: • • • BCBSNE or another Blue Plan is primary and a non-Blue plan is secondary, include the other carrier’s name and address on the claim filed to BCBSNE. If you do not include the other insurance information with the claim, the member’s Blue Plan may have to investigate the claim. This investigation could delay your payment or result in a post-payment adjustment, which will increase your volume of bookkeeping. A non-Blue Plan is the primary payer and BCBSNE or any other Blue Plan is secondary, submit the claim to BCBSNE with a copy of the Explanation of b=Benefits (EOB) from the primary carrier. Failure to include the primary EOB will result in your claim being denied followed by a post-payment adjustment once the primary eob is received. Both plans are Blue but from different Plans, file the primary claim first. Once the primary Blue claim has been adjudicated, file your secondary Blue claim with a copy of the primary EOB. Note: Unless both the primary and secondary carrier is BCBSNE, you must file the primary and secondary claims separately. It is important to carefully review the payment information from all payers involved on the remittance advice before balance billing the patient for any potential liability. The “patient responsibility” information posted on the remittance advice from the secondary payer may be 34 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents different than the patient liability reported on the primary remittance advice, even if there is no secondary payment made, due to agreed upon provider discounts and member benefit application. Coordination of Benefits Questionnaire To streamline claims processing and reduce the number of denials related to Coordination of Benefits, a universal Coordination of Benefits (COB) questionnaire is available to you on our website: www.nebraskablue.com/providers/forms-for-providers/ When you see a Blue member and are aware they might have other health insurance coverage, you can print out a copy of the questionnaire and have the member complete it at the time of service. Once the member has given you the completed form, send it to BCBSNE with your claim and we will gladly forward it to the member’s Blue Plan. Sending the Coordination of Benefits questionnaire will ensure that the member’s Blue Plan will have the most current information on file, and eliminate the potential for the claim to be denied for lack of coordination of benefits information. Claim Payment 1. BlueCard® claims are priced and adjudicated based on the NEtwork BLUE Provider Agreement you have with BCBSNE. As a participating NEtwork BLUE provider, you may collect amounts for any deductible, coinsurance, and billed charges for noncovered services directly from the patient or responsible party, just as you would for any BCBSNE patient. 2. Claim processing times may vary with BlueCard® Program claims. If you have not received payment for a claim, do not resubmit the claim unless you have verified that your claim was not received. The quickest and most efficient way to check claim status is by submitting a Claim Status Inquiry through NaviNet. 3. In some cases, a member’s Blue Plan may pend a claim because medical review or additional information is necessary. When resolution of a pended claim requires additional information from you, BCBSNE may either ask you for the information or give the member’s Plan permission to contact you directly. Claim Status/Inquiries BCBSNE is your single point of contact for all claim inquiries. You can verify claim status through NaviNet, or by calling GABBI at 800-635-0579. If an out-of-area member asks you a question about a claim, you should instruct the member to call the customer service phone number located on the back of their ID card. Please do not refer out-of-area members to BCBSNE Customer Service. 35 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The member’s Plan should not contact you directly regarding claim issues. If you are a NEtwork BLUE participating provider and the member’s Plan contacts you to ask that you submit the claim to them, refer the Plan to BCBSNE. BlueCard® Program Quick Tips The BlueCard® Program provides a valuable service that lets you file all claims for members from other Blue Plans with your local Plan. Here are some key points to remember: • Make a copy of the front and back of the member’s ID card. • Look for the three-character alpha prefix that precedes the member’s ID number on the ID card. • Verify member eligibility and benefits through the BCBSNE provider portal on NaviNet, or by calling BlueCard Eligibility at 800-676-BLUE (2583). • Submit your claim status inquiries through NaviNet, or by calling GABBI at 800-635-0579. 36 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 3 Federal Employee Health Benefits Program® BCBSNE administers the Federal Employee Health Benefits Program which is sometimes referred to as the Federal Employee Program (FEP). FEP members can select between Basic and Standard Option coverage within the Service Benefit Plan. The coverage and benefits available depend on the option type the member selects. Both options cover most of the same services and supplies. However, there are different costs and benefits associated with each option level. Notable differences between the options include: Under Standard Option, PPO (Preferred) benefits apply only when members use PPO (Preferred) providers, giving members covered services at reduced cost, with a few minor exceptions. Members who use Non-PPO providers receive benefits, but with a greater out-of-pocket cost than if they use NEtwork BLUE providers. Under Basic Option, members must use NEtwork BLUE providers in order to receive benefits and members do not have a deductible. Under Standard Option, members must use a PPO provider to receive PPO benefits. If no appropriate PPO provider is available or if the member chooses not to use a PPO provider, Non-PPO benefits will be applied. The entire FEP member benefit brochure can be viewed at www.fepblue.org. 37 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The ID number for FEP members always begins with an ‘R’. Below is a sample ID card: The Federal Employee Program® and Medicare A provision of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliations Act (OBRA) of 1993 applies the Medicare participation and physician payment rules and requirements to all retired individuals covered under the BCBS Federal Employee Program (FEP). These payment rules include CMS-approved demonstration projects. OBRA affects FEP reimbursement when the patient: • is 65 years of age or older; • does not have Medicare Part A, Part B, or both; • is an annuitant of the FEP as a former spouse OR as a family member of an annuitant of former spouse; and • is not employed in a position that offers FEP coverage Inpatient Reimbursement OBRA bases inpatient care reimbursement on an amount that is equivalent to Medicare’s payment amount unless the charge is less than the Medicare equivalent amount. FEP members are NOT responsible for any charges greater than the Medicare equivalent amount. The law prohibits a hospital from collecting more than the Medicare equivalent amount. FEP members who have Standard Option coverage are responsible for deductibles, coinsurance, and/or co-payments. Physician Reimbursement OBRA bases physician services reimbursement on the lesser of the Medicare approved amount or the actual charge. Member liability is dependent on the physician’s participating status with Medicare and/or the physician’s NEtwork BLUE contracting status. 38 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents If the physician participates with Medicare or accepts Medicare assignment and is in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments • Basic Option - copayments and coinsurance If the physician participates with Medicare or accepts Medicare assignment and is NOT in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount • Basic Option - all charges If the physician does not participate with Medicare and is in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount • Basic Option – copayments, coinsurance and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount If the physician does not participate with Medicare and is NOT in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount • Basic Option - all charges Waiver Copy Required for Denial Review Providers may ask FEP members to accept financial responsibility for services that the physician believes will be denied as not medically necessary, experimental/investigational, or cosmetic by asking the member to sign an advanced written notification such as a waiver or Advanced Beneficiary Notice of non-coverage (ABN). The notice must identify the proposed service, inform the member that such services may be deemed not medically necessary, experimental/investigational, or cosmetic by the Plan, and provide an estimate of the cost for such services. The member must agree in writing to be financially responsible in advance of receiving the services. If an FEP member files an appeal on a claim denied as not medically necessary and the member has signed a waiver, the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) requires the provider to send us a copy of the waiver for final review. If the provider cannot find the signed waiver, the member must be held harmless. OPM will not allow the submission of medical record documentation in lieu of 39 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 4 Member ID Card Information Identification The patient’s ID card lists special instructions about where to file claims and what numbers to call for information and precertification. The front and back of the patient’s current ID card should be photocopied to assist in identifying the member’s coverage during every visit. ID Number and the Alpha Prefix NEtwork BLUE ID cards are issued with an alpha prefix (three characters preceding the subscriber’s identification number on the card). Always include the prefix in your records and on claims. Note: Dependents, spouses and suffixes are not listed on a NEtwork BLUE ID card. Some group logos and names may also appear on the ID card. Always reference the NEtwork BLUE name in the lower left-hand corner to confirm a migrated member. If no copayment language is on the ID card, this indicates an HSA plan or non-HSA plan with no copays. 40 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 5 Member Cost-Share Information Member Responsibility — Cost Sharing BCBSNE members are responsible for paying a share of the cost of covered services. The member's cost includes a deductible, coinsurance, copayment or some combination of these payments. In limited circumstances, the member also may be responsible for the balance of the provider's charges not reimbursed by BCBSNE. Cost sharing amounts vary by benefit plan. If the information in this section differs from the applicable benefit plan, the terms of the member's benefit Contract apply. Allowable Charge: An amount we use to calculate our payment of Covered Services. This amount will be based on either the contracted amount for in-network providers or the out-of-network allowance for out-of-network Providers. Balance bill: "Balance bill" refers to the amount the member may be charged for the difference between an out-of-network provider's billed charges and the allowed amount. In-network providers must accept the allowed amount as payment in full for covered services and may not bill the member for the difference between their billed charges and the allowed amount. Out-of-network providers have no obligation to accept the allowed amount as payment in full. Therefore the provider can bill the member the difference between the billed charge and allowed amount paid plus any deductible and coinsurance amount. Any amounts paid for balance bills do not count toward deductible, coinsurance or coinsurance limit. Deductible: A "deductible" is the amount the member must pay for covered services within a 12-month period (e.g. calendar year or benefit plan year) before the benefit plan begins to pay for covered services. The deductible applies to every covered service, unless otherwise specified. • Calculation of deductible: The deductible is calculated based on the BCBSNE allowed amount for covered services. • Application of deductible: A contracted provider must file all claims for members, including those that may require payment of deductibles. The deductible amount is determined by the order in which claims are processed by BCBSNE, not the date services were rendered within the 12-month period. Plans typically have different deductible amounts for In-network and Out-of-network providers. Charges by either in-network or out-of-network provider will be credited and totaled for application to both deductibles. 41 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • What does not apply to the deductible: Amounts the member pays for copayments do not count toward the deductible in standard PPO benefit plans. • Individual and family deductibles: A deductible can be either embedded or aggregate. PPO plans are generally set up with an embedded deductible. A qualified high deductible health plan is most commonly set up with an aggregate deductible. This will vary based on the plan. o Embedded deductible – Embedded Deductible means that family members may combine their covered expenses to satisfy the required calendar year deductible. However, no one family member contributes more than the individual deductible amount. o Aggregate deductible– Aggregate Deductible means that if you have family coverage, the entire family deductible must be met prior to any benefits becoming available. • Carry over deductible: This only applies to a select few large group members with a calendar year deductible plan. Any amounts applied to the annual deductible for services provided in October, November or December, will be carried over and applied to the next year's annual deductible. Coinsurance: Coinsurance is a percentage amount that a member pays for covered services after meeting any applicable deductible and/or copy. Coinsurance applies to every covered service unless the applicable benefit plan states otherwise. • What does not apply to the coinsurance limit: Amounts the member pays for deductibles and copayments do not count toward the coinsurance limit in standard PPO benefit plans. • Calculation of coinsurance: BCBSNE normally calculates coinsurance based on the Contracted Amount. There is one exception. If the provider's billed charges are less than the provider's negotiated rate, BCBSNE will calculate coinsurance based on the lesser billed charge. The member coinsurance percentage is higher when an out-of-network provider is used. Coinsurance limits (individual and family): A coinsurance limit is the amount an individual member must pay each year as coinsurance before BCBSNE begins paying 100 percent of the allowed amount on most covered services for the remainder of the calendar year. The member is still responsible for other types of cost-share payments. • Plans typically have different coinsurance amounts for In-network and Out-of-network providers. Charges by either in-network or out-of-network provider will be credited and totaled for application to both coinsurance limits. • Individual and family coinsurance limits: A coinsurance limit can be either embedded or aggregate. PPO plans are generally set up with as embedded. A qualified high deductible health plan is most commonly set up with as aggregate. This will vary based on the plan. 42 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents o Embedded coinsurance – Embedded Family Coinsurance means family members may combine their covered expense to satisfy the family Coinsurance Limit. No one family member contributes more than the individual Coinsurance Limit to satisfy the family’s Coinsurance Limit. o Aggregate coinsurance – Aggregate Coinsurance means that after the family deductible is met, the entire family Coinsurance Limit must be met before coverage begins to pay at 100%. Copayment(s): A copayment (copay) is a fixed or specific dollar amount a member must pay to the provider for some covered services. If a copay applies to a covered service, the member must pay it at the time of service. Some copayment information is also displayed on the front of the member's ID card. The terms "copayment" or "copay" are used interchangeably in this guide. • Copay amount greater than allowed amount for services rendered: If the copay amount is greater than the BCBSNE allowed amount for the services rendered, the provider may not collect more than the allowed amount. If the provider knows the allowed amount at the time of service, the provider can simply collect the allowed amount. If the provider later determines that the allowed amount is less than the copay, the provider must refund the difference to the member. • Copays will continue to apply, even once the Coinsurance Limit or the combined Deductible and Coinsurance Limit for the year is reached, except for qualified high deductible health plans. • Most common types of services a copay might apply to: Office Visits or Office Services, Urgent Care Facilities and Emergency Room. Some plans apply copays to allergy injections and serum, ambulance services, inpatient admissions and some preventive services (those not required by health care reform). o Office visit copays typically include office visits, the initial visit to diagnosis pregnancy, consultations, psychological therapy and/or substance dependence and abuse counseling/rehabilitation and medication checks. o Office services copays typically include x-rays, laboratory and pathology services performed in the physician’s office, supplies used to treat the covered person in the office, drugs administered by the physician in the office, hearing examinations due to illness, vision examinations due to illness (excluding refractions) and allergy testing. o Office services copays on most plans do not include services such as, pregnancy services after the initial diagnosis, injections, advanced diagnostic imaging and other services, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, manipulations and adjustments, physical, occupational, speech therapy, including cognitive training, chiropractic or osteopathic physiotherapy, therapy evaluations, surgical procedures and anesthesia, sleep studies, durable medical equipment, biofeedback, psychological evaluations, assessments and testing. 43 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents o Copayments for emergency rooms are typically waived if admitted to the hospital within 24 hours of the same diagnosis. In most cases, after the copay BCBSNE will reimburse the provider 100% up to the allowable amount. However, some plans apply the coinsurance after the copay or even the deductible and coinsurance. The members specific plan of benefits would apply. • Precertification charges: It is important that you obtain precertification from BCBSNE for any service that requires it. Otherwise, the member may be subject to additional cost shares or complete loss of benefit, depending on the plan and determination of medical necessity upon a retrospective review. 44 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 6 Preventive Care Benefits Benefits for Preventive Services All our Individual and Group health plans follow the Patient Protection and Affordability Care Act (PPACA) for health care reform implemented on September 23, 2010. Benefits will be payable for Preventive Services provided by a Physician, including an oral surgeon, a Certified nurse midwife, a Certified nurse practitioner or Certified Physician's assistant, within the provider's scope of practice, regardless of the place of Service. Benefits will be provided for In-network Preventive Services, which are defined as: A. Evidence-based items or services that have in effect a rating of A or B in the current recommendations of the United States Preventive Services Task force; B. With respect to infants, children and adolescents, evidence-informed preventive care and screenings provided for in comprehensive guidelines supported by the Health Resources and Services Administration; C. With respect to women, evidence-informed preventive care and screenings provided for in comprehensive guidelines supported by the Health Resources and Services Administration; and D. Immunizations for routine use in children, adolescents, and adults that have in effect a recommendation from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preventive Services, as outlined above, will not be subject to cost-sharing requirements, such as Copayment, Coinsurance or Deductible, if provided by an In-network Provider. Some services are subject to gender, age and frequency limits. A quick listing of the Preventive Services and Guidelines for the above services can be located on our website at www.nebraskablue.com. Click on the Member Services tab at the top of the page, and then select Preventive Care. You will have access to the Preventive Services Chart, Preventive Health Guidelines, Five Steps to Safer Health Care, and information related to Colorectal Cancer Screening. Out-of-network Preventive Services and those not described above for In-network providers, including but not limited to laboratory services, radiology services, hearing screenings and examinations, and cardiac stress tests, will be paid as indicated on the members specific plan/contract. Benefits vary based on Individual Contracts, Group Contracts and self-funded group plans. 45 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Preventive services do not generally include services intended to treat an existing illness, injury or condition. Benefit will be determined based on how the provider submits the bill. Claims must be submitted with the appropriate diagnosis and procedure codes in order to be paid at the 100% benefit level. If during the preventive service visit the patient receives services for an existing illness, injury or condition, the member may be required to additional cost share for those covered services. 46 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 7 Routine Vision Services Unless specifically added to a group’s coverage, BCBSNE member contracts do not provide coverage for screening eye examinations, eye refractions, eyeglasses or contact lenses, eye exercises or visual training (orthoptics). An exception is an eye exam required for a patient taking medication which can have adverse effects on the eye function. If the eye exam is billed with a medical diagnosis, the claim is payable. NO preauth is required. The only other exception is listed under Vision Supplies. Member eligibility and benefits for routine vision services can be verified by contacting BCBSNE Customer Service. Ocular Photoscreening (Optomap) Code Optomap with 99174. It will deny as content to service. Pachymetry Charges for corneal pachymetry will be denied as content to the office visit. If a provider chooses to bill for this service and the procedure is done bilaterally, you should bill 76514 unmodified. If done unilaterally, you should bill 76514 with a modifier-52 and a reduced charge. The unit value is always “1” whether the procedure is done unilaterally or bilaterally. Visual Field Exams 92081-92083. If done bilaterally, bill the code unmodified. If done unilaterally, reduce your charge and bill the code with a modifier-52. The “Unit” value is always “1.” Vision Supplies All vision supplies are reviewed to see if the charges were a result of an intraocular surgery or ocular injury. BCBSNE allows payment for eyeglasses or contact lenses (or their replacement) if required because of a change in prescription of at least one diopter as a direct result of intraocular surgery or ocular injury. Covered Services must be provided within twelve months of the date of the surgery or Injury and must be ordered by a physician. Vision Discount Program This program primarily applies to contracting Optometrists. If an Ophthalmologist is interested in participating they should contact their Health Network Services Consultant. 47 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The Vision Discount Program is a value-added service from BCBSNE. When this program was initially formulated, routine vision care was not a covered benefit under any BCBSNE contract. Since then, various groups have added endorsements which include some routine vision coverage. If the member has vision coverage, the provider is required to file a claim to us. The provider is not required to offer the discount for services that are covered under a contract endorsement. Also, if a member requests that a claim be filed, then please file the claim on behalf of the member. Discount • 10% discount off the cost of routine vision exams • 17.5% discount off the retail price of frames, lenses and contacts Eligibility Who is eligible to receive the discount? All Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska members who do not have routine vision benefits are eligible to receive the discount. Who is not eligible to receive the discount? 1. Individuals who have coverage through another state’s Blue Cross Blue Shield Plan. 2. BCBSNE members who have routine vision benefits. How does a patient get the discount? The patient must present their Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska ID card to a Vision Discount participating Provider. • The discount is valid only at the time of purchase when the service or materials are provided. • If the patient fails to present their card at the time of service or purchase, providers are not required to give the discount. • The discount applies to services and materials where no medical diagnosis is related to the examination for glasses or contacts. Although no eye examination is really “routine,” eye examinations that result in the patient having no medical diagnosis are considered “routine exams.” Code those claims with diagnosis V72.0. If, during the course of a routine eye exam, a medical problem is diagnosed, the BCBSNE discount DOES NOT APPLY. If a medical diagnosis/condition is found during the course of the exam or if the patient’s coverage includes routine eye care benefits, the service should be billed to BCBSNE. 48 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Frames, Lenses and Contacts The discount applies to all regular retail price frames, lenses and contacts. If an item is on sale at a reduced price, the discount does not apply. Items already marked at a reduced price or part of a special package price (such as disposable contact lenses) are not eligible for the discount. Does the discount apply to more than one item? Yes. The discount applies to the regular retail price of frames, lenses and contacts. Does the discount apply to replacement parts? Yes. The discount applies to the regular retail price of frames, lenses and contacts. This includes replacement parts. Is there a limit per year? No. Are there any items not eligible for the discount? Yes. Industrial safety eye wear, nonprescription sunglasses, scratch resistance coatings, miscellaneous vision options and items marked at special package or discount prices are not eligible for the discount. Can the patient get a discount on materials without having an eye exam? Yes, subject to program guidelines. All regular priced frames, lenses, and contacts are eligible for the discount. Does the patient have to pre-authorize these benefits or get a referral? No. The Vision Discount Program is not an insurance program. It is simply a Value-Added Service Blue Cross Blue Shield of Nebraska has arranged with a select group of vision care professionals. No pre-authorization or referral is required. All changes are handled directly between the patient and the vision care professional. If the Dispensary is not owned by the Optometrist, does the discount apply? In this case the discount would only apply to the exam. Beginning January 2013, routine vision services through Davis Vision will be made available to our BCBSNE statewide membership. Those who purchase a Davis Vision policy will have coverage for a comprehensive routine eye exam and glasses or contact lens benefits to be used at participating Davis Vision offices in Nebraska. Davis Vision is a wholly-owned subsidiary of HVHC Inc. (a Highmark company). Headquartered in San Antonio, TX, Davis Vision provides full service vision plans to 17 million members and discount plans to an additional 38 million members. Their network consists of over 36,000 points of access to independent providers and retail locations including Visionworks, America’s Best, Walmart, Sam’s Club, Costco and Shopko retail providers. 49 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Participation with Davis Vision is encouraged by BCBSNE for all Network BLUE optometrists and BCBSNE’s Vision Discount Program is waived to Davis Vision providers servicing Davis Vision members. Go to www.DavisVision.com and follow the instructions on the web site to become a Davis Vision provider or call the Davis Vision provider call center at 1-800-584-3140. 50 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 8 Pharmacy Benefits Overview Prime TherapeuticsSM Promoting Quality Drug Therapy while Containing Costs 402-970-2600 800-821-4795 Prime Therapeutics LLC (Prime) is a leader in pharmacy benefit management strategies. Prime’s mission is to provide the highest quality care and service for members while focusing on delivering the lowest cost of care and empowering clients to make informed decisions in health care management. Together with Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE), Prime proves that the best outcomes are achieved by a different kind of business model - one that supports low net cost with client-aligned incentives, focused clinical programs including integration of pharmacy and medical management, and superior service that promotes collaboration, flexibility, and a positive member experience. Prime, privately owned by not-for-profit Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans including BCBSNE, works side by side with groups to manage overall health care benefits. Flexible benefit designs, sophisticated trend forecasting, comprehensive reporting, focused clinical strategies and administrative ease add up to a program that delivers outstanding service. Pharmacy and Medical Data Integration Only with Prime can BCBSNE realize the benefit of true medical and pharmacy data integration. Using medical and pharmacy data together in our analyses allows us to better identify opportunities for improved care and cost savings. It also means we can more effectively target members and physician populations for interventions based on diagnosis information, rather than just pharmacy or medical data alone. Prime measures the impact pharmacy decisions have on overall medical outcomes. Prime will not decrease pharmacy costs at the expense of medical costs or quality outcomes. Focused Clinical Strategies BCBSNE, through our partnership with Prime, has developed numerous programs that focus on driving appropriate drug therapy and educating members. We incorporate a strong emphasis on member education as a part of our program development, rather than simply creating limitations that drive cost savings. Pharmacy cost savings is one goal in program development; however, our partnership also provides our clients with the added value that comes from an ability to combine and analyze both pharmacy and medical data. BCBSNE and Prime believe the value of drug therapy is directly correlated with our ability to enhance health and/or disease-specific outcomes, not solely with attention to pricing and costs. Drug expense is important, and BCBSNE and Prime offer a variety of opportunities to manage drug costs. However, the optimal value we offer is a partnership with the real disease managers: 51 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents individual patients, physicians and other health care providers within the managed health care setting. We understand that to optimize pharmaceutical care value, drug considerations must be integrated into a comprehensive medical care plan. We offer a number of solutions designed to maximize the cost effectiveness of our programs. These include: • • • • Concurrent Drug Utilization Review Utilization Management Programs - Quantity Limitation Programs - Pre-authorization Programs Retrospective Drug Utilization Review Generic Utilization and Formulary Management Programs. To elaborate on one of the above, BCBSNE and Prime’s retrospective DUR programs analyze pharmacy claims history and identify opportunities to improve the cost and quality of pharmaceutical care. Retrospective DUR programs are designed to identify real problems that impact members, physicians and drug trend. Built on rigorous clinical rationale and sound methodology, the targeted interventions provide physicians with actionable information, and members with key educational materials. Changes in therapy are measured at defined intervals, and initiatives can be repeated to address persistent medication use problems. Retrospective DUR initiatives target both overuse and under use of drugs. Flexible Pharmacy Benefit Designs Prime supports a variety of benefit designs that are customized to meet the needs of participating employer groups. We provide a spectrum of benefit design options, program management tools, and customized modeling assessments to facilitate the decision making process. Benefit designs offered include those with a copay differential for brand/generic medications, coinsurance or flat copays. We work closely with groups to design a benefit strategy based on specific needs. The majority of the BCBSNE book of business is enrolled in formulary-based, three-tiered benefit plans that assign copays/coinsurance according to a drug’s status of generic, brand, or non-formulary brand. Formulary Focused on Safety and Low Net Cost Benefit designs are complemented by use of the BCBSNE formulary which provides members with broad access to safe, medically necessary products. The formulary is a list of medications which represent the current clinical judgment of physicians and other experts in the health care arena. The Prime Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee, comprised of actively practicing, independent physicians and pharmacists, make formulary decisions driven by four criteria considered in this order: • Safety • Efficacy 52 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • Unique properties of the drug Lastly net cost The Nebraska marketplace is represented on the Prime Pharmacy and Therapeutics committee. In addition to that representation, BCBSNE utilizes a local Formulary Business Committee to review decisions made by Prime’s committee. Use of formulary agents and generic products enhance our members’ pharmacy benefit. Contact Information Clint Williams, Pharm.D., MBA Director of Pharmacy and Network Administration Phone: 402-982-8531 E-mail: clint.williams@nebraskablue.com Casey Martin Senior Director, Client Engagement Prime Therapeutics LLC Phone: 612-777-5239 E-mail: cmartin@primetherapeutics.com How to Precertify/Certify Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska’s Pharmacy Services Department, in collaboration with our pharmacy benefit manager Prime Therapeutics, LLC., develops programs and resources to inform both physicians and their patients, our members, about the appropriate, cost-effective use of pharmaceuticals. Given the rising cost of health care, some groups have chosen to implement programs that promote appropriate therapy through pharmacy preauthorization programs. The preauthorization request forms for these pharmacy preauthorization programs are available at www.nebraskablue.com by clicking on the Providers link and then on the Policies and Forms link in the left column under Pharmacy Management. The forms are located below the subheading of Preauthorization Forms. A listing of medications that require preauthorization is also located on the same webpage as listed above. BCBSNE will NOT accept other preauthorization forms from sources such as www.covermymeds.com. Outpatient Prescription Drugs Under some Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE) plans, benefits for certain prescription drugs and covered services administered in an outpatient setting will only be available for in-network benefits if they are obtained from a participating pharmacy and processed under the member’s BCBSNE prescription drug plan. The list of medications that are no longer covered under the medical plan is available on our website at www.nebraskablue.com. 53 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents An outpatient setting includes a home, physician’s office, outpatient hospital or other outpatient facilities. It does not include a hospital emergency room. Medical providers who administer the drug(s) in the outpatient setting will be reimbursed only for the administration under the member’s medical plan. 54 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 9 Provider Responsibilities Following these terms ensures the least amount of “out-of-pocket” expense to the patient. NEtwork BLUE Health Care Professionals: • • Refer/Admit covered persons only to NEtwork BLUE hospitals.* Refer covered persons only to NEtwork BLUE medical specialists and other NEtwork BLUE health care providers.* Arrange vacation and call coverage to be provided by a NEtwork BLUE provider. • *Except under circumstances identified in the agreement. Cash Discounts If a cash discount is offered, that discount needs to be extended to BCBS patients. The discounted amount must be the amount billed on the claim. If a BCBS member requests a claim be filed for a noncovered service, the provider must file the claim. Changes of Address, telephone number, tax identification number or adding Practice Locations NEtwork Blue providers are required to notify BCBSNE of any changes of address, telephone number or tax identification number. If a Health Care Provider is already in our network and is adding a location with the same tax identification number, would like to extend their network status to an additional location with a different tax identification number while keeping the current/old location active, or is transferring network status to a new location under a new tax identification number, they need to complete a Provider Add/Extend/Transfer form. The form requires the practitioner’s signature and is available at www.nebraskablue.com by clicking the “Providers” button and then on “Forms for Providers” in the left column. The Tax ID Number that should be listed at the top of the form is the one tied to the current practice location and existing BCBSNE Provider Agreement. All required fields must be completed prior to printing out and submitting the form to BCBSNE. Non Discrimination NEtwork BLUE providers must not discriminate against any member and treat all members with dignity, respect and courtesy regardless of race, physical or mental ability, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, creed, age, religion or national original, cultural or educational background, economic or health status. 55 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Further, NEtwork BLUE providers must furnish services to all BCBSNE members without regard to the member’s enrollment in a managed care plan as a private purchaser of the plan or as a participant in publicly financed programs of health care services unless limitations are due to lack of training, skill, experience or licensing restrictions. Closing Practice to New Patients A provider may refuse to take new BCBS patients but only if their practice is closed to all new patients regardless of insurance coverage Continuity of Care In the event a Covered Person is receiving care as of the date a termination of the Agreement is effective, the Provider is contractually responsible to continue to render Covered Services to the Covered Person, and the Agreement shall continue to apply to those Covered Services, after the termination takes effect for the length of time indicated below: a. Inpatient Covered Services: 30 days or until discharge, whichever comes first; b. Non-surgical Cancer Treatment: 30 days or a complete cycle of radiation or chemotherapy, whichever is greater; c. End Stage Kidney Disease and Dialysis: 30 days; d. Symptomatic AIDS undergoing active treatment: 30 days; e. Circumstances where BCBSNE is required by applicable law to provide transition coverage of services rendered by Provider after Provider leaves the provider network accessed by BCBSNE. BCBSNE will make a good faith effort to arrange for the expedient transfer of all patients to another qualified provider upon termination of the Provider’s Agreement. Coordination of Benefits The Coordination of Benefits (COB) provision in a covered person’s group contract is designed to prevent duplicate benefit payments when a patient has two or more health or dental insurance plans providing coverage. Even if you do not contract with other insurance payer(s), if BCBSNE is secondary we will need the primary insurance’s EOB/remit in order to process the claim. • Primary BCBS/Secondary XYZ Payer– Contracting provider must file claim to BCBS; filing to secondary is optional based on office policy • Primary XYZ/Secondary BCBS – Primary claim filing based on office policy and provider must submit primary EOB/Remit to BCBS • Primary BCBS/Secondary BCBS – Contracting provider must file both primary and secondary claims to BCBS, unless, both policies are through BCBSNE. When both are BCBSNE policies, only the primary claim needs to be submitted. 56 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents COB rules dictate which payer is primary. When BCBSNE is the primary payer, benefits are determined as if no other plan provided coverage. When BCBSNE is the secondary payer, benefits are determined after the primary plan has decided its benefit amount. As the secondary payer, BCBSNE may reduce benefits due to the primary plan benefit responsibility. Payment will not be made for any amount for which the covered person is contractually held harmless by either the primary or secondary plan. Payment shall not exceed the amount paid under the BCBSNE Plan had it been primary. Most group health plans follow the most current National Association Insurance Commission (NAIC) COB model regulations when determining the order of benefits. The NAIC Coordination of Benefits model regulations dealing with “Order of Benefits Determination” sets forth six rules for determining the order of benefits between plans. Most plans follow the “birthday rule” to determine which parent’s plan is primary for children. The plan covering the parent whose birthday falls earlier in the year is considered the primary payer. “Birthday” refers only to the month and day in the calendar year – not the year of birth. If the parents share the same birthday, the primary plan is the plan that has been in effect for the longest time. There are exceptions in the case of parents that are separated/divorced. Unless specifically stated in the decree the primary plan is determined in the following order: 1. The plan covering the custodial parent; 2. The plan covering the custodial parent’s spouse; 3. The plan covering the non-custodial parent; and then 4. The plan covering the non-custodial parent’s spouse. However, in the event that we have actual knowledge that a divorce decree or a child support order requires one parent to be responsible for health care expenses, the Primary Plan will be the Plan provided by that parent. For questions regarding other COB rules, please contact the Coordination of Benefits department at 402-390-1840 or 800-462-2924. Hold Harmless and Balance Billing Provider will not bill or collect any amount from the Covered Person, or anyone responsible for the Covered Person for services, procedures, drugs, supplies or home medical equipment, if BCBSNE determines such care was not a Covered Service except for services identified by BCBSNE as Non-covered Services and/or amounts specifically identified by BCBSNE as Covered Person’s liability. For Non-covered Services, Provider may bill Covered Persons at its rate of Charges. 57 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Provider may only hold Covered Person financially liable, however, for such specific services, procedures, drugs, supplies or items of medical equipment where benefits are denied as not Scientifically Validated, Investigative, or not Medically Necessary by BCBSNE, if, prior to the service being provided, Provider has advised the Covered Person in writing that Covered Person may be financially liable for the services provided and use best efforts to provide the Covered Persona an estimate of potential financial liability. If written agreement cannot be obtained, verbal notification may be given by provider but must be documented in the patient’s medical records at the time such notification is given. For all other balances, Provider agrees not to bill or collect any amount from Covered Person. Medical Records NEtwork BLUE health care professionals and facilities agree to submit medical records requested by BCBSNE in a timely manner at no cost to the covered person or to BCBSNE. Covered persons have consented to release medical records to us. An additional release is not required. All information resulting from the review is confidential. Provider agrees that all medical information about members shall be kept confidential in accordance with state and federal law, including but not limited to, and to the extent applicable, Neb, Rev. Stat. §44-4110.01 and federal regulations at 42 C.F.R. Part II. The exception to a provider’s responsibility to submit medical records is HIPAA rule 164.522(a)(1)(vi) effective March 26, 2013, with a compliance date of September 23, 2013. If a member requests that a provider restrict disclosure of PHI to the health plan AND pays the provider in full, the request must be honored. The request is only applicable for those services/items specifically directed by the member, and paid in full. This does not apply to PHI required to be disclosed due to federal or state mandates and laws. For more information see the following: Federal Register January 25, 2013 – Final Rule http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2013-01-25/pdf/2013-01073.pdf. Onsite Review BCBSNE may designate an Onsite Review Coordinator to examine quality of care at an office where any issues of safety, privacy or environment have been brought to our attention. An assessment will be made by the Coordinator and a summary of findings will be provided to the Health Care Professional. If corrective action is deemed necessary, a repeat visit will be scheduled. Physical Presence NEtwork BLUE providers must have a physical presence in the state of Nebraska, unless an ancillary provider (Independent Laboratory, HME/DME, Specialty Pharmacy) has been extended a remote Provider Agreement, as determined by the BCBSNE Network Oversight Committee. Physical 58 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents presence means you have a brick and mortar location, which has to be a street location, not a P.O. Box. Preauthorization and Certification Preauthorization Preauthorization is based on the terms of the covered person’s contract and on the information submitted to BCBSNE. Preauthorization guidelines apply whether BCBSNE is primary or secondary payer to Medicare or to other third party payers. Any time there is a question whether a procedure or service is covered by BCBSNE, the provider should first search for that procedure/service within the BCBSNE Medical Policy manual. Providers can access the BCBSNE Medical Policy manual one of two ways: Go to Policies and Procedures on the provider page of www.nebraskablue.com and click on the Medical Policy Manual, or select “Medical Policy and Pre-cert Lists for all Blue Plans” located in the Resource Center on the provider page at www.nebraskablue.com and enter the alpha prefix at the beginning of the BCBSNE member’s ID card. Using the medical policy tool we have made available, you will have real-time access to the most current information, and can search for a medical policy by keyword, policy number, or procedure code. A Preauthorization Request Form section has been added to each medical policy within the manual, enabling providers to submit a preauthorization request online, and directly from the medical policy page applicable to the service scheduled. When submitting a preauthorization request, the user should include a contact name, phone number and email address in the Provider Address field. If multiple procedure codes are to be requested, the user will click on the ADD A ROW button and additional Procedure Code and Diagnosis Code fields will appear. The Treatment drop-down menu allows the tool to determine the appropriate questions to display. Variations in questions may be determined by the type of procedure requested, sex of the member, age of the member, etc. If a policy is not listed for that particular procedure or if the provider is not certain the member’s condition meets the coverage guidelines, the care should be preauthorized. The preauthorization form is available at www.nebraskablue.com by clicking on the “Providers” button and then on “Forms for Providers” in the left column. Preauthorization requests are prioritized based on the date of the scheduled procedure or service, then by the date of receipt of the request. If the procedure will not be scheduled until the preauthorization has been completed, use the date the doctor would ideally like to do the procedure as the scheduled procedure date. 59 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Preauthorizations that are not urgent will be processed within 15 calendar days of receipt, unless an extension is needed to obtain necessary information. If information is requested, the claimant/provider may be given not less than 45 calendar days from receipt of notice to submit the specified information. A preauthorization determination will be made within 15 calendar days of receipt of the information or the end of the extension period. In the case of an Urgent Preauthorization, the claimant/provider will be notified of the decision (whether adverse or not), not later than 72 hours after receipt of the preauthorization, unless further information is needed. If additional information is necessary, the claimant/provider may be afforded not less than 48 hours from the date of the request to provide the specified information. Notification of the decision will be provided not later than 48 hours after the earlier of receipt of the specified information or the end of the period allowed to provide the information. The following requests may be escalated as an Urgent Preauthorization: • • • • • MRI of the Breast (FEP only. Preauth requests for BCBSNE members must be submitted to AIM) MRT (FEP only. Preauth requests for BCBSNE members must be submitted to AIM) Clinical Trials Air Ambulance Infertility when the care is concurrent Based on the clinical nature of the services rendered, the following procedures will not be handled as Urgent Preauthorizations: • • • • • • • • • • Botox Injections Dental Procedures (no review required for anesthesia if <8) Durable Medical Equipment/Home Medical Equipment Infertility services when the diagnostics or treatment have not yet been initiated. Pre-existing conditions when services have not yet been initiated. Requests for medication to be covered under the medical contract when not mental illness/substance abuse or contraceptive coverage is available. Gastric Bypass Surgeries Cosmetic procedures Eximer Laser Requests where additional medical records were requested, but not received until after the procedure or service date. If a rush request is received for one of the above services, the request will not be placed in a rush status. The requestor will be notified that the anticipated decision date will be 15 days from the date of submission. An authorization is generally effective for six months, unless otherwise specified, and is based on the terms of the contract in effect on the date services are received. 60 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Changes in the patient’s coverage for any reason, including eligibility, benefit revisions, or contractual maximums, may affect the approval. Note: All medical policy criteria and preauthorization requirements applicable to out-of-state Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield patients are dictated by the Blue Plan that insures the member. Refer to the BlueCard® Program section of this manual for additional information. American Imaging Management (AIM) In March 2010, Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska implemented a Radiology Quality Initiative (RQI) Program to promote the most appropriate use of advanced imaging services provided to members. The program aligns with the goals of the Nebraska Health Care Reform Task Force – to promote high quality, affordable health care coverage and utilize best practices and practice guidelines to help reduce unnecessary medical expense. Ordering/referring non-radiology providers must contact AIM (via the Web or through the call center) to obtain an order number before scheduling elective outpatient high tech diagnostic imaging services. In addition, radiology providers/free standing imaging centers should confirm (via the Web or through the call center) that an order number has been obtained prior to service delivery. Radiology providers/free standing imaging centers are restricted from obtaining the order number on behalf of the ordering provider. What types of diagnostic imaging exams are included under this program? The RQI Program includes outpatient elective CT scans (excluding CCTA), MRI, MRA, MRM, MRS, PET scans, fMRI and Nuclear Cardiology studies. What types of diagnostic imaging exams are excluded? All other imaging services, and imaging services provided in conjunction with emergency room visits, inpatient hospitalization, outpatient surgeries (hospital or freestanding surgery centers), or 23-hour observation are excluded from the program and do not require an order number. How does the RQI Program work? Ordering physician offices submit order requests through ProviderPortal – AIM’s interactive Internet application (www.americanimaging.net) - or through the AIM Call Center (866-745-3265). Web users or callers will be guided through an interview where member and ordering physician information (name, member ID number, etc), diagnosis, symptoms, exam type, and treatment/clinical history is requested. If the information provided meets AIM’s clinical criteria and is consistent with BCBSNE medical policy (when applicable), the Web user/caller will then be guided to select an imaging provider where the imaging study will be performed, and an order number will be issued. If all criteria are not met and additional information or review is needed, the case is forwarded to a Registered Nurse (RN) who uses additional clinical experience and knowledge to evaluate the 61 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents request against clinical guidelines. The nurse reviewer has the authority to issue order numbers in the event that he or she is able to ensure that the request is consistent with AIM’s clinical criteria and BCBSNE medical policy, when applicable. If an order number still cannot be issued by the nurse reviewer, the case is forwarded to an AIM Physician Reviewer (MD), who contacts the ordering physician directly to discuss the case and diagnostic imaging guidelines prior to issuing the order number. AIM’s Diagnostic Imaging Clinical Guidelines serve as a foundation for this collegial discussion. These Guidelines are available for download on AIM’s Web site, www.americanimaging.net. The Physician Reviewer will issue an order number based on a review of information collected and/or through their discussion with the ordering physician. If the request does not meet AIM’s Clinical Guidelines, the request will be recorded as having received an order number without meeting clinical criteria. Please note that order requests for Cardiac MRI and MRI of the Breast that have been reviewed by AIM and do not meet BCBSNE medical policy will be redirected back to BCBSNE for further review. The claim may be denied if BCBSNE determines the service to be inconsistent with BCBSNE medical policy after this review. Does AIM need to know when the procedure is scheduled? No, however the order number must be issued prior to scheduling the study. Order numbers are valid for sixty (60) calendar days from the date of issuance. How long is the order number valid? Order numbers are valid for sixty (60) calendar days after the date of issue. Can providers obtain order numbers on a retrospective basis? No, providers must follow the process to obtain order numbers prior to performing diagnostic imaging services under this program. For those rare requests that are medically urgent, providers should contact AIM, online or through the AIM Call Center, within two business days of performing the exam. This also includes add-on exams. Are there any members who are excluded from the RQI Program? Yes. The RQI Program does not include the following members: • • • • • • 62 Medicare Supplement Medicare Advantage Medicaid FEP BlueCard/out-of-state BCBS Members (please note that compliance with other BCBS plans’ imaging management programs must still be fulfilled for these members) Members with BCBSNE Secondary Coverage Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Certification NEtwork BLUE physicians are encouraged to certify benefits for all medical, surgical, mental illness, and substance abuse admissions. This promotes an improved mutual understanding of medically necessary services between BCBSNE, the hospital and physicians prior to delivery of services, unless otherwise advised by BCBSNE. For BCBSNE members: Inpatient precertification guidelines for BCBSNE members are divided into three categories. The categories and guidelines are: • Critical access hospitals are not required to call us for precertification of acute hospitalizations; however, preauthorization is required if the patient is transferred to a lower level of care such as skilled nursing or home health. Omaha and Lincoln hospitals are required to call us on the patient’s fifth inpatient day. All other hospitals and Residential Treatment Centers must call us on the first inpatient day • • All FEP inpatient admissions must be certified by all hospitals within two (2) days of admission to avoid a penalty. Adhering to these requirements will prevent pre-certification penalties from being passed to members. Outpatient surgery does not require precertification. Note: All certification requirements for out-of-state Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield patients are dictated by the Blue Plan that insures the member. Refer to the BlueCard® Program section of this manual for more information. Peer-to-Peer Discussion When a noncertification determination is made by a Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska physician reviewer, the attending physician has the right to discuss the decision with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska physician who made the noncertification decision prior to an appeal. To discuss the case with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska physician who made the noncertification decision, call 402-390-1870 or 800-247-1103. If the Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska physician who made the denial is not available, the attending physician will be given the opportunity to discuss the case with a different Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska physician reviewer. The Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska physician reviewer discusses a case only with the attending physician and not with the patient. The peer-to peer discussion will occur within 24 hours of the request by the attending physician. If the attending physician disagrees with a noncertification decision, the attending physician is encouraged to discuss the case with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska physician reviewer. 63 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents It is important to include any additional information that Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska did not have when the original denial was issued. If the attending physician declines the peer-to-peer discussion or if the peer-to-peer discussion does not resolve a difference of opinion, the attending physician has the right to request an appeal. All Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska contracts offer two levels of appeal. Appeals are performed by physicians who were not previously involved in the review or appeal process. When requesting an appeal, it is important to submit all relevant information that may assist in conducting the appeal. Refer to Section 16 of this manual for additional information. Provision of Services Providers are contractually responsible to provide to each Covered Person accepted as a patient those services falling within the Provider’s normal scope of practice and expertise and as set forth by state law. Providers shall be responsible for the creation and maintenance of the patient relationship with a Covered Person and shall be solely responsible for all aspects of the delivery of medical care and treatment provided to each Covered Person by the Provider. No provision of the Agreement, however, shall require the Provider to enter into or continue a patient relationship with any Covered Person. No provision of the Agreement shall expand the scope of the Provider’s responsibility for the medical care provided beyond the usual provider-patient responsibility. Providers further agree to be a Participating Provider at all practice locations in the State of Nebraska and/or those locations specifically approved by BCBSNE. Referrals If the Provider determines that a Covered Person requires Covered Services not customarily provided by the Provider, including the services of physicians, hospitals, or other health care providers, Provider shall use best efforts to refer patients to providers that participate in BCBSNE’s provider networks or in the BlueCard Program. Further, Provider shall be guided by reasonableness and the Covered Person’s best medical interests in referring, admitting, or directing the Covered Person for such services and informing the Covered Person all known information about referral choices. Scope of Practice If a provider has questions if something is or is not within their scope of practice, they should check with the Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services, Professional and Occupational Licensure Regulations. 64 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Sliding Fee Schedules BCBSNE providers must be consistent in the amount they charge for their services. If you utilize a sliding fee scale for your disadvantaged clients, you must also apply this sliding fee scale to your BCBS covered members and bill that amount to BCBSNE. Submission of Claims Providers are responsible to submit Clean Claims for all services provided to Covered Persons by the Provider promptly in the format requested by BCBSNE, regardless of whether there are other sources of payment or reimbursement. The Provider agrees that charges for Covered Services provided to Covered Persons will be at the same rate as is charged to its other patients. The Provider also agrees to provide BCBSNE with any additional information which is reasonably necessary to determine benefits and to verify performance under the Agreement. Such information will be provided without charge and in a timely manner. Provider agrees to follow all policies on authorization, verification, precertification, and preauthorization of benefits where applicable as may be required by member’s Blue Plan, including working with vendors utilized by the Blue Plan to perform this service. Nothing in the Agreement shall convey to BCBSNE the right to release or obtain information which is declared to be confidential or privileged communication, or otherwise restricted, by federal or state statutes or regulations, without strict compliance with the disclosure requirements defined by such statute or regulation. Subrogation The health plans underwritten and/or administered by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska have a contractual right to recover amounts paid as a result of an injury/illness caused by a third party. This first priority lien of the health plan on proceeds paid by a third party applies whether or not the covered person has been fully compensated. The health plans also may have a contractual right of reimbursement from other proceeds to the extent benefits were also paid under the health plan for the same illness or injury. Before Sending in an Accident Claim As a network provider, you have agreed to file all claims to BCBSNE for any covered benefit provided to our members and to accept our allowance as payment in full. If a covered benefit involves claims that are a result of an accident or illness caused by a third party, you must file a claim including accident information to BCBSNE. We will provide benefits according to the member’s contract and supply payment to the provider of service pursuant to our agreement with them. 65 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Our Subrogation Department will begin the necessary procedures to recover paid amounts from the covered person or third party payer, which will not exceed the amount we paid in benefits. If you are notified of an injury or accident after filing claims to BCBSNE and have not included the accident information on the claim, you should notify our Subrogation Department immediately at 402-390-1847 or 800-662-3554. What is a subrogation or right of reimbursement term in a member contract? Subrogation is the right of a person to assume a legal claim of another or the right of a person who has paid a liability or obligation of another to be indemnified by that person. A right of reimbursement is a contractual term granting one party to a contract the right to obtain reimbursement from the other party to the contract under certain circumstances. All member contracts of insurance with BCBSNE and all health plans administered by BCBSNE contain subrogation and right of reimbursement provisions. How are BCBSNE members affected by subrogation and right of reimbursement? Members receive benefits under contracts or health plans that include an obligation to reimburse BCBSNE or the health plan if another party is responsible for payment or if the member is pursuing payment from another source and, in some circumstances, when certain conditions are met. BCBSNE enforces the terms of the contract or health plan and pursues recoveries through its Subrogation Department. The contract or health plan language in place at the time of the accident will determine the rights and obligations of the parties. How are BCBSNE Providers affected by subrogation and right of reimbursement? In general, providers are not affected by subrogation or right of reimbursement. In certain circumstances, there may be two insurers potentially responsible for payment, usually the member’s auto insurer or a third party’s auto insurer, and BCBSNE. When more than one insurer is responsible for payment, providers must file claims for all service to both insurers. Some BCBSNE member contracts have Coordination of Benefits language in them, and BCBSNE must coordinate benefits with the individual auto carriers. In some cases an insurer other than BCBSNE or any other third party will make payment directly to the provider and the provider may have received payment from BCBSNE, as well. If you receive a payment from two sources, the BCBSNE provider agreements indicate that you should return the overpayment to BCBSNE. Even if the payment received from the third party is less than the BCBSNE payment, you must send the third party payment to BCBSNE. In all cases, BCBSNE will follow the member contract or health plan when processing claims and payments from other sources. In no circumstance should providers send an overpayment to the other insurer or the member without direction from our Subrogation Department. For questions, please call the BCBSNE Subrogation Department 800-662-3554 or 402-390-1847. 66 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Utilization Review/Management Provider is contractually responsible to participate in programs to effectively manage the cost of health care services. Such programs are identified and described within the contents of the Policies and Procedures manuals. Verification of Enrollment Providers shall use reasonable efforts to utilize phone, Internet, or other methods available to ascertain if a patient is listed as an active, enrolled, and Covered Person before submitting a claim. The preferred method of checking eligibility and benefits is by submitting an Eligibility and Benefits inquiry through NaviNet. Through NaviNet, you can verify eligibility and benefits for all BCBS patients (BCBSNE members and BlueCard members), as well as FEP members. You may also check eligibility and benefits by calling: • 800-635-0579 (GABBI system to check eligibility and benefits for BCBSNE members) • 800-676-BLUE (BlueCard Eligibility Line to check eligibility and benefits for members insured by an out-of-state Blue Plan) • 402-390-1879 or 800-223-5584 (FEP Program Service to check eligibility and benefits for members enrolled under the Federal Employee Program) Waiver of Deductible/Coinsurance/Copayment BCBSNE strongly recommends collection of copayment at the time of service. The routine waiver of deductible/coinsurance/copayment may represent a breach of contract with BCBSNE. Routine waiver of deductible/coinsurance/copayment is unlawful because it results in false claims, violations of the anti-kickback statute and excessive utilization of items and services. In addition to being unlawful, the waiver discourages patients from using health care services responsibly by removing the economic obligation of receiving care, which in turn indirectly raises the cost of health care to other covered persons. Workers’ Compensation The health plans underwritten and/or administered by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska exclude benefits for services received as a result of injuries or illnesses related to employment. These provisions apply whether or not the covered person asserts rights to, or waives workers’ compensation coverage. Please send a copy of the First Injury Report, as this enables us to process claims accurately and reduces the likelihood that future refunds or adjustments will have to be made. For questions, please call 402-398-3615 or 800-821-4786. 67 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 10 Claims Submission and Provider Reimbursement You File, So They Don’t Have To We encourage you to remind your patients that YOU file the claims for the services they receive. If the patient is given a copy of the charges, please annotate the copy: “For your records only. We file your Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska insurance claim.” The advantage of submitting claims for your services directly to us is that it is not only a benefit to your patient, but also a benefit to you because: • • You have all of the required information in the patient’s file to complete a valid claim. Your expertise in completing insurance claims means you complete claims correctly at the time of submission. You control the accuracy of the information used to calculate benefits for your services. Patient submitted claims are often the cause of overpayments and payments to the wrong office. • • A verbal reminder may also help the patient to understand that this is one of the services you provide as part of your agreement with us. Billing • • • • Bill your usual charge. Don’t prepare claims using the fees on the reimbursement schedule as your charge. Don’t reduce the office visit charge by any copay that applies. BCBSNE billing guidelines must be followed for all claims submitted. Refer to Billing Guideline sections for more details. The exception to a provider’s requirement to submit claims is HIPAA rule 164.522(a)(1)(vi), effective March 26, 2013, with a compliance date of September 23, 2013. If a member requests that a provider restrict disclosure of PHI to the health plan AND pays the provider in full, the request must be honored. The request is only applicable for those services/items specifically directed by the member, and paid in full. This does not apply to PHI required to be disclosed due to federal or state mandates and laws. For more information see the following: Federal Register January 25, 2013 – Final Rule http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2013-01-25/pdf/2013-01073.pdf. 68 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Timely Filing Limit Providers are contractually responsible to file claims, and any adjustments or revisions to timely filed claims, within the timeframe specified in the applicable Provider Agreement, or the time limit set forth in the Master Group Application. Unless otherwise specified by the provider agreement or the Master Group Application, the filing time limit for a new claim is 180 days from the date of service and for adjustments or revisions 18 months from the date of the last payment. Claims denied due to exceeding the timely filing limit are the provider’s liability and cannot be billed to the member. Exceptions to the 18 month rule can apply to: • Coordination of Benefits • Subrogation • Workers’ Compensation • Fraud Abuse Waste Intentional Misconduct If a claim submission is rejected due to incorrect or invalid information, it is the provider’s responsibility to make the necessary corrections and resubmit the claim within the timely filing period. BCBSNE does not consider a rejected claim as proof of timely filing but will reconsider a claim listed on a BCBSNE accepted claim report if the claim shows no errors but was not processed. If a copay is collected from our member at the time of service and the claim is denied for timely filing, the copay does not need to be refunded to the member. Conversely, if monies for deductible or coinsurance are collected at the time of service from our member and the claim is denied for timely filing, either or both must be refunded to our member as they are calculated on allowed amounts and subject to the timely filing denial. When verifying benefits for any BCBS member, we recommend verifying time filing limitations stipulated in the Master Group Application (which is also known as the group or member contract). Electronic Claims Submission Electronic submission is the preferred method of filing claims for professional services. Benefits of electronic claim submission include: • Lower operating costs. You will spend fewer dollars for clerical work and postage. Most electronic claims are submitted in less than 60 seconds. • Greater control over claim data. Electronic claim submission is a more efficient way to submit claims. Submitting claims electronically will lead to a faster, more accurate payment. • When all necessary information is submitted electronically, fewer claims will be returned for missing or incorrect information. Our NEBLUEconnect Account Managers can tell you about the hardware and software that make electronic claim submission possible and can show you how electronic claims processing has helped 69 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents offices like yours. If you would like to speak with an Account Manager, please call 800-821-4787, Option 1. For more information, go to www.nebraskablue.com and click on “Providers”, then “NEBLUEConnect” in the left-hand column. Faxed Claims As of October 1, 2012, BCBSNE cannot accept faxed claims. Claims can only be accepted by electronic submission or by mail. 1500 Paper Claim Submission Paper claims are entered into our claim processing system by transforming information on paper claims to an electronic format. If the claim cannot be entered electronically, it is delayed for research and entered manually by an auditor. Claims can be mailed to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska P.O. Box 3248 Omaha, NE 68180-0001 To expedite paper claim processing: • • • • • • • • The text must be printed clearly. Keep all text inside the lines. Text must be dark. Dates must be numeric and six positions (mmddyy). Don’t use nicknames or “Baby Girl,” “Baby Boy” as the patient’s name. Print, do not write in script. Print the entire ID number in Box 1a - including any alpha prefixes. Current CPT codes (Box 24D) and current diagnosis (Box 21) codes are needed, but nomenclature is not needed unless you are billing an unlisted or miscellaneous CPT code. The provider name and identification numbers on CMS 1500 forms must correspond with information we have on our provider data file. • Box 24J - Rendering provider’s (not supervising) NPI in 24J. The NPI number must be assigned to the rendering provider name in Box 31. Exception: for solo practice providers, or providers who do not have a Type II NPI, you may instead include your Type I NPI in Box 33A. Box 25: Federal Tax ID Number o Enter your TAXPAYER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (TIN) in this box. o This number MUST be the same number you use to report the provider’s income to the IRS. • 70 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents o This number must be the same number BCBSNE has on your application and agreements. • Box 31: Who Provided the Service o Last name (space) first name (space) credentials (MD, DO, Ph.D., etc). • Box 33: “Pay-To” Name and Address • Box 33A - must include the Billing entity’s NPI. If there is not a Billing/Group/Type II NPI, an individual NPI can go in 33A. Do not put the supervising practitioner’s NPI number anywhere on the claim. Reimbursement Schedules Reimbursement methodologies for services provided to NEtwork BLUE covered members are available by contacting your Health Network Consultants. Payment NEtwork BLUE providers agree to accept our reimbursement as payment in full, except for the following amounts when applicable: • • • • Deductible Coinsurance Copayment Charges for services and supplies which are not covered in the member’s contract and are not provider liability The reimbursement amount received by the billing provider may differ slightly from the contractual reimbursement amount due to system rounding. Note: The member is not responsible for noncovered charges for services and supplies that are deemed not medically necessary by BCBSNE. However, on an exception basis, if prior to the services being provided, you have advised the member of this fact, in writing, and the member has agreed, in writing, to be responsible for payment, you may bill the patient. This may not be done as a standard practice. Note: Charges for noncovered services as well as any copay, deductible and coinsurance on covered services may be collected at the time of service. BCBSNE does not restrict providers from reducing charges to members on non-covered services. NEtwork BLUE institutional and professional claims are finalized on Tuesday night. Payments and remittance advices (checks and 835’s) are distributed weekly on Wednesdays. Assignment of Benefits BCBSNE does not recognize “Assignment of Benefits.” All covered services provided by non-participating providers will be paid to the member. 71 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Remittance Advice NEtwork Blue providers receive direct payment from BCBSNE. Direct payment and claim information assist patient accounting activities because: • The day a claim is processed; a remittance advice is generated. Most providers receive their remittance advices electronically. For those who receive their remittance advice on paper, the remittance advice is mailed the next working day. Claims payment is mailed with the remittance advice unless electronic funds transfer is requested. The subscriber and participating provider are notified of the processed claim status at the same time. Payment information is detailed for each claim on the remittance advice. Deductible, co-insurance, co-pay, and noncovered charges are identified. A denial explanation is given for all amounts not covered. Any amount that is the provider’s responsibility to write off is specifically identified. If a patient account number is submitted on a claim, that number is included on the remittance advice. Adjustment claims are clearly identified • • • • • • • Electronic Funds Transfer If you are interested in having your claim payments electronically deposited into your bank account please visit www.nebraskablue.com, click on “Forms for Providers” located on the left side of the provider page, and complete the Electronic Funds Transfer Enrollment Form. Filing instructions are noted on the form. If you have any questions regarding Electronic Funds Transfer, please call or send an email to: Phone: 800-821-4787 (option 3) E-mail: ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com NOTE: If you are changing EFT from one bank or account to another, you will receive paper checks until the effective date of the new bank account. Refund Offsetting BCBSNE implemented a refund offsetting process, effective January 1, 2010, for NEtwork BLUE providers. When a claim overpayment occurs, providers will be issued a 30-day advance notice of the impending offset. The provider can either return a check to BCBSNE for the amount of the refund requested, or allow BCBSNE to take an offset of the overpayment amount. If you prefer to continue to write BCBSNE a check for the overpayment, we must have the refund check in our office within 72 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 30 days, of the date on the letter. If the refund is not received within 30 days, the overpayment amount will be offset against a future payment. Remittance Advices will clearly indicate when an offset has been taken. Direct all questions concerning refunds to our Refunds Department at 402-398-3653 or 800-562-3381. Refund Requests BCBSNE will not initiate refund requests beyond the time specified in the applicable Provider Agreement; however, no time will apply to the initiation of refund requests based on a reasonable belief of fraud, abuse, or other intentional misconduct, if required by a state or federal government program or if another payor is involved (e.g. coordination of benefits, subrogation or right of reimbursement, and workers’ compensation coverage). Corrected Professional Claims Effective August 1, 2013, if the information on a processed 1500 professional claim is subsequently found to be incorrect or charges need to be added or voided, you must submit a corrected claim electronically. Place a value of ‘7’ (replacement of prior claim) or ‘8’ (void/cancel of prior claim) in the 2300 CLM 05-3 element in the 837P file. Enter the original claim number assigned by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska in the 2300 REF*8 segment of the 2300 loop. These two element/segment values on the electronic claim form correspond to Box 22, Resubmission Code and Original Reference Number, on the CMS claim form. If you are not able to file your corrected claim electronically because your claim will include attachments, your corrected paper claim must be filed to Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska attached to a Reconsideration Request Form as you have done in the past. Do not send only the claim with “corrected claim” or “replacement claim” written or typed on the claim itself, as it will be returned to resubmit with the form. Submitting a new claim to replace one that has already been filed may result in a duplicate denial. The Appeal/Reconsideration Request Form is located in the Forms for Providers section of the provider page on our website at: www.nebraskablue.com. Before attaching the Appeal/Reconsideration Request Form to your corrected claim, be sure you have filled out the form completely and legibly. Mark the box for the section titled, “Reconsideration”, then clearly document in the Comments section the error that was made on the original claim, i.e., incorrect CPT code, incorrect diagnosis code, incorrect POS, etc. 73 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 11 General Billing Guidelines - Professional Our goal is to provide you with information that encourages consistent, uniform billing practices among Nebraska health care professionals. Our intent is to provide correct reimbursement for services provided. This section is designed to clarify our medical policies and clarify coding guidelines that relate to those policies. This is a guide, not an all-inclusive policy. You will read about changes to these policies in our update newsletter or in direct mailings to your office. Covered services and benefits vary considerably within the various contracts administered by BCBSNE. In all cases, we follow the specific covered person’s contract provision. The following Policy and Coding section is an alphabetic listing of common medical policies and coding guidelines that apply to BCBSNE claim processing. Among the subjects are: • Allergy • Anesthesia • Chemotherapy • Obstetrical services • Office visits • Psychiatric • Routine medical E and M • and many, many more! Allergy Testing Medical necessity guidelines are applied to allergy testing. Therefore, medical rationale such as office records may be requested to verify documentation of medical necessity. The following allergy tests are scientifically validated: 1. Direct skin test • Percutaneous (prick, or puncture) • Intracutaneous (intradermal) 2. Patch test (application test) 3. Photo patch test Specific IgE in vitro tests: Radioallergosorbent test (RAST), Multiple radioallergosorbent tests (MAST), Fluorescent allergosorbent test (FAST) and Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are less sensitive than direct skin tests; therefore, the scientific data indicate they should be reserved for situations where direct skin testing is unsatisfactory. These situations are: 74 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • • • • • • Dermographism Widespread skin disease Concurrent use of drugs with antihistamine effect which can’t be stopped Concurrent use of beta blockers which can’t be stopped Suspected latex allergy Direct skin testing has been inconclusive and further diagnostic testing is necessary Children under two (2) years of age In cases of suspected life-threatening anaphylactic states, particularly in the diagnosis of penicillin and Hymenoptera allergy, skin tests are superior to RASTs. RAST, MAST, FAST and ELISA tests should be preauthorized. They may or may not be covered. The following allergy tests are considered investigative and therefore not covered: • • • • • • • • Provocative and neutralization tests (subcutaneous and sublingual) for food or food additive allergies Serial dilution end point titration (SDET or Rinkle method). (Code 95027) Nasal challenge test Conjunctival challenge test (ophthalmic mucous membrane test) Cytotoxicity testing (Bryan’s test Leukocyte histamine release test (LHRT). Rebuck skin window tes Passive transfer or P-X (Prausnitz-Kustner) test (obsolete replaced byRadioallergosorbent Tests) Allergy Immunotherapy (Desensitization) Allergen immunotherapy is the subcutaneous administration of increasing concentrations of allergen to which the patient has demonstrated sensitization and symptoms by skin test (or RAST) and history. Immunotherapy should be considered when pharmacotherapy and avoiding allergens fail to resolve symptoms or when pharmacotherapy produces unacceptable side effects or is not cost-effective. Allergen immunotherapy blocks both the immediate and the late-phase reaction. The specific mechanism by which it relieves symptoms is unclear, although it increases allergen-specific IgG, reduces allergen-specific IgE, decreases allergen-induced mediator release; decreases eosinophil chemotaxis, and appears to shift to cytokine profiles. Allergen immunotherapy using inhalant antigens and stinging insect venom antigens is scientifically validated treatment. Allergen specific IgE (Immunocap, CPT code 86003) and qualitative, multiallergen screen (dipstick, paddle or disk, CPT code 86005) are covered and do not require preauthorization. 75 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The following treatments are considered investigative and therefore not covered: • • • • Urine autoinjections (autogenous urine immunization) Repository emulsion therapy Intradermal and subcutaneous provocative and neutralization therapy for food allergies Rinkel method of immunotherapy for ragweed pollen hay fever The following treatments are considered exclusions and therefore not covered: • • Food Antigen Therapy Sublingual Therapy Allergy Injections Claims for allergy injections are submitted in two parts. This includes a charge for the injection (95115 or 95117) and a charge for the antigen/venom (95144 - 95170). Procedure Code 95115 and 95117 both have a frequency of “1.” Cluster immunology - If 95117 is submitted three 3 times on the same claim it must be billed with 3 lines, two of the lines having modifier 76. Procedure Code 95165 includes all antigen costs and the professional service for supervision and provision. Report the total number of doses when this code is used. The fee schedule allowed amount represents the amount of reimbursement per dose. The unit field must be used to report the total number of doses so that your claim will be processed correctly and accurate reimbursement will be calculated. Ambulatory Surgery (See “Surgery”) Ancillary Billing Guidelines In 2011, the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association mandated Plan compliance with the handling and processing of the following ancillary claims: • • • Independent Clinical Laboratory Durable Medical Equipment and Supplies Specialty Pharmacy Independent Labs are required to bill the claim to the Blue plan in whose state the specimen was drawn. Where the specimen is drawn is determined by what state the ordering (referring) provider is located to prevent physician offices from being impacted by the ancillary claim filing guidelines when submitting charges for laboratory services, it is important to use POS 11 (office) when filing your claim. Modifier -90 should be appended to the CPT code for the laboratory service. POS 81 is 76 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents to be used only by independent laboratory providers, which are defined as “a laboratory certified to perform diagnostic and/or clinical tests independent of an institution or a physician’s office.” Durable Medical Equipment claims must be filed to the Plan in whose state the equipment was shipped to or purchased in a retail store. Note: When billing a POS 12 (Home), the claim should always be filed to the Plan in the state where the patient resides. Equipment and/or supplies purchased in a retail store should be billed with a POS 17 and filed to the Plan in the state where the store is located. Specialty Pharmacies must bill to the Plan in whose state the member resides. Anesthesia Guidelines Anesthesia services are reported with procedure codes 00100 - 01999. Benefits for anesthesia services provided in the operating suite include: • • • • • Pre-anesthesia visits, services in the preoperative area and postanesthesia visits All preoperative visits, postoperative visits and/or monitoring (including consultations). Constant physical attendance while surgery is being performed and monitoring the patient’s vital signs throughout surgery Administration of fluids or blood incident to the anesthesia or surgery, the administration of drugs which change the state of sensation or consciousness, or in a very few cases, withholding such drugs deliberately where it is in the best interest of the patient Following the patient through recovery from the effects of drugs; (those administered before, during and immediately after the surgery) Anesthesia Time Anesthesia time begins with the initial administration of anesthetic agents by the anesthesiologist and ends when the patient is released to the recovery area. The total anesthesia allowed amount is an accumulation of base units plus time units. Base units will be internally assigned by BCBSNE using the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Relative Value Guide based on the CPT anesthesia procedure code submitted. Every 15 minutes is considered one time unit. LIST ONLY TOTAL NUMBER OF MINUTES IN THE UNITS FIELD. DO NOT LIST CALCULATED TIME UNITS NOR START/STOP TIMES ON THE CLAIM. The base units + time units are calculated by BCBSNE’s claims processing system. Reporting time units in the units field can result in an underpayment. Exceptions are OB anesthesia codes 01960, 01961, 01967 and 01968 which are priced at a flat fee and should be reported as one unit. Any non-ASA procedures (i.e. 62311) should also be reported with one unit. 77 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Anesthesia Modifiers An anesthesia modifier is not required. The physical status modifiers are: P1 A normal healthy patient P2 A patient with mild systemic disease P3 A patient with severe systemic disease P4 A patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life P5 A moribund patient who is not expected to survive without the operation P6 A declared brain-dead patient whose organs are being removed for donor purposes Other modifiers are also valid. Modifier 30 is not valid. The modifiers do not affect payment. CRNAs who are an employee of a hospital will need to obtain an NPI and advise BCBSNE of their NPI for claim filing. NPI notification forms can be found online at https://www.nebraskablue.com/providers/forms-forproviders/. In addition to needing their individual NPI, we need their date of birth and social security number. Once we have received this information, we will update our provider files. Services provided by a CRNA who is an employee of a hospital must adhere to the following billing guidelines: • • • Anesthesia claims must be billed with minutes, not units Never put the surgeon’s NPI number on the claim Do not write start and stop times on the claim Paper Claims Guidelines • Box 24J must include the CRNA’s individual NPI • Box 31 must include Prof Serv CRNA with the CRNA’s first and last names underneath Prof Services CRNA. No punctuation. Example: Prof Serv CRNA Smith Jane CRNA Box 33A must include the entity’s NPI number in box 33A if one is assigned. Electronic Claim Guidelines • The 2310B Loop (Rendering) should include the CRNA’s name and individual NPI. • The 2010AA Loop (Billing) should include the billing entity’s name and organizational NPI. 78 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Anesthesia Risk and Qualifying Circumstances Services involving administration of anesthesia must be reported using the CPT anesthesia code 00100-01999 plus modifier codes (P1-P6) if applicable. There will be no additional reimbursement for P1-P6 modifiers. Qualifying circumstance codes (99100, 99116, 99135 and 99140) can be used to report difficult circumstances. There will be no additional reimbursement for the following qualifying circumstance codes: 99116, 99135, 99140. CPT codes 99100, 99116, 99135, 99140 are considered content of service and are not separately reimbursed. Anesthesia Billing Situations, Specific Anesthesia for Multiple Procedures If anesthesia has been given for a procedure and a secondary procedure is also done, the primary procedure will be reimbursed the normal base plus time units, the secondary procedure will be reimbursed base units only. Anesthesia Standby Non-active participation by an anesthesiologist who is physically present during a surgical procedure is not a covered service. Charges for anesthesia standby will be denied as not covered, subscriber liability. Anesthesia Supervision Beginning with dates of service July 1, 2008, and after, BCBSNE will reimburse the physician for medical direction of a CRNA. BCBSNE will not accept “split” claims for medical direction services. Submission of claims by the physician and the CRNA for medically directed anesthesia services will result in the CRNA bill being denied as content of service. Reimbursement for anesthesia services when medically directed by a physician will be reimbursed if the following criteria are met: - Not more than four anesthesia procedures are being performed concurrently. - The physician is physically present in the immediate area of the operating suite(s). - Medical direction is a Covered Service only if: a) the physician performs a pre-anesthetic examination and evaluation; b) the physician prescribes the anesthesia plan; c) the physician personally participates in the most demanding procedures of the anesthesia plan, including, if applicable, induction and emergence, block placement if regional anesthesia and/or start of intravenous sedation if MAC anesthesia; d) the physician ensures that a qualified anesthetist performs any procedures in the anesthesia plan that he or she does not perform; e) the physician monitors the course of anesthesia administration at frequent intervals; f) the physician remains physically present and available for immediate diagnosis and treatment of emergencies; and g) the physician provides indicated post-anesthesia care. 79 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents - The physician does not perform any other services that require leaving the immediate area of the operating suite, devote extensive time to an emergency case, or is otherwise not available to respond to the needs of surgical patients during the same time period. A physician directing the administration of not more than four anesthesia procedures may provide the following without affecting eligibility of his/her medical direction services: a) b) c) d) e) f) Address an emergency of short duration in the immediate area; Administer an epidural or caudal anesthetic to ease labor pain; Provide periodic, rather than continuous, monitoring of an obstetrical patient; Receive patients entering the operating suite for the next surgery; Check or discharge patients in the recovery room; Handle scheduling matters. The medically directing physician is personally responsible for determining the diminishment of his or her directing capability while involved in the performance of a procedure and to provide service consistent with these policies. Conscious Sedation Effective with dates of service January 1, 2012, and after, CPT codes 99143 and 99144 will be allowed separate reimbursement when billed with a procedure code that is not listed in Appendix G of the CPT manual. If conscious sedation codes are billed for dates of service prior to January 1, 2012, or after January 1, 2012 with a procedure code listed in Appendix G of the CPT manual, the sedation will be denied as content of service. If an anesthesiologist is doing the conscious sedation and is documenting the monitoring of all the vitals as expected for someone under anesthesia, then that anesthesiologist may bill for the service using the anesthesia codes. All of the usual anesthesia documentation is expected to be in place for this service to qualify as anesthesia. Oral Surgeons or Dentists should bill conscious sedation with the appropriate codes: • D9241 – intravenous conscious sedation/analgesia – first 30 minutes • D9242 – intravenous conscious sedation/analgesia – each additional 15 minutes Epidural Anesthesia When an epidural is inserted to introduce the anesthetic agent for surgery and for postoperative pain management: • Bill the CPT anesthesia procedure code, the surgical procedure code for the catheter placement (CPT code 62318-62319), and 01996 for the daily management of the continuous epidural. When general anesthesia is used for the surgical procedure and an epidural is inserted for postoperative pain management: 80 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • Bill the CPT anesthesia procedure code, the surgical CPT procedure code for the catheter placement (CPT code 62318-62319), and the appropriate E and M code for the daily management of the continuous epidural. When an epidural is used for pain management only: • Bill the CPT surgical procedure code for the catheter placement (CPT code 62318-62319), and the appropriate E and M code for daily management of the continuous epidural. Intravenous Analgesia Intravenous Analgesia is defined as the administration of analgesic, narcotic, neuroleptic, hypnotic or amnesic agents for the purpose of rendering a patient insensible to pain during surgical, obstetrical and certain other medically necessary procedures. Benefits for the administration of intravenous analgesia is considered to be content to the administration of anesthesia. Local Infiltration, Digital Block Anesthesia, Regional Block Anesthesia (Spinal, Saddle, Caudal Blocks) by the Surgeon or Assistant Surgeon When administered by the surgeon or assistant surgeon, charges for these procedures are considered to content of service. Local Infiltration, Digital Block Anesthesia, Regional Block Anesthesia (Spinal, Saddle, Caudal Blocks) by the Surgeon or Assistant Surgeon When administered by the surgeon or assistant surgeon, charges for these procedures are considered to content of service. If the nerve block is the mode by which anesthesia and pain control are administered, it is considered part of the anesthesia and the anesthesia code should be billed. Obstetric Anesthesia Services CPT codes 01960, 01961, 01967, 01968, and 01969 are used for anesthesia maternity services. Codes 01960 or 01961 should be used when the MD or CRNA only attends the delivery and no anesthesia was provided prior to delivery. Code 01967 should be used to report services for vaginal delivery in which neuraxial labor analgesia/anesthesia is used. This includes any repeat subarachnoid needle placement and drug injection and/or necessary replacement of an epidural catheter during labor. Codes 01967 and 01968 should both be used to report labor analgesia/anesthesia. This includes any repeat subarachnoid needle placement and drug injection and/or any necessary replacement of an epidural catheter during labor for a planned vaginal delivery that resulted in a cesarean section. Note: Time units do not apply for 01967 and 01968. The allowance is a flat fee. Codes 01967 and 01968 should be billed with a single date of service (to and from date should be the same) and a unit of one. 81 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Code 01969 should be used for cesarean hysterectomy following neuraxial labor analgesia/anesthesia and is to be reported in addition to with 01967 and 01968. For codes 01960, 01961, 01967 and 01968 report only one unit of time in box 24G on the CMS 1500. For code 01969 report one time unit for each 15 minute increment or fraction thereof. We only accept one claim from one provider per labor and delivery encounter. Do not split charges or codes to report the services of more than one professional involved in the care. Services Not Related to Anesthetic Administration When the anesthesiologist/anesthetist performs a service not related to anesthetic administration, the services must be billed under the appropriate CPT code which describes the service. Apnea Monitor Use A4556 for electrodes for Apnea monitor (per pair) if monitor has been purchased. Use A4557 for lead wires for apnea monitor (per pair) if monitor has been purchased. If monitor is rented, electrodes and lead wires are already included in the apnea monitor allowable and will not be separately reimbursed. Assistant Surgery (See “Surgery”) Audiology Testing BCBSNE member contracts exclude audiological function tests except for limited circumstances. However, participating providers are to offer the following discounts to BCBSNE members: o 10% discount off the cost of hearing exams o 10% discount off the retail price of hearing aids Avastin When billing for Avastin for ophthalmologic purposes (macular degeneration), you must bill C9257 on BCBS claims. When billing for Avastin for chemotherapy purposes, you must bill J9035. Any claims submitted inaccurately will be returned requesting a corrected claim. Bilateral Procedures Modifier -50 A breakdown for each side is required when reporting bilateral procedures. The first side should be submitted unmodified and with a charge for the first side. The second side should be submitted with modifier -50 and a charge for the second side. (See also Bilateral Surgery.”) 82 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Biofeedback Biofeedback training is a therapeutic technique and training experience by which the patient is taught to exercise control over a physiologic process occurring within the body. Biofeedback is considered acceptable medical practice with payable benefits when used as adjunctive therapy with a diagnosis of mental illness. Birth Doula Services BCBSNE does not contract with birth doula providers. Birth doula providers may bill their services with 59899 (unlisted maternity care) and the charges will deny as non-covered. Board Certification Board Certification is not a requirement to contract with BCBSNE. If Board Certification is included with credentialing information, BCBSNE will verify. Bone Mineral Density Beginning March, 1, 2010, Bone Mineral Density Measurements billed with CPT code 77080 will be reviewed against BCBSNE’s Medical Policy. To view this policy, go to www.nebraskablue.com, click on the “Providers” button and then on “Policies and Procedures” in the left column. CT Bone Mineral Density Studies represented by CPT codes 77078 and 77079 must be preauthorized through American Imaging Management (AIM). Refer to Section 9 of this manual for additional information concerning BCBSNE’s Radiology Quality Initiative (RQI) Program. Breastfeeding Support, Supplies and Lactation Counseling As of August 1, 2012, breastfeeding support, supplies and counseling benefits are available to small groups and individual policies. Large groups will take the benefit upon renewal and ASO groups can choose exemption. There is no cost to the member when obtained from an in-network provider, and following the billing and coding guidelines specified below: Breast Pump Billing Guidelines Breast pump benefits are only available under the mother’s benefits. BCBSNE does not provide breast pump benefits to the baby. Be sure to file breast pump claims with the mother as the patient. • E0602 Breast pump, manual, any type • E0603 Breast pump, electric (AC and/or DC), any type • E0604 Breast pump, hospital grade, electric (AC and/or DC), any type The HCPCS code must be appended with modifier RR or NU to indicate rental versus purchase. Benefits will be provided for one pump, per pregnancy, at no cost to the member. Benefits are also available for the following breast pump supplies on a purchase-only basis: • A4281 Replacement breast pump tubing • A4282 Replacement breast pump adapter 83 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • • A4283 Replacement of breast pump cap A4284 Replacement breast pump shield A4285 Replacement of breast pump bottle A4286 Replacement of breast pump locking ring Note: Since this is a federal mandate providing 100% coverage for breast pumps, BCBSNE will not allow providers to balance bill members for any of the breast pump models. Providers are not allowed to have members sign waivers accepting additional liability. BCBSNE will not consider any waiver signed by a member to be valid where the patient has accepted additional liability. FEP members must obtain breastfeeding pump kits via mail order through CVS Caremark by calling (800) 262-7890. Benefits are limited to one kit per year for women who are pregnant and/or nursing. Members can choose between a manual or electric pump. Benefits are not available for breast pumps or supplies dispensed or purchased from any other provider. A prescription is not needed to receive a breast pump kit. Breastfeeding Support and Counseling Billing Guidelines The following CPT/HCPCS codes are appropriate for lactation support and counseling services provided by an IBCLC: • 99211 • 99401 • 99402 • 99403 • 99404 • Lactation classes: S9443, 99411, 99412 The following CPT codes are appropriate for lactation support and counseling services provided by an MD: • 99211 • 99401 • 99402 • 99403 • 99404 • Lactation classes: 99411, 99412 In order for benefits to be paid at 100%, V24.1 must be the primary diagnosis code on the claim. There is no limit in the frequency or number of counseling sessions or classes payable under this benefit. Note: Lactation services, including breast pumps and supplies, provided to a covered member during an inpatient hospitalization are considered inclusive in the reimbursement made to the hospital and cannot be billed separately. 84 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Network Requirements Individuals who are designated as an International Board-Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) are eligible to apply to become a participating provider with BCBSNE, and must meet all credentialing requirements as established and approved by the BCBSNE Credentialing Committee. To request an application packet, call (800) 821-4787, option 4, or email credentialingrequests@nebraskablue.com. Be sure to include your name, mailing address, and identify yourself as an IBCLC to ensure you are sent the correct forms for completion. IBCLCs who are a salaried employee of a hospital or home health agency are still required to be credentialed by BCBSNE and file claims under their own name and individual NPI number. Questions regarding credentialing should be emailed to CredentialingRequests@nebraskablue.com. Cardiac Rehabilitation Effective August 1, 2009, cardiac rehab will no longer require preauthorization. Cardiac Rehabilitation is defined as the use of various modalities of treatment to improve cardiac or pulmonary function as well as tissue perfusion and oxygenation through which selected patients are restored to and maintained at either a pre-illness level of activity or a new and appropriate level of adjustment. Cardiac rehabilitation is scientifically validated if started within four (4) months of: • • • • • • An acute myocardial infarction; Coronary artery angioplasty, with or without stent placement, or other scientifically validated procedure to clear blocked coronary vessels; Heart or coronary artery surgery; Heart transplant; or Heart-lung transplant. Cardiac rehabilitation is scientifically validated for treatment of congestive heart failure and stable angina initially and after significant changes in clinical status. All other uses of cardiac rehabilitation are investigative. Note: The diagnosis and time frame may vary based on the member’s contract and/or endorsements. If the member has benefits for Cardiac Rehabilitation but does not meet the contract criteria, then it is denied as a contract exclusion and not investigative. To be considered for reimbursement, providers must be JCAHO accredited for cardiac rehabilitation. Case Management/Care Plan Oversight Services Case Management codes 99366-99368 and Care Plan Oversight Services codes 99374-99380 are not separately reimbursed. They are considered content of service and no additional reimbursement is allowed regardless of whether or not they are submitted with another E and M service. The denial is 85 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents provider liability. CPT codes 99441-99443: Since member contracts specifically exclude telephone consultations, these charges are member liability. Cash Discounts If a cash discount is offered, that discount needs to be extended to BCBS patients. The discounted amount must be the amount billed on the claim. If a BCBS member requests a claim be filed for a noncovered service, the provider must file the claim. Casts and Strapping Initial Cast Application during Fracture Care Fracture care includes the application and removal of the first cast or traction device only. Casting or traction is an integral part of fracture care so our allowable reflects reimbursement for the total service. Do not bill separately. Replacement Casting or Strapping Cast application or strapping as a replacement procedure used during the period of follow-up care can be reimbursed separately. Our allowable for these codes includes casting materials, including fiberglass materials. Cast Repair Cast repair must be coded with the supply code A4580. The allowance paid to a physician for application of a cast normally covers repairs. Cast Removal Cast removal must be coded with the unlisted Code 29799. This service will be denied regardless of who performed the service, even if a physician other than the physician who applied the cast removes the cast. Light Casts Reimbursement for supplies related to use of fiberglass cast materials may be billed separately from the application of the cast. Cataracts Splitting of the 90 day post-operative period is not permitted. If an Ophthalmologist and Optometrist share post-operative care, only one should bill for the service. Catheterization Simple catheterization is considered part of the “global charge” to an emergency room, office visit or inpatient room charge. No additional reimbursement is allowed. 86 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Cerumen (Ear Wax) Removal When a charge for 69210 ear wax removal is billed in conjunction with an E and M service, the E and M will deny as content unless it is billed with modifier 25. If both ears are cleaned, bill as bilateral service with two lines, one unit each and second line with modifier 50. Chemotherapy Chemotherapy Drugs The chemotherapy drug used must be indicated by the specific HCPCS code. If there is not a specific HCPCS code for the chemotherapy drug, an unlisted J code should be billed along with a valid National Drug Code (NDC) number. Chemotherapy Administration Procedure Codes 96400-96549 Chemotherapy administration procedure codes will be considered for payment when the service was performed by a physician. If the service was performed by a nurse, the service is considered global and will be denied. Monitoring services by the physician are not covered. When chemotherapy administration is performed in a place of service other than the office, the claim will pend for review for content of service determination. If the service is performed by a nurse in other than the office setting, the service is considered global and will be denied. When a heparin flush and chemotherapy are given on the same day, the heparin flush will be considered content of service and no additional reimbursement will be allowed. Separate reimbursement is not provided for supplies used in the office setting for chemotherapy services. Supplies necessary for the delivery of chemotherapy are already considered within the reimbursement level for the services performed. Clinical Trials and/or Research Studies BCBSNE member contracts do not provide benefits for services for medical treatment and/or drugs, whether compensated or not, which are directly related to or resulting from the Covered Person’s participation in a voluntary, investigative test, or research program or study unless authorized in writing by BCBSNE. These services may be pre-authorized through our Medical Support Department. To preauthorize these services, please fax the informed consent document and specific information for evaluation to 402-392-4141 or 800-255-2838. Closing Practice to New Patients A provider may refuse to take new BCBS patients, but only if their practice is closed to all new patients regardless of insurance coverage. CMS 1500 Claim Form A printable copy of the CMS 1500 claim form is available at: http://www.wcc.state.md.us/PDF/MFG/cms1500_blank.pdf 87 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Co-Surgery (See “Surgery”) Coding School/Sports Physicals If a school or sports physical is scheduled and performed, the diagnosis should be coded V70.3 (Other Medical Examination for Administrative Purposes). Some Blues members do not have coverage for a school physical, but it should not be coded as a routine physical. Collection and Handling Reimbursement for laboratory tests includes payment for the collection and handling. CPT codes 36591, 36592, 99000-99002, if billed, will be denied as content of service. Consultation Codes BCBSNE will not accept CPT codes 99241 - 99245 or 99251 - 99255. These consultation codes will be non-covered as provider liable services. The denial reason will instruct the provider to resubmit with a more appropriate Evaluation and Management (E and M) code. Consults in the Office or as an Outpatient These services should be submitted using the new or established patient office or other outpatient visit codes (99201 - 99215). New and established patient visit criteria remain according to the CPT definition. An established patient is defined as patient who has been seen within the past three years by the rendering provider, even if that patient was seen at another facility or clinic by that rendering provider. Consults in the Emergency Room When a consultation takes place in the emergency room, the service may be submitted as either an addition ER visit or as an outpatient visit using the appropriate place of service (POS) code 23. Documentation must support the CPT code definition. Consultations during Observation Only the admitting physician can use the initial observation care codes (99218-99220). Other physicians performing a consult should use the new or established patient office or other outpatient visit codes. Consultations during an Inpatient Stay The first time a physician sees a patient in consultation, an initial hospital care code (99221-99223) may be billed regardless of when the visit occurs during the inpatient stay. There may be multiple initial hospital care codes on the admit date or other dates, depending on the physician(s) who assesses the patient in consult. However, there should never be more than one initial hospital care code per physician. Subsequent visits to the patient must be billed using subsequent care hospital visit codes (99231-99233). The admitting physician may append modifier Al to the initial hospital care code to identify the admitting physician of record. There should only be one initial hospital care code with modifier Al. Any additional initial care codes with this modifier will be noncovered as a duplicate service. 88 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents When a second physician sees a patient as an initial consult and all other required components are performed and documented, an initial hospital care code may be used (99221-99223). If the criteria for an initial hospital care code is not met and the documentation and criteria supports a subsequent hospital care code (99231-99233), those codes should be used even if an initial care code has not been submitted by that physician. Rarely would code 99499 (unlisted E and M service) be used if documentation does not meet criteria for subsequent care. Documentation must establish that a medically necessary service was rendered and where the service took place. Claims submitted for services with code 99499 will be individually reviewed. Consultations in a Nursing Facility The first time a physician sees a nursing facility patient in consult, an initial nursing facility care code (99304-99306) may be billed regardless of when the visit occurs during the nursing facility stay. Multiple initial nursing facility care codes may be billed depending on the physician(s) who assesses the patient in consult. However, there should never be more than one initial nursing facility care code per physician. Subsequent visits to the patient must be billed using subsequent care codes (99307-99310). The admitting physician may append modifier Al to the initial nursing facility care code to identify the admitting physician of record. There should only be one initial nursing facility care code with modifier Al. Any additional initial care codes with this modifier will be noncovered as a duplicate service. When a second physician sees a patient as an initial consult and all of the required components are performed and documented, an initial nursing facility care code may be used (99304-99306). If the criteria for an initial nursing facility care code is not met and the documentation and criteria supports a subsequent nursing facility care code (99307-99310), those codes should be used even if an initial code has not been submitted by that physician. Only rarely would code 99499 (unlisted E and M service) be used if documentation does not meet criteria for subsequent care. Documentation must establish that a medically necessary service was rendered and where the service took place. Claims for services submitted with code 99499 will be individually reviewed. Consults Submitted on a UB-04 Any of the consultation codes submitted on the UB-04 claim form will be noncovered, and denied as provider liability. The denial reason will instruct the provider to resubmit with a more appropriate E and M code. Content of Service Content of service refers to specific services and/or procedures, supplies and materials that are considered to be an integral part of previous or concomitant services or procedures, or all inclusive, to the extent that separate reimbursement is not recognized. Charges denied as “content of service” are the participating physician’s liability and may not be billed to the member. 89 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Contrast Media Low and High Osmolar Contrast Agents Low and high osmolar agents are used with the 70xxx-77999 range of CPT codes. Low osmolar agents (i.e. Isovue) are used primarily in patients with sensitivities to the high osmolar agents or patients whose medical condition (i.e. cardiac disease, asthma) warrants the use of the low osmolar agent. BCBSNE currently recognizes and allows benefits for the low osmolar agents. If you are working with the low osmolar agents, you should check the HCPCS manual. A4641 is for a “radiopharmaceutical” agent and should not be used to bill for the low or high osmolar (i.e. Hypaque) “contrast” agent. These are two separate and distinct types of agents and the appropriate codes should be used for the type of agent used. High osmolar agents are already calculated into the RVU and reimbursement rate for each code. The cost of these agents is “content” to the procedure. Therefore, charges for high osmolar agents should not be billed. Radiopharmaceutical Agents Radiopharmaceutical Agents are used with the 78xxx and 79xxx range of CPT codes. When billing for a radiopharmaceutical, you must be as specific as possible with your coding. If you bill A4641 and there is a more specific HCPCS code available for the agent billed, the claim will be returned. Include the name of the radiopharmaceutical used and bill under the appropriate code in the HCPCS manual (A9500-A9605, Q3000-Q3012, etc.). A4641 is an unlisted code and doesn’t identify the specific agent used. Since HCPCS now carries a large volume of codes that identify these specific agents, the specific code (if available) must be used rather than the unlisted code of A4641. Some agents have medical policies tied to them and others may be affected by a policy in the future. The introduction of a needle or intracatheter, vein (36000) used as the delivery mode for the radiopharmaceutical contrast agent for 78800-78816 is incidental and will be denied as such. Because 36000 is a necessary part of delivering the radiopharmaceutical agent, it is already considered part of and is included in the calculation of the allowance for the 78xxx code. Note: When claims are returned requesting more information, do not just attach the pharmacy slip for the agent or just give the radiopharmaceutical name. This does not complete the coding process because you still have not assigned the specific code for that agent but have simply resubmitted it still using the A4641. This is considered improper coding. When there is a specific code for the agent that is the code that should be used. If you’re having difficulty knowing how to code the agent, search on the internet for “radiopharmaceutical agents generic name”. This search will lead you to an online educational 90 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents document for nuclear pharmacy which provides the name of the different radiopharmaceuticals, their trade names, and their primary use. Using this document, a provider can easily refer to the HCPCS manual and find the appropriate code. The URL for this site is www.nuclearonline.org. As an example, if the agent used was Choletec, then the individual could reference the trade name column and find that the name of the specific radiopharmaceutical agent is Tc-99m Mebrofenin. They would then go to their HCPCS manual and look for that agent in the A9500-A9605, Q3000Q3012 etc. range and code the agent accordingly on the claim. In the example listed, Mebrofenin would be A9513. Another resource would be to contact your dispensing department for the particulars on the agent. They should be able to provide you with both the trade name and the radiopharmaceutical agent’s name. Using that, you could then find the HCPCS code. Special Note: If the radiopharmaceutical used is FDG 18 you must use A9552 for dates of service January 1, 2006 and after. CPT and HCPCS Codes CPT (Level 1) Codes Category I Use the code which most accurately reflects the service provided. If there is no valid CPT code, an unlisted code with description should be used. Category II The use of these codes is optional. These codes may not be used as a substitute for a Category I code. Category III Used for emerging technology, services and procedures. If a Category III code is available, this code must be reported instead of the Category I unlisted code. HCPCS (Level II) Codes A Codes Used for Ambulance, Medical Surgical Supplies as well as Administrative, Miscellaneous and Investigational services. Most medical supplies are content to the office visit and should not be billed separately. Radiopharmaceutical Agents A95xx and A96xx may be found in this area. B Codes Used for HME billing. Acceptable for primary or secondary billing to BCBSNE. C Codes Used for CMS billing. If BCBS is primary or secondary (not a supplement), a valid CPT should be used unless you have been specifically instructed by BCBSNE to use a C Code for a particular service. 91 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents D Codes Dental codes. Acceptable for primary or secondary billing to BCBSNE. E Codes Used for HME billing. Acceptable for primary or secondary billing to BCBSNE. G Codes If billing to BCBS as primary, a valid CPT code should be used if one is available. Exceptions are when billing for diabetes education (G0108 or G0109). When BCBS is secondary to Medicare, whether as supplement or secondary insurer, the G codes will be recognized/accepted. H Codes Codes required by Medicaid to report services. A CPT code should be used for billing to BCBSNE. J Codes If a drug or biological has a valid HCPCS code, that code should be billed. Units should be billed in accordance with the nomenclature of the code. If there is no valid code, an unlisted code should be used along with the National Drug Code (NDC) number. Effective July 1, 2014, per contract BCBSNE will reimburse for office-administered medications at a percentage of Average Sales Price. Prior to this date BCBSNE had reimbursed drugs and biologicals at a percentage of CMS rates. The reimbursement methodology may vary for PHO and oncology providers. K Codes Acceptable for primary or secondary billing to BCBSNE. L Codes Acceptable for primary or secondary billing to BCBSNE. M Codes If billing to BCBS is either primary or secondary, a valid CPT code should be used. P Codes If billing to BCBS is either primary or secondary, a valid CPT code should be used. Q Codes Temporary code. If there is a valid CPT code, that code should be used. Otherwise Q codes will be accepted. R Codes These codes are for the transportation of portable X-ray and/or EKG equipment. Acceptable for primary or secondary billing to BCBSNE. S Codes Home Infusion therapy codes are found in this section. If you are billing for a surgical procedure and billing BCBS as either primary or secondary, a valid CPT code should be used. If there is no valid CPT 92 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents for a surgery, the service should be billed under an unlisted surgical procedure code with a description. T Codes Medicaid codes. A CPT code should be used for billing to BCBSNE. V Codes Acceptable for primary or secondary billing to BCBSNE. Computerized Corneal Topography (92025) CCT is considered content to service to the doctor visit and is denied provider liability. Critical Care Codes 99468-99476 Per CPT, the following codes are now considered to be part of the critical care codes. Critical care involves high complexity decision making to assess and support vital system functions, to treat single or multiple organ system failure or to prevent further deterioration of the patient’s condition. The following CPT codes will be denied as content of service if billed with the critical care codes: 31500, 36140, 36430, 36440, 36510, 36000, 36400, 36405, 36406, 36420, 36600, 36620, 36660, 43752, 51100, 51701, 51702, 62270, 94002, 94003, 94004, 94375, 94610, 94660, 94760, 94761, 94762, 94780, 94781 Developmental Testing CPT Codes 96110, 96111 Developmental testing is normally considered part of a preventative medicine visit. If a 96110 or a 96111 is billed with a routine diagnosis, along with a preventative medicine visit, the developmental testing will be denied as content to the exam. If the 96110 or 96111 is billed with a medical diagnosis, documentation will be requested and the services reviewed. Decompression Therapy Decompression Therapy (S9090) is often done using a DRX 9000 machine. Decompression Therapy is considered investigative by BCBSNE and is therefore not covered. S9090 is the correct code to use when billing for decompression therapy. Our medical policy for decompression therapy (VII.61) can be located in our Medical policy that is available at www.nebraskablue.com. Click on the “Providers” button and then on “Policies and Procedures” in the left column. Diabetes Education (See Section 12 for complete description and billing guidelines) 93 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Dietician (Registered) Registered Dieticians who have not billed to BCBSNE previously should e-mail ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com to complete a Health Care Professional Questionnaire. BCBSNE does not contract with Registered Dieticians. Most BCBSNE member contracts do not cover services by an RD. Benefits should be verified prior to providing services. Discontinued Services Discontinued services are reimbursed at 80% of the professional fee schedule. Bill with modifier -53 and a 20% reduction will be taken from the allowed amount. Documentation General Principles of Medical Record Documentation The principles of documentation listed below are applicable to all types of medical and surgical services in all settings. For E and M services, the nature and amount of physician work and documentation varies by type of service, place of service, and the patient’s status. The general principles listed below may be modified to account for these variable circumstances in providing E and M services. 1. Must be complete and legible. 2. Each patient encounter record should include: • Reason for the encounter and relevant history, physical examination findings, prior diagnostic test results; • Assessment, clinical impression, or diagnosis; • Plan for care; and • Date and legible identity of the observer. 3. The rationale for ordering diagnostic and other ancillary services must be documented. 4. Past and present diagnoses should be accessible to the treating and/or consulting physician. 5. Appropriate health risk factors should be identified. 6. The patient’s progress, response to and changes in treatment, and revision of diagnosis must be documented. 7. The CPT and ICD-9-CM codes reported on the claim form must be supported by the documentation in the medical record. BCBSNE Documentation Policy for E & M Services BCBSNE follows CMS documentation guidelines for Evaluation and Management (E & M) services. 94 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Modifiers and Modifier Usage: Modifiers are two-digit numbers and/or letters attached to a HCPCS/CPT code when conditions are appropriate. Modifiers provide pertinent information necessary to process claims correctly. The medical record must support the use of any modifier. Diagnosis Codes Must Support: • The E & M level of service • Any modifier attached to the CPT code (i.e. -25 separate procedures) • All Medicine and Surgical Procedures • Need for lab and X-ray studies • Any and all services billed on the claim form The appropriate code(s) must be used to identify diagnoses, symptoms, conditions, problems, complaints, or other reason(s) for the encounter/visit. For accurate reporting of diagnosis codes, the documentation should describe the patient’s condition, using terminology which includes specific diagnoses as well as symptoms, problems, or reasons for the encounter. Code the condition being treated and the underlying cause, if known. For patients receiving pre-op evaluations only, code with V72.81, V72.82, V72.83 or V72.85 to describe the pre-op consultation. Tips to Remember 1. Documentation should be complete and accurate before the claim is submitted. 2. Accurate documentation in the medical record facilitates: • The ability of the physician and other health care professionals to evaluate and plan the patient’s immediate treatment, and to monitor his/her health care over time; • Communications and continuity of care among physicians and other health care professionals involved in the patient’s care; • Accurate and timely claims review and payment; • Appropriate utilization review and quality of care evaluations; and • An appropriate documented medical record can reduce frustration associated with claims processing and may serve as a legal document to verify the care provided if necessary. 3. All documentation in the medical record must be patient specific. Cloning of documentation which fails to take into account patient specific variations will be considered a misrepresentation of the medical necessity requirement for coverage of services. 95 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Discharge Management - Hospital 99238 is allowed if another provider under the same tax ID has not billed for the same day. Drugs Dispensed in Office A valid HCPCS code must be used for any drug given in the physician’s office. If there is no valid J code for the drug given, then use an unlisted J code and include the name and National Drug Code (NDC) number of the drug. When filing electronically, the NDC number must be submitted in loop 2410 and in the following format: xxxxx-xxxx-xx. If there is a valid J code, the units billed will be reflective of the nomenclature associated with that particular J code. If an unlisted J code is billed, then the units should be reflective of the nomenclature associated with the NDC number. Eyecare Refractions Eye refractions (92015) should be billed separately from the eye exam code. Unless a group has a specific endorsement covering eye refractions, these charges will be denied as member liability. Visual Field Examinations These services generally include the checking of both eyes and should always be billed with a unit of “1” in Box 24G of the CMS 1500. If the physician only checks one eye, the code should be submitted with modifier -52, to indicate that only one eye was checked. Federal Employee Program (FEP) and Medicare A provision of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliations Act (OBRA) of 1993 applies the Medicare participation and physician payment rules and requirements to all retired individuals covered under the BCBS Federal Employee Program (FEP). These payment rules include CMS-approved demonstration projects. OBRA affects FEP reimbursement when the patient: • is 65 years of age or older; • does not have Medicare Part A, Part B, or both; • is an annuitant of the FEP as a former spouse OR as a family member of an annuitant of former spouse; and • is not employed in a position that offers FEP coverage 96 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Inpatient Reimbursement OBRA bases inpatient care reimbursement on an amount that is equivalent to Medicare’s payment amount unless the charge is less than the Medicare equivalent amount. FEP members are NOT responsible for any charges greater than the Medicare equivalent amount. The law prohibits a hospital from collecting more than the Medicare equivalent amount. FEP members who have Standard Option coverage are responsible for deductibles, coinsurance, and/or co-payments. Physician Reimbursement OBRA bases physician services reimbursement on the lesser of the Medicare approved amount or the actual charge. Member liability is dependent on the physician’s participating status with Medicare and/or the physician’s NEtwork BLUE contracting status. If the physician participates with Medicare or accepts Medicare assignment and is in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - Deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments • Basic Option - Copayments and coinsurance If the physician participates with Medicare or accepts Medicare assignment and is NOT in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - Deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount • Basic Option - All charges If the physician does not participate with Medicare and is in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - Deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount • Basic Option - Copayments, coinsurance and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount If the physician does not participate with Medicare and is NOT in the NEtwork BLUE network, the FEP member is responsible for: • Standard Option - Deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, and any balance up to 115% of the Medicare approved amount • Basic Option - All charges Fertility Testing/Treatment Consults A consult to a fertility specialist to establish the diagnosis of infertility is considered a payable benefit. If the member previously had infertility established through their OB/GYN or family practice M.D. (such as previous infertility treatment with Clomid) and are seeing the fertility specialist for other options, then this would be considered infertility treatment. If the plan of treatment involves further diagnostic studies to establish or rule out other conditions (such as endometriosis or polycystic ovarian disease), then this would be considered a payable benefit. 97 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Diagnostic Testing Infertility is a symptom of a disease. Diagnostic testing to determine the cause of the symptom is a covered benefit. If disease is determined to be the cause, benefits are available for the appropriate treatment of the disease. However, if the treatment received is not specifically disease related and the treatment purpose is to facilitate fertility, then benefits are subject to the varying contractual language and endorsements concerning fertility related services. Diagnostic testing done to determine the diagnosis of infertility, treatment of polycystic ovary disease, and treatment of endometriosis, are not considered to be Infertility treatment. Infertility Diagnosis Codes Diagnosis codes 606.XX (Male Infertility), 628.XX (Female Infertility) and V26.XX (Procreative Management) are defined as infertility. Other diagnosis codes may or may not be related to infertility. Infertility Treatment Once the member has completed the evaluation and the treatment proceeds to infertility related treatment such as serial ultrasounds and labs, then the claims will be reviewed/processed as infertility treatment. This is regardless of the diagnosis submitted on the claim. Therefore, even if the provider bills with a diagnosis of polycystic ovarian disease or endometriosis, if the records indicate they are monitoring the woman’s cycle in response to infertility medications or prior to ART, the claim will be processed as infertility treatment. Certain Reproductive Clinics require screening blood tests to be completed to both partners prior to initiation of the ART procedure. These tests may include: HIV, Hepatitis B and C, RPR, Cycle Day 3 FSH (female partner only), CMV (female partner only). The male partner must have a recent semen analysis. Since these tests are considered part of the ART procedure, they will be processed as infertility treatment. A diagnosis of Habitual Aborter has been defined as a history of two or more prior miscarriages. Tests/procedures related to the evaluation and/or work up for this diagnosis is considered a payable benefit. Tests that may be performed are Hysterosalpingogram, Cardiolipin phospholipid antibody, and Coagulation studies. The use of donor eggs may be requested for ART procedures. Benefits are available for the use of donor eggs based on the member’s contract. Any services/charges directly related to the donor should be submitted under the donor’s name and ID, since the donor is considered a non-eligible dependent under the recipient’s contract. Benefits will be determined based on the donor’s contractual benefits. Procedures to repair or reconstruct the fallopian tubes will be reviewed to determine if iatrogenically caused and whether benefits are available. For example, if injury to the fallopian tube 98 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents occurred during previous abdominal surgery, and the patient was insured with us at the time of the previous surgery, benefits would be available for the repair of the fallopian tube. There are several codes that have a frequency edit placed on them. These codes include: 84702 and 84703 (Gonadotropin, Chorionic HCG); 82670 (Estradiol); 84144 (Progesterone); 76856 and 76857 (Pelvic Ultrasounds). Tests that exceed the frequency established will be denied as “Not Medically Necessary” unless the group has a fertility endorsement. Coverage for artificial insemination will depend on the member’s contract. If the charges for the artificial insemination are not covered, then all other services performed on the same day will be rejected. Reversal of voluntary sterilization is a contract exclusion. Evening, Weekend or Holiday Office Hours BCBSNE does not reimburse at a higher rate for non-typical office hours. content to the basic service. 99051 will deny as Flu Shots Coverage for the injectable influenza virus vaccine depends on the member’s contract. The charge for the vaccine product is billed separately from the immunization administration codes for vaccines/toxoids. In order to bill an office visit in conjunction with the immunization, the service must exceed what is normally considered part of and included within the immunization code. Fluoride Treatments Fluoride treatments are not covered under medical benefits. Fracture Care (See “Casts and Strapping”) Free/No-cost Vaccine Billing If you are administering a free vaccine to a Blues member (e.g. Vaccine for Children program), bill only for the administration fee and describe the free vaccine in the comments section on the claim. Do not bill the vaccine on a line charge. Health Fairs By definition, a health fair is an educational and interactive event designed for outreach to provide basic preventive medicine and medical screening to employees at work in conjunction with workplace wellness. 99 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Health fairs where network providers collect member payment upfront for covered services such as immunizations and health screenings are not allowed by BCBSNE. Network providers who perform health fair services must follow contract guidelines to file the claims to BCBSNE as with any other covered service and be paid according to the lesser of the billed charge or fee schedule allowance. Hospitals conducting health fairs must bill all charges on a CMS 1500 claim form with the hospital’s medical director as the rendering. Hearing Examinations Screening audiological examinations and testing (except infant hearing exams); external and surgically implantable devices and combination external/implantable devices to improve hearing, including audiant bone conductors or hearing aids and their fittings are not covered unless the member’s contract has a specific coverage endorsement for these services. Noncovered services are the member’s liability. However, participating providers are to offer the following discounts to BCBSNE members: • 10% discount off the cost of hearing exams • 10% discount off the retail price of hearing aids Heparin Flushes Heparin flushes performed by physicians or their employees should be billed as CPT code 90784 (Therapeutic or diagnostic injection [specify material injected]; intravenous) if: • This is the only service provided, or • This and an office visit are the only services provided. When chemotherapy or intravenous therapy are given on the same day, no reimbursement will be allowed for the Heparin flush since it is considered content of service. HITECH Act BCBSNE encourages our network providers to comply with applicable Interoperability Standards and to demonstrate meaningful use of health information technology in accordance with the HITECH Act (Public Law 111-5, The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act). For more information about the HITECH Act, go to www.hhs.gov/ocr/privacy, and select the following links: 1. “HIPAA Administrative Simplification Statute and Rules” 2. “Enforcement Rule” Home Medical Equipment Ancillary Billing Guidelines In 2011, the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association mandated Plan compliance with the handling and processing of home medical equipment and supplies. Durable medical equipment claims must be filed to the Plan in whose state the equipment was shipped to or purchased in a retail store. 100 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Note: When billing a POS 12 (Home), the claim should always be filed to the Plan in the state where the patient resides. When the equipment/supplies are purchased at the retail store location, bill using POS 17 and file your claim to the Plan in the state where the store is located. Home Medical Equipment - RR or NU Modifier Required The following list of HCPCS codes require an RR (Rental) or NU (Purchase) modifier or they will be returned for proper coding. A4000 - A8999 A9270 - A9300 A9900 - A9999 B4000 - B9999 E0100 - E9999 K0001 - K9999 L0000 - L8699 S8096 - S8490 S8999 - S9015 V2624 V2625 V2626 V2628 V2700 HME rental (RR) will require a beginning and ending date. Purchase items should be billed with the date dispensed, delivered or received by the member and not with a date span. Note: Prebilling for HME/DME rental is not permitted. Only purchased items may be billed at the time of delivery/pick-up. If multiple modifiers are used, the RR or NU modifier must be in the first position. If more than one item is dispensed, each item would need to be billed on a separate line. Example: L3090 NU RT L3090 NU LT NOTE: Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASC’s) are required to always bill implant codes (ex. L8699) with an NU modifier. Immediate Family BCBSNE member contracts exclude “Charges for Services provided by a person who is a member of the Covered Person’s immediate family by blood, marriage or adoption.” “Immediate Family” is defined as the provider, the spouse of the provider, the children of the provider (including adult offspring) and stepchildren of the provider living in the provider’s home. 101 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Immunization Administration On January 1, 2011, codes 90460 and 90461 became effective for billing immunization administration. The new codes require each component of a vaccine to be reported separately. CPT defines a component as all antigens in a vaccine that prevents disease(s) caused by one organism. Combination vaccines are those vaccines that contain multiple vaccine components. Use code 90460 to report the first (or only) vaccine/toxoid component of each vaccine. Use code 90461 to report each additional component of that particular vaccine. As an example, if you administer Tdap and Hib, you would bill 90460 with a unit of two and 90461 with a unit of two. Claims submitted with multiple line items of either code will be denied. In addition, all lines of 90460 and 90461 must be on one claim form. Multiple pages containing 90460 and 90641 will result in these codes being denied as duplicates. For immunization administration of any vaccine that is not accompanied by face-to-face physician or qualified health care professional counseling to the patient/family or for administration of vaccines to patients over 18 years of age, report codes 90471-90474. If a significant separately identifiable Evaluation and Management service (new or established patient office or other outpatient services (99201-99215), emergency department services (99281-99285), preventative medicine services (99381-99429) is performed during the same visit that the vaccine is administered, the appropriate E/M service code must be append with the -25 modifier to the E/M code or it will deny as inclusive to vaccine administration code. NOTE: 99211 is never payable when billed with an administration code, regardless of modifier 25. Immunizations, Pediatric Nebraska Law mandates that pediatric immunizations for children age six and under are payable and NOT subject to deductible. Groups that are self-insured may elect NOT to provide this benefit. Pediatric Immunizations include: Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Poliomyelitis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Hemophilus Influenza B, Chicken Pox, Hepatitis B, TB Tine for Tuberculosis (86580 and 86585), Prevnar, and as otherwise provided by state or federal law. Prevnar (90669) was approved by the FDA on February 17, 2000. The vaccine is delivered in a fourshot series and is given to prevent meningitis, blood poisoning, and ear infections in infants and children through the age of four. If the patient is age five or older, the vaccine will be denied as Investigative. Report CPT code 90465-90474 in addition to the applicable codes for vaccines and toxoids. If you are administering to a Blues member a free vaccine (ex. Vaccine For Children program) bill only for the administration fee and describe the free vaccine in the Comments section on the claim. Do not bill the vaccine on a line charge. 102 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Independent Clinical Laboratory In 2011, the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association mandated Plan compliance with the handling and processing of independent clinical laboratory claims. Independent labs are required to bill the claim to the Blues plan in whose state the specimen was drawn. Where the specimen is drawn is determined by the state where the ordering (referring) physician is located. If the referring provider in Box 17 is not a Nebraska provider, BCBSNE will reject the claim and direct the lab to file to the Blues plan where the referring provider is located. If the referring provider is in Nebraska and the independent lab is in another state, the lab must file the claim to Nebraska with its independent lab name and NPI as the rendering and not with a pathologist’s name and NPI. Physician offices who bill for laboratory services sent to an independent clinical laboratory should NOT assign POS 81 to the service line(s) in which the laboratory is reported on the claim. POS 81 is to be used only by Independent Laboratory providers, defined as “a laboratory certified to perform diagnostic and/or clinical tests independent of an institution or a physician’s office.” To prevent physician offices from being impacted by the Ancillary Claim Filing Guidelines when submitting charges for laboratory services, it is important to use POS 11 (office) when filing your claim. Modifier -90 should be appended to the CPT code for the laboratory service. Influenza Vaccines The charge for the vaccine product is billed separately from the immunization administration codes for vaccines/toxoids. In order to bill an office visit in conjunction with the immunization, the service must exceed what is normally considered part of and included within the immunization code. Infusion The following therapeutic or diagnostic infusion codes, when performed in places of service other than office, may be considered for payment only if the medical documentation reflects that the physician provided the service. 90780 - IV infusion for therapy/diagnosis, administered by physician or under direct supervision of physician; up to one hour. 90781 - IV infusion for therapy/diagnosis, administered by physician or under direct supervision of physician; each additional hour, up to eight hours. 90784 - Therapeutic or diagnostic injection (specify material injected); intravenous. Injectafer Effective July 1, 2014 the proper code for Injectafer is Q9970 per 1mg. The NDC number must be included on the claim. 103 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Intraocular Lens Implants Surgeons cannot bill for intra-ocular lens implants. Only the surgery facility (hospital or ambulatory surgery center) can bill for an IOL as it is part of the reimbursement built into the facility contract. For dates of service beginning October 1, 2013, pre-testing for specialty lenses only should be billed under CPT 92136 with the Place of Service (POS) of 11 (office). Billing for pre-testing services with a surgical CPT code in the range of 66982-66984 with a modifier 22 is no longer recommended. It is not appropriate to bill the additional time for pre-testing or additional surgery time under V2787 (Astigmatism correcting function of IOL) or V2788 (Presbyopia correcting function of IOL). It is also not appropriate to have our members sign waivers agreeing to pay for the pre-testing or additional surgery time. Intraoperative Monitoring 95940-95941 only reported when continuous attendance is required. Codes are only reported for actual time spent monitoring and excludes time to set up, record, and interpret base studies, and to remove electrodes at the end of the procedure. When the service is performed by the surgeon or anesthesiologist, the professional services are included in the surgeon’s or anesthesiologist’s primary service code(s) for the procedure and are not reported separately. Do not report these codes for automated monitoring devices that do not require continuous attendance by a professional qualified to interpret the testing and monitoring. The monitoring professional must be solely dedicated to performing the intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring and must be available to intervene at all times during the service as needed. Both codes are add-on codes. Code 95940 is reported in 15 minute increments (1 unit = 15 minutes) and only the portion of time the monitoring professional was physically present in the operating room providing one-on-one patient monitoring. If billing code 95940, personal attendance is required. Code 95941 should be billed once per hour and requires the monitoring of neurophysiological data that is collected from the operating room continuously on-line in real time via a secure data link. Do not report 95941 if the monitoring lasts 30 minutes or less. Code 95941 should be billed for remote use only and codes 95938-95939 must be also be billed as the primary code. Code 95938 requires modifier – 26. Cannot bill 95940 with 95938. Cannot place both modifiers – TC/ -26 on claim. If billing for global services should bill unmodified. POS 11 is appropriate if provider is remote and billing 95941, must bill to the Blue plan where the monitoring provider is located. POS 21 or 22 is appropriate if the provider is present in the operating room. When billing POS 21 or 22, the claim must be filed to the Blue Plan where the facility is located. Please see the CPT professional edition manual for further coding explanation. Intravenous Analgesia (See “Anesthesia”) 104 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Itinerant Surgeon (See “Surgery, Proration”) Jail or Prison Benefits BCBSNE will allow for covered services provided to a member serving in a correctional facility if the services are not a result of the member’s engagement in an illegal occupation or his/her commission of or attempt to commit a felony. Jaundice (Neonatal) Jaundice is a medical condition common in newborns. The diagnosis of jaundice billed with medical procedures codes will be processed as medical. If the claim is received with a routine diagnosis for services that would normally be considered medical, the claim will be returned for verification of routine vs. medical. Claims received with a diagnosis of Neonatal Jaundice (Hyperbilirubinemia) will be denied as normal newborn services unless there is a special coverage endorsement for normal newborn services. Language Interpreter or Translation Services Charges for an interpreter or translator are considered content to service and not payable. Locum Tenens A Locum tenens (Latin: “holding the place,” i.e., “Placeholder”) is a person who is temporarily fulfilling the duties and responsibilities of a particular office in the absence of the appointed holder of that office. Often used for a physician who substitutes for another physician. When a locum tenens is used, services should be billed under the physician who is temporarily gone. Likewise, if a physician is serving as locum tenens for a midlevel practitioner, the services must be billed under the midlevel practitioner who is temporarily absent. The contracting status of the physician/practitioner under whose name the services are being billed will be used for claim payment. If the substitution lasts for more than ninety days, then the physician filling in should be credentialed. A locum tenens is not a new permanent physician or a physician going through credentialing. Mammography BCBSNE accepts the following codes when billing for a digital mammography: • • • G0202 G0204 G0206 The BCBSNE policy change will allow these codes to be accepted regardless of patient age. 105 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Code G0202 will deny incidental if billed with 77056 and 77057. Codes 77051, 77052 are set to pay with no incidentals. Codes 77056 and 77057 will deny as incidental if billed with G0202 or G0204. Massage Therapist Services provided by a massage therapist must be billed under his/her name, credentials, and NPI number. Massage Therapist who have not billed to BCBSNE previously should e-mail ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com to complete a Health Care Professional Questionnaire. Note: BCBSNE does not contract with Massage Therapists. Most BCBSNE member contracts do not cover services by a Massage Therapists. Benefits should be verified prior to providing services. Maternity Claims (See “Obstetrical Services”) Medical Necessity BCBSNE, or the applicable Blue Plan, will determine whether services are Medically Necessary. Services will not automatically be considered Medically Necessary because they have been ordered or provided by a Provider. Medically Necessary or Medical Necessity is defined as: Health Care Services ordered by a Treating Physician exercising prudent clinical judgment, provided to a Covered Person for the purposes of prevention, evaluation, diagnosis or treatment of that Covered Person’s Illness, Injury or Pregnancy that are: 1. Consistent with the prevailing professionally recognized standards of medical practice; and, known to be effective in improving health care outcomes for the condition for which it is recommended or prescribed. Effectiveness will be determined by validation based upon scientific evidence, professional standards and consideration of expert opinion, and; 2. Clinically appropriate in terms of type, frequency, extent, site and duration for the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of the Covered Person’s Illness, Injury or Pregnancy. The most appropriate setting and the most appropriate level of Service is that setting and that level of Service, considering the potential benefits and harms to the patient. When this test is applied to the care of an Inpatient, the Covered Person’s medical symptoms and conditions must require that treatment cannot be safely provided in a less intensive medical setting, and; 106 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 3. Not more costly than alternative interventions, including no intervention, and are at least as likely to produce equivalent therapeutic or diagnostic results as to the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of the patient’s Illness, Injury or Pregnancy, without adversely affecting the Covered Person’s medical condition; and 4. Not provided primarily for the convenience of the following; a. the Covered Person; b. the Physician; c. the Covered Person’s family d. any other person or health care provider; and 5. Not considered unnecessarily repetitive when performed in combination with other prevention, evaluation, diagnoses or treatment procedures. Medical Records (See also “Documentation”) Any additional information which is reasonably necessary to determine benefits and to verify performance under the Provider’s Agreement shall be provided without charge and in a timely manner. Note: If a member is applying for coverage (not already covered) and medical records are requested, providers can charge the member for sending medical records to BCBSNE. Medical/Surgical Supplies When provided in physician’s office are considered content of service and not separately reimbursed. Medicare and Federal Employee Program (FEP) Please see “Federal Employee Program (FEP) and Medicare. Midlevel Providers Physician Assistants (PA), Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRN) and Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMW) need to contract individually with Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska. Services by a PA, APRN and CNMW must be billed under the midlevel’s name and rendering NPI. A PA or APRN may bill for surgical assist. Surgical assists by a PA or APRN should be billed with an – AS modifier. Effective with admissions April 1, 2011, and after, inpatient services performed by an APRN who is a salaried employee of the hospital will be eligible for professional claim submission. The BCBSNE policy pertaining to billable services by an APRN has been revised as follows: “Healthcare services performed by a duly licensed APRN who is a salaried employee of a licensed healthcare facility, hospital, or clinic, may be submitted as a professional claim, provided the 107 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents registered nurse meets the requirements established in Neb. Rev. Stat. 71-1722 and performs services in collaboration and consultation with physicians as evidenced by an Integrated Practice Agreement on file with the State of Nebraska.” For Mental Health Providers, please refer to Section 14 of this manual for additional information. Mist Therapy Mist therapy for wound care should be billed under 97602. Charges billed under this code will be denied as content of service. Moderate Sedation Beginning with dates of service January 1, 2012, BCBSNE will allow 99143 and 99144 when billed with a CPT code not listed in the CMS Appendix G guidelines on moderate sedation: http://www.cms.gov/transmittals/downloads/R1324CP.pdf Modifier -AS Physician Assistants, Advanced Practice Registered Nurses and Certified Nurse Midwives are to use the “AS” modifier when billing for assistant surgery. Physicians should continue to use the “80” modifier. Claims will be returned if the appropriate modifier is not used. Modifier - RR or NU Modifier - HME Equipment - Required The following list of HCPCS codes require an RR (Rental) or NU (Purchase) modifier or they will be returned for proper coding. A4000 - A8999 A9270 - A9300 A9900 - A9999 B4000 - B9999 E0100 - E9999 K0001 - K9999 L0000 - L8699 S8096 - S8490 S8999 - S9015 V2624 V2625 V2626 V2628 V2700 HME rental (RR) will require a beginning and ending date. Purchase items should be billed with dispense date and not with a date span. Note: Prebilling for HME/DME rental is not permitted. Only purchased items may be billed at the time of delivery/pick-up. 108 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents If multiple modifiers are used the RR or NU modifier must be in the first position. If more than one item is dispensed each item would need to be billed on a separate line. Example: L3090 NU RT L3090 NU LT NOTE: Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASC’s) are required to always bill implant codes (ex. L8699) with an NU modifier. Modifier -21 Modifier -21 indicates prolonged E/M services. No additional reimbursement is available when a CPT code is billed with this modifier. Modifier -22 Modifier-22 indicates unusual procedural services. When the service(s) provided is greater than that usually required for the listed procedure, it may be identified by adding Modifier-22 to the usual procedure code. Claims submitted with Modifier-22 and an operative report and/or appropriate documentation will be reviewed for special consideration. Modifiers -25 and -26 In order to bill an office visit in conjunction with the immunization and administration codes, the service provided must be separately identifiable and documented in the medical records. You must append the -25 modifier to an E & M code. It is improper billing to submit charges for the E &M on a separate claim from the immunization and administrative codes when the services have been provided on the same date of service. Modifier 25 and Modifier 26 are invalid for surgery procedures (CPT codes 10000-69999). Claims with either modifier on a surgery code(s) billed to Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska will be returned. Modifier -52 Modifier -52 should be appended to denote a reduced service. The allowance will be reduced by 20% when modifier -52 is submitted. Modifier -53 Modifier -53 is used to denote when a surgical or diagnostic procedure was started but discontinued. Pricing will be reduced by 20% when a service is discontinued. Modifier -76 Modifier -76 indicates repeat procedure by same physician. 109 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Modifier -81 Modifier 81 is used to indicate an assistant surgeon who provides services that are less extensive than those described by modifier -80. This modifier should not be used to report non-physician service assistance during a surgical procedure. Motor and/or Sensory Nerve Conduction Test BCBSNE does not consider CPT procedure code 95905 Motor and/or sensory nerve conduction as a medically necessary alternative to the electrophysiological nerve conduction study combined with needle electromyography. Claims billed with 95905 will be reviewed for medical necessity. BCBSNE strongly recommends submitting a preauthorization for 95905. Multiple Claims Pages If you are submitting a paper claim with more than one page, leave the Total Charges field blank until the last page. The total charge on the last page should tally the charges for all pages. Multiple “Pay-to” Locations BCBSNE does not separate out payments for multiple office locations that share the same tax identification number. Nerve Blocks (See “Anesthesia”) Neurofeedback Effective March 20, 2013, BCBSNE will consider neurofeedback as investigative and will no longer provide benefits for this service. NEtwork BLUE providers should notify members undergoing neurofeedback therapy prior to 3.20.13 that this service will be their liability for dates of service 3.20.13 and after. Neurofeedback is not the same as biofeedback and should not be billed under the biofeedback codes. If the only service provided is neurofeedback, you should bill 90899 and include the neurofeedback in the comments/remarks section. If neurofeedback and psychotherapy are provided during the same visit, you should bill 90899 and include neurofeedback and psychotherapy in the comments/remarks section. Noncovered Services If a BCBS member requests a claim be filed for a noncovered service, the provider must file the claim. Nutritional Therapist Medical Nutritional Therapists who have not billed to BCBSNE previously should e-mail ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com to complete a Health Care Professional Questionnaire. BCBSNE does not contract with Medical Nutritional Therapists. 110 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Most BCBSNE member contracts do not cover services by Medical Nutritional Therapists. Benefits should be verified prior to providing services. Obstetrical Anesthesia (See “Anesthesia”) Obstetrical Services Guidelines “Obstetrical Guidelines” include: • Definitions • Diagnosis Codes • Obstetrical Complications: - External Cephalic Version - In Hospital Treatment of Complications - Multiple Deliveries - Procedure Codes Global vs. Non-Global Services - Partial OB Care - Total OB Care The services normally provided in uncomplicated maternity cases include antepartum care, delivery, and postpartum care. Antepartum care includes the initial and subsequent history, physical examinations, recording of weight, blood pressures, fetal heart tones, routine chemical urinalysis, and related office visits. Delivery services include admission to the hospital, the admission history and physical examination, management of uncomplicated labor, and vaginal/ cesarean delivery. Postpartum care includes hospital and office visits following vaginal/ cesarean delivery. Definitions Abortion Antepartum E and M EDD The termination of pregnancy - spontaneous or induced Before the onset of labor; also known as prenatal Evaluation and Management Expected Delivery Date (can be determined by using the maternity wheel with the LMP date) Gestation Period of fetal development in the womb LMP Last menstrual period Miscarriage Spontaneous abortion; referring to the interruption of Pregnancy Postpartum Occurring after childbirth; also known as postnatal Diagnosis Codes: V22 - Normal pregnancy V23 - Supervision of high risk pregnancy V24 - Postpartum care 630-667 - Pregnancy 111 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Procedures Codes: 59400, 59510, Total OB Care (antepartum, delivery, and postpartum) 59610, 59618 59425, 59426 Antepartum Only 59409, 59514, Delivery Only 59612, 59620 59430 Postpartum Only 59410, 59515 Delivery and Postpartum 59614, 59622 Global vs. Non-Global Service: Global maternity services include antepartum care, delivery, and postpartum care. The total global service is submitted after delivery with the delivery date as the date of service. Non-global maternity services are payable as separate services outside of the total global service. Non-global maternity services include: 59000-59051 59100-59160 59200 59412 59525 59812-59857 59866 59870 59871 7XXXX.....................Ultrasounds and X-Rays 8XXXX.....................Lab Charges 99241-99245.............Consultations 36415/G0001............Venipuncture Initial OB Visit Consistent with American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommendations, BCBSNE considers the “Initial OB visit” the visit when the OB (prenatal/antepartum) record is begun and therefore part of “Global OB care” (CPT codes 59400, 59510, 59610, or 59618) typically billed with a diagnosis code of V22.0 or V 22.1 (unless the pregnancy is high-risk in which case a V22.X would be used). Any earlier visit where the diagnosis of pregnancy was made with a urine or serum pregnancy test (CPT codes 81025, 84702, 84703) would be expected to be billed with the appropriate E and M code and diagnosis code V72.42. Obstetrical Complications For complex obstetrical patients with frequent antepartum visits or a complicated delivery, bill the appropriate procedure code with a modifier-22 and include medical rationale (example: repair to a third or fourth degree perineal tear that occurs during delivery). Your claim will be reviewed to determine if extra reimbursement is warranted. 112 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Services such as hemorrhage, hypertension, pre-eclampsia, infections, diabetes, etc., are not considered part of the global maternity services. Those services must be billed using the appropriate E and M code(s) and not the antepartum visit code. Standby Services (CPT 99360) Standby services during a C-section are not payable unless the standby physician actually performs some service/procedure during the delivery. The specific services/procedures performed should be billed rather than using the standby code. Standby services (CPT 99360) are a contract exclusion for BCBSNE and will be denied as member liability. If services are being rendered in a facility which requires “stand by” (for example “at time of delivery”), the member should be advised by the facility and/or the physician that this charge will be their liability. Newborn Delivery and Initial Stabilization (CPT 99464) Attendance at delivery and initial stabilization of newborn (CPT 99464) should not be billed to BCBSNE unless medically necessary. If documentation substantiates the medical necessity for 99464, the charges will be payable. If the claim is denied as not medically necessary, the claim will be provider liability. External Cephalic Version The reimbursement for total obstetric care does not include medically necessary external cephalic versions when performed after the 34th week of pregnancy. Reimbursement is limited to no more than two external cephalic version procedures during any one pregnancy. In-Hospital Treatment of Complications When hospitalization is required for severe complications during either the antepartum or postpartum period, in-hospital medical care fees may be made for the management of the condition. Payment will be subject to medical necessity review of medical records which support the additional care and direct attendance. Multiple Deliveries If both twins are delivered vaginally, the provider should bill 59400 for Twin A and 59409-51 for Twin B. For dates of service beginning January 1, 2014, BCBSNE will consider additional reimbursement for twin birth by Caesarian. Claims submitted with 59510, 59514 or 59515 and modifier 22 and an operative report and/or appropriate documentation will be reviewed for special consideration. Claims submitted with Modifier-22 and an operative report and/or appropriate documentation will be reviewed for special consideration. If one twin is delivered vaginally and one twin is delivered via cesarean, bill 59510 for Twin B and 59409-51 for Twin A. 113 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Partial OB Care In those instances where it is inappropriate to bill global OB care (i.e., transfer of care, coverage termination mid-term of the pregnancy, spontaneous abortion situations), the antepartum care should be billed using the applicable CPT code as follows: 1-3 visits: Bill the appropriate E and M code for each visit separately. 4-6 visits: Bill 59425 on one line. 7 or more visits: Bill 59426 on one line. When billing 59425 or 59426, the beginning and ending date of the antepartum visits the “FROM and TO” Dates of Service must be reported as the first date the patient was seen for antepartum care. As an example, if the first antepartum visit was on May 15, you would put May 15 in both the FROM and TO DATES in Box 24A of the CMS (CMS 1500 claim form. Box 24 G should always have a unit value of “1.” If a patient is transferred permanently from one physician to another, the initial physician should bill for the prenatal care provided prior to the delivery using the Partial OB billing guidelines. The claim must clearly indicate a transfer of the patient to another physician. On a paper claim, note the transfer below the last item charge. For electronic filers, note the transfer in the available narrative field. Please indicate the name of the physician who will be assuming care for the patient. If the transfer of care is between physicians or mid-level providers under the same tax ID number (regardless of location or specialty), we will accept only one claim for the total OB care. It is not permitted for an OB provider to bill total OB care when a provider under another tax ID provides partial OB services to the patient. If a physician under a different tax ID than the primary OB renders services (ex. delivery only) that provider must bill separately his or her services according to partial OB billing guidelines. If an OB provider changes tax ID’s (e.g. transfers to another clinic) and continues to see a patient who was seen under the previous tax ID, transfer of care guidelines apply. Postoperative Pain Control Continuous infusion of anesthetic agents to operative wound sites using an elastomeric pump is scientifically validated as a technique for postoperative pain control for surgeries typically requiring oral or parenteral narcotics for pain relief. Trade names of elastomeric pump and associate catheters that have received approval for marketing from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), include, but are not limited to, Infusor SystemTM, On-Q® Post Op Pain Relief System, On-Q SoakerTM catheter delivery system, and the Pain BusterTM Pain Management System. While the charge for the elastomeric pump may be covered, the insertion will be denied as global to the surgery. The insertion charge should be billed under 49999. 114 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Total OB Care If total OB care is provided, the claim with charges for total OB care must not be submitted for payment until after the patient delivers. If any portion of the total OB care (with the exception of non-global maternity services) is billed separately, the claim will be rejected to be submitted after delivery. The date of service should be the date of delivery. Occupational Therapy (See “Therapy”) Outreach Clinic/Specialty Care Billing POS 11 vs. POS 22 When physician services are rendered from an outpatient hospital department or another hospital-based entity (other than rural health clinics), use Place of Service 22. Physicians will use POS code 11 (office) when services are performed in a separately maintained physician office space in the hospital or on hospital campus and that physician office space is not considered a provider-based department of the hospital. The patient medical record, scheduling, and registration must be through the physician’s office and not considered part of the hospital record. Oximetry Regardless of what other charges are billed, pulse oximetry (94760-94762) will be denied as content of service. Pachymetry Charges for corneal pachymetry will be denied as content to the office visit. If a provider chooses to bill for this service and the procedure is done bilaterally, bill it unmodified. If done unilaterally, the charge should be reduced and the code 76514 should be billed with a modifier-52. The unit value is always “1” whether the procedure is done unilaterally or bilaterally. Pap Smears Our allowed amounts for CPT Codes 88150-88155 have been calculated to include payment for collection and handling costs. Any billing of CPT Code 99000 will be denied as “content of service.” Coverage under a member’s contract for “pap smears” does not always include coverage for the routine exam. It is recommended you verify the member’s benefits. Pathology The usual fee for pathology is generally considered to include the costs of equipment and supplies used in performing a test or examination as well as the performance of the test and the professional evaluation and report. 115 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents For hospital-based physicians, the usual professional fee is expected to represent just the charge for examination and opinion of laboratory specimens (collected at the expense of a facility or institution) that require a pathologist for interpretation. Payment for these professional interpretations is generally considered to be available only for anatomical tests. When all-inclusive codes exist for multiple component tests, the all-inclusive code must be used. Modifier 76 should be used when billing a pathology code more than one time by the same physician on the same date of service. The collection and or handling fee of a specimen is considered content of service to the laboratory/surgical procedure and/or the level of service being performed, regardless of whether the physician bills for the laboratory tests or if the specimen is sent to an outside laboratory. Specimen collection and handling codes deny as content to service, regardless if billed alone or with other charges, and include 36591, 36592 and 99000-99002. Venipuncture CPT 36415 may be separately billed and reimbursed. Pharmacy In 2011, the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association mandated Plan compliance with the handling and processing of Specialty Pharmacy claims. Pharmacies must file their claim to the Plan in whose state the member resides. Note: Home Infusion providers who have an HME contract to bill for home infusion administration and supplies should file their claim according to the DME/HME billing guidelines. Physical Therapy (See “Therapy”) Physical Presence Physical presence means you have a brick and mortar location, which has to be a street location, not a P.O. Box. Physician Attendance Attendance/standby services are not covered. If a physician performs a service, the specific CPT code that describes the service should be billed. Place of Service (POS) 20 Urgent care facilities are required to bill POS 20 and not POS 11 Clinic. Place of Service (POS) 99 Place of Service 99 is not valid. If services are provided in patient’s home, use place of service 12. Professional and Institutional Claims for the Same Day 116 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents When professional and institutional services are billed on the same day for the same patient, the procedure codes and diagnosis codes must match. If the codes do not match, claims will be returned to seek clarification. It is important that professional and institutional billers communicate prior to submitting claims and will expedite claim processing. Prolonged Physician Service (Codes 99358-99359) Prolonged Physician Service without face-to-face patient contact are considered “content of service” and therefore, not separately reimbursable. Proration (See “Surgery, Proration”) Provider ID Numbers BCBSNE no longer issues Legacy provider ID numbers. Any clearinghouse or vendor enrollment forms or software setup procedures that require a Provider PIN or ID number will need to be modified so it is not required by the provider. This number is not necessary for filing claims and as part of HIPAA guidelines, we will not accept any claim with a Legacy ID number. Only the tax ID and NPI numbers should be used when filing a claim. Psychiatric Psychiatric benefits and the certification of the health care professional who can provide them vary from one member/group contract to contract. Please contact Provider Service Department for information about a specific patient’s benefits. When verifying benefits with BCBSNE or any other BCBS Plan, you should ask about the member’s coverage and about any restrictions on the type of provider covered under the contract for these services. Non-Covered Services: Contract Exclusions and Limitations Payment will not be made for: • Programs of co-dependency • Family intervention • Intake or referral • Employee assistance • Probation • Prevention • Educational or self-help programs • Programs which treat obesity or gambling, except as mandated by the Affordable Care Act • Residential, halfway house or methadone maintenance programs, or • Programs ordered by the court which are not medically necessary as determined by BCBSNE Not Medically Necessary Benefits will not be provided for the following services which do not fit the criteria of medically necessary treatment: 117 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Services directed toward making one’s personality more forceful or dynamic • • • • • • Consciousness raising Vocational or religious counseling Group socialization Activities primarily of an educational nature Behavioral modification The following treatment modalities: - Primal therapy - Rolfing or structural integration - Bioenergetic therapy - Carbon dioxide therapy - Guided imagery - Z-therapy - Obesity control therapy, except as mandated by the Affordable Care Act - Training analysis - Sleep therapy - Sedac therapy - Dance therapy - Music therapy - Psychodrama Note: This is general information that applies to many of our group contracts. However, groups can and do request variations. Contact the Provider Service Department to determine a specific patient’s actual contract benefits and limitations. Pharmacologic Management Pharmacologic Management (90862) includes prescription, use, and review of medication with no more than minimal medical psychotherapy. When payable according to a patient’s coverage, we allow benefits for this procedure once per day. Pulmonary Rehabilitation Outpatient Pulmonary Rehabilitation must be preauthorized with BCBSNE. Benefits vary according to various member/group contracts. Contact the Provider Service Department for specific patient benefits. Because of the many benefit variations, preauthorization is required. The pulmonary rehabilitation program must be accredited by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations, or as otherwise approved by BCBSNE. Radiopharmaceutical (See “Contrast Media”) 118 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Radiology The usual fee for therapeutic radiology does not include: • Consultations regarding need for radiotherapy • Treatment planning • Concomitant surgical, diagnostic radiology or laboratory services If more than one of the same x-ray is taken of a location (e.g., because patient moved or film not clear) only one x-ray is considered payable and the others would be considered content of that service. If more than one physician “reads” an X-ray, only one will be paid. BCBSNE does not pay for “overreads.” When both professional (modifier-26) and technical (modifier-TC) components are included in the charge, the usual fee is considered to include the cost of materials and technical operation costs as well as the professional fee for the administration of diagnostic ultrasound/imaging and other high energy modalities. When the professional (modifier-26) component only is charged, the usual fee is considered to represent the charge for the administration of radiology and follow-up care as defined above. The charge for such services would be lower than if technical costs were included. Repeated Procedures on Same Day Modifier 50, -76 or -77 Charges should be billed out as separate lines when the same radiology procedure is repeated by the same or different doctor on the same day. Following is an example of how the charges should be submitted: 1st charge line: 71020-26 ............................................................... 1 unit 2nd charge line: 71020-26 76 ........................................................ 1 unit Rapid Flu Test CPT Codes: 87804 Infectious agent antigen detection by immunoassay with direct optical observations; influenza (CPT code 87804) is covered. For Influenza A and B, (two tests) code 87804 with 2 units. RAST Testing (See “Allergy”) Reduced Services For Network BLUE claims, use modifier -52 on a procedure code to reduce the allowance by 20%. Research Studies and/or Clinical Trials BCBSNE member contracts do not provide benefits for services for medical treatment and/or drugs, whether compensated or not, which are directly related to or resulting from the Covered Person’s participation in a voluntary, investigative test, or research program or study unless authorized in writing by BCBSNE. These services may be pre-authorized through our Medical Support 119 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Department. To preauthorize these services, please fax the informed consent document and specific information for evaluation to 402-392-4141 or 800-255-2838. Resident Students Patient services provided by a resident as part of their education and training are not billable by either the resident or their supervising physician. Risk Adjustment Under the Affordable Care Act, everyone will have access to health insurance irrespective of their health status. In order to try and create a system in which some payers and their networks of providers are compensated for the risk associated with the members they treat (known as risk adjusted payments), a complete and accurate capture of each individual patient’s health status through claims and encounter data is critical. MD’s need to code any chronic conditions from the patient’s medical record whether it had anything to do with that day’s visit or not. Robotic Assistance BCBSNE does not allow additional reimbursement for the use of the Da Vinci Robot or any other robotic surgical assistance. Routine vs. Medical Office visits should be coded: • • According to the information documented in the patient’s medical record for that visit, and To reflect the actual services provided and not the reason the visit was scheduled. If multiple services are provided, the primary diagnosis code for each line item should be reflected in Box 24E of the CMS 1500. Preventive Medicine CPT Codes Preventative Medicine CPT Codes (99381-99429) must be billed with a “routine” diagnosis code. Should a condition be discovered during a screening (e.g., polyps found during colon cancer screening), then code the condition as an additional diagnosis to the screening exam. If a patient has a medical diagnosis in their history that requires management or follow-up, bill that diagnosis on screenings and lab work rather than a routine/preventative diagnosis. Counseling and/or Risk Factor Reduction Intervention Counseling codes are denied according to our member contracts which exclude benefits for self-help or educational services. The only exception would be if the group has a special coverage endorsement for these services. 120 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Rural Health Clinics When BCBSNE is the primary payor, rural health clinics (RHC) must always file claims on a CMS 1500 claim form under the provider of service name, credentials and individual NPI with Place of Service 72 using standard BCBS billing guidelines. BCBSNE does not follow CMS’s incident-to-rules. When BCBSNE is the supplemental or secondary payor to CMS, you must include the attending provider’s name and NPI and the CPT and/or HCPCS codes identifying the services provided on the UB-04. The claims should automatically cross over to BCBSNE from Medicare and the RHC will be paid directly if the appropriate information is on the claim. RHCs should never submit Medicare supplemental/secondary claims on a CMS 1500. If you haven’t received payment after 30 days of the CMS paid date on your remit, you should check the claim status. If the claim has not crossed over from Medicare, you will need to submit a UB-04 claim with the EOMB for processing. School/Sports Physicals If a school or sports physical is scheduled and performed, the diagnosis should be coded V70.3 (Other Medical Examination for Administrative Purposes). Some Blues members do not have coverage for a school physical, but it should not be coded as a routine physical. School Place of Service (POS 03) BCBSNE member contracts no longer cover services provided in a school (Place of Service 03). Services will be considered member liability. Sclerotherapy (See “Varicose Veins”) Scope of Practice If a provider has questions if something is or is not within their scope of practice, they should check with the Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services, Professional and Occupational Licensure Regulations. Simple Catheterization of the Bladder Under sterile conditions, a catheter, either straight or Foley, is passed through the urethra into the bladder as ordered by a physician. The simple catheterization is considered part of the “global charge” in the 1) emergency room, 2) office visit, 3) inpatient room charge. Therefore, no additional reimbursement will be allowed. Sliding Fee Schedules BCBSNE providers must be consistent in the amount they charge for their services. If you utilize a sliding fee scale for your disadvantaged clients, you must also apply this sliding fee scale to your BCBS covered members and bill that amount to BCBSNE. 121 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Smoking Cessation When billing for smoking cessation classes or treatment, 99406 or 99407 should be used. For patients over age 65 use G0436 or G0437. If billed in concert with an E and M code, the smoking cessation will deny as inclusive. Specimen Collection and Handling Specimen collection and handling codes deny as content to service, regardless if billed alone or with other charges, and include 36591, 36592 and 99000-99002. Speech Therapy (See “Therapy”) Spider Veins Spider veins should be billed under 36468 and 36469 and are not a covered service. Sprains/Strains Not Accident-Related Sprain/Strain diagnosis codes require an accident date. If there is no accident date and the claim indicates that the sprain/strain was not due to an accident, it is appropriate to describe the symptom such as neuralgia, myalgia, swelling, cramping or pain. Diagnosis code 729 would be submitted to describe this condition. Standby (See “Physician Attendance”) Stat or After Hours Laboratory Charges These are charges submitted to perform laboratory procedures immediately or outside scheduled laboratory hours. Benefits in addition to those allowed for laboratory procedures are not covered when such are ordered to be performed “stat” or outside of the scheduled laboratory hours. Stat 1 Testing / Rapid Service Time Stat 1 testing/rapid service time charges are not covered. If rapid service time is submitted, the charge will be denied as “content of service.” Subrogation If a covered benefit involves claims that are a result of an accident or illness caused by a third party, you must file a claim including accident information to BCBSNE. We will provide benefits according to the member’s contract and supply payment to the provider of service pursuant to our agreement with them. Our Subrogation Department will begin the necessary procedures to recover paid amounts from the covered person or third party payer, which will not exceed the amount we paid in benefits. If you are notified of an injury or accident after filing claims to BCBSNE and have not included the accident information on the claim, you should notify our Subrogation Department immediately. 122 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Supplies - RR or NU Modifier - Required Charges for medical and surgical supplies when used in the physician’s office are considered to be included as “total service charges” (content of service) for all BCBSNE lines of business. Charges denied as content of service are not separately reimbursed and are not billable to the patient. If supplies must be billed, use the appropriate HCPCS code and not CPT code 99070. (i.e., cast protectors, heel caps, etc. would be billed with A4649 with make, model, and manufacturer or attach a cost invoice). If a patient is given medical equipment and supplies (listed below) to be used in their home, Place of Service 12 (Home) should be used. The following list of HCPCS codes must have an RR (Rental) or NU (Purchase) modifier or they will be returned for proper coding. Also, HME rental (RR) will require a beginning and ending date. Note: Prebilling for HME/DME rental is not permitted. Only purchased items may be billed at the time of delivery/pick-up. If multiple modifiers are used, the RR or NU modifier must be in the first position. If more than one item is dispensed each item would need to be billed on a separate line. Example: L3090 NU RT L3090 NU LT A4000 - A8999 A9270 - A9300 A9900 - A9999 B4000 - B9999 E0100 - E9999 K0001 - K9999 L0000 - L8699 S8096 - S8490 S8999 - S9015 V2624 V2625 V2626 V2628 V2700 Surgery Guidelines “Surgery Guidelines” include: • Assistant surgery • Assistant surgery and postoperative care 123 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Assistant surgery and preoperative care Assistant-multiple assistants during surgery Bilateral surgeries Co-surgery Iatrogenic surgery Major surgical procedures Minor surgical procedures Multiple surgeries - one surgeon Postoperative care only Preoperative care only Surgical care only Surgical proration Surgical team Surgical Guidelines Chart Assistant Surgery NOTE: Effective December 1, 2011, BCBSNE began following CMS’ Post- Op and Assistant Surgery Policy. This policy, updated annually in November, can currently be found online at www.cms.gov. CPT codes with an indicator of 2 allow an assistant. CPT codes with indicators 0, 1, and 9 in the assistant surgery column do not allow payment for assistant surgeon. If the CMS indicator is 0 and the service is denied, you may submit an appeal along with the appropriate medical record documentation and the claim will be reviewed. If two like procedures are performed, you must submit each procedure on a separate line with a unit of one. Modifier-80 and -AS Assistant surgery is considered only when the physician actively assists the operating physician at the operating table; being available or standing by to assist does not constitute assistant surgery. Effective August 1, 2009, Physician Assistants, Advanced Practice Registered Nurses and Certified Nurse Midwives are to use the “AS” modifier when billing for assistant surgery. Physicians should continue to use the “80” modifier. Claims will be returned for proper coding received after August 1, 2009. Modifier 81, Minimum Assistant Surgeon Modifier 81 should be used to indicate an assistant surgeon who provides services that are less extensive than those described by modifier -80. This modifier should not be used to report non-physician service assistance during a surgical procedure. This modifier should not be used to report surgical assistance by a Registered Nurse First Assist. Benefits are not payable for surgical assistance by a Registered Nurse First Assist. The amount payable for covered surgical assistance by a physician will not exceed 20% of the physician fee schedule for the surgery. If the assist is performed by a midlevel practitioner, an additional 15% differential will apply. 124 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents When assistant surgeon charges are billed for a procedure that does not require or allow an assist, the denial will be provider liability. Assistant Surgery and Postoperative Care When surgery only is performed by a surgeon, and the assistant surgeon provides surgical assistance and postoperative care, charges for the postoperative care may be allowable in addition to the assistant surgery charge as follows: • • Bill the surgical CPT code and modifier-80 with the charge for assistant surgery, and Bill the surgical CPT code and modifier-55 with the charge for postoperative management Assistant Surgery and Preoperative Care When surgery only is performed by a surgeon, and the assistant surgeon provides surgical assistance and preoperative care, charges for the preoperative care may be allowable in addition to the assistant surgery charge as follows: • Bill the surgical CPT code and modifier-80 with the charge for assistant surgery, and bill the preoperative care as follows: - E and M code with actual date of care - Modifiers may or may not be applicable - No modifier if one of the modifiers below are not applicable: -25 modifier is applicable if a separately identifiable E and M service performed on same day of surgery by same physician (surgeon or assistant surgeon) -57 modifier is applicable if E and M visit on the same day of surgery resulted in initial decision for surgery Assistant-Multiple Assistants During Surgery The use of more than one assistant surgeon is subject to individual consideration and covered only upon substantiation of medical necessity. Participating physicians agree to accept our medical director’s decision in such cases. Bilateral Surgeries Modifier -50 A breakdown for each side is required when reporting bilateral surgery. The first side should be submitted unmodified and with a charge for the first side. The second side should be submitted with modifier -50 and a charge for the second side. Co-Surgery Modifier-62 Under certain circumstances, the skills of two surgeons (with different skills) may be required in the management of a specific surgical procedure: • The procedure can generally be described by one procedure code and therefore both surgeons must use the same procedure code with modifier -62 to identify co-surgery. 125 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • Surgeons may indicate the percentage of split; however, if there is no indication on the claim, we will apply 60% and 40% (+20% if the second surgeon also assisted). Our liability will not exceed 100 percent of the maximum benefit amount plus 20 percent of the maximum benefit amount if the procedure allows an assistant surgeon. Iatrogenic Surgery No additional charge should be made for surgery for any adverse condition in a patient occurring as the result of a treatment by a physician or surgeon. Major Surgical Procedures Major surgical procedures have either a ten (10) or ninety (90) day post-operative period. Minor Surgical Procedures • Proration guidelines do not apply • Bill Surgical CPT code with no modifier • Date of service is the date of surgery • Appropriate E and M codes applicable when seen one day before, on the same day, or following surgery Multiple Surgeries - One Surgeon Modifier-51 For claims with dates of service July 1, 2013 and after, the procedure with the highest RBRVS value will be considered the main procedure regardless of the charges. If two procedures are submitted and both have the same weight, you must submit the code with the highest charge on the first line item. When BCBSNE is secondary to Medicare and multiple surgery pricing has been applied prior to the claim crossing over to BCBSNE, we will use highest profile amount payable on the secondary claim. Effective for dates of service beginning August 1, 2012, providers who bill CPT codes that are subject to the multiple procedure guidelines as established by CMS may submit multiple units of one surgical CPT code as separate line items or may bill as one line item with the appropriate number of units. Include modifier -51 as appropriate. Multiple surgery reductions will not be applied in the following situations: When the procedure is an add-on code and cannot be billed alone: Example: 17000 = one lesion, 17003 = second through fourteen lesions (each) 17003 would not be subject to multiple surgery rules When the procedure is a minor diagnostic procedure: Example: 29870 - Diagnostic knee arthroscopy. When two (or more) surgical procedures are performed on the same date or during the same hospitalization, if multiple surgery guidelines apply to one procedure, but not to the other procedure. 126 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents When the procedure is a modifier-51 exempt code: Example: 20900 - Bone graft, any donor area; minor or small (e.g. dowel or button). When multiple surgery rules do apply, the procedure with the highest RBRVS value will be reimbursed at 100% of the contracted rate or billed charge, whichever is less. All remaining covered procedures will be priced at the lesser of 50% of the contracted rate or billed charge. Post-Operative Care If a provider other than the surgeon manages post-operative care only, their claim must be billed with the surgical procedure code, the -55 modifier, and the date of surgery as the date of service. In order for post-operative care only to be payable, the surgeon would need to bill their claim with modifier -54. When billing for post-operative care, the place of service (POS) used should be the POS where the surgery was performed. For example, surgery was done in an ASC, postoperative visits were done in the physician’s office. The POS used would be 24 for ASC. Reimbursement for the post-operative care only will be at the lesser of the charge or 10% of the contracted rate of the surgical procedure. Unrelated Post-Operative Care: If the surgeon or assistant surgeon sees the patient for an unrelated E and M service during the postoperative period, include a -24 modifier with the E and M service. The appropriate documentation of this circumstance must be present in the patient’s medical record. Postoperative Pain Control Continuous infusion of anesthetic agents to operative wound sites using an elastomeric pump is scientifically validated as a technique for postoperative pain control for surgeries typically requiring oral or parenteral narcotics for pain relief. Trade names of elastomeric pump and associate catheters that have received approval for marketing from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), include, but are not limited to, Infusor SystemTM, On-Q® Post Op Pain Relief System, On-Q SoakerTM catheter delivery system, and the Pain BusterTM Pain Management System. While the charge for the elastomeric pump may be covered, the insertion will be denied as global to the surgery. The insertion charge should be billed under 49999. Preoperative Care: Bill the E&M code with the actual date of care. Modifiers may or may not be applicable. No modifier if one of the modifiers below are not applicable: 127 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents (NOTE: Preoperative Management Only should be billed with the appropriate E and M code and without modifier -56) -25 modifier is applicable if a separately identifiable E and M service performed on same day of surgery by same physician (surgeon or assistant surgeon). Modifier -25 is not valid on a surgery (10000-69999) CPT. -57 modifier is applicable if E and M visit resulted in initial decision for surgery. Pre-Operative Services performed by surgeon - Day before or same day of surgery. When billing for pre-operative services on the day before or same day of surgery, bill one of the following: • E&M service with a -25 modifier if the visit is a separately identifiable E and M service on the same day of the procedure or surgery. • E&M service with a -57 modifier if the visit resulted in the initial decision for surgery. Surgical Care Only Use the Surgical CPT code with -54 modifier to report surgical care only. We reimburse the lesser of the charge or 90% of the contracted rate to the surgeon for surgical care only. Date of service is the date of surgery. Surgical Proration Proration is a method of allocating the total contracted rate for a major surgical procedure and office/outpatient/inpatient care to more than one physician. Proration of services only applies to major surgery and visits. (Proration does not apply to obstetric services. For billing of obstetric services performed by more than one physician, see “Obstetrical Services, Billing for Partial OB Care.”) Surgical Team Modifier-66 A highly complex procedure requiring the concomitant services of several physicians, often of different specialties, plus other highly skilled, specially trained personnel and various types of complex equipment (e.g. patient requiring surgical correction of an ankle fracture by an orthopedic surgeon, treatment of a head injury by a neurosurgeon and complex laceration repair by a plastic surgeon all operating in the same surgical suite) is described with modifier-66: • • Each physician’s claim should be submitted with modifier-66 indicating team surgery. Because each surgeon is operating independently, benefits would be determined as if they were separate operative sessions. Surgical Standby (See “Physician Attendance”) Surgical Trays in the Office 128 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Surgical trays are considered “content of service” and therefore not separately reimbursed and are not billable to the patient. Telemedicine/Telehealth Telemedicine is the use of interactive video equipment to link practitioners and patients in different sites. Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska benefit contracts will be enhanced to provide for both the distant provider’s professional services and the facilities fee charged by the provider where the patient was physically located (originating site). Policy/Criteria BCBSNE will reimburse Nebraska network providers for telemedicine/telehealth when all of the following conditions are met: 1) Actual visual contact (face-to-face) is maintained between the distant provider and the patient; 2) billed services are for interactive, real-time communication; 3) the patient is present and participating in the visit; 4) the services are within the provider’s scope of practice as defined by state law; 5) services are medically appropriate and necessary; 6) documentation to support the services is included in the clinical record; 7) both providers must be BlueCard® participating providers in the continental United States; and 8) a designated room with appropriate equipment, including cameras, lighting, transmission and other needed electronics and the appropriate medical office amenities, is established in both the Originating and Distant Sites. NOTE: Using Skype or any other Internet programs is not permissible and is not a covered benefit. Reimbursement will be for services covered under BCBSNE’s member benefit contracts.. This benefit policy applies to BCBSNE members only and excludes any FEP or out-of-state Blue Cross and Blue Shield members. Reimbursement Exclusions: Provider-to-provider consultations, video conferencing, telephone conversations, facsimile or e-mail communications will not be reimbursed (stored and transmitted data does not qualify for telemedicine/telehealth benefits). There will be no additional reimbursement for equipment, technicians or other technology or personnel utilized in the performance of the telemedicine/telehealth service. Inpatient services. Medical interpretation or translation services. Covered Services: Professional office or outpatient services such as Evaluation and Management services, psychiatric diagnostic interview and individual psychotherapy services that are related to psychiatric treatment 129 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents and are listed in the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) of the American Medical Association. Only those services currently covered in an office or outpatient setting will be allowed for payment. Reimbursement will be based on the current fee schedule in place at the time services are rendered. NOTE: Professional Services should always be billed on a CMS 1500 under the actual provider of service and their NPI. The covered CPT Codes are: • Office and Outpatient visits (99201-99215) • Psychiatric Diagnostic Interview (90791) • Individual Psychotherapy Services (90832-90839) • Pharmacologic Management (90863 or the appropriate E & M code) Benefits will be provided to the originating facility when HCPCS Q3014 (telehealth originating site facility fee) is billed. Only the Originating Site will receive payment for the facility fee. The allowable is $24. NOTE: Telehealth originating site facility fee can be billed on a UB 04 or CMS 1500. BCBSNE will only accept one claim per encounter for the Telehealth originating site facility fee. Definitions: Originating Site means the location of an eligible member at the time the service is being provided via a telecommunications system. Originating site includes hospital outpatient department, critical access hospital outpatient department, federally qualified health centers, rural health clinics, physician and practitioner offices. Distant Site means the site where the provider rendering the professional service is located. All conditions of reimbursement are subject to audit by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska. Additionally, an onsite visit may be made to the originating telemedicine/telehealth facility to address quality issues. Coding/Billing Information When billing for the Telehealth Origination Site facility fee on a UB 04, please follow these guidelines: FL4 - Bill Type 131 FL42 - Revenue Code 780 FL44 HCPCS Code Q3014 FL46 Units 1 FL51 Acute care hospital NPI When billing for the Telehealth Origination Site facility fee on a CMS 1500, please follow these guidelines: • HCPCS Code Q3014 in Box 24D 130 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • Units of 1 in Box 24G Box 31 must include the last name, first name and credentials of the health care professional whose office was used as the originating site. • The NPI number of the health care professional is required in Box 24J. Exception: for solo practice providers, or providers who do not have a Type II NPI, you may instead include your Type I NPI in Box 33A. When billing for the professional service that is provided via Telehealth, please follow standard billing practices on a CMS 1500. Telephone Consultations Between Patient and Provider: To qualify as a professional service, actual visual contact (face to face) must be maintained between physician and patient. CPT codes 99441-99443 will be denied as “member liability.” Member contracts specifically exclude benefits for telephone consultations between patient and physician. Between Provider and Provider: No Provider to Provider telephone consultations will be reimbursed. Telepsychiatry (Please see Telemedicine) Therapy (Physical, Occupational and Speech) The number of covered therapy sessions per calendar year can vary depending on the member’s benefit contract. Ongoing preventative/maintenance therapy is not a covered benefit once the maximum therapeutic benefit has been achieved for a given condition and continued supportive therapy no longer results in some functional or restorative improvement. A session is defined as one visit. Therapies must be medically necessary. Physical Therapy Outpatient and/or home physical therapy session must be provided by a Licensed Physical Therapist or Licensed Physical Therapist Assistant. To be an approved provider, the Licensed Physical Therapist Assistant must be assigned to, supervised, and billed for, by a Licensed Physical Therapist. Physical therapy must be ordered or prescribed by a Physician. Multiple modalities on the same day count as one visit. If a physical therapist is providing services at a clinic primarily run by medical doctors, the physical therapist must still bill under their own NPI. Physical Performance Test or Measurement (97750) should be billed in unit increments of 15 minutes (1 unit =15 minutes) 131 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Occupational Therapy Outpatient and/or home occupational therapy sessions must be provided by a Licensed Occupational Therapist or Licensed Occupational Therapist Assistant. To be an approved provider, the Licensed Occupational Therapist Assistant must be assigned to, supervised, and billed for, by a Licensed Occupational Therapist. Occupational therapy must be ordered or prescribed by a Physician. Multiple modalities on the same day count as one visit. Speech Therapy Outpatient and/or home session of speech therapy or Cognitive Training must be provided by a Licensed Speech-Language Pathologist or Registered Communication Assistant practicing under the supervision of a Licensed Speech-Language Pathologist. The Registered Communication Assistant must be assigned to, supervised, and billed for, by a Licensed Speech- Language Pathologist. Multiple modalities on the same day count as one visit. TENS When billing supplies for a TENS unit, use: E0270 TENS device two lead, localized stimulation E0730 TENS device four or more lead, for multiple nerve stimulation A4595 Wires and electrodes (2 leads per month) A4630 Replacement batteries for TENS A4557 Lead wires, per pair Third Party Providers BCBSNE will not separately reimburse third party providers rendering services including, but not limited to, monitoring or equipment in an inpatient/outpatient or Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) setting. These services or supplies are considered “Content of Service”. The purpose of the denial for Content of Service refers to specific services and/or procedures that are considered to be an integral part of a previous or concomitant services or procedures to the extent that separate reimbursement is not recognized. Examples and settings for Content of Service may include: • • • • Use of ASC facilities Patient preparation area, operating and recovery rooms, waiting rooms, and other areas used by the patient or offered for use by the patients relatives in connection with surgical services Nursing services, services of technical personnel and other related services. Services in connection with covered procedures furnished by nurses, technical personnel, and others who are employees of the ASC involved in patient care 132 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • Drug, biological, surgical dressings, supplies, splint, casts, orthopedic hardware, appliances and equipment All supplies and equipment commonly furnished by the ASC in connection with surgical procedures Anesthesia equipment and supplies Note: Some Content of Service issues related to specific services and/or procedures are identified throughout the Policies and Procedures document. If a third party provider is present and/or provides services or equipment based on physician’s or facility’s behest then payment to that provider will need to be coordinated between the two parties. A third party provider should never bill BCBSNE or the member for these services. Trauma Code Edits BCBSNE has identified specific diagnosis codes as trauma codes. When submitting a claim with a diagnosis code represented in the list below, additional information is needed to properly process the claim. UB 04: Form locators 32 (Occurrence Code and Date) and 77 (E-code) must be completed Because of space limitation, you may not have an E code for every trauma code, but there should be at least one E code on the claim if there are trauma codes listed on the UB 04. CMS 1500: Box 10 must be completed. Please keep in mind when the claim contains an accident date and indicator, the primary diagnosis code must be from the list below. Trauma Codes V01.5 V04.5 V15.5 V15.6 V67.4 V71.3 thru V71.6 071 692.6 692.71 thru 692.74 800.00 thru 994.99 995.50 thru 995.59 995.81 Traveling Surgeon When a surgeon travels to another city and provides surgery-only services, you should bill the Surgical CPT Code with a ‘-54’ modifier. 133 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Unlisted Procedure or Service Unlisted procedure codes have been designated to report services or procedures that are not found in the CPT manual. These codes usually end in the number 99. Do not bill an unlisted code if there is a designated CPT code available for the service provided. When billing an unlisted code, the claim must include a description of the service. Procedures represented by an unlisted CPT code should also include the appropriate medical records, such as an operative report, for review. If you are billing an unlisted code for equipment, supplies, orthotics/prosthetics, the claim cannot be reviewed without a cost invoice which indicates the make, model and manufacturer. A computer screen printout is not acceptable. If you are billing an unlisted code for a drug/biologic, you must provide the full NDC number on the claim. When filing electronically, the NDC number must be submitted in loop 2410 and in the following format: xxxxx-xxxx-xx. Varicose Veins Endovascular Laser Ablation Endovascular Laser Ablation of varicose veins should be billed using CPT codes 36475 and 36476. Sclerotherapy Sclerotherapy of varicose veins should be billed under CPT codes 36470 or 36471. Note: Spider veins should be billed under 36468 and 36469 and are not a covered service. 134 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 12 General Billing Guidelines – Hospital and Facility Ambulance Services Ambulance (Hospital-Based) Submit hospital-based helicopter, fixed wing and ground ambulance charges separately on a UB04 claim form with the appropriate Level II HCPCS Codes. Hospital-based providers shall bill BCBSNE directly for these services, regardless of patient destination. UB04 (ANSI 837I) claim format with a bill type of 13X, 14X. Revenue Code 542 can be billed with A0425, A0426, A0427, A0428, A0429. Revenue Code 545 can be billed with A0430, A0431, A0435, A0436. Charges shall include all fees for the aircraft, flight and transport crew, supplies, medications, oxygen and use of equipment. Revenue Code 546 can be billed with A0225. Revenue Code 541 can be billed with A0382, A0384, A0392, A0394, A0396, A0398. Revenue Code 544 can be billed with A0422. Revenue Code 547 can be billed with J3490. Summarize all medication charges under J3490. The ambulance mileage must be specific regarding distance and must contain a decimal when it is less than 100 miles. Report Mileage in Loop 2400 SV205 on the 837I or in Form Locator 46 on the UB04. FL 56 must include the hospital acute care NPI. All charges submitted under the following codes will be considered content to the transport service billed: A0382 BLS Disposable Supplies A0384 BLS specialized service disposable supplies; defibrillation A0422 ALS/BLS Oxygen and related supplies J3490 ALS Specialized Medications and IVs) A0396 ALS Specialized service disposable supplies; esophageal intubation A0392 ALS Specialized service disposable supplies etc. A0394 ALS Specialized service disposable supplies IV drug therapy A0398 ALS routine disposable supplies It is important to verify benefits for non-emergency transports (A0426 and A0428) prior to providing the service because benefits are not included in all BCBSNE member contracts. 135 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Non hospital-based A hospital may not bill charges from an ambulance provider for a patient brought to their facility. Ambulance providers shall bill BCBSNE directly for these services on the CMS 1500 claim form. CMS 1500 (837P) claim format Bill the most appropriate HCPC code: A0426 ALS Non-Emergency Transport, Level 1 A0427 ALS Emergency Transport, Level 1 A0428 BLS Non-Emergency Transport A0429 BLS Emergency Transport A0430 Fixed Wing Transport Charge shall include all fees for the aircraft, flight and transport crew, supplies, medications, oxygen and use of equipment. Include copy of the in-flight patient treatment record. A0431 Helicopter Transport Charge shall include all fees for the aircraft, flight and transport crew, supplies, medication, oxygen and use of equipment. Include a copy of the in-flight patient treatment record. A0432 Paramedic Intercept A0433 ALS Emergency Transport, Level 2 A0434 ALS Specialty Care Transport (Neonatal) A0435 Fixed Wing Transport. The number of loaded miles should be shown with this code number in form locator 24g. Round the miles to the nearest whole mile (anything greater than .5 of a mile should be rounded to the next whole mile). A0436 Helicopter Transport. The number of loaded miles should be shown with this code number in form locator 24g. Round the miles to the nearest whole mile (anything greater than .5 of a mile should be rounded to the next whole mile). All charges submitted under the following codes will be considered content to the transport service billed: A0382 BLS Supplies A0398 ALS Supplies A0422 ALS/BLS Oxygen and related supplies J3490 ALS Specialized Medications and IVs A0396 ALS Specialized service disposable supplies; esophageal intubation A0392 ALS Specialized service disposable supplies etc. A0394 ALS Specialized service disposable supplies IV drug therapy A0398 ALS routine disposable supplies It is important to verify benefits for non-emergency transports (A0426 and A0428) prior to providing the service because benefits are not included in all BCBSNE member contracts. 136 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Summary of Instructions for CMS 1500 billers: The appropriate alpha modifiers that denote Pick Up and Destination are required. D – Diagnostic or therapeutic site other than “P” or “H” when these are used as origin codes E – Residential, domiciliary, custodial facility (other than 1819 facility) G – Hospital-based ESRD facility H – HospitaI – Site of transfer (e.g. airport or helicopter pad) between modes of ambulance transport J – Free-standing ESRD facility N – Skilled nursing facility (SNF) P – Physician’s Office R – Residence S – Scene of accident or acute event X – Intermediate stop at physician’s office on way to hospital (destination code only) Additional Claim Requirements When a patient is transported to the nearest hospital for emergency treatment and stabilization by an ambulance services and it is determined that the patient needs to be transferred to a more specialized hospital by the same ambulance service, all transport charges must be included on one claim form as two separate base rate charges, two separate mileage charges, etc. Be sure to note the two pick up and destination sites via a modifier on the transport code or via a narrative description in box 19. Ambulance providers should populate the “destination” in box 32. Never put a patient’s home address in box 32. Ground Transport Transport Charge: Bill the appropriate transport code that best describes the level of service rendered. Use appropriate alpha modifiers to denote Pick Up and Destination. Mileage: Bill the total charge for mileage according to the mileage instructions noted above. Transport Charge: For ground transport units, supplies should be billed by combining all supply charges into one charge line, using the appropriate code previously listed. When transmitting 837P claims utilizing the NSF format, including the following information can contribute to faster claim processing. Under records name - Ambulance Cert Record, record type GOA: Field 7.0 Type of Transport Field 15.0 Transport To / For Field 18.0 Origin Information Field 19.0 Destination Information Field 24.0 Service Available 137 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The following boxes must be completed when filing a paper claim: 1, 1a, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 12, and 13, 14, 21, 24a-g, 25, 26, 28, 31, 32, and 33. Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) There are two acceptable claim formats for submission of charge for Ambulatory Surgery Facility Charges (ASC). Those formats are the paper CMS 1500 (12/90 Version) claim form or the 837P Electronic claim transaction. Billing for Facility Fee (Technical Component) and Other Applicable Services: Submit all claims directly to Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska with the required claim information. The Facility Fee (Technical Component) charge is to be billed in Section 24F of the CMS 1500. The facility fee charge for each coded procedure is considered to be all-inclusive of the facility costs for that procedure, excluding those procedures where BCBSNE has indicated that specified surgical procedures may receive separate reimbursement for the implant(s) or implantable device(s) used in that procedure. An appropriate Level II HCPCS code is required for billing the implant/device. Submit the CPT code for each procedure performed in compliance with CPT and Correct Coding Initiative (CCI) coding rules. The agreed upon payment amount as specified in the Provider Agreement for any Covered Service will be reduced by the Covered Person’s liability of any co-payment, deductible or coinsurance amount(s). Single Procedures: When one operative / diagnostic procedure is performed in an encounter, the billing for the Facility Fee (Technical Component) shall be billed with the appropriate CPT code of the procedure performed. Multiple Procedures: When two or more operative / diagnostic procedures are performed in an encounter, the billing for the Facility fee (Technical Component) shall be billed with the appropriate CPT code. BCBSNE normally follows CMS policy for procedures that can be performed in an ambulatory surgery center (ASC) place of service. If CMS does not allow a CPT code to be billed by an ASC, BCBSNE will not price the code and recommends submitting a preauthorization before scheduling the procedure. The primary procedure (procedure with the highest RBRVS value) will be priced at 100% of the ASC fee schedule amount. Additional covered surgical procedures will be reduced by 50% of the ASC fee schedule amount. 138 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Bilateral Procedures: Bill bilateral procedures on two lines with modifier -50 on the second line. Example: 64483 64483 50 Post Procedure Overnight Observation: For those facilities licensed by the State of Nebraska to provide continuous 24-hour per day nursing services for the post procedure treatment and follow up observation of a surgical patient, and so approved by BCBSNE to perform those services, additional reimbursement outside of the surgical procedure reimbursement will be provided as specified in the Provider Agreement. CPT code 99236 must be used to bill the charge for the overnight observation and treatment services. Implants Implants are defined as materials inserted into the body, including living, inert, or biological material (e.g., screws, grafts, plates or fixation devices) used for the purpose of creating stability (to correct, protect, or stabilize a deformity) where the majority of the product is left under the skin after surgery. Effective September 1, 2013, the following changes will be made to the implant policy: 1. Separate reimbursement will no longer be paid for ear tubes and catheters, regardless of their individual acquisition cost. If billed, these items will be denied as content of service. 2. Screws have been added to the list of items that will be priced separately if the individual cost exceeds $100 (less shipping and handling, tax, and any rebates of discounts). 3. Covered implants, along with mesh, sutures, suture anchors, screws, staples, and wire that exceeds $100 in individual acquisition cost, will be priced at the lesser of billed charge or 100% of the actual acquisition cost (minus shipping, handling, tax, and any rebates of discounts). As a reminder, items/services charged by the Ambulatory Service Center that are determined by BCBSNE to be content of service are not billable to the member. If covered by the member’s contract, BCBSNE will reimburse separately for mesh, sutures, suture anchors, screws, staples or wire if the individual item cost exceeds $100. If the individual mesh, sutures, suture anchors, screws, staples or wire is less than $100, these charges will be considered content of service, not separately reimbursed, and not billable to the member. Covered implants will be reimbursed at the lesser of billed charges or 100% of actual acquisition cost, minus shipping, handling and tax, and less any rebates or discounts received by the Ambulatory Surgery Center. 139 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Implants must be billed with L8699-NU, a narrative description of the item, the charge for the item, and a copy of the vendor invoice for the item. Implant charge(s) must be billed on the same claim as the related surgical procedure(s). Discontinued Services When a surgical case is discontinued in an ASC setting, the proper modifiers to use are -73 for a discontinued procedure prior to the administration of anesthesia and -74 for discontinued procedure after administration of anesthesia. Discontinued procedures are priced at 50% of BCBSNE’s allowed amount. Cataract Surgery and Lens Insertion Procedure codes 66982 through 66986 involve the removal of the cataract and the insertion of an intraocular lens (IOL) which may be the standard lens or one of the new technology IOLs. The new technology IOLs are marketed by the trade names of Cristalens, ReZOOM and ReSTOR. Only the surgical facility (hospital or ambulatory surgery center) can bill for an IOL as it is part of the reimbursement built into the facility fee reimbursement. Ambulatory Surgery Centers that offer cataract removal in their facility should bill for accommodating intraocular lenses (when applicable), using the appropriate Level II HCPCS code: V2787 Astigmatism Correcting Function (Toric Lens) V2788 Presbyopia Correcting Lens (Crystalens, Crystalens HD, ReZoom, ReStor) Q1003 New technology, intraocular lens, category 3, reduced spherical aberration (Acrysof IQ) Q1005 New technology, intraocular lens, category 5 as defined in Federal Register notice The ASC facility fee for the surgery includes $200 for a standard monofocal lens (V2630, V2631, V2632). When an accommodating intraocular lens is used, it must be billed on the ASC claim using the appropriate Level II HCPCS code. The cost invoice for the lens must be attached. When covered by the member’s benefit contract, BCBSNE will calculate the reimbursement at the lesser of billed charge or 100% of the acquisition cost minus the $200 already included in the facility fee allowance. If 100% of the acquisition cost of the lens is less than $200, it is not necessary for the lens to be billed separately. Note: Surgeons cannot bill for intra-ocular lens implants. Fluroscopic Guidance of Needle Procedures 77001-77003 done in an ASC will be reimbursed only the technical component for these procedures. (A separate professional component for each of these procedures may also be payable and should be submitted by the physician with modifier -26 on a separate CMS1500). 140 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Tissue Expanders When implantable tissue expanders are inserted in an ASC, the procedure should be billed under 11960. The implantable tissue expander itself should be billed under L8699 and the invoice should be sent with the claim. Birthing Centers Birthing Centers are to bill on the CMS 1500 using the facility NPI in Box 24J and birthing center name in Box 31. Procedure codes must have the SB modifier. Contracted birthing center facility charges are separately payable in addition to the professional provider’s charge. Bone Mineral Density Beginning March, 1, 2010, Bone Mineral Density Measurements billed with CPT code 77080 will be reviewed against BCBSNE’s Medical Policy. To view this policy, go to www.nebraskablue.com, click on the “Providers” button and then on “Policies and Procedures” in the left column. CT Bone Mineral Density Studies represented by CPT codes 77078 and 77079 must be preauthorized through American Imaging Management (AIM). Refer to Section 9 of this manual for additional information concerning BCBSNE’s Radiology Quality Initiative (RQI) Program. Cancelled Procedure When a patient is admitted as an inpatient for surgery or some other specific treatment, and the procedure needs to be cancelled due to medical circumstances with the patient, and the patient is discharged, BCBSNE will pay the case at the contracted rate for the DRG category of that stay. Cardiac Rehabilitation (Outpatient) Cardiac Rehabilitation is defined as the use of various modalities of treatment to improve cardiac or pulmonary function as well as tissue perfusion and oxygenation through which selected patients are restored to and maintained at either a pre-illness level of activity or a new and appropriate level of adjustment. The cardiac or pulmonary rehabilitation program must be accredited by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations or as otherwise approved by BCBSNE. Benefit Provisions Benefits are provided for medically necessary outpatient facility rehabilitation programs, according to the terms of the subscriber’s contract. In addition, the following services are covered when provided as part of the approved rehabilitation program: 1. Initial rehabilitation evaluation; 2. Exercise sessions; 3. Concurrent monitoring during the exercise session for high risk patients. The patient’s condition must be such that rehabilitation can only be carried out safely under the direct, continuing supervision of a physician and in a controlled hospital environment. 141 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Services are provided at any therapeutic level, limited to the number of sessions listed in the subscriber’s contract, for the following diagnoses occurring during the four months prior to the start date of a cardiac program: • • • • • • An acute myocardial infarction Coronary bypass surgery Coronary artery angioplasty or other procedure to clear blocked vessels Heart transplant Heart-lung transplant Heart valve surgery All other uses of cardiac rehabilitation are investigative. Cash Discounts If a cash discount is offered, that discount needs to be extended to BCBS patients. The discounted amount must be the amount billed on the claim. Circumcision Bill circumcision with revenue code 723. Do not use 761 Treatment Room. Clinical Trials and/or Research Studies BCBSNE member contracts do not provide benefits for services for medical treatment and/or drugs, whether compensated or not, which are directly related to or resulting from the Covered Person’s participation in a voluntary, investigative test, or research program or study unless authorized in writing by BCBSNE. These services may be pre-authorized through our Medical Support Department. To preauthorize these services, please fax the informed consent document and specific information for evaluation to 402-392-4141 or 800-255-2838. Content of Service Content of service refers to specific services and/or procedures, supplies and materials that are considered to be an integral part of previous or concomitant services or procedures, or all inclusive, to the extent that separate reimbursement is not recognized. Charges denied as “content of service” are the provider’s liability and may not be billed to the member. Consults submitted on a UB-04 Any of the consultation codes submitted on the UB-04 will be non-covered as provider liable services. The denial reason will instruct the provider to resubmit with a more appropriate E and M code. 142 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Continued Stay Denial If a continued stay denial notice is issued to the member and the member elects to remain in the facility, the claim must be split so that the charges for the days extending beyond the approved days are on a separate claim. Contracted Rate Payment Exceptions When a patient is admitted as an inpatient for surgery or some other specific treatment, and the procedure needs to be cancelled due to medical circumstances with the patient, and the patient is discharged, BCBSNE will pay the case at the contracted rate for the DRG category of that claim. Critical Access Hospitals (CAH) This is a Medicare (CMS) designation. Hospitals should bill according to standard BCBS billing guidelines. CRNA Charges Bill charges for CRNAs who contract with or who are employed by a hospital on the CMS 1500 claim form. CRNAs who are an employee of a hospital will need to obtain an NPI and advise BCBSNE of their NPI for claim filing. NPI notification forms can be found online at www.nebraskablue.com, under “Forms for Providers.” Services provided by a CRNA who is an employee of a hospital must adhere to the following billing guidelines: • Anesthesia claims must be billed with minutes, not units. • Never put the surgeon’s NPI number on the claim. • Do not write start and stop times on the claim. Paper claims guidelines Box 24J must include the CRNA’s individual NPI. Box 31 must include Prof Serv CRNA with the CRNA’s first and last names underneath Prof Services CRNA. No punctuation. Example: Prof Serv CRNA Smith Jane CRNA Box 33A must include the entity’s NPI number in box 33A. Electronic claim guidelines The 2310B Loop (Rendering) should include the CRNA’s name and individual NPI. The 2010AA Loop (Billing) should include the billing entity’s name and organizational NPI. Bill Revenue Codes 370-374 on the UB04 only when charges are specific to anesthesia agent(s) or supplies. 143 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Diabetes Education Who can provide these services? • Certified Diabetes Educators (CDEs) working independently, in a medical office setting, or in a facility whose program is not Recognized by the American Diabetes Association. • Individuals working in a facility whose program is Recognized by the American Diabetes Association. How does one join the BCBSNE network? • Independent CDEs not already in the BCBSNE network will need to complete a Request to Participate form, online under the “Forms for Providers” section at www.nebraskablue.com/providers, to start the credentialing process. • Facilities with Recognized programs will need to sign and return a Diabetes Self-Management Educator Program Agreement and submit a copy of the Recognition letter. Does diabetes education need to be ordered by a physician? Yes, diabetes education must be ordered by a physician and must be medically necessary. How should diabetes education be billed? Hospitals whose diabetes education program is recognized by the American Diabetes Association are to bill the education services on a UB-04 under the hospital name and acute care NPI number. Coding is to be as follows: • • • • Bill Type: 13x Revenue Code: 942 HCPCS Code(s): G0108 (Individual Sessions); G0109 (Group Sessions) Units: One unit for every 30 minutes Time spent for Medical Nutrition Therapy, when provided as part of the patient’s diabetes education, should be factored in to the time units reported for the diabetes education session. Independent Certified Diabetes Educators will bill on a 1500 claim form with their individual NPI and tax ID. • • G0108 for Individual sessions – one unit per each 30 minutes G0109 for Group sessions – one unit per each 30 minutes If a patient is enrolled in your Diabetes Education Program and the only service provided on a given day is Medical Nutrition Therapy, this service is billed using G0108 or G0109 (Box 24D) with the appropriate time units in Box 24G (30 minutes = 1 unit). If Medical Nutrition Therapy is provided to someone who is not a diabetic patient and /or not enrolled in your Diabetes Education Program, you should bill one of the Medical Nutrition Therapy codes (97802-97804) which is a non-covered service. 144 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents All supplies and materials that are considered to be an integral part of Diabetes Education are inclusive of the provider contract reimbursement for G0108 and G0109, and are not to be charged separately. If a BCBSNE member has the RX Nebraska endorsement and this endorsement includes diabetes supplies and insulin coverage, the insulin and diabetes supplies need to be obtained and billed by an RX Nebraska Pharmacy. If a BCBSNE member does not have the RX Nebraska endorsement, the diabetes supplies need to be obtained through and billed by a participating BCBSNE Home Medical Equipment provider. Diabetic Supplies Diabetic and ostomy supplies as well as self-administered inhalants are to be billed with revenue code 273. Dialysis Dialysis services must be billed on a UB04 claim form. Valid Level I, II and III HCPCS Codes must be utilized. The valid and acceptable Revenue Codes used to assess the charge for Dialysis Services are: Revenue Codes 820 – 825 • Hemodialysis, Outpatient or Home Revenue Codes 830 – 835 • Peritoneal Dialysis, Outpatient or Home Revenue Codes 840 – 845 • CAPD, Outpatient or Home Revenue Codes 850 – 855 • CCPD, Outpatient or Home Revenue Code 636 • Level II HCPCS coded Pharmaceuticals Revenue Codes 634 – 635 • Erythropoietin (EPO) Revenue Codes 270 – 273 • Medical Supplies Revenue Code 250 • Non-Level II HCPCS coded Pharmaceuticals BCBSNE will discontinue reimbursement of dialysis services when usage is terminated for any of the following reasons: • End of need of the service • Institutionalization of the Covered Person • Death of the Covered Person • Termination of Coverage The contracted payment amount for any Covered Service will be reduced by the Covered Person’s liability of any co-payment, deductible or coinsurance. Dietary counseling Dietary counseling (i.e. eating disorder, nutrition therapy) is non-covered, except for diabetes education. 145 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Discharge Planning Discharge planning is a process that assesses a patient’s needs in order to help arrange for the necessary services and resources to affect an appropriate and timely discharge or transfer from current services or level of care. The facility and the attending physician have major responsibility for this function. BCBSNE Care Coordination promotes and assists the facility discharge planners. All provider-submitted inpatient or outpatient institutional claims (UB Form) require a discharge status to be populated in FL 17. Claims filed without FL 17 populated will be rejected and returned to the provider. NOTE: Institutional claim that automatically cross over from Medicare without a discharge status in FL 17 will be processed by BCBSNE. Donor Charges for Transplant (“See Transplant Services”) Emergency Room Services ER visit leading to inpatient admission If the patient is seen in the emergency room within twenty-four hours of an inpatient admission for the same diagnosis, the charges for the emergency room should be included on the inpatient claim. Multiple visits same day If a patient visits the emergency room more than once on the same day, the visits can be rolled into one if the same diagnosis was the reason for the visit. If each visit was for a different diagnosis, the charges should be billed separately. Federal Employee Program (FEP) and Medicare When a patient is age 65 or over and does not have Medicare Part A, Part B or both: Under the FEHB law, payments for inpatient hospital care and physician care are limited to those benefits the patient would have received if they had Medicare. The physician and hospital must follow Medicare rules and cannot bill the patient for more than they would bill if the patient had Medicare. Outpatient hospital care is not covered by this law. Fertility Testing/Treatment Consults A consult to a fertility specialist to establish the diagnosis of infertility is considered a payable benefit. If the member previously had infertility established through their OB/GYN or family practice M.D. (such as previous infertility treatment with Clomid) and are seeing the fertility specialist for other options, then this would be considered infertility treatment. If the plan of treatment involves further diagnostic studies to establish or rule out other conditions (such as endometriosis or polycystic ovarian disease), then this would be considered a payable benefit. 146 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Diagnostic Testing Infertility is a symptom of a disease. Diagnostic testing to determine the cause of the symptom is a covered benefit. If disease is determined to be the cause, benefits are available for the appropriate treatment of the disease. However, if the treatment received is not specifically disease related and the treatment purpose is to facilitate fertility, then benefits are subject to the varying contractual language and endorsements concerning fertility related services. Diagnostic testing done to determine the diagnosis of infertility, treatment of polycystic ovary disease, and treatment of endometriosis, are not considered to be Infertility treatment. Infertility Diagnosis Codes Diagnosis codes 606.XX (Male Infertility), 628.XX (Female Infertility) and V26.XX (Procreative Management) are defined as infertility. Other diagnosis codes may or may not be related to infertility. Infertility Treatment Once the member has completed the evaluation and the treatment proceeds to infertility related treatment such as serial ultrasounds and labs, then the claims will be reviewed/processed as infertility treatment. This is regardless of the diagnosis submitted on the claim. Therefore, even if the provider bills with a diagnosis of polycystic ovarian disease or endometriosis, if the records indicate they are monitoring the woman’s cycle in response to infertility medications or prior to ART, the claim will be processed as infertility treatment. Certain Reproductive Clinics require screening blood tests to be completed to both partners prior to initiation of the ART procedure. These tests may include: HIV, Hepatitis B and C, RPR, Cycle Day 3 FSH (female partner only), CMV (female partner only). The male partner must have a recent semen analysis. Since these tests are considered part of the ART procedure, they will be processed as infertility treatment. A diagnosis of Habitual Aborter has been defined as a history of two or more prior miscarriages. Tests/procedures related to the evaluation and/or work up for this diagnosis is considered a payable benefit. Tests that may be performed are hysterosalpingogram, Cardiolipin phospholipid antibody, and Coagulation studies. The use of donor eggs may be requested for ART procedures. Benefits are available for the use of donor eggs based on the member’s contract. Any services/charges directly related to the donor should be submitted under the donor’s name and ID, since the donor is considered a non-eligible dependent under the recipient’s contract. Benefits will be determined based on the donor’s contractual benefits. Procedures to repair or reconstruct the fallopian tubes will be reviewed to determine if iatrogenically caused and whether benefits are available. For example, if injury to the fallopian tube occurred during previous abdominal surgery, and the patient was insured with us at the time of the previous surgery, benefits would be available for the repair of the fallopian tube. 147 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents There are several codes that have a frequency edit placed on them. These codes include: 84702 and 84703 (Gonadotropin, Chorionic HCG); 82670 (Estradiol); 84144 (Progesterone); 76856 and 76857 (Pelvic Ultrasounds). Tests that exceed the frequency established will be denied as “Not Medically Necessary” unless the group has a fertility endorsement. Coverage for artificial insemination will depend on the member’s contract. If the charges for the artificial insemination are not covered, then all other services performed on the same day will be rejected. Reversal of voluntary sterilization is a contract exclusion. Health Fairs By definition, a health fair is an educational and interactive event designed for outreach to provide basic preventive medicine and medical screening to employees at work in conjunction with workplace wellness. Health fairs where network providers collect member payment upfront for covered services such as immunizations and health screenings are not allowed by BCBSNE. Network providers who perform health fair services must follow contract guidelines to file the claims to BCBSNE as with any other covered service and be paid according to the lesser of the billed charge or fee schedule allowance. Hospitals conducting health fairs must bill all charges on a CMS 1500 claim form with the hospital’s medical director as the rendering. Hospital HME Billing Any equipment or supplies used by an inpatient in an acute care facility must be billed to BCBSNE by the facility, not by the HME provider. When HME for patient home use is dispensed out of the hospital’s freestanding HME business, the HME should be billed on a CMS 1500 claim form under the HME provider’s NPI number. When HME for patient home use is dispensed from the central supply or PT area of the hospital, the HME should be billed on the inpatient/outpatient claim form. Hospital Services by Non-MD Behavioral Health Providers As deemed appropriate by BCBSNE, non-MD’s (ex. Psychologists, LMHP’s) must have their services billed on a UB claim form when provided under a hospital based Tax ID. Incremental Nursing; Revenue Code 23X This billing protocol is only acceptable when coupled with the following revenue codes: Medical/Surgical Intensive Care Unit ICU - 20x Coronary Care Unit CCU - 21x Nursery Level IV 174 148 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Indian/Tribal Members When filing an institutional claim for hospital services authorized by Indian Health Services (HIS), Tribal, and urban Indian organization programs, bill your usual charge amounts(s) and include a copy of the Purchase Order with your claim. Reimbursement will be calculated at Medicare Like Rates (MLR). This billing requirement applies to all hospitals that participate in Medicare, including any hospital-clinics located offsite and Critical Access Hospitals. “Hospitals” include Acute Care Hospitals, Psychiatric Hospitals, Rehabilitation Hospitals, Long Term Care Hospitals, Critical Access Hospitals, Children’s Hospitals, Cancer Hospitals, Skilled Nursing Facilities and Swing Beds. Inhalants Self-administered inhalants need to be billed with revenue code 273. Inpatient Services Services Provided by Another Facility Charges for non-professional services provided by any provider in conjunction with an acute care stay should be included on an inpatient claim. These charges are considered content of that inpatient stay and are included in the reimbursement amount for that stay. Services provided during a stay at a freestanding skilled nursing facility may be billed on an outpatient claim if the skilled nursing facility does not normally provide such services and the facility is allowed contractually to bill for such services. A patient cannot be considered an inpatient at one facility and an outpatient at another facility during the same period. Professional Services The professional component must be billed separately on a CMS 1500 claim form under the name and NPI number of the rendering provider. Institutional and Professional Claims for the Same Day When both a facility and a professional claim are submitted for the same service/procedure on the same date of service, the procedure codes and diagnosis codes must match. If the codes do not match, claims will be returned to seek clarification. Interim Billing Submit interim bills with the appropriate third digit in the Bill Type (xx2-xx4) as stated in the UB04 Manual in FL 4. Enter a Patient Status Code of 30 in FL 22. Submit billings in chronological order. Submit all interim billings to BCBSNE even if the charges are paid in full by another payer. The claims are posted to the patient’s claim history and may be used to credit out-of-pocket expenses such as deductible and coinsurance. 149 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents When an interim claim is prepared, be sure to coordinate the “Bill Type” and the “Discharge Status” for the first, continuing and final claims. Interim inpatient claims (bill types xx2 and xx3) should not be for time periods less than 30 days. Billing periods should not over-lap. Interim Billing - Reimbursement Inpatient Where an appropriate interim inpatient bill is submitted, and where a specific Inlier/Outlier Contracted Rate has been established for the DRG category for that claim, the first interim claim will be paid based on the contracted rate calculation. Subsequent interim claim(s) reimbursement will be made via the combined calculation of the payment amount(s) made on the previous claims(s) plus any additional amounts due for the current claim based on the resultant DRG category of the billing combination process. The final payment (or refund) on the claim will be based on the regrouping of all previous interim claim data and all previous payments made subject to the reimbursement amount for the final DRG category. Outpatient Interim billings may be submitted for outpatient services that are expected to occur over a period of time (i.e., physical therapy, cardiac rehabilitation, etc.). Appropriate use of the third digit of the bill type code is essential to proper claim payment. Jail or Prison Benefits BCBSNE will allow for covered services provided to a member serving in a correctional facility if the services are not a result of the member’s engagement in an illegal occupation or his/her commission of or attempt to commit a felony. Jaundice (Neonatal) Jaundice is a medical condition common in newborns. The diagnosis of jaundice billed with medical procedure codes will be processed as medical. If the claim is received with a routine diagnosis for services that would normally be considered medical, the claim will be returned for verification of routine vs. medical. Laboratory In 2011, the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association mandated Plan compliance with the handling and processing of independent clinical laboratory claims. Independent labs are required to bill the claim to the Blues plan in whose state the specimen was drawn. Note: This applies to freestanding, independent clinical laboratories only. Claims for laboratory services provided in a hospital setting or billed by a physician office should be sent to the Blue Plan in the state where the laboratory services were performed. Language Interpreter or Translation Services 150 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Charges for an interpreter or translator are considered content of service and not payable, nor are they billable to the patient. Late Charges (See “Replacement Claims”) Leave of Absence When a Leave of Absence day (or days) is incurred, record the applicable number of leave days in FL 8 (non-covered days) using Revenue Code 018X. Record the number of covered (billable) days in FL 7. The total of the days in Form Locators 7 and 8 must equal the span of days in FL 6. A charge for the leave day(s) is not reimbursable. Medical Necessity BCBSNE, or the applicable Blue Plan, will determine whether services are Medically Necessary. Services will not automatically be considered Medically Necessary because they have been ordered or provided by a Provider. Medically Necessary or Medical Necessity is defined as Healthcare Services ordered by a Treating Physician exercising prudent clinical judgment, provided to a Covered Person for the purposes of prevention, evaluation, diagnosis or treatment of that Covered Person’s Illness, Injury or Pregnancy that are: 1. Consistent with the prevailing professionally recognized standards of medical practice; and, known to be effective in improving health care outcomes for the condition for which it is recommended or prescribed. Effectiveness will be determined by validation based upon scientific evidence, professional standards and consideration of expert opinion, and 2. Clinically appropriate in terms of type, frequency, extent, site and duration for the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of the Covered Person’s Illness, Injury or Pregnancy. The most appropriate setting and the most appropriate level of Service is that setting and that level of Service, considering the potential benefits and harms to the patient. When this test is applied to the care of an Inpatient, the Covered Person’s medical symptoms and conditions must require that treatment cannot be safely provided in a less intensive medical setting; and 3. Not more costly than alternative interventions, including no intervention, and are at least as likely to produce equivalent therapeutic or diagnostic results as to the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of the patient’s Illness, Injury or Pregnancy, without adversely affecting the Covered Person’s medical condition; and 4. Not provided primarily for the convenience of the following; a. The Covered Person; b. The Physician; c. The Covered Person’s family d. Any other person or health care provider; and 151 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 5. Not considered unnecessarily repetitive when performed in combination with other prevention, evaluation, diagnoses or treatment procedures. Medical and Routine-Same Claim If possible, routine and medical services should be billed on separate claims to ensure the appropriate policy benefits and out-of-pocket expenses, when applicable, are applied correctly to the services rendered. Medical Records Additional information which is reasonably necessary to determine benefits and to verify performance under the Provider’s Agreement must be provided without charge and in a timely manner. If the medical records requested are not received within twenty-one (21) calendar days from the date of the request, the claim will be denied. Once we receive the requested medical records, the claim will be reopened and processed. Mental Illness Admissions All inpatient admissions to a hospital or treatment center for treatment of mental illness, alcoholism and drug abuse must be certified. Medical Emergency If a person receives initial inpatient care at a non-NEtwork BLUE hospital or treatment center or receives care from a non-NEtwork BLUE physician during a medical emergency, this admission will be reviewed to determine if it was for a medical emergency. The 24-hour period prior to the admission and the 24-hour period after such admission will be reviewed to determine if the covered person’s condition and treatment would have hindered his or her ability to notify us. Mid-Level Reimbursement Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska (BCBSNE) applies a 15% differential to the applicable Physician fee schedule for covered Services performed or provided by Physician Assistants (PAs), Nurse Practitioners (NPs), Advanced Practice Registered nurses (APRNs), and Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMWs). Note: Effective with admissions April 1, 2011, and after, inpatient services performed by an APRN who is a salaried employee of the hospital will be eligible for professional claim submission. The BCBSNE policy pertaining to billable services by an APRN has been revised as follows: Healthcare services performed by a duly licensed APRN who is a salaried employee of a licensed healthcare facility, hospital, or clinic, may be submitted as a professional claim, provided the registered nurse meets the requirements established in Neb. Rev. Stat. 71-1722 and performs 152 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents services in collaboration and consultation with physicians as evidenced by an Integrated Practice Agreement on file with the State of Nebraska. The 15% differential does not apply to the following codes which will be reimbursed at the applicable physician fee schedule amount: • • • • Radiology Codes 70000 - 79999 Pathology and Lab Codes 80000 - 89999 Rx All J Codes; P Codes (P9000 - P9999, CPT codes 90000 - 90799); Q codes (Q0140 - Q0199, Q2000 - Q3999, and Q4070 - Q4085) All HCPCS Level II Codes Multiple Claims Pages If you are submitting a paper claim with more than one page, leave the Total Charges field blank until the last page. The total charge on the last page should tally the charges for all pages. Multiple Surgeons/Multiple Surgical Sessions When two or more surgical sessions occur on the same patient, it is considered one surgical encounter. Multiple ASC claims will be combined into one claim. Neurofeedback Effective March 20, 2013, BCBSNE will consider neurofeedback as investigative and will no longer provide benefits for this service. NEtwork BLUE providers should notify members undergoing neurofeedback therapy prior to 3.20.13 that this service will be their liability for dates of service 3.20.13 and after. Neurofeedback is not the same as biofeedback and should not be billed under the biofeedback codes. If the only service provided is neurofeedback, you should bill 90899 and include the neurofeedback in the comments/remarks section. If neurofeedback and psychotherapy are provided during the same visit, you should bill 90899 and include neurofeedback and psychotherapy in the comments/remarks section. Non-covered Services If a BCBS member requests a claim be filed for a non-covered service, the provider must file the claim. Obstetrical Services Guidelines “Obstetrical Guidelines” include: • Mothers and Newborns • Obstetrical Complications 153 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Mothers and Newborns Submit separate claims for a mother and her newborn. Obstetrical Complications Standby services during a C-section are not payable unless the standby physician actually performs some service/procedure during the delivery. The specific services/procedures performed should be billed rather than using the standby code of 99360. Occupational Therapy (See “Therapy”) Ostomy Supplies Ostomy and diabetic supplies as well as self-administered inhalants are to be billed with revenue code 273. Outpatient Services Outpatient Charges Related to an Inpatient Admission Emergency inpatient admissions Include outpatient charges on the UB04 as part of the inpatient billing. Non-emergent and scheduled admissions Include any outpatient services related to the same condition and reason for the admission that were provided within 24 hours prior to the inpatient admission as part of the inpatient billing. Note: Critical Access Hospitals may bill the ER charges separate from the Inpatient claim. Observation Observation services refers to the period of treatment when the physician is evaluating the patient’s medical condition to determine whether the patient can be released from the outpatient department or admitted to the facility as an inpatient or transferred to another facility; or the period of treatment following an outpatient procedure when the physician is evaluating the patient’s medical condition to determine whether the patient can be released from the outpatient department. A physician must justify and provide the order on the patient. Medical record documentation must prove that the patient was admitted to observation. BCBSNE will follow the Medicare definition, which requires the use of a bed and nursing services. Observation is NOT: • A substitute for an inpatient admission • For continuous monitoring • For medically stable patients who need diagnostic testing or outpatient procedures • For patients who routinely need therapeutic procedures provided in an outpatient setting 154 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • For patients waiting for nursing home placement To be used as a convenience to the patient, his or her family, the hospital or the attending physician For routine prep or recovery prior to or following diagnostic or surgical services Also note the following: • Observation services will only be defined under revenue code 762. • Revenue code 761 is for a treatment room and should not be used in place of an observation room. Observation services will be paid as an outpatient service type under the outpatient provider contract provisions. NEtwork BLUE Observation Claim Billing Elements: a. Outpatient bill type (i.e.131) b. FL 42 must be revenue code 762 c. FL 44 must include a valid CPT or HCPC code d. Each observation day must be billed as a separate line item with the actual date of service in FL 45 e. FL 46 must equal 1 for each 762 line item f. The admit date can be equal to or after the “from” date, but cannot be prior to the “from” date. g. The “from” date indicates the patient’s first contact with the provider for services. The “admit” date is the date the patient was admitted as an inpatient to the hospital. The “from” date and “admit” date can be the same. There are no limits or parameters around the number of hours of observation or a requirement to roll into an inpatient claim if the patient is admitted and BCBSNE is the primary payer. For each 24-hour increment or day of an observation stay in the outpatient setting, a separate line item must be billed under revenue code 762 with the service date on each line. Revenue code 762 for observation requires a CPT or HCPCS code on the line. Claims will be returned if the code is not provided on the claim. In relation to inpatient admissions— When an observation stay results in an inpatient admission, the observation and inpatient stays must be billed together as an inpatient claim in the following manner: • Bill the first day as an observation room charge in Revenue Code 762. • Bill subsequent days as inpatient room charges. The billing period in FL 6 reflects the “From” date as the date of observation admission, and the “Through” date as the discharge date. The Admit Date in FL12 should be the first inpatient day following observation. 155 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Revenue Code 769 is not valid for reporting observation services and will be returned for proper coding. Outpatient Surgical Encounters- Multiple Procedures When one or more separately codable surgical procedures are performed in one outpatient surgical encounter, all applicable surgical CPT procedure codes should be shown on the claim (unless coding rules indicate one or more of the procedures are content of a code that better describes that procedure). When a surgical procedure is performed bilaterally, the CPT surgical procedure code should be shown twice on the claim. Oximetry Regardless of what other charges are billed, pulse oximetry (94760-94762) will be denied as content of service. Pathology The usual fee for pathology is generally considered to include the costs of equipment and supplies used in performing a test or examination as well as the performance of the test and the professional evaluation and report. For hospital-based physicians, the usual professional fee is expected to represent just the charge for examination and opinion of laboratory specimens (collected at the expense of a facility or institution) that require a pathologist for interpretation. Payment for these professional interpretations is generally considered to be available only for anatomical tests. When all-inclusive codes exist for multiple component tests, the all-inclusive code must be used. The collection and or handling fee of a specimen is considered content of service to the laboratory/surgical procedure and/or the level of service being performed, regardless of whether the physician bills for the laboratory tests or if the specimen is sent to an outside laboratory. Venipuncture CPT 36415 may be separately billed and reimbursed. If the revenue code is not 0311 or 0923 and the HCPC is equal to codes P3000, P3001, Q0091, 88141, 88142, 88150, 88152, 88155, 88164 or 88166, then it will be rejected. Physical Rehabilitation (Acute Inpatient Programs) Physical rehabilitation is defined as the restoration of a person who was totally disabled as the result of an injury or an acute physical impairment to a level of function which allows that person to live as independently as possible. A person is totally disabled when such person has physical disabilities and needs active assistance to perform the normal activities of daily living, such as eating, dressing, personal hygiene, ambulation and changing body position. Patients requiring a single modality are not considered totally disabled 156 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents and therefore do not qualify (examples: fractured extremity, total hip/knee replacement, cervical strain). For benefits to be available for a physical rehabilitation program, the provider must be accredited for comprehensive inpatient rehabilitation by the Commission on the Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities (CARF) or the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO). Benefit Provisions Benefits will be provided for medically necessary covered services according to the subscriber’s contract. In addition to all services defined as covered services for inpatient care, the following will be covered services when provided as part of the physical rehabilitation program: • Recreational therapy • Social service counseling • Prosthetic devices • Psychological testing Benefits are not available under Physical Rehabilitation Benefits for the treatment of chronic medical conditions or a disabling disease. Benefits for further rehabilitation will stop under any of the following circumstances: • Further progress toward the established rehabilitation goal is minimal or unlikely; • Such progress can be achieved in a less intensive setting; • Treatment can be continued on an outpatient basis; • The patient no longer meets criteria for eligibility. Services will be provided for patients who are totally disabled and who meet specifications for coverage as set forth by the BCBSNE Physical Rehabilitation Program Guidelines. The covered person must require intense daily involvement in two or more of the following treatment modalities for not less than three hours daily: • Physical therapy • Occupational therapy • Speech therapy Inpatient rehabilitation must follow within 90 days of discharge from the acute hospitalization of the injury, illness, or condition causing the disability. Physical Therapy (See “Therapy”) Physical Presence Physical presence means you have a brick and mortar location, which has to be a street location, not a P.O. Box. Physician Attendance 157 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Attendance/standby services are not covered. If a physician performs a service, the specific CPT code that describes the service should be billed. Postoperative Pain Control Continuous infusion of anesthetic agents to operative wound sites using an elastomeric pump is scientifically validated as a technique for postoperative pain control for surgeries typically requiring oral or parenteral narcotics for pain relief. Trade names of elastomeric pump and associate catheters that have received approval for marketing from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), include, but are not limited to, Infusor SystemTM, On-Q® Post Op Pain Relief System, On-Q SoakerTM catheter delivery system, and the Pain BusterTM Pain Management System. While the charge for the elastomeric pump may be covered, the insertion will be denied as global to the surgery. POA Indicator for Acute Care On January 1, 2010, BCBSNE implemented the requirement for the Present on Admission (POA) Indicator on all acute care inpatient hospital claims for discharges related to conditions listed below as Never Events. Sometimes interchanged as Hospital Acquired Conditions or HAC’s, Never Events and HAC’s are occurrences that should not happen from a quality perspective. Never Events are defined as adverse events or errors in medical care that are clearly identifiable, preventable and serious in their consequences for patients. A participating acute care hospital is not permitted to receive or retain reimbursement for inpatient services related to Never Events. All participating acute care hospitals are required to hold members harmless for any inpatient services related to Never Events. Bill Audit Staff will report findings from post payment audits to Health Network Staff. Any findings for Never Events in regards to POA reporting by the provider would be subject to the same appeal process as any other Bill Audit findings. All post payment findings will also be directed to Health Network Services (HNS) area for further research and determination of the process with the provider. BCBSNE’s list of Never Events are: • Pressure ulcers, stages III and IV • Catheter-associated urinary tract infections • Vascular catheter-associated infection • Surgical site infection, mediastinitis, following coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) • Air embolism • Blood incompatibility • Foreign object retained after surgery • Falls and trauma (fracture, dislocation, intracranial injury, crashing injury, burn, electric shock) • Surgical-site infections following certain orthopedic procedures • Surgical-site infections following bariatric surgery for obesity 158 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • • • Manifestations of poor glycemic control Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism following certain orthopedic procedures Surgery performed on a wrong body part Surgery performed on a wrong patient Wrong surgical procedure performed Filing the POA Indicator: The indicator must be used on all claims for the above conditions to indicate whether it was present at time of admission. Values: Y – Diagnosis was present at time of inpatient admission. N – Diagnosis was not present at time of inpatient admission. U – Documentation insufficient to determine if condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. W – Clinically undetermined. Unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of the inpatient admission. Blank – Unreported/not used/exempt from POA reporting, UB-04. Paper Claims: On the UB-04, the POA indicator is the eighth digit of Field Locator (FL) 67, principal diagnosis, and the eighth digit of each of the secondary diagnosis fields, FL 67 A-Q. Report the applicable POA indicator (Y, N, U or W) for the principal and any secondary diagnoses and include this as the eighth digit; leave this field blank if the diagnosis is exempt from POA reporting. Electronic Claims: Using the 837I, submit the POA indicator in segment K3 in the 2300 loop, data element K301. Acute care facilities include: critical access hospitals, children’s inpatient facilities, and cancer hospitals. Private Room Charges When a Private Room accommodation is utilized, indicate the reason for the private room charges on the UB04 using the following appropriate Condition Codes in FL 24-30, and Revenue Codes in FL 42: Private Room Medically Necessary: Condition Code 39, Revenue Code 11x or 14x Isolation Room Medically Necessary: Condition Code 39, Revenue Code 11x, 14x or 164 Semi-private Room Not Available: Condition Code 38, Revenue Code 11x or 14x Use Value Code 01 when Billing Revenue Code 011X with the facility’s most common semi-private room rate amount, or Value Code 02 to indicate the hospital is a private-room only facility. Never use Value Code 02 if your claim includes a semi-private room charge. A claim will be returned if a semi-private room Revenue Code is submitted with Value code 02, if a private R & B is submitted with neither 01 or 02, or if 01 and 02 are submitted on the same claim. 159 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Institutional and Professional Claims for the Same Day When both a facility and a professional claim are submitted for the same service/procedure on the same date of service, the procedure codes and diagnosis codes must match. If the codes do not match, claims will be returned to seek clarification. Psychiatric Services Psychiatric benefits can vary from one member/group contract to another. It is recommended member eligibility and benefits be verified prior to rendering services, whenever possible. When verifying benefits with BCBSNE or any other BCBS Plan, you should also ask if there are any restrictions on the type of provider covered under the contract for these services. BCBSNE Non-Covered Services: • Programs of co-dependency • Family intervention • Intake or referral • Employee assistance • Probation • Prevention • Educational or self-help programs • Programs which treat obesity or gambling, except as mandated by the Affordable Care Act • Residential, halfway house or methadone maintenance programs, or • Programs ordered by the court which are not Medically Necessary as determined by BCBSNE. Benefits will not be provided for the following services which do not fit the criteria of medically necessary treatment: • Services directed toward making one’s personality more forceful or dynamic • Consciousness raising • Vocational or religious counseling • Group socialization • Activities primarily of an educational nature • Behavioral modification • The following treatment modalities: - Primal therapy - Rolfing or structural integration - Bioenergetic therapy - Carbon dioxide therapy - Guided imagery - Z-therapy - Obesity control therapy, except as mandated by the Affordable Care Act - Training analysis 160 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents - Sleep therapy Sedac therapy Dance therapy Music therapy Psychodrama Note: This is general information that applies to many of our group contracts. However, groups can and do request variations. Contact the Provider Service Department to determine a specific patient’s actual contract benefits and limitations. BCBSNE does not restrict providers from reducing charges to members on non-covered services. Psychiatric Evaluation for Bariatric Surgery For the psychiatric evaluation prior to bariatric surgery to determine patient’s ability to undertake the surgery and aftercare, bill with one of the following diagnoses: V70.2- GENERAL PSYCHIATRIC EXAMINATION, OTHER AND UNSPECIFIED; or V72.84- PRE-OPERATIVE EXAMINATION, UNSPECIFIED/V72.85- OTHER SPECIFIED EXAMINATION. Pulmonary Rehabilitation (Outpatient) Services are provided at any therapeutic level, limited to the number of sessions listed in the subscriber’s contract under the following circumstances: • lung transplant during the preceding four months • heart-lung transplant during the preceding four months • preoperative and postoperative care for lung volume reduction surgery Benefits are not available for pulmonary rehabilitation if cardiac rehabilitation is provided for a heart-lung transplant. Outpatient Pulmonary Rehabilitation must be preauthorized with BCBSNE. Pulmonary Rehab services must be billed under revenue code 948 with the appropriate HCPCS codes G0237-G0239 or G0424 as defined in the HCPCS manual. The pulmonary rehabilitation program must be accredited by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations, or as otherwise approved by BCBSNE. Radiology The usual fee for therapeutic radiology does not include: • Consultations on need for radiotherapy • Treatment planning • Concomitant surgical, diagnostic radiology or laboratory services If more than one of the same X-ray is taken of a location (i.e., because patient moved or film not clear) only one X-ray is considered payable and the others would be considered content of that service, provider liability. If more than one physician “reads” an X-ray, only one will be paid. BCBSNE does not pay for “over-reads.” 161 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents When both professional (modifier-26) and technical (modifier-TC) components are included in the charge, the usual fee is considered to include the cost of materials and technical operation costs as well as the professional fee for the administration of diagnostic ultrasound/imaging and other high energy modalities. When the professional (modifier-26) component only is charged, the usual fee is considered to represent the charge for the administration of radiology and follow-up care as defined above. The charge for such services would be lower than if technical costs were included. Rehabilitation (See “Physical Rehabilitation ‘Acute Inpatient Programs’”) Reimbursement Schedules Total reimbursement to the facilities and agencies from BCBSNE and the Covered Person or person responsible for the Covered Person, for Covered Services, may be calculated by one or more of the following payment methodologies: a. Inlier Rate/Outlier Threshold: The Inlier Rate is the base reimbursement amount for a DRG. The Outlier Threshold is the point at which additional reimbursement will be added to the base reimbursement to determine the total payment. When Charges for Covered Services are less than the Outlier Threshold, the Hospital will be reimbursed the Inlier Rate. When Charges for Covered Services exceed the Outlier Threshold, the total reimbursement is the combination of the Inlier Rate and the difference between the Outlier threshold and total Covered Charges. A percentage discount is then applied in the calculation of final payment. In 2012, BCBSNE implemented the All Patient Refined Diagnosis Related Groups (APR-DRG). The methodology incorporates patient severity of illness and risk of mortality as well as resource intensity. The patient’s severity is measured by four indicators: minor, moderate, major, or extreme severity of illness or risk of mortality. There are 314 DRG’s with a weight assigned for each of the four patient severity levels, making a total of 1256 possible APR-DRG’s. DRG payment (Inlier) equals the weight multiplied by the base rate and is compared against a cost threshold. Note: Actual payment from BCBSNE may be reduced by member liability (deductible, coinsurance, etc.) Example of how an APR-DRG reimbursement is calculated for an Inlier Knee Joint Replacement, Low Severity: Hospital Base Rate = $7500, and Ratio of Costs-to-Charges (RCC) = 0.48 APR-DRG weight = 1.9839 Cost threshold = $48,008 Charges = $21,000 162 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Case Rate = $7500 x 1.9839 = $14,879 Hospital Cost = $21,000 x 0.48 = $10,080 Since calculated cost < the cost threshold, there is no add on payment Payment = $14,879 To identify if an outlier is achieved, the total charge is multiplied by a hospital’s RCC. Lesser of logic applies on APR-DRG’s. If the charge is less than the calculated DRG payment, then the amount charged is what is paid. b. Transfer Per Diem (Applicable when an Inlier/Outlier rate is set.): When a patient is transferred between two or more Hospitals, and a Transfer Per Diem has been set for the applicable DRG at the transferring hospital, the reimbursement will be the Transfer per Diem for each covered Inpatient day when the covered charges are less than the Outlier Rate for the applicable DRG. If the Covered charges are greater than the Outlier Rate for the applicable DRG, the reimbursement amount will be calculated via the Inlier/Outlier reimbursement rate computation. When a patient is transferred between two or more Hospitals, and there is no Inlier/Outlier Rate of Per Diem set, the Hospital will be reimbursed for each day of the stay, based on the Covered Charges, less the agreed upon percentage. When a patient is transferred between two or more Hospitals, the receiving Hospital shall be reimbursed according to the contract amount in effect at the time of the admission at that hospital. Discharge codes include 02 Short Term General Hospital, 05 Designated Cancer Center or Children’s Hospital, 43 Discharged/Transferred to a Federal Health Care Facility and 66 Transferred to a Critical Access Facility. They do NOT include 62 Inpatient Rehab Facility or 63 Medicare Certified Long-Term Care Hospital. c. Percent of Charges for Covered Services: If a specific payment rate has not been established for a DRG, the Hospital will be reimbursed Charges for Covered Services less an agreed upon percentage. d. Outpatient: Facility outpatient claims are paid utilizing a combination of a fee schedule allowance or contracted discount percentage from covered charges. This outpatient payment methodology affects designated providers who bill services on a UB04. This methodology is applicable to all NEtwork BLUE claims when BCBSNE is the primary payer, the secondary payer under Coordination of Benefits or when BCBSNE is the claims processor. 1) Claim level processing for BCBSNE designated CPT codes: Claim level processing calculates the contracted payment amount based on the entire claim. When one claim level designated CPT code is submitted on the claim, and a fee schedule amount is set for that code, the contracted rate is calculated as the lower of the following amounts: 163 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • Covered charge for each line, or • The fee schedule amount for each. A separate payment will not be made for any other Level I (CPT), Level II HCPCS code(s) or Revenue Code(s). If there is no fee schedule amount set for the designated CPT code, the reimbursement calculation will be based on Line Level Processing. 2) Line Level Processing: Line level processing does not have a payment rate set for the claim as a whole. The claim is processed at the “line level”. Line level processing calculates payment for each CPT/HCPCS line at the contracted amount for that service: a) For each Revenue Code line with a CPT/HCPCS code that has an applicable fee schedule amount, the reimbursement amount is calculated as the lower of the following amounts: • Covered charge for each line, or • The fee schedule amount for each. b) Where no fee schedule amount is set for the CPT/HCPCS code, the reimbursement amount calculation will be the covered charge less the contracted discount percentage. c) For a Revenue Code line without a CPT/HCPCS code, the reimbursement amount calculation will be the covered charge less the contracted discount percentage. d) For each Revenue Code line with a claim level designated CPT code and no rate set, the reimbursement amount will be the covered charge less the contracted discount percentage. Replacement Claims List the appropriate bill type when submitting a replacement claim (xx7) or a late charge claim (xx5). The replacement claim bill type indicates the previously submitted claim should be voided and the replacement claim should be substituted. A late charge claim bill type indicates the charges should be appended to the previously submitted claim. Both late charge and replacement claims will be monitored, and any abnormalities will be brought to the attention of the facility. Note: Do not use bill type xx7 if your original claim submission was not adjudicated by BCBSNE. If your original claim was rejected/returned due to a billing or coding error, do not submit your corrected claim as a replacement claim. Residential Treatment – Hospital Based Residential treatment services must be billed on a UB04 using Type of Bill 86x, Revenue Code 1001 or 1002, and HCPCS code H0017. 164 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The claim should not be submitted under the hospital’s acute care NPI number when a separate NPI number has been enumerated for residential treatment. Bill with the appropriate NPI number to ensure accurate claims processing. Residential treatment is not payable for most contracts. Be sure to verify member eligibility and benefits prior to a member’s admission to the residential treatment facility. Revenue Codes Requiring CPT/HCPCS Codes Revenue Code 251-259 26X 272 273 274 Revenue Code 275 276 280 289 29X 30X 31X 32X 0330-0333 335 339 0340-0344 349 0350-0352 359 0360-0362 367 369 38X 39X0400-0405 409 0410-0413 165 Description Pharmacy: Specified IV Therapy Sterile Supply Take-home supplies Medical Surgical : Prosthetic/Orthotic Description Pacemaker Intraocular Lens Oncology Other Oncology Durable Medical Equipment Laboratory Laboratory Pathology Radiology Diagnostic Radiology – Therapeutic and/or Chemotherapy Administration Radiology – Therapeutic and/or Chemotherapy Administration Radiology – Therapeutic and/or Chemotherapy Administration Nuclear Medicine Nuclear Medicine CT Scan Other/CT Scan Operating Room Services Operating Room Services Operating Room Services Blood and Blood Components Administration, Processing and Storage for Blood and Blood Components Other Imaging Services Other Imaging Services Respiratory Services Revenue Code 45X 46X 47X 0480-0483 489 Description Emergency Room Pulmonary Function Audiology Cardiology Cardiology Revenue Code 49X 51X 54X 0550-0552 56X 57X 61X 621 623631-637 0720-0724 729 0730-0732 739 74X 75X 760-762 769 0770-0771780 789 Description Ambulatory Surgical Care Clinic Ambulance Skilled Nursing Home Health-Med Social Services Home Health Aid Magnetic Resonance Technology Medical Surgical Supplies Medical Surgical Supplies Pharmacy Home IV Therapy Services Hospice Services Hospice Services Hospice Services Labor Room/Delivery Labor Room/Delivery EKG/ECG (Electrocardiogram) EKG/ECG (Electrocardiogram) EEC (Electroencephalogram) Gastro-Intestinal (GI) Services Specialty Services Specialty Services Preventive Care Telemedicine Telemedicine 790 799 Extra-Corporeal Shock Wave Therapy Extra-Corporeal Shock Wave Therapy 64X0651-0652 655-656659 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 419 0420-0424 429 43X 44X Respiratory Services 820 Hemodialysis – Outpatient or Home Physical Therapy Physical Therapy Occupational Therapy Speech Therapy Room Rate Changes Starting July 1, 2012, it will no longer be necessary for institutional providers to send BCBSNE room rate listings. The room rate listing form has been removed from www.nebraskablue.com. Routine and Medical-Same Claim Hospital outpatient routine and medical services should not be billed on the same claim, but split into separate claims to ensure accuracy of claim processing and appropriate benefits. Rural Health Clinics This is a Medicare (CMS) designation. When BCBSNE is the primary payor, rural health clinics (RHC) must always file claims on a CMS 1500 claim form under the provider of service name, credentials and individual NPI with Place of Service 72 using standard BCBS billing guidelines. BCBSNE does not follow CMS’s incident-to-rules. When BCBSNE is the supplemental or secondary payor to CMS, the UB-04 and EOMB must be submitted. The claims should automatically cross over to BCBSNE from Medicare and the RHC will be paid directly if the appropriate information is on the claim. RHCs should never submit Medicare supplemental/secondary claims on a CMS 1500. If you haven’t received payment after 30 days of the CMS paid date on your remit, you should check the claim status. If the claim has not crossed over from Medicare, you will need to submit a UB-04 claim with the EOMB for processing. Simple Catheterization of the Bladder Under sterile conditions, a catheter, either straight or Foley, is passed through the urethra into the bladder as ordered by a physician. The simple catheterization is considered part of the “global charge” in the 1) emergency room, 2) office visit, 3) inpatient room charge. Therefore, no additional reimbursement will be allowed. Skilled Nursing Benefit Provisions Benefits are payable according to the subscriber’s contract for skilled nursing facility care provided in a semiprivate room for a covered person confined in a licensed facility. Such facility or part of a facility must be licensed to provide medically necessary room and board, 24-hours per day skilled nursing care and other related non-custodial services for the care and rehabilitation of injured, disabled or sick persons. 166 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents To be eligible to receive benefits, the covered person’s confinement must have been ordered by a Physician and be medically necessary. The covered person must be receiving skilled nursing care for an unstable health condition meeting the following criteria: • • • Daily skilled observation of the patient’s medical status is required; and Daily therapeutic treatment by a skilled professional is required; and The condition must interfere with the patient’s ability to perform the activities of daily living unassisted. Exclusions and Limitations A skilled nursing facility does not include a place that is primarily used for rest, care and treatment of mental illness, alcoholism or drug abuse; or for custodial care or educational or non-medical personal services. Note: To have custodial care charges auto-deny, place “Custodial Care” in the comments section on the UB claim. Medical records and review of charges will not be required. Skilled Nursing Facility / Swing Bed (Inpatient Billing) Provider must preauthorize services with case management. BCBSNE considers coverage if the following criteria is met: • Patient is an inpatient and treatment is appropriate to the illness • Patient is receiving skilled nursing services on a daily basis (PT, OT, ST, Medication Adjustment). • Coverage for the following conditions is conditional (TPN, Wound Care, Teaching, Trach Care, G-Tube Care, IV Therapy). Billing Guidelines UB04 Claim Format Bill Type 21X 0 = Non-Payment / Zero Claim 1 = Admit Through Discharge 2 = Interim - First Claim 3 = Interim - Continuing Claim 4 = Interim - Last Claim 5 = Late Charge(s) Only Claim 7 = Replacement of Prior Claim 8 = Void / Cancel of Prior Claim Bills should cover 0 - 30 day increments and include all inpatient charges on same claim. Revenue Codes: 10x - 21x Room and Board accommodations equivalent to number of covered days 25x - Summarize all Pharmacy charges 27x - Summarize all Supply charges 42x - Physical Therapy 167 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 43x - Occupational Therapy 44x - Speech Therapy All charges for like revenue codes should be grouped together and submitted as one line item. Other required information: • Principal diagnosis code (do NOT use routine diagnosis codes) • Date of birth, sex, patient status If a patient is required to leave your facility for a service outside of the normal SNF services (i.e. hospital outpatient testing or services), the services must be billed separately by the actual provider of service. Do not bill any of the nursing facility provided services separately or on another claim. Any equipment or supplies used by an inpatient in a Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) must be billed to BCBSNE by the facility, not by the HME provider. Skilled Nursing Facility / Swing Bed (Outpatient Billing) Billing Guidelines UB04 Claim Format Bill Type 23X 0 = Non-Payment / Zero Claim 1 = Admit Through Discharge 2 = Interim - First Claim 3 = Interim - Continuing Claim 4 = Interim - Last Claim 5 = Late Charge(s) Only Claim 7 = Replacement of Prior Claim 8 = Void / Cancel of Prior Claim Revenue Codes 42x - Physical Therapy 43x - Occupational Therapy 44x - Speech Therapy Charges for like revenue codes should be submitted as individual line items with a valid HCPCS code to accurately identify the therapy provided, and Form Locator 45 must include the actual date of service. Other required information: • Principal diagnosis code (do NOT use routine diagnosis codes) • Date of birth, sex, patient status Sleep Lab 168 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The sleep lab is a facility where patients are referred by their physicians to evaluate or diagnose sleep disorders, including neurological disorders, movement disorders and breathing disorders during the hours of sleeping. A lab can be hospital-based or independent. Independent Sleep Lab Independent sleep labs are required to be licensed as a “clinic” with the State of Nebraska to be eligible to participate with BCBSNE, and must be approved by the BCBSNE Network Oversight Committee to be considered for network status. CPT codes 95805, 95807, 95811 should be billed on the professional claim form with a Place of Service 11 for Clinic. Do not bill sleep lab claims with POS 81 Independent Lab. For technical component billing, codes should be billed on the professional claim form with modifier TC and under the lab’s name and NPI number. Professional component charges should be billed with modifier 26 under the physician’s name and NPI number. If a physician owns the clinic and wishes to bill global, the appropriate CPT code should be billed without a modifier under the physician’s name and NPI number. Hospital-Based Sleep Lab Sleep lab charges are billed under the hospital’s acute care NPI number, Bill Type 141, Revenue Code 920, and the appropriate CPT code. Sliding Fee Schedules BCBSNE providers must be consistent in the amount they charge for their services. If you utilize a sliding fee scale for your disadvantaged clients, you must also apply this sliding fee scale to your BCBS covered members and bill that amount to BCBSNE. Smoking Cessation Bill these services on a UB 04 using revenue code 942 and CPT 99406 or 99407. Speech Therapy (See “Therapy”) Sprains/Strains Not Accident-Related Sprain/Strain diagnosis codes require an accident date. If there is no accident date and the claim indicates that the sprain/strain was not due to an accident, it is appropriate to describe the symptom such as neuralgia, myalgia, swelling, cramping or pain. Diagnosis code 729 would be submitted to describe this condition. Stat or After Hours Laboratory Charges These are charges submitted to perform laboratory procedures immediately or outside scheduled laboratory hours. 169 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Benefits in addition to those allowed for laboratory procedures are not covered when such are ordered to be performed “stat” or outside of the scheduled laboratory hours. If a charge for rapid service time is submitted, the charge will be denied as “content of service”, provider liability. Submitting a Facility Name Change When a facility changes its name but keeps the same tax ID, ownership, location and providers, BCBSNE must be notified by letter or email (ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com) requesting the name be changed from [current name] to [new name] and include in the request the tax ID that the new name will appear under. If the facility has multiple NPI’s and lines of business (skilled nursing, home health, hospice, HME, etc.) those entities must also be listed in the request. The request needs to also include the effective date. Revenue codes 36x and 49x must be billed with a valid surgical code. If revenue code 36x or 49x is billed, and no HCPC is listed or the HCPC listed is not a surgical code, then it will be rejected. Surgical codes include the following: 10000-38203, 38205, 38206, 38216-51797, 51799-69999, 92018, 95873, 95874, 96920-96922, C9713-C9721, C9724, C9726-C9728, G0002, G0104, G0105, G0121, G0127, G0159 G0170 G0171, G0256, G0259-G0261, G0267-G0269, G0272, G0289, G0293, G0294, G0297-G0300, G0341-G0343, G0364, G0392, G0393, S2066-S2068, S2070, S2075-S2080, S2082, S2083, S2085, S2090, S2091, S2095, S2113, S2114, S2117, S2120, S2130, S2131, S2135, S2152, S2213, S2215, S2225, S2230, S2235, S2250, S2255, S2260, S2262, S2265-S2267, S2300, S2325, S2344, S2348, S2350, S2351, S2360-S2363, S2370, S2371, S2400-S2405, S2409, S2900, 0001T, 0002T, 0005T, 0006T, 0008T, 0009T, 0012T-0018T, 0021T, 0024T, 0027T, 0031T-0037T, 0046T-0057T, 0061T-0063T, 0071T, 0072T, 0075T-0081T, 0084T, 0088T, 0090T-0102T, 0120T, 0123T, 0124T, 0133T, 0135T, 0137T, 0141T-0143T, 0153T, 0155T-0158T, 0163T-0167T, 0169T-0173T, 0176T, 0177T, 0243T When billing for bilateral surgery, you must bill the first line without a modifier and the second line with modifier -50. If claims are received with one line item modifier -50 appended, the claim will be rejected as it cannot be processed. Surgical Standby (See “Physician Attendance”) Take Home Medications Any medications that are sent home with the patient need to be billed with Revenue Code 253. Technical vs. Professional Components Bill technical components of a facility based service on the UB04. Bill professional components of a facility based service, where specified by BCBSNE, on a CMS 1500 claim form under the name and NPI number of the rendering provider. 170 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents All professional component fees for covered services which are not specified by BCBSNE to be submitted separately on a CMS 1500 claim form are considered part of the contracted payment amount paid to the facility for the applicable service. Telemedicine/Telehealth Telemedicine is the use of interactive video equipment to link practitioners and patients in different sites. BCBSNE benefit contracts will be enhanced to provide for both the distant provider’s professional services and the facilities fee charged by the provider where the patient was physically located (originating site). Policy/Criteria BCBSNE will reimburse Nebraska network providers for telemedicine/telehealth when all of the following conditions are met: 1) Actual visual contact (face-to-face) is maintained between the distant provider and the patient; 2) billed services are for interactive, real-time communication; 3) the patient is present and participating in the visit; 4) the services are within the provider’s scope of practice as defined by state law; 5) services are medically appropriate and necessary; 6) documentation to support the services is included in the clinical record; 7) both providers must be BlueCard® participating providers in the continental United States; and 8) a designated room with appropriate equipment, including cameras, lighting, transmission and other needed electronics and the appropriate medical office amenities, is established in both the Originating and Distant Sites. NOTE: Using Skype or any other Internet programs is not permissible and is not a covered benefit. Reimbursement will be for services covered under BCBSNE’s member benefit contracts. This benefit policy applies to BCBSNE members only and excludes any FEP or out-of-state Blue Cross Blue Shield members. Reimbursement Exclusions: Provider to provider consultations, telephone conversations, facsimile or e-mail communications will not be reimbursed (stored and transmitted data does not qualify for telemedicine/telehealth benefits). There will be no additional reimbursement for equipment, technicians or other technology or personnel utilized in the performance of the telemedicine/telehealth service. Inpatient services. Medical interpretation or translation services. Covered Services: Professional office or outpatient services such as Evaluation and Management services, psychiatric diagnostic interview and individual psychotherapy services that are related to psychiatric treatment and are listed in the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) of the American Medical Association. 171 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Only those services currently covered in an office or outpatient setting will be allowed for payment. Reimbursement will be based on the current fee schedule in place at the time services are rendered. NOTE: Professional Services should always be billed on a CMS 1500 under the actual provider of service and their NPI. The covered CPT Codes are: • Office and Outpatient visits (99201-99215) • Psychiatric Diagnostic Interview (90791) • Individual Psychotherapy Services (90832-90839) • Pharmacologic Management (90863 or the appropriate E & M code) Benefits will be provided to the originating facility when HCPCS Q3014 (telehealth originating site facility fee) is billed. Only the Originating Site will receive payment for the facility fee. The allowable is $24. NOTE: Telehealth originating site facility fee can be billed on a UB 04 or CMS 1500. BCBSNE will only accept one claim per encounter for the Telehealth originating site facility fee. Definitions: Originating Site means the location of an eligible member at the time the service is being provided via a telecommunications system. Originating site includes hospital outpatient department, critical access hospital outpatient department, federally qualified health centers, rural health clinics, physician and practitioner offices. Distant Site means the site where the provider rendering the professional service is located. All conditions of reimbursement are subject to audit by BCBSNE. Additionally, an onsite visit may be made to the originating telemedicine/telehealth facility to address quality issues. Coding/Billing Information When billing for the Telehealth Origination Site facility fee on a UB 04, please follow these guidelines: FL4 - Bill Type 131 FL42 - Revenue Code 780 FL44 HCPCS Code Q3014 FL46 Units 1 FL51 Acute care hospital NPI When billing for the Telehealth Origination Site facility fee on a CMS 1500, please follow these guidelines: • HCPCS Code Q3014 in Box 24D • Units of 1 in Box 24G • Box 31 must include the last name, first name and credentials of the health care professional who office was used as the originating site. 172 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • The NPI number of the health care professional is required in Box 24J. Exception: for solo practice providers, or providers who do not have a Type II NPI, you may instead include your Type I NPI in Box 33A. When billing for the professional service that is provided via Telehealth, please follow standard billing practices on a CMS 1500. Telepsychiatry (Please see “Telemedicine”) Therapy (Hospital) The number of covered therapy session per calendar year can vary depending on the member’s contract. Ongoing preventative/maintenance therapy is not a covered benefit once the maximum therapeutic benefit has been achieved for a given condition and continued supportive therapy no longer results in some functional or restorative improvement. A session is defined as one visit. Therapies must be medically necessary. Inpatient Claims: BCBSNE does not have any contract limitations for inpatient physical therapy. Therapy modalities do not have to be billed out separately with a HCPCS code. Bill all charges for therapy provided during the hospital stay with one charge applicable to the appropriately assigned Revenue Code(s). Outpatient Claims: Revenue Codes applicable to physical, occupational and speech therapy require a CPT/HCPCS code to be included that accurately describes the modality provided. All therapy modalities must be charged out separately per day under the appropriate Revenue Code. The units assigned should be based on the description of the CPT/HCPCS code. Occupational Therapy Outpatient and/or home occupational therapy sessions must be provided by a Licensed Occupational Therapist or Licensed Occupational Therapist Assistant. A Licensed Occupational Therapist Assistant must be supervised by a Licensed Occupational Therapist. Occupational therapy must be ordered or prescribed by a Physician. Multiple modalities on the same day count as one visit. Revenue code 434 is for occupational therapy evaluation/re-evaluation and should only be billed with CPT codes 97003 or 97004. For training, use revenue code 430. Physical Therapy 173 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Outpatient and/or home physical therapy session must be provided by a Licensed Physical Therapist or Licensed Physical Therapist Assistant. A Licensed Physical Therapist Assistant must be supervised by a Licensed Physical Therapist. Physical therapy must be ordered or prescribed by a Physician. Multiple modalities on the same day count as one visit. Physical Performance Test or Measurement (97750) should be billed in unit increments of 15 minutes (1 unit =15 minutes). Speech Therapy Outpatient and/or home session of speech therapy or Cognitive Training must be provided by a Licensed Speech-Language Pathologist or Registered Communication Assistant practicing under the supervision of a Licensed Speech-Language Pathologist. The Registered Communication Assistant must be supervised by a Licensed Speech-Language Pathologist. Multiple modalities on the same day count as one visit. Third Party Providers BCBSNE will not separately reimburse third party providers rendering services including, but not limited to, monitoring or equipment in an inpatient/outpatient or Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) setting. Reimbursement for technical component services and equipment used during a procedure or surgery is included in the overall reimbursement to the facility, and if a third party provider is present and/or provides services or equipment based on physician’s or facility’s behest then payment to that provider will need to be coordinated between the two parties. A third party provider should never bill BCBSNE or the member for these services. Transplant Services Coverage for donor services will vary depending on the member’s contract. Under some contracts services are only covered if the recipient is covered under a BCBSNE policy. For members covered under this type of policy, BCBSNE does not cover organ donation if the recipient is not covered under a BCBSNE policy. Under other BCBSNE member contracts, if the donor and the recipient are both covered under the same policy then all services will be processed under the recipient. Member eligibility and benefits should be verified. Bone Marrow / Stem Cell Transplants: All donor related services for allogenic bone marrow / stem cell transplants must be billed with revenue code 819. 174 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents All donor related services for autologous bone marrow /stem cell transplants can be billed either with revenue code 819 or under the appropriate revenue code based on the services performed (i.e. 300 for lab, 320 for X-ray, etc.). Cadaver Donor: Donor services must be billed under revenue code 812 for all cadaver donor transplants. Donor Complications: The member’s contract may have maximums or restrictions for donor services and/or complications. If there are no restrictions then the claim will be processed according to normal contract benefits. Donor Maximums: Please check with Provider Service since coverage and restrictions can vary. Living Donor: Donor services must be billed under revenue code 811 for all living donor transplants. Living donor services should be billed with a donor diagnosis and should include the donor name and relationship to the transplant recipient in FL 84 of the UB04 or in Box 19 of the CMS 1500 claim form. In addition, Box 6 of the CMS 1500 claim form should indicate “Other”. The name of the donor is needed to avoid possible duplicate denials since there may be more than one potential donor. Nebraska Organ Retrieval Services (NORS): NORS performs the service of removal of organs from patients that have expired to be used for transplants. Reimbursement for these services should be provided to the hospital and should not be submitted to either the patient’s family or to BCBSNE. Search Activation: Coverage for search activation fees are dependent on the member’s contract with BCBSNE. Trauma Code Edits BCBSNE has identified specific diagnosis codes as trauma codes. When submitting a claim with a primary diagnosis from the codes listed below, additional information is needed to properly process the claim. UB04: Form locators 32 (Occurrence Code and Date) and 77 (E-code) must be completed when the primary diagnosis code is one of the following: 800-994.90 995.5-995.89 175 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Because of space limitation, you may not have an E code for every trauma code, but there should be at least one E code on the claim if there are trauma codes listed on the UB04. CMS 1500: Box 10 must be completed. Please keep in mind when the claim contains an accident date and indicator, the primary diagnosis code must be from the list below. V01.5 V04.5 V15.5 V15.6 V67.4 V71.3 thru V71.6 071 692.6 692.71 thru 692.74 800.00 thru 994.99 995.50 thru 995.59 995.81 Unbundling Procedure Elements Multiple variations of billing procedures are encountered when billing for various diagnostic services, particularly within the Radiology, Cardiology and Other Diagnostic Services Revenue Codes. These situations usually involve the use of multiple variations of Revenue Codes 25x, 27x, 329, 62x, 63x and 76x. A “complete procedure” billing approach encompasses all elements of the above noted categories into the Revenue Code line charge for the CPT code for the procedure. An “unbundling” of the procedure charge involves splitting out the various procedure elements into the CPT procedure code and one or more of the Revenue Code series as noted above. BCBSNE will monitor the use of and effect of situations where unbundling of charges occurs. Unlisted Procedure or Service Unlisted procedure codes have been designated to report services or procedures that are not found in the CPT manual. These codes usually end in the number 99. When an unlisted procedure code is submitted, the claim cannot be reviewed without a description of the service. Documentation such as visit or operative notes clearly detailing the service provided should be submitted with the claim. Zero Charge Revenue Code Line(s) The only circumstance when a zero charge Revenue Code line is acceptable is when two or more BCBSNE defined outpatient surgical codes need to be shown on a claim. 176 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 13 Home Medical Equipment, Home Infusion, Home Health, and Hospice Ambulatory Infusion Center (AIC) For services provided to BCBSNE covered members, nursing charges for services provided in an ambulatory infusion center should be billed on a UB 04 as if the services were provide in the patient’s home. If the member has coverage through another BCBS Plan that does not cover nursing in the home but will cover services in an AIC, then charges may be billed on a CMS 1500 using CPT code 99601 and POS code 11. Apnea Monitor Use A4556 for electrodes for Apnea monitor (per pair) if monitor has been purchased. Use A4557 for lead wires for apnea monitor (per pair) if monitor has been purchased. If monitor is rented, electrodes and lead wires are already included in the apnea monitor allowable and will not be separately reimbursed. BlueCard Coverage for Home Medical Equipment (HME) items provided to a member covered by another state’s BCBS Plan need to be verified and/or preauthorized through that member’s Blue Plan. Capped Rental (See “Medicare Related Issues”) Certificate of Medical Necessity Many items require an order from a physician indicating the item ordered is medically necessary. This needs to be on file but is not required to be submitted with the claim. Physician Assistants (PA) can prescribe drugs and devices as delegated by their supervising physician. If an HME provider has concerns with a script written by a PA, they should ask for clarification from the PA and/or supervising physician prior to filling the script. CPAP 12V battery and battery charger for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine are each billed under E1399. The cost invoice should be included with the claim. Date Span For rental equipment, providers need to bill for 30 day increments even at the end of the year. 177 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Drugs Dispensed or Administered A valid HCPCS code must be used for any drugs dispensed or administered. If there is no valid J code for the drug given, then use an unlisted J code with the National Drug Code (NDC) number associated with the drug that was given. If there is a valid J code, the units billed will be reflective of the nomenclature associated with that particular J code. If an unlisted J code is billed, then the units should be reflective of the nomenclature associated with the NDC number. Equipment Rental Policy BCBSNE member contracts provide benefits for purchase or rental of various HME, up to the maximum benefit amount (MBA). HME providers who rent equipment to our members should identify rental of the HME by using the “-RR” modifier on the claim. Our general guideline for rental of HME is that we provide benefits for rental, up to the allowable purchase price, as long as equipment is medically necessary. This includes, but is not limited to, oxygen therapy equipment, ventilation equipment, CPAP devices, and apnea monitors. The rental allowance is generally based on 10 percent of the purchase price allowance. Following ten months of rental, we consider the equipment to be purchased with ownership transferring to the member. Home Health Care Home Health Services provided to BCBSNE covered members must be preauthorized. When home health services are not preauthorized, medical records will be needed for review. Documentation should include the physician order, nursing notes, and care plans. BCBSNE will request this information if it is not submitted with the claim. Billing Guidelines (when BCBS is primary) UB-04 billing format NOTE: Type of Bill 033X will be discontinued on October 1, 2013. New claims received on and after October 1, 2013, regardless of date of service, will require Type of Bill 032X or 034X. If you have a replacement claim in need of submission for service dates prior to October 1, 2013, BCBSNE will accept the claim provided the Type of Bill submitted is 0337. Type of Bill 32X or 34X Revenue Code 572 with either S9122 or G0156 Revenue Code 552 with S9123, S9124 or G0154 Revenue Code 561 with S9127 or G0155 Revenue Code 441 with S9128 or G0153 Revenue Code 431 with S9129 or G0152 Revenue Code 421 with S9131 or G0151 178 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents S9122 Home health aide or certified nurse assistant in the home, per hour. FL 44 must include S9122. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = one hour). Time units must include all travel time, time in the patient’s home, and charting time. G0156 Services of home health aide, in the home, each 15 minutes. FL 44 must include G0156. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = 15 minutes). Actual date(s) of service and units Form Locator must be completed with the time units needed for total patient care. Time units must be include all travel time (to and from patient’s home to your office or to another patient’s home), time in the patient’s home, and charting time. S9123 Nursing care, in the home, by registered nurse, per hour. FL 44 must include S9123. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = one hour). Time units must include all travel time, time in the patient’s home, and charting time. S9124 Nursing care, in the home, by licensed practical nurse, per hour. FL 44 must include S9124. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = one hour). Time units must include all travel time, time in the patient’s home, and charting time. G0154 Services of a skilled nurse in the home, each 15 minutes. FL 44 must include G0154. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = 15 minutes). Time units must be include all travel time (to and from patient’s home to your office or to another patient’s home), time in the patient’s home, S9127 Social work visit, in the home, per diem for each visit. FL 44 must include S9127. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with unit of 1. G0155 Services of a clinical social worker, in the home, each 15 minutes. FL 44 must include G0155. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = 15 minutes). S9128 Speech therapy, in the home, per diem for each visit. FL 44 must include S9128. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with unit of 1. G0153 Services of a speech and language pathologist, in the home, each 15 minutes. FL 44 must include G0153. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = 15 minutes). 179 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents S9129 Occupational therapy, in the home, per diem for each visit. FL 44 must include S9128. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with unit of 1. (one visit equals up to two hours of care). G0152 Services of an occupational therapist, in the home, each 15 minutes. FL 44 must include G0152. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = 15 minutes). S9131 Physical therapy, in the home per diem . FL 44 must include S9131. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with unit of 1. G0151 Services of a physical therapist, in the home, one unit equals 15 minutes. FL 44 must include G0151. FL45 must include the actual date(s) of service. FL 46 must be completed with the time units for total patient care (one unit = 15 minutes). Additional Billing Instructions Each day’s visit must be on a separate line. If more than one visit is performed on the same day, you should combine the hours from both visits and bill the authorized hours on the same line. EXCEPTION: If you elect to bill authorized and non-authorized hours, you must split the authorized and non-authorized hours on different lines. For example, if four hours of care have been authorized and six hours of care was provided, you must split the care as follows: 01. Rev 552 S9123 4 units 09/09/11 02. Rev 552 S9123 2 units 09/09/11 • • • • • • Do not mix and match S and G codes for the same discipline on the same day. A Principal Diagnosis code is required. Indicate additional diagnosis codes as applicable. The Form Locators for Birth Date, Sex and Discharge Status must be completed. The Form Locator for Patient Status must be completed. The Attending (Ordering) Physician Form Locator must be completed with the UPIN number of the physician. (The Nebraska license number will not meet the billing requirement.) Supplies and drugs must be billed separately on a CMS 1500 under the HME/Infusion provider name, TIN and NPI number. Home Infusion Billing Guidelines When providing any services related to Home Infusion (Enteral or IV therapy), the Home Infusion or HME provider must bill the appropriate S code (S9325-S9379). Since the S codes include supplies and equipment and are paid on a per diem basis, providers must not line itemize or bill separately for any supplies or equipment. 180 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Home Medical Equipment or Home Infusion providers can line itemize any drugs or enteral formula on the same claim as the S code services. Nursing visits must be billed by the home health agency on a UB-04. S9340, S9341, S9342, and S9343 are per diem codes for Enteral Therapy. If a Home Medical Equipment, Home Infusion or Pharmacy provider sends supplies or meds to a physician’s office that are dispensed to the member, they must have a financial arrangement with the physician’s office to obtain reimbursement from them. The policy above applies when BCBS is primary. When Medicare is primary, B codes are acceptable when BCBS holds the secondary or supplemental contract for the member. Conversely, when a home medical equipment provider dispenses wheelchairs, canes, walkers, oxygen, etc., they must bill these items with the appropriate HCPC code and modifier (-NU or –RR). S9340 includes home therapy, enteral nutrition, administrative services, professional pharmacy services, care coordination and all necessary supplies and equipment. Enteral Formula and nursing visits are coded separately. S9341 includes home therapy, enteral nutrition via gravity; administrative services, professional pharmacy services, care coordination and all necessary supplies and equipment. Enteral Formula and nursing visits are coded separately. S9342 includes home therapy, enteral nutrition via pump; administrative services, professional pharmacy services, care coordination and all necessary supplies and equipment. Enteral Formula and nursing visits are coded separately. S9343 includes home therapy, enteral nutrition via bolus; administrative services, professional pharmacy services, care coordination and all necessary supplies and equipment. Enteral Formula and nursing visits are coded separately. The S (per diem) codes are payable regardless of whether the enteral nutrition is payable or not. The appropriate S code is billed in addition to the Enteral Nutrition codes (B4102-B4162) as separate line items. If there is no appropriate code for a specific enteral formula, the product should be billed using the NDC number and an appropriate unlisted HCPCS code and number of cans (as units). Formulas with a specific HCPCS code should be billed using that code. Units should be calculated based on the description of the HCPCS code (e.g. 100 calories = 1 unit). All S code per diem charges must have the appropriate date span and units. Billing one date of care with multiple units will result in the claim being returned. 181 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Specialty tubing for enteral feeding is payable outside of the S (per diem) code and must be billed using B4083-B4086. Nasogastric tubing and extension tubing are part of the perdiem. B4034, B4035, and B4036 are per diem supply codes for enteral feeding and are inclusive to S9340, S9341, S9342, and S9343. The S and B codes are reported in Box 24D on a CMS 1500 claim form. No modifiers are required on the S and B codes. Box 24G must indicate a unit of one. Box 31 must read: Infusion Therapy Specialists do not indicate an individual’s name or credentials Box 33 needs to read: Practice Name Practice Address Practice City, State and Zip Your NPI is required in Box 24J. Note: If an HME, Home Infusion or Pharmacy provider sends supplies or medicine to a physician’s office that are dispensed to the member, they must have a financial arrangement with the physician’s office to obtain reimbursement. Home Medical Equipment - RR or NU Modifier Required The following list of HCPCS codes require an RR (Rental) or NU (Purchase) modifier or they will be returned for proper coding. Also, HME rental (RR) will require a beginning and ending date. Note: Prebilling for HME/DME rental is not permitted. Only purchased items may be billed at the time of delivery/pick-up. If multiple modifiers are used, the RR or NU modifier must be in the first position. If more than one item is dispensed ,each item would need to be billed on a separate line. Example: L3090 NU RT L3090 NU LT A4000 - A8999 A9270 - A9300 A9900 - A9999 B4000 - B9999 E0100 - E9999 K0001 - K9999 182 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents L0000 - L8699 S8096 - S8490 S8999 - S9015 V2624 V2625 V2626 V2628 V2700 Hospice (Inpatient / Outpatient) Hospice Services provided to BCBSNE covered members must be preauthorized. Billing Guidelines (when BCBS is primary): Inpatient Respite/Non-Respite Services Bill Type 081X or 082X Use Revenue code 0655 as an all-inclusive entry for ancillary, room and board charges for inpatient Respite care with the appropriate Q code. Use Revenue code 0656 as an all-inclusive entry for ancillary, room and board charges for inpatient non-Respite care with the appropriate Q code: Q5002 Hospice care provided in assisted living facility Q5003 Hospice care provided in nursing Long Term Care facility (LTC) or non-skilled nursing facility Q5004 Hospice care provided in Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Q5005 Hospice care provided in inpatient hospital Q5006 Hospice care provided in inpatient hospice facility Q5007 Hospice care provided in Long Term Care facility Q5008 Hospice care provided in inpatient psychiatric facility Q5009 Hospice care provided in place Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) You may bill each day as a separate line item with a unit of one or bill one line item of Revenue Code 655/656 with the total number of units equivalent to the total number of covered days. Room and board should not be line itemized under revenue code 0115. Home (Outpatient) Hospice billing guidelines Bill Type: 081X or 082X Revenue Code 651 - to be used for hospice skilled nursing visits by an RN or LPN, home health aide services and hospice social worker services. Revenue code 651 must be billed with the appropriate Q code: 183 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Q5001 Hospice care provided in patient’s home/residence Q5002 Hospice care provided in assisted living facility Q5003 Hospice care provided in nursing Long Term Care facility (LTC) or non-skilled nursing facility Q5004 Hospice care provided in Skilled Nursing Facility (SNFf) Q5005 Hospice care provided in inpatient hospital Q5006 Hospice care provided in inpatient hospice facility Q5007 Hospice care provided in Long Term Care facility Q5008 Hospice care provided in inpatient psychiatric facility Q5009 Hospice care provided in place Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) For each day that a hospice nurse, an aide or a social worker saw the patient in an outpatient/home setting, the provider should bill the 651 Revenue Code (with the appropriate Q code). If more than one discipline has seen the patient that day, all charges must be lumped together under Revenue Code 651 and billed on a single line. Use discharge status code of 40 if patient expires at home. Use “3” in FL 19 for “elective” in Type of Admission/Visit. Hospital HME Billing When HME for patient home use is dispensed out of the hospital’s free-standing HME business, the HME should be billed on a CMS 1500 claim form under the HME provider’s name and NPI number. Supplies and drugs dispensed during an outpatient hospice visit must be billed separately on a CMS 1500 under the HME provider. When HME for patient home use is dispensed from the central supply or PT area of the hospital, the HME should be billed by the hospital on the UB 04 inpatient/outpatient claim form. Hospital - Billing for HME Equipment and Supplies Any equipment or supplies used by an inpatient in an acute care facility must be billed to BCBSNE by the facility, not by the HME provider. Insulin Pump and Supplies Insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring devices are noncovered items on the drug card and should be billed on a CMS 1500 under the hospital’s HME’s NPI or if dispensed in a physician’s office, under the rendering provider’s NPI. The claim is to be coded with Place of Service 12 (home) and the appropriate HME modifier (NU or RR). This includes Paradigm real-time glucose sensors. Lift Chairs (Recliner with elevating seat) The mechanism should be billed under E0627. Use E1399 for the chair portion (include make, model and manufacturer information). 184 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents If you are breaking out the charge for the mechanism (because of primary payer requirements) E0627 should be used for the mechanism and E1399 for the chair portion (include make, model and manufacturer information). When the chair is a coverable item under a BCBSNE contract, the entire chair will be covered, not just the mechanism. Lift Chairs are reviewed for medical necessity. Preauthorization is strongly recommended. Question: What if a member wants a luxury lift chair. Can the HME provider charge the member the difference between what the allowable would be for a regular seat-lift chair and the luxury version? Answer: Yes, providing you have the member sign a form up front indicating: they want the upgrade, they understand that these features are outside of what BCBSNE considers to be standard and that this amount (specify the charge for the upgraded features) would be their responsibility. Loan Equipment Bill loan equipment with K0462 and for correct pricing indicate on the claim what equipment is being repaired or temporarily replaced. The date range on the claim should only be for the days the loan equipment was used. Lymphedema Sleeve/Glove Bill under A6549 and include the cost invoice with the claim. Medicare-Related Issues Medicare and Oxygen Concentrators Question: When the customer has Medicare Prime, Medicare has them rent the concentrator for 36 months, but BCBSNE is now saying it’s purchased. The issue is that for Medicare to pay for the supplies, they have to bill the rental. Answer: You can continue to bill Medicare for rental if it is appropriate according to Medicare guidelines. The benefits as a secondary payer, however, are limited to the purchase price. Coinsurance liability once Purchase Price Met Question: When the customer has Medicare and according to BCBSNE the purchase price of an item has been met, whose responsibility is the Medicare coinsurance? Answer: The provider may bill the member for the coinsurance. Ostomy Supplies Beginning in 2014, BCBSNE is removing this benefit from our prescription drug plans and will add it to medical plan coverage for fully insured and self-funded groups. 185 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Oxygen Specific Questions Question: Does BCBSNE pay for oxygen contents E0441-E0444 when only a portable is being rented? Answer: Not normally. The contents are considered to be inclusive of the rental of the system. The only exception has been if the patient is on a high liter flow, and then the provider needs to submit documentation of the liter flow prescribed. Question: How should we bill for a patient who is on a high liter flow? Answer: Use the correct HCPCS code for either liquid or gas fills. Include documentation such as the prescription from the physician for the high liter flow with the first claim submitted. Question: We will be providing liquid oxygen to a patient who has received a hyperbaric oxygen chamber from another DME provider. How should we bill for the liquid oxygen? Answer: Bill for the liquid oxygen using S8121. Bill one unit for every one pound of liquid oxygen provided. A cost invoice must be included with your claim submission. Physical Presence Physical presence means you have a brick and mortar location, which has to be a street location, not a P.O. Box. Place of Service for Home versus Store Bill items purchased by the member and dispensed at your walk-in location with Place of Service 17 (Retail Clinic). Bill Place of Service 12 (Home) for items delivered or shipped to the patient’s home. When the equipment/supply is purchased in the retail store, the claim must be submitted to the Blue Plan in the state where the retail store is located. For items delivered/shipped to the patient’s home, the claim must be filed to the Blue plan located in the service area where the member resides. Prescriptions Many items require an order from a physician indicating the item ordered is medically necessary. This needs to be on file, but is not required to be submitted with the claim. Physician Assistants (PA) can prescribe drugs and devices as delegated by their supervising physician. If an HME provider has concerns with a script written by a PA, they should ask for clarification from the PA and/or supervising physician prior to filling the script. Supplies for an original scripted HME item (e.g. prosthetic device) do not require additional or ongoing scripts. 186 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Pricing Methodology Reimbursement rates for HME, supplies, procedures, orthotics/prosthetics, and medications identified by National Level II HCPCS codes shall be the lesser of the following rate setting methodologies: • Published Medicare payment rates plus 8% for home medical equipment, procedures, supplies, or medications; or • Published Medicare payment rates plus 15% for orthotics and/or prosthetics; or • The manufacturer’s suggested retail price less a 15% discount or the provider’s acquisition cost plus 35%, whichever is less; or • A separately implemented fee schedule utilized for drugs and biologicals. Payment for these items, including, but not limited to the “J” code series of the Level II HCPCS codes, will be reimbursed to non-clinical providers at 105% of the value as determined in the Medicare drug payment rates known currently as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Average Sales Price (ASP). This ASP information is available as a public use file on the CMS website or the Part B carriers’ websites. Adjustments to these payment values will be made in concert with the CMS updates to these values. Drugs and biologicals that do not have a specific Level II HCPCS code and associated reimbursement amount will be reimbursed at Average Wholesale Price (AWP) based on the NDC number for the product. The pricing source for these items will be the Facts and Comparisons MediSpan pricing supplied under license to BCBSNE. Claims submitted for drugs and biologicals that do not have a specific Level II HCPCS code must include the specific drug name and associated NDC number, dosage/units administered and the associated charge; or • Using market analysis of charges submitted by providers for like procedures, a relative value scale that compares the complexity of services provided, or any other factor BCBSNE deems necessary, fee schedule allowances may be adjusted. When CMS does not set a rate for a piece of equipment, BCBSNE will need the cost invoice to price the claim. All claims are paid according to the member’s contract. Provider may ask for a reconsideration of the reimbursement level of a submitted charge, and must supply all data necessary for BCBSNE to make a determination of appropriate reimbursement. In all cases, BCBSNE will make a final determination of reimbursement level based upon the criteria detailed above. The covered person is not responsible for payment of disputed charges during the appeal process. The provider may not bill the covered person for any payment under dispute. 187 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Purchase HME BCBSNE will preferentially purchase, not rent the HCPCS coded equipment items listed below for its primary insured customers. This policy doesn’t apply to situations where BCBSNE is the secondary payer. Claims for preferentially purchased items must be submitted with the “NU” modifier following the code. The date of sale must be listed as the date of service. When submitting the claim, list the “from and through” date as the same date. HCPCS Codes: E0110, E0114, E0135, E0141, E0143, E0163, E0470, E0471, E0472, E0480, E0562, E0570, E0571, E0574, E0600, E0601, E0720, E0730, E0860, E2360, E2361, E2362, E2363, E2364, E2365 K0097, K0102, K0104. Reminder: In all cases, rental payment may apply to the purchase price of Home Medical Equipment. This includes, but is not limited to, oxygen therapy equipment, ventilation equipment, CPAP devices, and apnea monitors. Rent to Purchase (HME Equipment - RR or NU Modifier - Required) BCBSNE member contracts provide benefits for purchase or rental of various HME, up to the maximum benefit amount (MBA). HME providers who rent equipment to our members should identify rental of the HME by using the “-RR” modifier on the claim. If a claim is billed with any of the following codes and no modifier, the claim will be returned requesting the appropriate modifier. A4000 - A8999 A9270 - A9300 A9900 - A9999 B4000 - B9999 E0100 - E9999 K0001 - K9999 L0000 - L8699 S8096 - S8490 S8999 - S9015 V2624 V2625 V2626 V2628 V2700 Our general guideline for rental of HME is to provide benefits for rental, up to the allowable purchase price, as long as equipment is medically necessary. This includes, but is not limited to, oxygen therapy equipment, ventilation equipment, CPAP devices, and apnea monitors. 188 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Our rental allowances are typically based on 10 percent of the purchase price allowance. At the end of ten months we consider this equipment to be purchased with ownership transferring to the member. Specific Questions: Question: Member rented equipment for seven (7) months. Now, almost a year later, they need it again. Does the number of months the item was previously rented count toward the ten-month rent to purchase? Answer: No, unless there’s just a few months between the different rental periods. Question: Do oxygen concentrators convert to purchase? Answer: Yes. Question: What is the policy if a member opts for a piece of used HME instead of new? Answer: BCBSNE would pay rental on such an item (if covered) but would not purchase. If multiple modifiers are used the -RR or -NU modifier must be in the first position. If more than one item is dispensed each item would need to be billed on a separate line. Example: L3090 NU RT L3090 NU LT Rental Proration BCBSNE will prorate monthly rental charges (i.e. apply a daily rate) for Home Medical Equipment when usage is terminated for any of the following reasons. - Return of the equipment to the Provider End of need for the equipment Institutionalization of the Covered Person Death of the Covered Person Termination of Coverage Repair of Equipment Reimbursement will only be made to an HME or medical supply company for Medically Necessary repair, adjustment, and maintenance of purchased Home Medical Equipment. Technician repair time (per 15 minutes) should be billed under K0739 (K0740 for oxygen equipment repair). Do not use modifier “MS” on any HC PCS code unless BCBSNE is secondary to Medicare. Other payable codes include maintenance and repair parts. 189 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents While an original item is in the shop, a replacement can be rented. (See “Loan Equipment”) Replacement of Existing Equipment A second or subsequent purchase of an item of Home Medical Equipment may be preauthorized under the following conditions: - there is a significant change in the covered Person’s condition; growth of a Covered Person; the item is irreparable and/or the cost of repairs exceeds the expense of purchasing a second piece of equipment; the item is five or more years old (unless replacement is Medically Necessary prior to that time); or as otherwise determined to be reasonable and necessary. - Note: Even if an item is five or more years old, preauthorization is still strongly recommended if replacement is being considered. Roller Aid Bill a roller aid with E1399 and in claim narrative indicate “roller aid.” Do not bill as E0118. Roller aids are not covered and will deny member liability. Skilled Nursing Facility - Billing for HME Equipment and Supplies Any equipment or supplies used by an inpatient in a Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) must be billed to BCBSNE by the facility, not by the HME provider. Transcutaneous and/or Neuromuscular Electrical Nerve Stimulator (TENS) Unit When renting a TENS unit, all supplies are inclusive with the reimbursement for the TENS unit and cannot be billed out separately. If a member has purchased a TENS unit, supplies can be billed out separately. E0270 E0730 A4595 A4630 A4557 TENS device two lead, localized stimulation TENS device four or more lead, for multiple nerve stimulation Wires and electrodes (2 leads per month) Replacement batteries for TENS Lead wires, per pair Unlisted Procedure or Service Unlisted procedure codes have been designated to report services or procedures that do not have a specific HCPCS code to identify the service/item provided. 190 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents When an unlisted procedure code is submitted (e.g. E1399), the claim cannot be reviewed without a description of the item. Documentation clearly detailing the item provided (make, model and manufacturer) should be submitted with the claim. Specific Questions: Question: How are unlisted codes reimbursed? Answer: Reimbursement is based on ASP or CMS ASP rates, or the cost shown on the cost invoice for a drug. Charges for covered items billed unlisted are reimbursed at the lesser of the charge, 15% off retail, or 35% above acquisition. Question: How is a 3ml vial of saline billed? Answer: Since there is no code, either bill the code for a 10ml vial with your charge or bill the item unlisted with NDC number. Question: What nomenclature should we use to calculate units … the wording associated with the HCPCS code? Or the NDC? Answer: When billing a specific HCPCS code, units should be calculated using the nomenclature associated with the HCPCS code. If there is no valid HCPCS code that corresponds to the drug, then a J3490 miscellaneous code (along with an NDC number) should be used and the units calculated using the nomenclature associated with the NDC number. Used HME items (See “Rental to Purchase” ) Ventilators Ventilators do not convert to purchase. You can also bill for a backup ventilator, if necessary. It should be billed on the same claim with E1399 and -RR modifier and “back up ventilator” should be indicated on the claim. The date spans should be the same for both the initial and back up ventilator. Wound Care - Pump and Supplies Pump When billing for a negative pressure wound therapy electrical pump, stationary or portable, E2402 should be used. This item is rental only and should be billed with an –RR modifier. Supplies All supplies and accessories, including canisters for the negative pressure wound therapy electrical pump should be billed under A6550. Notes 191 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents In all cases, rental payments may apply to purchase price of Home Medical Equipment. This includes, but is not limited to, oxygen therapy equipment, ventilation equipment, CPAP devices, and apnea monitors. BCBSNE will prorate monthly rental charges (e.g., apply a daily rate) for Home Medical Equipment when usage is terminated for any of the following reasons: • Return of the equipment to the Provider • End of need for the equipment • Institutionalization of the Covered Person • Death of the Covered Person • Termination of Coverage All skilled nursing care must meet criteria established under BCBSNE Skilled Nursing Guidelines and must be preauthorized. Skilled Nursing Care claims must be filed on the appropriate form designated for submission of these procedures. Agencies providing Skilled Nursing services will be reimbursed at the rates established under the Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska’s Home Health Provider Agreement. Participating Home Health Providers are eligible for direct payment under the Home Health Agreement. When submitting claims for medications, the specific drug name(s) and associated NDC number(s) must be submitted on the claim. Medication submissions must include the actual dosages, number of units (e.g., vials, milligrams, etc.) and the associated charges. 192 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 14 Mental Health Our goal is to provide you with information that encourages consistent, uniform billing practices among Nebraska health care professionals. Our intent is to provide correct reimbursement for services provided. This section is designed to clarify our medical policies and clarify coding guidelines that relate to those policies. This is a guide, not an all-inclusive policy. You will read about changes to these policies in our update newsletter or in direct mailings to your office. Covered services and benefits vary considerably. In all cases, we follow the specific covered member contract when making a benefit determination. The following Policy and Coding section is an alphabetic listing of common medical policies and coding guidelines that apply to BCBSNE claim processing. Alcohol and Drug Assessments Bill the code that most accurately describes the assessment. Most member contracts do not cover alcohol and drug assessments. Applied Behavioral Therapy Bill with 90899 and indicate “Applied Behavioral Therapy” in the claim narrative field. Applied Behavioral Therapy is considered investigative. Auxiliary Provider A Certified Social Worker, Psychiatric Registered Nurse, Provisional Licensed Mental Health Practitioner, Provisional PhD, Provisional Certified Master Social Worker, Provisional Alcohol and Drug Counselor or other approved provider who is performing services within his or her scope of practice and who is supervised, and billed for, by a qualified Physician or Licensed Clinical Psychologist, or as otherwise permitted by state law. Certified Master Social Workers or Certified Professional Counselors performing Mental Health Services who are not Licensed Mental Health Practitioners are included in this definition. Note: If a PLP is also an LMHP, they may choose to continue to provide services as an LMHP until they are fully licensed as an LP. The reimbursement for an LMHP is a Level 2 versus a Level 3 for a PLP. The ability to have their services covered at in-network levels is tied to the participating status of the supervising provider. Payment for covered services provided by an auxiliary provider is at the Level 3 reimbursement level. 193 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Community Treatment Aide Services should be billed under G0177. Indicate Community Treatment Aide in the narrative/remarks field if billing electronically. If billing paper, indicate on front of claim. CMS 1500 Box 31: Provider’s name followed by CTA Box 33: Billing name and address Community Treatment Aides who have not billed to BCBSNE previously should e-mail ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com to complete a Healthcare Professional Questionnaire. BCBSNE does not cover Community Treatment Aides. G0177 will deny as a non-covered service. Copay for Mental Health The mental health copay can only be obtained from talking with a provider service representative. The copay listed on the member’s identification card is only for medical services and is not the person’s mental health copay. Some groups with mental health coverage do not have a mental health copay. In that situation, services are subject to deductible and coinsurance. Custody Evaluations Meeting with the child and doing a report to the court should be billed under 90899 with a description of the service provided. If individual, group, or family therapy is done, those charges should be billed under the appropriate CPT code with the patient’s diagnosis. Just because a service is ordered by the court does not make it payable under the member’s contract. Drugs Dispensed in Office Effective July 1, 2014, per contract BCBSNE will reimburse for office-administered medications at a percentage of Average Sales Price. Prior to this date BCBSNE had reimbursed drugs and biologicals at a percentage of CMS rates. The reimbursement methodology may vary for PHO and oncology providers. A valid HCPCS code must be used for any drug given in the physician’s office. If there is no valid J code for the drug given, then use an unlisted J code and include both the name and National Drug Code (NDC) number associated with the drug that was given. If there is a valid J code, the units billed must be reflective of the nomenclature associated with that particular J code. If an unlisted J code is billed, then the units should be reflective of the nomenclature associated with the NDC number. 194 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Dual License If you are already an LMHP and add your LADC license or vice versa, you do not have to credential again. Simply notify BCBSNE of your additional credentials and license. Dual Therapists If there are two therapists present in either an individual session or a group session, only one therapist can bill for their services. Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)- 90870 Reimbursement for this code includes the necessary monitoring. Faxed Claims As of October 1, 2012, BCBSNE cannot accept faxed claims. Claims can only be accepted by electronic submission or by mail. Hospital Psychotherapy Sessions Only MDs, DOs, PAs and APRNs can bill and receive reimbursement for therapy sessions done while the member is in the hospital. Hypnotherapy Benefits may be available for hypnosis when used as an adjunct to psychotherapy. Provider Service should be contacted to verify benefits. Initial Assessment (Psychiatric Diagnostic Interview) Only Level I and LMHP’s with advanced training in diagnostic evaluations should bill 90791. All other providers should include an initial assessment as part of the first therapy session. Inpatient Psychiatric Sessions Only M.D’s may bill for psychiatric sessions while patient is inpatient. PhD’s cannot bill inpatient psychiatric sessions. Intensive Outpatient/Day Treatment/Partial Care Intensive, medically necessary day/evening programming services such as treatment programs, group and individual therapy, and psychiatric, psychological, nursing and social work assessments. Provision of these services in an organized program, serves as an alternative to hospitalization for those who need a structured, psychiatrically directed, multi-disciplinary treatment program. Such activities must be provided at least eight hours per week, usually in sessions of three hours or more in duration, three to five times per week. The expected duration of a program is not less than five weeks, and no more than twelve weeks. These program services must be provided in a hospital or facility Licensed by the Department of Health and Human Services Regulation and Licensure (or equivalent state agency) or CARF. 195 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Free-Standing Intensive Outpatient/Day Treatment/Partial Care Programs For a qualified free-standing program to receive in-network benefits, they must have signed an “Outpatient Mental Illness or Alcoholism and Drug Abuse Treatment Program” Agreement. Depending on the services provided, two numbers may be issued: one for mental health and one for drug/alcohol rehab. Billing for non-hospital based providers is done on a CMS 1500. All program charges are reimbursed at a flat rate per day. 90853-TC is the only code that should be used when billing for these services on a CMS 1500. The name of provider listed in Box 31 of the CMS 1500 should be the program name, NOT the name of any individual provider. The Place of Service Code that should be listed is 53. Dollar and day maximums often apply, so please verify benefits prior to providing services. Some coverage may also require preauthorization. Benefits will not be provided for treatment modalities which are identified as Noncovered Services in the member’s contract. For example: gambling. Hospital-Based Intensive Outpatient/Partial Care/Day Treatment Services for are billed on a UB04. All claims for Day Treatment, Partial Care and Outpatient Programs from a hospital-based program must be billed in the UB04 claim format as follows: Revenue Code 912 913 914 915 944 945 Description Partial Hospitalization/Less Intensive Partial Hospitalization/Intensive Individual Therapy Group Therapy Other Therapeutic Services - Drug Rehabilitation Other Therapeutic Services - Alcohol Rehabilitation Special Note: Provider must be certified and a participating provider to be payable under mental illness and drug abuse. The above codes are to be used for either partial care or day care. • • • • • One Revenue Code and one Unit may be billed for each day of program attendance. Services must be billed by line item and each line must have a date of service. Psychological Testing may be billed on a separate line item under Revenue Code 918. Do not submit psychological testing by a hospital employee on a CMS 1500 claim form. Separate claims may not be submitted by or for program personnel. 196 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents If an employee is doing the psychiatric evaluation, it is included in the per diem. IQ Testing (See “Psychological Testing”) Marital Counseling Only covered under certain contracts. Medicaid Claims Medicaid is always the payor of last resort. BCBSNE requires that providers bill the appropriate CPT codes for services they provide. If there is no code to describe the services rendered other than the H code required by Medicaid, please contact your Health Network Consultant. Mental Health Parity and Substance Use Disorders Federal mental health parity requirements initially began in 1996 with the federal Mental Health Parity Act. The 1996 act was amended and supplemented by the Paul Wellstone and Pete Domenici Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008 (MHPAEA). MHPAEA’s statutory provisions generally became effective for plan years beginning after October 3, 2009. Interim final regulations (IFR) were generally effective for group health for plan years beginning on or after July 1, 2010. MHPAEA requires that the financial requirements (such as coinsurance) and treatment limitations (such as visit limits) imposed on mental health (MH) and substance use disorder (SUD) benefits cannot be more restrictive than the predominant financial requirements and treatment limitations that apply to substantially all medical/surgical benefits. Additionally, non-quantitative treatment limits (medial management, step-therapy, utilization review, etc.) for MH/SUD benefits must be comparable to and applied no more stringently than non-quantitative treatments limits for medical/surgical benefits. MHPAEA does not require that a plan/insurer provide MH/SUD benefits, but if such benefits are provided, they must be provided in parity with medical/surgical benefits. The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) extended MHPAEA to the individual health insurance market. (ACA § 1563(c)(4) amends PHSA § 2726 to extend the Mental Health Parity rules – including the provisions of the MHPAEA – to generally apply to individual health insurance coverage.) The DOL, HHS and Treasury issued final MHPAEA regulations on November 8, 2013. BCBSNE implemented MHPAEA in conjunction with the IFR (and subsequent amendments thereto), and complies with all mental health parity requirements for all lines of business. 197 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Modifier-22 Modifier-22 indicates unusual procedural services. When the service(s) provided is greater than that usually required for the listed procedure, it may be identified by adding Modifier-22 to the usual procedure code. Claims submitted with Modifier-22 AND an explanation will be reviewed for special consideration. Modifiers and Modifier Usage Modifiers are two-digit numbers and/or letters attached to a HCPCS/CPT code when conditions are appropriate. Modifiers provide pertinent information necessary to process claims correctly. Modifiers add important information to the CPT code. The medical record must support the use of any modifier. Diagnosis Codes Must Support: • • Any modifier attached to the CPT code (i.e. -25 separate procedures) Any and all services billed on the claim form The appropriate code(s) must be used to identify diagnoses, symptoms, conditions, problems, complaints, or other reason(s) for the encounter/visit. For accurate reporting of diagnosis codes, the documentation should describe the patient’s condition, using terminology which includes specific diagnoses as well as symptoms, problems, or reasons for the encounter. Code the condition being treated and the underlying cause if known. Tips to Remember 1. Documentation should be complete and accurate before the claim is submitted. 2. Accurate documentation in the medical record facilities: - The ability of the physician and other health care professionals to evaluate and plan the patient’s immediate treatment, and to monitor his/her health care over time. - Communications and continuity of care among physicians and other health care professionals involved in the patient’s care. - Accurate and timely claims review and payment. 198 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents - An appropriate documented medical record can reduce frustration associated with claims processing and may serve as a legal document to verify the care provided if necessary. 3. All documentation in the medical record must be patient specific. Cloning of documentation which fails to take into account patient specific variations will be considered a misrepresentation of the medical necessity requirement for coverage of services. Neurofeedback Effective March 20, 2013, BCBSNE will consider neurofeedback as investigative and will no longer provide benefits for this service. NEtwork BLUE providers should notify members undergoing neurofeedback therapy prior to March 20, 2013 that this service will be their liability for dates of service March 20, 2013 and after. Neurofeedback is not the same as biofeedback and should not be billed under the biofeedback codes. If the only service provided is neurofeedback, you should bill 90899 and include the neurofeedback in the comments/remarks section. If neurofeedback and psychotherapy are provided during the same visit, you should bill 90899 and include neurofeedback and psychotherapy in the comments/remarks section. Pharmacologic Management (CPT Code: 90862) Pharmacologic management includes prescription, use, and review of medication with no more than minimal medical psychotherapy. When payable according to a patient’s coverage, BCBSNE allows benefits for this procedure once per day. This code is billed by an MD, DO, PA, APRN only. Provider Levels Verify benefits for members covered by other Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield Plans by calling BlueCard Eligibility® at 800-676-BLUE (2583). Level 1 Psychiatrist, Licensed Clinical Psychologist, Advanced Practice Registered Nurse, Physician Assistant Level 2 Special Licensed Psychologist, Licensed Mental Health Practitioner, Licensed Alcohol and Drug Counselor Level 3 Auxiliary Providers: Provisionally Licensed Mental Health Practitioners, Provisionally Licensed LPs, Provisionally Licensed Drug and Alcoholism Counselors, Certified Social Workers, Certified Masters Social Workers (without an LMHP license), Psychiatric Registered Nurse 199 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Psychiatric Psychiatric benefits and the certification of the health care professional who can provide them vary from one member/group contract to contract. Please contact Provider Service Department for information about a specific patient’s benefits. When verifying benefits with BCBSNE or any other BCBS Plan, you should ask about the member’s coverage and about any restrictions on the type of provider covered under the contract for these services. Psychiatric Diagnostic Interview (90791 [without medical evaluation] and 90792 [with medical evaluation]) Only Level I and LMHP’s with advanced training in diagnostic evaluations should bill 90791. All other providers should include an initial assessment as part of the first therapy session. Codes 90791 and 90792 are used for the diagnostic assessment(s) or reassessment(s), if required, and do not include psychotherapeutic services. Psychotherapy services including for crisis may not be reported on the same day. Report services as being provided to the patient and not the informant or other party. Codes 90791 and 90792 may be reported once per day and not on the same day as an evaluation and management service performed by the same individual for the same patient. Psychotherapy - insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive - in an office, home or outpatient setting (90833, 90834, 90836, 90837, and 90838) • • 90832 90833 • 90834 • 90836 Psychotherapy – 45 minutes with patient and/or family member when performed with an E & M • 90837 Psychotherapy – 60 minutes with patient and/or family member • 90838 Psychotherapy – 60 minutes with patient and/or family member when performed with an E & M • 90839 for Psychotherapy for crisis first 60 minutes and 90840 each additional 30 minutes. Psychotherapy – 30 minutes with patient and/or family member Psychotherapy – 30 minutes with patient and/or family member when performed with an E & M service Psychotherapy – 45 minutes with patient and/or family member Codes 90839 and 90840 are used to report the total duration of face-to-face with patient and/or family spent by the physician or other qualified health care professional providing psychotherapy for crisis, even if the time spent on that date is not continuous. The patient must be present for all or some of the visit. Do not report 90839 or 90840 in conjunction with 90791, 90792, psychotherapy codes 90832-90838 or other psychiatric services 90785-90899. 200 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Pharmacologic management includes prescription and review of medications when performed with psychotherapy services. Pharmacologic management can be billed with 90863 or the appropriate E & M code (99201-99238, 99304-99337, 99341-99350), using key components. Code 90863 can be billed in conjunction with 90832, 90834, or 90837. Code 90785 interactive complexity, is an add-on code that refers to specific communication factors that complicate the delivery of a psychiatric procedure. Common factors include more difficult communication with discordant or emotional family members and engagement of young and verbally undeveloped or impaired patients. Typical patients are those who have third parties, such as parents, guardians, other family members, interpreters, language translators, agencies, court offices, or schools involved in their care. Code 90785 interactive complexity can be reported with 90791, 90792, 90832, 90833, 90834, 90836, 90837, 90838, 90853, 99201-99238, 99304-99337, 99341-99350 when appropriate. Code 90785 interactive complexity cannot be reported with 90839, 90840, 90846, 90847, 90849 or in conjunction with an E & M service when no psychotherapy is also reported. Family Psychotherapy (90846 and 90847) Family Psychotherapy is billed under the patient’s name and diagnosis whether or not the patient is present. Units will always be one. Group Psychotherapy (90853) Services are billed for each member in the group. Psychological Testing (96101-96120) The testing codes reflect who does the testing: a psychologist, a technician or a computer. • 96101, for psychological testing, interpretation and reporting per hour by a psychologist. • 96102, for psychological testing per hour by a technician. • 96103, for psychological testing by a computer, including time for the psychologist’s interpretation and reporting. Neuropsychological testing is billed under: • 96118, for neuropsychological testing, interpretation and reporting per hour by a psychologist. • 96119, for neuropsychological testing per hour by a technician. • 96120, for neuropsychological testing by a computer, including time for the psychologist’s interpretation and reporting. The neurobehavioral status exam is coded as 96116. There is only a single code reflecting the psychologist’s work in administering the exam, which is typically not administered by a technician or a computer. Billing will be based on who administers the test and how long it takes. 201 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Testing conducted by psychologist is billed in hourly units, based on the number of hours spent administering the test and interpreting and reporting the results. If you go into the next hour, you may bill for the whole hour. Testing conducted by a technician is based on the number of hours the technician spends administering the test. When billing, it is important to note in the client’s record who administered the test and for how long. The following scenarios offer examples for how to bill under the testing codes. Billing Example 1: If a psychologist conducts five hours of psychological or neuropsychological testing and three hours of interpreting and reporting the test results, he or she would bill for eight units of the psychologist-based code. Billing Example 2: If a technician conducts two hours of testing and a psychologist conducts 3.5 hours of testing and 2.5 hours of interpretation and reporting, he or she would bill for two units of the technician-based code and six units of the psychologist-based code or two units of 96119 and six units of 96118. Billing Example 3: If a patient completes two hours of computerized testing and a psychologist conducts two hours of testing and one hour of interpretation and reporting, he or she would bill for the computer-based code (which is a single, flat-payment rate that is not measured in units) and three units of the psychologist-based code. Question: What type of testing work by a technician is billable under the new technician-based codes? Answer: The time a technician is with the patient, administering tests, or supervising the patient as he or she completes the tests, is considered billable under the technician-based code. The technician must be with the patient, face-to-face, during the testing in order for the psychologist to be able to bill for the time. Question: If a Provisionally Licensed Provider or an LMHP (who is also a Provisionally Licensed Psychologist) does the testing and interpretation and feedback, should they bill under 96101/96118 or 96102/96119? Answer: They would bill under 96102 or 96119 since they are not yet fully licensed Psychologists and so services therefore are considered done by a technician. 202 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Question: When is psychological testing reviewed? Answer: If more than four hours of psychological testing is billed in a calendar year, a letter of medical necessity and the records to support the additional psychological testing should be sent with the original claim. If the claim has already been submitted and the extra hours denied, then the denial can be appealed. The provider should submit a reconsideration form with a letter of medical necessity and the reason additional testing was needed. Psychologist (PhD) Inpatient Psychiatric Billing Only M.D’s may bill for psychiatric sessions while patient is inpatient. PhD’s cannot bill inpatient psychiatric sessions. Request for Medical Records The American Psychiatric Association recommends that the following information when documented by the treating therapist, not be disclosed to anyone other than the therapist who created the note, and should be kept separately from the rest of the treatment record: • • • • • • Intimate personal content of facts Details of fantasies and dreams Process interactions Sensitive information about other individuals in the patient’s life The therapist’s formulations, hypotheses, or speculations Topic/themes discussed in therapy sessions When BCBSNE requests medical records, do NOT submit the psychotherapy notes indicated above. Risk Factor Reduction Intervention and/or Counseling Counseling codes are denied according to our member contracts which exclude benefits for self-help or educational services. The only exception would be if the group has a special coverage endorsement for these services. School Conferences Attendance by a therapist at school conferences are not covered. Services should be billed under 90899 with “school conference” indicated. Place of Services listed would be “03.” School Place of Service (POS 03) BCBSNE member contracts no longer cover services provided in a school (Place of Service 03). Services will be considered member liability. School - Psychotherapy The appropriate psychotherapy code should be used along with a place of service 03 (school). 203 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 15 Quality Management BCBSNE maintains a Quality Management (QM) Program to support corporate objectives and strategies. Activities undertaken in support of the BCBSNE vision (“To be the catalyst for affordable, easy-to-navigate, high quality health care.”), and in compliance with regulatory requirements, are evaluated on a regular basis and reported annually to the Board of Directors. The Quality Improvement (QI) Department coordinates and facilitates the QM program including but not limited to: • • • • • • • URAC accreditation for Utilization Management and Case Management Services. Primary Blue patient–centered medical home Preventive Health and Wellness Consumer Safety and Transparency Clinical quality improvement activities Health care safety and quality Provider office standards for: - Office Facility - Medical Records Documentation - Appointment Availability and Access to care Programs are initiated and facilitated by the Quality Improvement Department to enhance care delivery, contribute to a positive member experience and create a collaborative atmosphere with the provider community with a goal of improving the care and services your patients, our members, receive. Accreditation The Case Management and Utilization Management programs at BCBSNE are fully accredited by URAC, which reviews our operations to ensure we are conducting business in a manner consistent with national standards. For more information on URAC and to view our approval status, please click on the link below or visit “Ratings and Accreditations,” in the “About” section of www.nebraskablue.com. http://www.nebraskablue.com/about/ratings-and-accreditations/ Primary Blue Medical Home Primary Blue is Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska’s patient centered medical home program. A patient centered medical home is a medical office or clinic where a team of health care professionals work together to provide a new and expanded type of patient care. Its primary mission is: • 204 To give the patient timely access to a personal primary care physician; Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • To establish a continuous relationship between the patient and a personal primary care physician; To have the majority of the patient’s health care needs met in one office; and To have the patient’s care coordinated and monitored in a proactive manner. BCBSNE believes the patient centered medical home can: • • • Improve the health of individuals; Increase patient satisfaction; and Reduce hospitalizations, emergency room visits, and decrease overall healthcare costs. Primary Blue focuses on chronic disease management (diabetes, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, hypertension, metabolic syndrome and asthma), as well as preventive services (BMI recording, colorectal cancer screening, breast cancer screening, cervical cancer screening, and immunizations). For more information about this program and an application to participate, contact your BCBSNE Health Network Consultant. Preventive Health and Wellness Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska’s BlueHealth Advantage consultative program helps employer groups with the tools and resources needed to implement a worksite wellness program that can improve employees health and productivity. All members have access to a health and wellness website (www.bluehealthadvantagene.com) that provides information to free and high quality health resources; such as the wellness newsletters, a health library, monthly health challenges and a variety of other tools and resources. Blue Distinction Centers (BDC) Blue Distinction is a national designation program which recognizes those facilities that demonstrate expertise in delivering quality specialty care safely, efficiently, and cost effectively. True to its original commitment as a quality-based program for specialty care, Blue Distinction has evolved to become a value-based designation awarded to facilities that meet stringent quality measures, focused on patient safety and outcomes, as well as cost of care criteria. Nebraska currently has facilities in all BDC specialty care categories, including Cardiac Care, Bariatric Surgery, Transplants, Rare and Complex Cancers, Spine Surgery and Knee/Hip Replacement. Consumer Safety and Transparency BCBSNE supports the focus on clinical performance and cost transparency for services and products provided to our members. This initiative is designed to enable members to actively participate in their health care decision making. The following tools have been developed and are displayed online as part of our customer transparency initiative. 205 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents National Consumer Cost Tool An interactive tool that helps consumers evaluate the cost of healthcare services and make informed decisions regarding their health care and related expenses. Blue Physician Recognition The Blue Physician Recognition program is designed to identify doctors, physician groups and/or practices who have demonstrated their commitment to delivering high quality, patient-centered care. This designation is determined by the local health plan based on participation and/ or achievement in collaborations and statewide or national programs. Physician Quality Measurement The Physician Quality Measurement initiative provides details on a physician’s performance on selected Healthcare Effectiveness Data Information Set (HEDIS) measures and helps consumers select a doctor or facility that best meets their needs. Patient Review of Physicians The Patient Review of Physicians is a resource for member feedback regarding overall experience with a physician following an encounter with the practitioner. This resource also helps other consumers select a physician that’s right for them. Complaint Investigation and Process The Quality Improvement (QI) Department tracks, trends, analyzes, investigates and facilitates resolution of complaints from members, providers, employer groups and brokers as well as internal sources. Investigation of these potential issues may involve: • Obtaining medical record documentation related to the concern. • Contacting the provider’s office directly to discuss service or access issues. • Soliciting additional information directly from the practitioner to supplement medical record findings. • Complaints related to the quality of care rendered to a member are reviewed by the BCBSNE Medical Director or designee to determine if a quality of care issue exists and its severity. Significant quality of care issues are presented for peer review at the BCBSNE Quality Management Committee comprised of practicing network physicians not employed by BCBSNE. Recommendations for further action, if appropriate, are determined by the committee. The QI complaint process enables tracking and trending of issues of concern and serves as a valuable tool for maintaining high quality provider networks as well as improving processes and services our members expect from their health plan. 206 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Office Standards Each provider office/facility shall maintain compliance with the facility standards in order to provide a safe and confidential environment that is conducive to the delivery of effective patient care for members as well as the protection of the office staff. These standards are based on the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) “Guidelines for Facility Review.” Facilities are reviewed when necessary against each applicable standard. For more information on these standards, go to www.nebraskablue.com/providers/credentialing/ Medical Records Standards Each physician office/facility shall maintain the medical records of members in a manner that is current, detailed, organized and permits effective and confidential patient care and quality review. The standards are based on the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) “Guidelines for Medical Records Review”. Each standard has a relative weight assigned to it. The standard and weight assignments have been approved by the BCBSNE Credentialing Committee and Quality Improvement Committee. For more information, go to www.nebraskablue.com/providers/credentialing/ Appointment Availability and Access Standards BCBSNE has established standards for access to care for in-network providers. Performance against these standards is assessed on a practice-specific and an organization-wide basis. Compliance to Appointment Availability/Access to Care Standards may be monitored as part the Quality Management Program. Member complaints and applicable member satisfaction survey results are also used by the plan to evaluate performance. For more information on the Office Standards, Medical Record Standards, and Appointment Availability/Access Standards, go to www.nebraskablue.com/providers/credentialing/ The Quality Management Program is an ongoing effort that may focus on a variety of opportunities for improvement as they become apparent through analysis. Communication and collaboration with providers in the BCBSNE networks, as well as professional and community organizations in Nebraska and nationally, contributes to the success of our program and demonstrates our commitment to high quality care and service in Nebraska and beyond. 207 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 16 Member Benefit Appeal, Network Termination and Appeal, and Provider Corrective Actions All BCBSNE contracts adhere to the applicable state and/or federal guidelines governing appeals. Appeals are performed by nurses and/or physicians who were not previously involved in the review or appeal process. When requesting an appeal, it is important to submit all relevant information that may assist in conducting the appeal. Expedited Appeal An expedited appeal is offered to the attending / ordering provider, patient/enrollee, and facility when a determination is made not to certify services and the situation meets the requirements for an expedited appeal as defined by BCBSNE. An expedited appeal is a request to review a second level reviewer (SLR) noncertification determination when the situation meets one or more of the following: a. The service is imminent or ongoing; or b. A delay in decision making might seriously jeopardize the life or health of the patient/enrollee or would jeopardize the member’s ability to regain maximum function. First Level of Appeal The first level of appeal may be expedited or nonexpedited, and should be submitted in writing. Providers are encouraged to use the Appeal/Reconsideration form found at www.nebraskablue.com by clicking on the “Providers” button and then on “Forms for Providers” in the left column. For most groups covered by BCBSNE, the time frame for requesting a first level appeal is six (6) months from the initial denial of benefits. The following information will assist the attending provider in requesting an appeal. A written request for an appeal can be faxed to 402-392-4111 or 800-991-7389; or it can be mailed to: Appeals Department Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska P.O. Box 3248 Omaha, NE 68180-0001 The laws and regulations governing appeals do not allow the plan to delay or postpone an appeal decision if additional information is requested but not received. For an expedited first level appeal, a determination will be made within 72 hours of the request for the appeal. If additional information was requested but not received, the appeal decision will be made based on the information available. For a non-expedited first level appeal, a decision will be made on either the 15th working day or 30th calendar day (depends upon the group’s contract) from receipt of the appeal request. 208 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents The attending provider will be notified of the appeal determination within 72 hours of the request for the appeal when care is expedited. Written notification of the appeal determination will be sent for expedited and non-expedited appeal determinations. Second Level of Appeal (if applicable) A second level of appeal is available when the first level of appeal results in a denial of benefits. Most groups covered by BCBSNE allow sixty (60) days from the first level appeal denial to request the second level appeal. There are different second level appeal processes. The denial of benefits letter following the first level of appeal will provide the necessary information and the process to use to request a second level of appeal. The second level appeal request must also be in writing. Additional information not included in the first appeal may be submitted. A written request for an appeal can be faxed to 402-392-4111 or 800-991-7389; or it can be mailed to: Appeals Department Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska P.O. Box 3248 Omaha, NE 68180-0001 If the second level appeal results in a denial of benefits, then the appeal process at BCBSNE has been exhausted and no further appeals are available. Denial Upheld on Appeal When a denial is upheld on first or second level appeal, the attending provider has the right to request in writing: • A copy of the rule, guideline, protocol, or other similar criterion that was relied upon in making the decision (if applicable); and • Either an explanation of the scientific or clinical judgment for the determination, applying the terms of the plan to the claimant’s medical circumstances (if the denial is based on medical necessity or experimental treatment or similar exclusion or limit). Network Termination and Appeals BCBSNE may terminate a contracted Provider from plan Provider networks, with or without cause, based on contract provisions of the Provider Agreement. BCBSNE may require termination of a Provider for purposes of this Agreement if such provider; a. submits a pattern of claims which willfully and intentionally misrepresents the services provided or the charge for such service, or demonstrates a pattern of fraud, waste, or abuse; b. no longer maintains the applicable unrestricted state or federal license; c. no longer provides services to patients within the State of Nebraska; d. is convicted of a felony or is expelled or suspended from the Medicare or Medicaid programs (Title XVIII or XIX of the Social Security Act). 209 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Subject to applicable laws, such Provider may be given an opportunity to enter into and complete a corrective plan of action, except in cases of fraud or imminent harm to patient health or when the Provider’s ability to provide services has been restricted by action, including probation or any compliance agreement, by the Nebraska Department of Health or other governmental agency before BCBSNE would terminate a physician or other health care professional. Appeal and Fair Hearing Process The notification of termination will contain the applicable reason(s) for the termination, the grounds upon which the adverse action is based, and any other relevant subject matter that was considered. When the reason for termination is appealable, the notification will inform the Provider that he/she shall have thirty (30) business days from receipt of such notice in which to submit a written request for a hearing. Within thirty (30) business days after receipt of a request for appeal, BCBSNE will furnish the Provider written notice of the date and time of the hearing, which will be at BCBSNE’s offices. The hearing will be held as soon as reasonable arrangement can be made, but not more than forty-five (45) business days from the date of receipt of the provider’s request for hearing, except at the Provider’s or Hearing Committee’s inability to participate within that time frame. In this case, the hearing will be held within ninety (90) business days of the request. Within fifteen (15) days after final adjournment of the hearing, the Hearing Committee shall make a decision. A majority vote is required to overturn the original adverse recommendation. A second level appeal is available only to participating Providers whose participation in the plan networks is being terminated for cause. The second level appeal must be made in writing, and requested within thirty (30) business days from receipt of the notice regarding the initial appeal hearing to request a second appeal. BCBSNE will furnish written notice of the date, time and place of the hearing within thirty (30) business days after receipt of a request for a second appeal. The hearing will be held as soon as reasonable arrangements can be made, but not more than forty-five (45) days from the date of receipt of the provider’s request for a second hearing, except at the provider’s or Hearing Committee’s inability to participate within that time frame. In this case, the hearing will be held within ninety (90) days of the request. Within fifteen (15) business days after final adjournment of the hearing, the Hearing Committee shall make a decision. A majority vote is required to overturn the original adverse recommendation. Note: In both the first and second appeal, the provider’s right to the hearing will be forfeited if the provider fails, without good cause, to appear at the scheduled hearing. Corrective Action Plan Prior to the effective date of any termination, the provider has the opportunity to enter into and complete a corrective action plan as determined by BCBSNE. 210 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Exception: There is no corrective action plan available for cases of fraud or imminent harm to patient health or when the provider’s ability to provide services has been restricted by an action, including probation or any compliance agreements, by the Department of Health or other governmental agency. Non-appealable Decisions Non-appealable issues include, but are not limited to: 1. Contracting issues: a. Lack of privileges at a contracting facility b. Lack of covering contracting practitioners c. Not participating in the organized delivery system or group model required by particular network d. No geographic need e. No need for particular specialty f. Change in practice affiliation or location 2. If the provider’s license to practice his/her profession is currently revoked, terminated, or suspended. 3. If the practitioner’s Federal DEA or CDC issued number is currently revoked or suspended (if it is required for practitioner’s profession). 4. If the provider’s professional liability insurance coverage does not meet the coverage requirements of BCBSNE. 5. Any material misrepresentation made by the provider during network participation. 6. Primary office location is not in Nebraska or contiguous county. 7. Lack of office facility, cessation of business or insolvency of the provider. 8. Denial of reapplication. Administrative Disputes All administrative disputes are received and tracked by the Provider Relations department. Administrative disputes with participating Providers include, but are not limited to, issues with the timely filing of claims, network accessibility and not submitting requested medical records. Providers have a right to consideration by an authorized representative of the organization, not involved in the initial decision that is the subject of the dispute. The authorized representative will notify the practitioner of any decisions or recommendations of follow up activities. Providers can contact Provider relations via email at Providersolutions@nebraskablue.com or via telephone at 402-982-7711 or 800 821 4787 opt. 4 with any questions, concerns, and/or complaints. Provider Corrective Actions BCBSNE gives Providers the opportunity to correct situations when administrative disputes, quality issues, utilization issues, or noncompliance with credentialing criteria/policies are identified. Quality issues, utilization issues and issues concerning noncompliance with credentialing criteria/policies are reported to the Quality Improvement Coordinator for investigation and reviewed by the Medical Director. In cases where the Medical Director has determined that circumstances place a patient/member in imminent harm, the Medical Director will take action to 211 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents prevent harm to members, including, but not limited to, temporary suspension of participation with BCBSNE as a contracting Provider. In the event the Committee does not have sufficient information to make a determination, the Committee may recommend the following actions: 1. The Medical Director send a written request for additional information from the practitioner(s); or 2. Additional administrative data be obtained regarding the practitioner(s), peer practitioners or member data to assess the general level of care or utilization; or 3. Arrange for outside consultant(s) to review the case and render an opinion; or 4. Any other action deemed appropriate by the Committee. Once the Committee has sufficient information and knowledge about the circumstances of the care/issue, they will make a determination that: 1. No (quality, utilization or credentialing dispute) issue exists and no action is required; or 2. An issue exists requiring corrective action. When an issue exists, the practitioner will be notified in writing explaining the findings of the Committee. The letter shall: 1. Notify the practitioner that he/she is being given 30 days to cure the deficiency(ies) cited as the reason for the action and that within 10 days of receipt of the letter, a response must be submitted to BCBSNE outlining an action plan which will result in correction of the identified deficiency(ies) within 30 days or as soon as reasonable; or 2. Ask the practitioner(s) to meet with the Medical Director or Committee to discuss the issue, or in the case of an administrative dispute, to meet with an authorized representative of BCBSNE that was not involved in the initial decision of the subject of the dispute; or 3. Request the practitioner(s) to provide documentation that a continuing education course related to the issue has been or will be taken; or 4. Identify any other action deemed appropriate by the Committee to resolve or correct the situation. The practitioner’s response and attempt to correct the situation will be evaluated by the Committee, or in the case of an administrative dispute, by the authorized representative of BCBSNE. If the corrective action is sufficient, the Committee or authorized representative will determine the next course of action to be taken, if any, which may involve a specified number of audits of the practitioner’s members for a specified time period, complete a study of the practitioner’s members that have a specified diagnosis and/or procedure, conduct an on-site office/facility and/or medical record review, monitor for a specified time for similar concerns or issues, or take any other action deemed appropriate by the Committee or authorized representative. The results of the follow-up action(s) will be reported back to the Committee or authorized representative who may: • Determine that acceptable improvement has been made and not further action or review is needed; 212 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • • • Continue monitoring the practitioner through audits or special studies; Recommend additional continuing education; or Recommend that the practitioner’s participation with BCBSNE managed care networks be terminated. The Medical Director will notify the practitioner of Committee decisions or recommendations for any follow up activities. When a determination is made to recommend a practitioner’s participation with BCBSNE be terminated, based on a quality, utilization or credentialing dispute, the practitioner will be given the right to appeal the decision. 213 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 17 Non-Covered Services BCBSNE member contracts do not provide benefits for the following Non-Covered Services or for amounts above Allowable Charges for Covered Services. BCBSNE does not restrict providers from reducing charges to members on non-covered services. BCBSNE Member contracts’ non-covered services include but are not limited to any Service for, or related to: 1) Services not covered by the member benefit contract. 2) Services determined by BCBSNE to be not medically necessary. 3) Services considered by BCBSNE to be Investigative, or for any directly related Services. 4) Voluntary, Investigative Test or Research 5) Screening audiological examinations and testing (except infant hearing exams); external and surgically implantable devices and combination external/implantable devices to improve hearing, including audiant bone conductors or hearing aids and their fitting. 6) Preventive vision examinations or care and screening eye examinations, including eye refractions, except as specifically covered in the member benefit contract. 7) Eyeglasses or contact lenses, eye exercises or visual training (orthoptics), except as specifically covered in the member benefit contract. 8) Services for or related to any surgical, laser or nonsurgical procedure or alteration of the refractive character of the cornea including, but not limited to, correction of myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism. Benefits for eye glasses and contact lenses are not available after this surgery. 9) Hospital or Physician charges for standby availability. 10) Personal expenses while hospitalized, such as guest meals, television rental and barber services. 11) Services, supplies, equipment, procedures, drugs or programs for the treatment of nicotine addiction, except as mandated by the Affordable Care Act. 12) Dietary counseling (i.e., eating disorder, nutrition therapy), except diabetes nutrition management. 13) Except as mandated by the Affordable Care Act, treatment and monitoring for obesity or weight reduction, regardless of diagnosis, including but not limited to surgical operations, weight loss 214 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents programs, health and athletic club memberships, physical conditioning programs such as athletic training, body-building exercise, fitness, flexibility and diversion or general motivation. 14) Services, except as otherwise covered in the member benefit contract, including related diagnostic testing, which are primarily: a) Recreational, such as music or art therapy. b) Educational. c) Work-hardening therapy; vocational training. d) Medical and nonmedical self-care. e) Self-help training. 15) Alternative therapies, including, but not limited to: a) Massage therapy, including rolfing; b) Acupuncture; c) Aromatherapy; d) Light therapy; e) Naturopathy; f) Vax-D therapy (vertebral axial decompression) 16) Treatment or removal of corns, callosities, or the cutting or trimming of nails. 17) Infertility treatment and related services, which includes, but is not limited to: a) Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART), such as artificial insemination, sperm washing, gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT), zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT), and in vitro fertilization; b) Embryo transfer procedures; c) Drug and/or hormonal therapy for fertility enhancement; d) Ultrasounds, lab work and other testing in conjunction with infertility treatment; e) Reversal of voluntary sterilization; f) Surrogate parenting, donor eggs, donor sperm and host uterus; and g) Storage and retrieval of all reproductive materials. Diagnostic testing done to determine the diagnosis of infertility, treatment of polycystic ovary disease, and treatment of endometriosis are not considered to be infertility treatment. 18) Services provided for, or related to, sex transformation surgery. 19) Interest and sales or other taxes or surcharges on Covered Services, drugs, supplies or Durable Medical Equipment, other than those surcharges or assessments made directly upon employers or third party payers. 20) Repairs, maintenance or adjustment of Durable Medical Equipment provided other than by a Durable Medical Equipment or a medical supply company. Repair or replacement of an item of Durable Medical Equipment will not be covered if damage occurred due to misuse, malicious damage, gross neglect or to replace lost or stolen items. 215 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 21) The following items of Durable Medical Equipment, even if prescribed by a Physician: a) Enuresis alarm; b) Non-wearable external defibrillator; c) Mouth guards. 22) Genetic Treatment or Engineering. Any service performed to alter or create changes in genetic structure. 23) Genetic testing, unless scientifically validated by BCBSNE medical policy. 24) Lodging or travel, even though prescribed by a Physician for the purpose of obtaining medical treatment. 25) Charges for any office or facility overhead expenses including, but not limited to, staff charges, copying fees, facsimile fees and office supplies. 26) Custodial care, domiciliary care, rest cures, or services provided by personal care attendants. 27) Charges for failure to cancel a scheduled appointment. 28) Nutrition care, nutritional supplements, FDA-Exempt infant formulas, supplies or other nutritional substances, including but not limited to Neocate, Vivonex and other over-the-counter nutritional substances. 29) Enteral feedings, even if the sole source of nutrition. 30) Equipment for purifying, heating, cooling or otherwise treating air or water. 31) The building, remodeling or alteration of a residence; the purchasing or customizing of vans or other vehicles. 32) Exercise equipment. 33) Orthopedic shoes; orthotics for the feet; except when such podiatric appliances are necessary for the prevention of complications associated with diabetes, or when necessary to treat a congenital anomaly, as determined by BCBSNE. 34) Food antigens and/or sublingual therapy. 35) Services, drugs, medical supplies, devices or equipment which are not cost effective compared to established alternatives or which are provided for the convenience or personal use of the Covered Person. 36) The reduction or elimination of snoring, when that is the primary purpose of treatment. 216 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 37) Automated external defibrillator. 38) Calls or consults by telephone or other electronic means, video or Internet transmissions and telemedicine, except in conformance with BCBSNE policies and procedures. 39) Blood, blood plasma or blood derivatives or fractionates, or Services by or for blood donors, except administrative and processing charges for blood used for a Covered Person furnished to a Hospital by the American Red Cross, county blood bank, or other organization that does not charge for blood. 40) Cosmetic Services, or any routine complications thereof, except for Covered Services: a) Required as a result of a traumatic Injury; b) To correct a congenital abnormality of a Covered Person, only when the defect severely impairs or impedes normal essential functions; c) To correct a scar or deformity resulting from cancer or from noncosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery is available only when required to restore, reconstruct or correct any bodily function that was lost, impaired or damaged as a result of Injury or Illness. Except as stated above, this exclusion applies regardless of the underlying cause of the condition or any expectation that the cosmetic procedure may be psychologically or developmentally beneficial to the patient. Procedures for liposuction, telangiectasias, dermabrasion, protruding ears and spider veins are examples of excluded Services. Benefits for treatment of complications are payable, only if such treatment is normally covered under this Contract. 41) Services considered to be obsolete or for any related Services. Procedures will be considered to be obsolete when such procedures have been superseded by more efficacious treatment procedures and are generally no longer considered effective in clinical medicine. 42) Wigs, hair prostheses and hair transplants, regardless of the reason for the hair loss. 43) Hair analysis, including evaluation of alopecia or age-related hair loss. 44) Massage therapy provided by a massage therapist. 45) Acupuncture. 46) Electron beam computed tomography for vascular screening, including but not limited to screening for cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and peripheral vascular disease. 47) Autopsies are non-covered. No charges after the person dies are covered. 48) Private Duty Nursing. 49) Respite care when not provided as part of a covered Hospice benefit. 217 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 50) The following Services related to home health aide, Skilled Nursing Care, or Hospice Services: a) Services performed by volunteers; b) Pastoral Services, or legal or financial counseling services; c) Services primarily for the convenience of the patient, or a person other than the patient; d) Home delivered meals. 51) Shipping and Handling charges. 52) Services provided at the following places of service, not including Covered Services provided at a health fair approved by BCBSNE: a) Daycare; b) School; c) Library; or d) Church. 53) Supplies, equipment and similar incidental Services for personal comfort, including, but not limited to: a) Batteries and battery chargers, unless the device is covered by BCBSNE; b) Hot tubs; c) Humidifiers; d) Jacuzzis; e) Medical alert systems; f) Music devices; g) Personal computers; h) Pillows; i) Radios; j) Saunas; k) Strollers; l) Safety equipment; m) Video players; n) Whirlpools. 54) Services otherwise covered under the member benefit contract, when: a) Required solely for the purpose of camp, travel, career, employment, insurance, marriage or adoption; b) Related to judicial or administrative proceedings or orders; c) Conducted for the purpose of medical research; d) Required to obtain or maintain a license of any type; e) Foreign language and sign language services; f) Driving tests or exams. 218 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents In addition, the following are not covered under the Rx Nebraska: 1) Diet or appetite suppressant drugs. 2) Nutrition care, nutritional supplements, FDA-Exempt infant formulas, supplies or other nutritional substances, including but not limited to Neocate, Vivonex and other over-the-counter nutritional substances. 3) Drugs or medicinals for treatment of fertility/infertility. 4) Cosmetic alteration drugs, including but not limited to health and beauty aids such as Vaniqa, Propecia and Renova. 5) Home infusion therapy. (Covered under Other Covered Services only.) 6) Home Medical Equipment or devices of any type, including, but not limited to: contraceptive devices; therapeutic devices; or artificial appliances. 7) Investigative drugs or drugs classified by the FDA as experimental. 8) Prescription medications used to treat nicotine addiction. 9) Non-prescription medications. 10) Over-the-counter medications. 11) Prescription medications determined to be “less than effective” by the Drug Efficacy Study Implementation Program (DESI). 12) Supplies other than ostomy designated injectable, diabetic and insulin pump supplies. 13) Services, drugs and medical supplies which are not cost effective compared to established alternatives or which are provided for the convenience or personal use of the Covered Person. 14) Prescription medications purchased in a foreign country. Exception: If the covered person is living in another country, or has an emergency medical condition while traveling in that country, evidence of residency or an emergency medical condition must be provided with the claim, or the claim will be denied. This evidence may be reviewed by BCBSNE. Foreign drug policy is subject to change with changes in federal legislation regarding importation. Mental Health Benefit Exclusions 1) Mental health services, psychological or substance abuse counseling services which are not within the scope of practice of the provider or services provided by one of the following: a) Qualified Physician or Licensed Psychologist. 219 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents b) Licensed Special Psychologist, Licensed Clinical Social Worker, Licensed Professional Counselor or Licensed Mental Health Practitioner. c) Auxiliary Providers who are supervised and billed for by a professional provider listed at a), or as otherwise permitted by state law. All Licensing or Certification shall be by the appropriate state authority. Supervision and consultation requirements shall be governed by state law. 2) Programs for co-dependency; employee assistance; probation; prevention; educational or self-help. 3) Programs that treat obesity, gambling, or nicotine addiction, except as mandated by the Affordable Care Act. 4) Residential Treatment Programs for Mental Illness. 5) Residential Treatment Programs, halfway house or methadone maintenance programs that treat Substance Abuse. 6) Programs ordered by the Court determined by BCBSNE to be not Medically Necessary. Services Provided 1) Services provided to or for: a) Any dependent of a Subscriber who has a Single Membership, except as specified in this Contract for newborn or adopted children. b) Any person who does not qualify as an Eligible Dependent. c) Any Covered Person before his or her effective date of coverage, or after the effective date of cancellation or termination of coverage. d) Any Covered Person for any Pre-existing Condition for which coverage is not available because of any Contract Waiting Periods. 2) Services for Illness or Injury related to military service. 3) Non-approved Facility: A health care facility that does not meet the Licensing or Accreditation Standards required by BCBSNE. 4) Services provided in or by: a) A Veterans Administration Hospital where the care is for a condition related to military service; or b) Any non-Participating Hospital or other institution which is owned, operated or controlled by any federal government agency, except where care is provided to non-active duty Covered Persons in medical facilities. 220 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents 5) Services required by an Employer as a condition of employment including, but not limited to immunizations, blood testing, work physicals and drug tests. 6) Services for any Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant or Autologous Bone Marrow Transplants. Charges for Services 1) Interest and sales or other taxes or surcharges on Covered Services, drugs, supplies or Home Medical Equipment, other than those surcharges or assessments made directly upon employers or third party payors. 2) Charges made while the patient is temporarily out of the Hospital. 3) Charges made for filling out claim forms or furnishing any records or information or special charges such as dispensing fees, admission charges, Physician’s charge for Hospital discharge services, after-hours charges over and above the routine charge, administrative fees, technical support or utilization review charges which are normally considered to be within the charge for a service. 4) Charges received when there is inadequate documentation that a service was provided. 5) Services available at government expense, except as follows: If payment is required by state or federal law, the obligation to provide benefits will be reduced by the amount of payments a Covered Person is eligible for under such program (except Medicaid). With respect to persons entitled to Medicare Part A and eligible for Part B benefits, the obligation to provide benefits will be reduced by the amount of payment or benefits such person receives from Medicare. This provision will not apply if the Covered Person is still actively at work or is an Eligible Dependent of a Subscriber who is actively at work and has elected this Contract as primary, unless otherwise provided by federal law. Services provided for renal dialysis and kidney transplant Services also will be provided pursuant to federal law. 6) Services for which there is no legal obligation to pay, include: a) Recreational, such as music or art therapy. b) Educational. c) Work-hardening therapy; vocational training. d) Medical and nonmedical self-care. e) Self-help training. f) Services for which no charge would be made if this coverage did not exist. g) Any charge above the charge that would have been made if no coverage existed. h) Any service which is primarily furnished without charge. 7) Services arising out of or in the course of employment, whether or not the Covered Person fails to assert or waives his or her rights to Workers’ Compensation or Employers’ Liability Law. This 221 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents includes Services determined to be work-related under Workers’ Compensation laws, or under a Workers’ Compensation Managed Care Plan, but which are not payable because of noncompliance with such law or Plan. 8) Charges for Services provided by a person who is a member of the Covered Person’s immediate family by blood, marriage or adoption. 9) Charges for Services by a health care provider which are not within the scope of practice of such provider; or charges by a non-Approved Provider. 10) Charges in excess of the Contracted Amount or the Reasonable Allowance. 11) Charges made separately for Services when they are considered to be included within the charge for a total Service payable under this Contract or if the charge is payable to another provider. EXCEPTION: If such charges are made separately when they are considered to be included within the charge for a total service performed by a BCBSNE NEtwork BLUE provider, then this amount is not the Covered Person’s liability. 12) Charges made pursuant to a Covered Person’s engagement in an illegal occupation or his or her commission of or attempt to commit a felony. 222 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 18 Definitions, Terms and Abbreviations These definitions, terms and abbreviations are useful in understanding the structure, organization and language of BCBSNE benefit plans and administrative functions. Admission Review: Admission Review is the review of the Medical Necessity and appropriateness of non-elective or emergency Hospital admissions. The review takes place within 24 hours of admission or the next working day. Affiliate: A corporation at least 51% owned by BCBSNE, which is entitled to the rights and bound by the obligations of this Agreement. Agreement: A document, all attachments, and exhibits, any applicable applications, applicable Reimbursement Schedules, the Policies and Procedures Manual, and such other documents and modifications as made pursuant to the Agreement, signed by the Network Provider and BCBSNE which outlines the terms that each party agrees to abide. Alcoholism or Drug Treatment Center (Treatment Center): A facility licensed by the Department of Health and Human Services Regulation and Licensure, whose program is certified by the Division of Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Addiction Services (or equivalent state agency), accredited by the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) or the Commission on the Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities (CARF). Such facility is not licensed as a hospital, but provides Inpatient or Outpatient care, treatment, services, maintenance, accommodation or board in a group setting primarily and exclusively for individuals having any type of dependency or addiction to the use of alcohol or drugs. Allowable Charge: Payment is based on the Allowable Charge for Covered Services. • Inpatient Contracting Hospital or other Institutional Facility: The Allowable Charge for Covered Services provided by a Contracting institutional facility is the Contracted Amount for such Services. • Outpatient Contracting Hospital and other Institutional Provider: The Allowable Charge for Covered Services provided by an Outpatient Contracting institutional facility is the lesser of the Contracted Amount or the billed charge. • Contracting Professional and other Noninstitutional Preferred Providers: The Allowable Charge for a Covered Service provided by a professional or other noninstitutional Preferred Provider is the lesser of the Preferred Fee Schedule Amount or the billed charge. The Allowable Charge for Covered Services in another Service Area is the amount agreed upon by the Onsite Plan and its Participating Providers. 223 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Alpha Prefix: The three characters preceding the subscriber identification number on Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield Plan ID cards. The alpha prefix identifies the member’s Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield Plan or national account and is required for routing claims. Ambulatory Surgical Facility: A certified facility which provides surgical treatment to patients not requiring inpatient hospitalization. Such facility must be licensed as a health clinic as defined by state statutes, but shall not include the offices of private physicians or dentists, whether for individual or group practice. Approved Provider: A licensed practitioner of the healing arts who provides Covered Services within the scope of his or her license or a licensed or certified facility or other health care provider, payable according to the terms of the member/subscriber contract, Nebraska law or the direction of the Board of Directors of BCBSNE. Auxiliary Provider: A certified physician assistant, nurse practitioner, nurse midwife, social worker, psychiatric registered nurse or other Approved Provider who is performing services within his or her scope of practice and who is supervised by a qualified Physician or licensed psychologist, or as otherwise permitted by state law. Certified master social workers or certified professional counselors performing Mental Health Services who are not Licensed Mental Health Practitioners are included in this definition. BCBSNE: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska. Benefit Maximum: Amount of total dollars or total days of care beyond which a policy will no longer pay benefits. When a service is billed after a benefit max has been met, the provider can collect the billed charge. However, if there is a service in which there is an amount remaining after a benefit max is applied, then the provider can only collect up to the allowed amount for the service. Benefit Period: A continuous period which starts with the first day a Covered Person is confined in an acute care Hospital, acute rehabilitation facility, mental health facility, Alcoholism or Drug Treatment Center or Skilled Nursing Facility. It ends when the Covered Person has not been in such a facility for sixty (60) days in a row. It includes the day of admission, but not the day of discharge. (Applicable only to Base Major Medical Contracts.) Bereavement Counseling: Treatment that is goal oriented in assisting the Covered Person to effectively cope with the loss of a family member. Bereavement Counseling must be performed by a counselor that is affiliated with a participating Hospice within six (6) months after the death of a Covered Person who had received Hospice care. BlueCard Access® 1.800.810.BLUE: A toll-free 800 number for you and members to use to locate healthcare providers in another Blue Plan’s area. This number is useful when you need to refer the patient to a physician or healthcare facility in another location. BlueCard Eligibility® 800-676-BLUE (2583): A toll-free 800 number for you to verify membership and coverage information, and obtain pre-certification on patients from other Blue Plans. 224 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents BlueCard PPO: A national program that offers members traveling or living outside of their Blue Plan’s area the PPO level of benefits when they obtain services from a physician or hospital designated as a BlueCard PPO provider. BlueCard PPO Member: Carries an ID card with this identifier on it. Only members with this identifier can access the benefits of the BlueCard PPO. BlueCard Program: This Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association (“BCBSA”) out-of-area or reciprocal programs allowing claims to be covered by another Licensed Blue Cross and Blue Shield Plan (“Blue Plan”) to permit the submission of claims for payment to BCBSNE for BCBSNE’s coordination with the appropriate Blue Plan in adjudicating the claim according to the covered person’s Contract. The provisions of this agreement shall apply, including provisions related to charges for Covered Services, under the Blue Cross and Blue Shield out-of-area and reciprocal programs. Provider shall accept reimbursement by BCBSNE as payment in full for Covered Services provided to such Covered Persons except to the extent of Deductibles, Coinsurance, Copayments, and/or Charges associated with non-covered services. BlueCard Worldwide®: A program that allows Blue members traveling or living abroad to receive nearly cashless access to covered inpatient hospital care, as well as access to outpatient hospital care and professional services from healthcare providers worldwide. The program also allows members of foreign Blue Cross and/or Blue Plans to access domestic (United States) Blue provider networks. Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association: National Association of Independent Blue Cross and Blue Shield Plans; the organization which works to coordinate the efforts of onsite Blue Cross and Blue Shield Plans at the national level. CMS: Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services are a branch of the Department of Health and Human Services which issues rules and regulations for the Medicare program. CMS 1500: The form originally developed by the Health Care Financing Association for submitting Medicare Part B claims. Other third party payors also use the form. CMS1500 12-90 is the most recent revision of the form and is the paper claim format requested by BCBSNE. CPT - Current Procedural Terminology: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) is a book published and updated by the American Medical Association. This book lists descriptive terms and identifying codes for reporting medical services. The procedure code that best describes the services provided is required on claims. Cardiac Rehabilitation: Use of various modalities of treatment to improve cardiac function as well as tissue perfusion and oxygenation through which selected patients are restored to and maintained at either a pre-illness level of activity or a new and appropriate level of adjustment. 225 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Case Management: The organized effort to identify hospitalized patients whose care may be high-cost, lengthy, and/or have complicated discharge planning needs; to locate and assess medically appropriate alternative settings for these patients; and to manage their health care benefits as cost-effectively as possible. Certification (Certified): Successful voluntary compliance with certain prerequisite qualifications specified by regulatory entities. Agencies and programs may be deemed to be in compliance when they are accredited by the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health care Organizations (JCAHO), the Commission on the Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities (CARF), American Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC), American Association for Accreditation of Ambulatory Plastic Surgery Facilities (AAAAPSF), Medicare or as otherwise provided in the Contract provisions or state law. Charges: The amount per service or supply regularly established by the Provider which is billed to the general patient population. Clean Claim: A claim for payment of health care services provided to a Covered Person by a Provider on a UB04 or CMS 1500 (or successor forms) or an equivalent electronic form that is submitted in compliance with BCBSNE's Policies and Procedures, with all required fields completed and with all information necessary to adjudicate the claim. Cognitive Training: A rehabilitative intervention aimed at retraining or facilitating the recovery of mental and information processing skills including perception, problem-solving, memory storage and retrieval, language organization and expression. Coinsurance: The percentage of the allowable charge which the Covered Person must pay after the Deductible has been satisfied, and based on the applicable Contract. Concurrent Review: The review of an ongoing inpatient hospitalization to assure that it remains the most appropriate setting for the care being rendered. NEtwork BLUE hospitals and physicians are encouraged to obtain extensions in benefits beyond precertification through the Concurrent Review program. If we have been advised of the admission, we will contact the hospital, treatment center or the physician to determine the treatment plan. Onsite concurrent review may be performed when necessary. Congenital Abnormality: A condition existing at birth which is outside the broad range of normal, such as cleft palate, birthmarks, webbed fingers or toes. Normal variations in size and shape of the organ, such as protruding ears, are not considered a Congenital Abnormality. Consultations: Physician services by providers with different specialties or subspecialties for a patient in need of specialized care requested by the attending physician who does not have that expertise or knowledge. Consumer-Directed Healthcare/Health Plans (CDHC/CDHP): Consumer Directed Healthcare (CDHC) is a broad umbrella term that refers to a movement in the healthcare industry to empower 226 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents members, reduce employer costs, and change consumer healthcare purchasing behavior. CDHC provides the member with additional information to make an informed and appropriate healthcare decision through the use of member support tools, provider and network information, and financial incentives. Content Of Service: Refers to specific services and/or procedures, supplies and materials that are considered by BCBSNE to be an integral part of previous or concomitant services or procedures, or all inclusive, to the extent that separate reimbursement is not recognized by BCBSNE. Contract: An insurance contract or administrative services agreement outlining the Covered Services, benefits allowed for those Covered Services, and other related topics. The Contract includes any endorsements, the Master Group Application, subgroup applications, addenda and individual enrollment forms of subscribers, and any health plan documents designated or qualified as such under applicable federal or state law. Contracted Amount: The payment mutually agreed to by BCBSNE and Provider for services and supplies received by a Covered Person. Coordination Of Benefits (COB): Ensures that members receive full benefits and prevents double payment for services when a member has coverage from two or more sources. The member’s contract language gives the order for which entity has primary responsibility for payment and which entity has secondary responsibility for payment. Copayment: The fixed dollar amount payable by the Covered Person for the Covered Services identified in the applicable Contract and/or Master Group Application. Cosmetic: Any services provided to improve the patient’s physical appearance, from which no significant improvement in physiologic function can be expected, regardless of emotional or psychological factors. Covered Charge: That part of a charge for which benefits would be provided under the terms of the Contract except for any Coinsurance and Deductible amount. Covered Person: Any person entitled to benefits at the time services are rendered for Covered Services pursuant to a Contract underwritten or administered by BCBSNE, including but not limited to: NEtwork BLUE, Federal Employees Health Benefit Program (“FEP”), or any other member contract that is part of the Blue Card Program. Covered Services: Hospital, medical or surgical procedures, treatments, drugs, supplies, home medical equipment or other health, mental health, substance use disorder or dental care, including any single service or combination of services, provided to Covered Persons for which benefits are payable under the terms of a Contract underwritten or administered by BCBSNE pursuant to all applicable state and federal laws, including but not limited to, if applicable, federal mental health parity laws. 227 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Crisis Care: Skilled Nursing Care provided at the home of the Covered Person for up to 24 hours per day. Benefits for such care are provided in lieu of a Medically Necessary inpatient hospitalization. Custodial Care: The level of care that consists primarily of assisting with the activities of daily living such as bathing, continence, dressing, transferring and eating. The purpose of such care is to maintain and support the existing level of care and preserve health from further decline. Care given to a patient who: • Is mentally or physically disabled; and • Needs a protected, monitored or controlled environment or assistance to support the basics of daily living, in an institution or at home; and • Is not under active and specific medical, surgical or psychiatric treatment which will reduce the disability to the extent necessary to allow the patient to function outside such environment or without such assistance, within a reasonable time, which will not exceed one year in any event. A custodial care determination many still be made if the care is ordered by a Physician or Services are being administered by a registered or Licensed practical nurse. Deductible: An amount which the Covered Person must pay each calendar year for Covered Services before benefits are payable based on the applicable Contract. Diagnosis Admission: Hospitalization for the purpose of performing tests and examinations without administering any active treatment. Diagnosis Code: Specific description for the reason a person is seeking medical care. ICD-9-CM is the appropriate coding method to describe the reason for the encounter. Discharge Planning: Discharge Planning is the process of assessing a Covered Person’s need for medically appropriate and timely discharge. The Hospital and the attending Physician have major responsibility for this function. Blue Cross and Blue Shield Case Management promotes and assists the Hospital discharge planners. Eligibility Waiting Period: Applicable to new Members only, the period between the first day of employment and the first date of coverage under the group or individual applicant Contract. Eligible Dependent: 1. The spouse of the Subscriber unless the marriage has been ended by a legal, effective decree of dissolution, divorce or separation. 2. Children to age 26. 228 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents "Children" means: the Subscriber's biological and adopted sons and daughters, a grandchild who lives with the Subscriber in a regular child-parent relationship where the grandchild receives no support or maintenance from the parent and where the Subscriber is a court-appointed guardian of the grandchild, a stepchild (i.e. the son or daughter of the Subscriber’s current spouse), or a child, other than a grandchild or stepchild, for whom the Subscriber is a court-appointed guardian, but does not include a foster child. Reaching age 26 will not end the covered child's coverage under the benefit Contract as long as the child is, and remains, both: a. incapable of self-sustaining employment, or of returning to school as a full-time student, by reason of mental or physical handicap, and b. dependent upon the Subscriber for support and maintenance. Proof of the requirements of paragraphs a. and b. from the Subscriber must be received within thirty-one (31) days of the child's reaching age 26 and after that, as required (but not more often than yearly after two years of such handicap). Determination of eligibility under this provision will be made by BCBSNE. Any extended coverage under this paragraph will be subject to all other provisions of the member’s benefit Contract. Emergency Medical Condition: A medical or behavioral condition, the onset of which is sudden, that manifests itself by symptoms of sufficient severity, including, but not limited to, severe pain, that a prudent layperson, possessing an average knowledge of medicine and health, could reasonably expect the absence of immediate medical attention to result in: • • • • Placing the health of the person afflicted with such condition in serious jeopardy or, in the case of a behavioral condition, placing the health of such persons or others in serious jeopardy; Serious impairment to such person's bodily functions; Serious impairment of any bodily organ or part of such person; or Serious disfigurement of such person. Employee: An individual hired by an Employer or an association who enrolls for health coverage under this Contract, and is named on an identification card issued pursuant to this Contract. Enrolled employee is referred to as a Member. Employee/Spouse Membership: This option provides benefits for covered services provided to the employee / member and his or her spouse. Enrolled employee / member is referred to as a Member. Employer: A Group Applicant who signs a master group application for health coverage on behalf of its Employees. 229 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Endorsement: A provision which expands or modifies a contract. EPO: An Exclusive Provider Organization or EPO is a health benefits program in which the Member receives no benefits for care obtained outside the network except emergency care and does not include a Primary Care Physician selection. EPO benefit coverage may be delivered via BlueCard PPO and is restricted to services provided by BlueCard PPO providers. Exclusion: A provision in the Covered Person’s Contract stating situations or conditions for which there is no coverage. Explanation Of Benefits (EOB): The BCBSNE notice which informs the Covered Person of the benefits allowed on a specific claim. The EOB reports a breakdown of charges, our payment, and the Covered Person’s liability; Coinsurance, Deductible, and Non-covered amounts. Explanation Of Medicare Benefits (EOMB): A notice sent to the Medicare beneficiary explaining the Medicare payment. Family Membership: Membership option providing benefits for Covered Services provided to the Member and his or her Eligible Dependents. Federal Employee Program (FEP): The largest nationally underwritten group covering employees of the federal government and their dependents. FEP members have an identification number that starts with the single alpha prefix “R.” GABBI (Greater Access To Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Nebraska): The voice response service for health care professionals who need to obtain benefit eligibility information or claim status. Call 800-635-0579. Hours are 7 a.m. - midnight, Monday - Friday and 7 a.m. - 1 p.m. on Saturday. You will need your NPI, cardholder’s name and ID number, the patient’s date of birth and the dates of service. Group Applicant: The Employer or association making application for health coverage under a contract. HCFA (Health Care Financing Administration): Health Care Financing Administration is a branch of the Department of Health and Human Services which issues rules and regulations for the Medicare program. HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System): Medicare’s National Level II codes – the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System is a 5-digit alpha-numeric code. This system of coding is an expansion of the CPT coding structure and includes coding for ambulance, Home Medical Equipment, injectibles, etc., which are not available with CPT coding. Health Care Programs: Insurance underwritten or health care administrative services provided by BCBSNE, other Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans, or other Blue Card Programs. 230 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): An entity or organized system of health care that provides, offers or arranges for coverage of designated health care services to a voluntarily enrolled population in a geographic area for a fixed, prepaid premium. Hold Harmless: An agreement with a healthcare provider not to bill the member for any difference between billed charges for covered services (excluding coinsurance) and the amount the healthcare provider has contractually agreed on with a Blue Plan as full payment for these services. Home Health Aide Services: Medically Necessary personal care services provided by a licensed or Medicare certified home health agency to a Covered Person that relate to the treatment of his or her medical condition. Such services must be ordered by a Physician, and performed under the supervision of a registered nurse. Such services include, but are not limited to, bathing, feeding, and performing household cleaning duties directly related to the Covered Person. Home Infusion Therapy: Medically Necessary Covered Services and supplies required for administration of a Home Infusion Therapy regimen when ordered by a Physician. Home (Durable) Medical Equipment (HME): Equipment and supplies medically necessary to treat an Illness or Injury, to improve the functioning of a malformed body member, or to prevent further deterioration of the patient’s medical condition. Such equipment and supplies must be designed and used primarily to treat conditions which are medical in nature, and able to withstand repeated use. Home medical equipment includes such items as prosthetic devices, orthopedic braces, crutches and wheelchairs. It does not include sporting or athletic equipment or items purchased for the convenience of the family. Homebound: An individual will be considered to be essentially homebound if he or she has a condition due to an illness or injury which considerably restricts the ability to leave his or her residence without the aid of supportive devices, the use of special transportation or the assistance of another person. The patient who does leave the residence may still be considered homebound if the absences from the place of residence are infrequent or for periods of relatively short duration and attributable to the need to receive medical treatment that cannot be provided in the home. Hospice: Hospice care is a program of care for person diagnosed as terminally ill, and their families. Hospice services include: • Home Health Aide Services; • Hospice Nursing Services provided in the home; • Respite Care; • Medical Social Services; • Crisis Care; and • Bereavement Counseling. Hospital: An institution or facility duly licensed by the State of Nebraska or the state in which it is located, which provides medical, surgical, diagnostic and/or treatment services with 24-hour per day nursing services to two or more nonrelated persons with an illness, injury, or pregnancy, under the supervision of a staff of physicians licensed to practice medicine and surgery. 231 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Illness: A condition which deviates from or disrupts normal bodily functions or body tissues in an abnormal way, and is manifested by a characteristic set of signs or symptoms. Injury: Physical harm or damage inflicted to the body from an external force. Inlier Rate: Base reimbursement amount for a DRG. When Covered Charges are less than Inlier Rate, the reimbursement is the Inlier Rate. Inpatient: A patient admitted to a Hospital or other institutional facility for bed occupancy to receive acute care services consisting of active medical and nursing care to treat conditions requiring continuous nursing intervention of such an intensity that it cannot be safely or effectively provided in any other setting. Inpatient Stay: The period from entry (admission) into an acute care Hospital, acute rehabilitation, mental health facility, skilled nursing facility, or alcoholism or drug treatment center until discharge from that facility. International Classification Of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM): ICD-9-CM is a comprehensive list of diagnosis codes and narrative. ICD-9-CM is based on the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision; Clinical Modification codes and instructions; as well as Medicare regulations and manuals issued by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and by the Health Care Financing Administration (HCFA). Diagnosis is required on claims submitted to BCBSNE. Investigative: A technology, a drug, biological product, device, diagnostic, treatment or procedure is investigative if it has not been Scientifically Validated pursuant to all of the factors set forth below: • Technologies, drugs, biological products, devices and diagnostics must have final approval from the appropriate government regulatory bodies. A drug or biological product must have final approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). A device must have final approval from FDA for those specific indications and methods of use that are being evaluated. FDA or other governmental approval is only one of the factors necessary to determine Scientific Validity. • Evidence must permit conclusions concerning the effect of the technology on health outcomes. The evidence should consist of well-designed and well-conducted investigations published in peer-reviewed journals. The quality of the body of studies and the consistency of the results are considered in evaluating the evidence. • The evidence should demonstrate that the technology can measure or alter the physiological changes related to a disease, injury, illness or condition. In addition there should be evidence based on established medical facts that such measurement or alteration improves the health outcomes. 232 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • Opinions and evaluations by national medical associations, consensus panels or other technology evaluation bodies are evaluated according to the scientific quality of the supporting evidence and rationale. Our evidence includes, but is not limited to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Technology Evaluation Center technology evaluations; Hayes Directory of New Medical Technologies' Status; Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Technology Assessments, and United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals. • The technology must improve the net health outcome. • The technology must improve the net health outcome as much as or more than established alternatives. • The improvement must be attainable outside the investigational settings. BCBSNE, or the applicable Blue Plan, will determine whether a technology is Investigative or not Scientifically Validated. BCBSNE shall post those technologies that it has previously determined to be Investigative or Not Scientifically Validated and shall make such determinations available on its website. The absence of a medical policy on a particular matter shall not prohibit BCBSNE or the applicable Blue Plan from concluding that a matter is or is not Investigative or Not Scientifically Validated. Licensure: Permission to engage in a health profession which would otherwise be unlawful in the state where services are performed, and which is granted to individuals who meet prerequisite qualifications. Licensure protects a given scope of practice and the title. Managed Care: A system of health care delivery that influences utilization and cost of services and measures performance. The goal is a system that delivers value by giving access to quality, cost-effective health care. Master Group Application (MGA): A document reflecting the terms of a member’s Contract and/or administrative services agreement outlining the Covered Services, benefits allowed for those Covered Services, and other related topics. The Master Group Application includes the Contract, any endorsements, subgroup applications, addenda and individual enrollment forms of subscribers. Maximum Benefit Amount (MBA): The MBA will be the Contracted Amount agreed upon between BCBSNE Provider for the Covered Service or if no amount has been agreed to for a Covered Service, BCBSNE will set the MBA by considering the Charges submitted by other providers for like procedures, a relative value scale that compares the complexity of services provided or any other factors deemed necessary to determine a reimbursement amount. Maximum Coinsurance Liability Limit: The coinsurance limit is the total of the Covered Person’s Coinsurance payment amounts under all parts of the Contract, except those specified, during each calendar year. 233 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Medicaid: Grants to states for Medical Assistance Programs, Title XIX of the Social Security Act, as amended. A program designed to assist low-income families in providing healthcare for themselves and their children. It also covers certain individuals who fall below the federal poverty level. Other people who are eligible for Medicaid include low-income children under age 6 and low-income pregnant women. Medicaid is governed by overall Federal guidelines in terms of eligibility, procedures, payment level etc., but states have a broad range of options within those guidelines to customize the program to their needs and/or can apply for specific waivers. State Medicaid programs must be approved by CMS; their daily operations are overseen by the State Department of Health (or similar state agency). Medically Necessary Or Medical Necessity: Health care Services ordered by a Treating Physician exercising prudent clinical judgment, provided to a Covered Person for the purposes of prevention, evaluation, diagnosis or treatment of that Covered Person’s illness, injury or pregnancy, that are: • Consistent with the prevailing professionally recognized standards of medical practice, and known to be effective in improving health care outcomes for the condition for which it is recommended or prescribed. Effectiveness will be determined by validation based upon scientific evidence, professional standards and consideration of expert opinion; and • Clinically appropriate in terms of type, frequency, extent, site and duration for the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of the Covered Person's illness, injury or pregnancy. The most appropriate setting and the most appropriate level of Service is that setting and that level of Service, that is the most cost effective considering the potential benefits and harms to the patient. When this test is applied to the care of an inpatient, the Covered Person's medical symptoms and conditions must require that treatment cannot be safely provided in a less intensive medical setting; and • Not more costly than alternative interventions, including no intervention, and are at least as likely to produce equivalent therapeutic or diagnostic results as to the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of the patient's illness, injury or pregnancy, without adversely affecting the Covered Person's medical condition; and • Not provided primarily for the convenience of the following: o The Covered Person; o The Physician; o The Covered Person's family; or o Any other person or health care provider; and • Not considered unnecessarily repetitive when performed in combination with other prevention, evaluation, diagnosis or treatment procedures. BCBSNE, or the applicable Blue Plan, will determine whether services are Medically Necessary. Services will not automatically be considered Medically Necessary because they have been ordered or provided by a Provider. 234 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Medicare: Health Insurance for the Aged and Disabled, Title XVIII of the Social Security Act, as amended. Medicare Advantage: “Medicare Advantage” (MA) is the program alternative to standard Medicare Part A and Part B fee-for-service coverage; generally referred to as “traditional Medicare.” MA offers Medicare beneficiaries several product options (similar to those available in the commercial market), including health maintenance organization (HMO), preferred provider organization (PPO), point-of-service (POS) and private fee-for-service (PFFS) plans. Medicare Crossover: The Crossover program was established to allow Medicare to transfer Medicare Summary Notice (MSN) information directly to a payor with Medicare’s supplemental insurance company. Medicare Supplemental (MEDIGAP): Pays for expenses not covered by Medicare. Medigap is a term for a health insurance policy sold by private insurance companies to fill the “gaps” in original Medicare Plan coverage. Medigap policies help pay some of the healthcare costs that the original Medicare Plan doesn’t cover. Medigap policies are regulated under federal and state laws and are “standardized.” There may be up to 12 different standardized Medigap policies (Medigap Plans A through L). Each plan, A through L, has a different set of basic and extra benefits. The benefits in any Medigap Plan A through L are the same for any insurance company. Each insurance company decides which Medigap policies it wants to sell. Most of the Medigap claims are submitted electronically directly from the Medicare intermediary to the member’s Blue Plan via Medicare Crossover process. Medigap does not include Medicare Advantage products, which are a separate program under the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). Members who have a Medicare Advantage Plan do not typically have a Medigap policy because under Medicare Advantage these policies do not pay any deductibles, copayments or other cost-sharing. Member: A person named on an identification card issued pursuant to a Member, group or individual Contract. Enrolled employee is referred to as a Member. Mental Health Services: Assessment, treatment and supportive maintenance, activities delivered within a program which has as its primary mission the delivery of care for Mental Illness. These services are designed for persons with a diagnosis classified in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders other than individuals with solely mental retardation or Substance Abuse diagnosis. Mental Health Services Provider: A qualified physician, licensed psychologist, licensed special psychologist, and licensed mental health practitioners who are payable providers under the covered person’s contract. A mental health practitioner may also be called a licensed professional counselor or a licensed social worker who is a duly certified/licensed professional acting within the scope of 235 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents his or her practice according to state law. It also includes, for purposes of the contract, auxiliary providers; who are working under supervision and billed for by a professional as permitted by state law. All mental health services must be provided under appropriate supervision and consultation requirements as set forth by state law. • Licensed clinical psychologist - Psychologist shall mean a person licensed to engage in the practice of psychology in this or another jurisdiction. The terms certified, registered, chartered, or any other term chosen by a jurisdiction to authorize the autonomous practice of psychology shall be considered equivalent terms. • Licensed special psychologist - A person who has a doctoral degree in psychology from an institution of higher education accredited by the American Psychological Association, but who is not certified in psychology. Such person shall be issued a special license to practice psychology that continues existing requirements for supervision by a licensed psychologist or qualified physician for any practice that involves major mental and emotional disorders. This psychologist may provide mental health services without supervision. • Licensed mental health practitioner - A person Licensed to provide treatment, assessment, psychotherapy, counseling, or equivalent activities to individuals, families or groups for behavioral, cognitive, social, mental, or emotional disorders, including interpersonal or personal situations. Mental health practice shall include the initial assessment of organic mental or emotional disorders (as defined by state law), for the purpose of referral or consultation to a qualified physician or a licensed psychologist. Mental Health Practice shall not include the practice of psychology or medicine, prescribing drugs or electroconvulsive therapy, treating physical disease, Injury, or deformity, diagnosing major mental illness or disorder except in consultation with a qualified physician or a licensed psychologist measuring personality or intelligence for the purpose of diagnosis or treatment planning, using psychotherapy with individuals suspected of having major mental or emotional disorders except in consultation with a qualified physician or licensed psychologist, or using psychotherapy to treat the concomitants of organic illness except in consultation with a qualified physician or licensed psychologist. Mental Illness: A pathological state of mind producing clinically significant psychological or physiological symptoms (distress) together with impairment in one or more major areas of functioning (disability) wherein improvement can reasonably be anticipated with therapy. Also referred to as Psychiatric (Mental Illness, Drug Abuse and Alcoholism). Modifier: A means by which the reporting Physician can indicate that a service or procedure performed has been altered by some specific circumstance, but not changed in its definition or code. National Account: A group which has employees in more than one Plan area. Claims are processed by the onsite Plan servicing the area where care was received. 236 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Network BLUE Provider (Or Preferred Provider): Any licensed hospital, practitioner of the healing arts, or qualified provider of health care services, supplies, or home medical equipment who has contracted to provide Covered Services to Covered Persons as a part of the NEtwork BLUE Provider network. Network Provider: Physicians, group practices of physicians, mid-level professionals employed by or supervised by such physicians, and other health care or affiliated providers that have entered into an agreement with BCBSNE, have met all BCBSNE credentialing standards, and have been approved as a Network Provider by BCBSNE. Noncovered Person: A person who is not covered under the Contract and for whom benefits are not available. Noncovered Services: Services for which benefits are not provided under the Covered Person's Contract. Observation Period: The period of treatment when the physician is evaluating the patient’s medical condition to determine whether the patient can be released from the outpatient department or admitted to the facility as an inpatient; or the period of treatment following an outpatient procedure when the physician is evaluating the patient’s medical condition to determine whether the patient can be released from the outpatient department. Other Party Liability (OPL): Cost containment programs that ensure that Blue Plans meet their responsibilities efficiently without assuming the monetary obligations of others and without allowing members to profit from illness or accident. OPL includes Coordination of Benefits, Medicare, Workers’ Compensation, Subrogation, and no-fault auto insurance. Outlier Threshold: The defined point at which Covered Charges exceed the expected charges for a DRG category, and additional reimbursement is added to the base reimbursement (Inlier Rate). When Covered Charges are less than the Outlier Threshold, the reimbursement is the Inlier Rate. When Covered Charges exceed the Outlier Threshold, the reimbursement is the total of the Inlier Rate plus a percentage of the amount above the defined Outlier Threshold. Outpatient: A person treated in the outpatient department or emergency room of an institutional facility, or in an ancillary facility, or in an ambulatory surgical center, or a physician’s office. Outpatient Program: An organized set of resources and services for a substance abusive or mentally ill population, administered by a certified provider, which is directed toward the accomplishment of a designed set of objectives. Day treatment, partial care and outpatient programs which provide primary treatment for mental illness or substance abuse must be provided in a facility which is licensed by the Department of Health and Human Services Regulation and Licensure and whose program is certified by the Division of Alcoholism, Drug Abuse and Addiction Services (or equivalent state agency) or accredited by the Joint Commission on Accreditation of 237 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) or the Commission on the Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities (CARF). This definition does not include programs of co-dependency, family intervention, employee assistance, probation, prevention, educational or self-help programs, or programs which treat obesity, gambling, or nicotine addiction. It also does not include residential or day rehabilitation services for mental illness, or residential, halfway house or methadone maintenance programs for substance abuse. Benefits will not be provided for programs ordered by the court which are not medically necessary as determined by BCBSNE. Outpatient Services: A variety of diagnostic and treatment services in a non-residential setting. These services may include preadmission screening; assessment; individual group and family therapy. PPO: Preferred Provider Organization. Participating Provider: Any licensed hospital, practitioner of the healing arts, or licensed and qualified provider of health care services, supplies, or home medical equipment who has contracted with BCBSNE or other plan through the BlueCard Program to provide Covered Services to Covered Persons. Patient Days: Inpatient Hospital, acute care, acute rehabilitation facility, mental health facility, Alcoholism or Drug Treatment Center or Skilled Nursing Facility days. The day of admission shall be counted, but the day of discharge shall not be counted. (Exception: When the patient is discharged on the same day as admitted or is transferred to another acute care facility on the same day as admitted.) Per Diem: An all-inclusive Contracted Amount for each Day of Inpatient Covered Services. Physical Rehabilitation: The restoration of a person who was totally disabled as the result of an Injury or an acute physical impairment to a level of function which allows that person to live as independently as possible. A person is totally disabled when such person has physical disabilities and needs active assistance to perform the normal activities of daily living, such as eating, dressing, personal hygiene, ambulation and changing body position. Physician: Any person holding a license who is duly authorized to practice medicine, practice surgery and prescribe drugs. Plan: An individual organization participating in the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association. Point Of Service (POS): A plan which incorporates Managed Care through a primary care Physician who coordinates care within a network of providers with the option to self-refer out of the network to a provider of choice at the time of treatment. Reimbursement levels vary based on the option selected. 238 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Policies And Procedures Manuals: These manuals published by BCBSNE set forth the billing, payment, utilization management, certain medical policies and other administrative guidelines under the Agreement. These manuals are updated by BCBSNE from time to time by the Update Newsletter and, where applicable, under the Modification terms of the Agreement. The Policies and Procedures Manuals are incorporated as Attachment I of the Agreement. Provider will follow all applicable BCBSNE Policies and Procedures and those applicable to the covered Person, and Provider agrees to provide appropriate information to Provider employees, agents and representatives consistent with this commitment. Preauthorization: Prior written approval of benefits. Preauthorization is based on the terms of the Covered Person’s Contract and is based on the information submitted to the applicable Blue Plan for review. Preferred Provider: A qualified health care provider (Hospital, physician, or other health care provider or ancillary facility) who meets BCBSNE or applicable Blue Plan credentialing standards and has contracted with BCBSNE to provide Covered Services to Covered Persons as a part of the NEtwork BLUE provider networks. Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): A panel of Hospitals, Physicians and other health care Providers who belong to a network of Preferred Providers, which agrees to more effectively manage health care costs. Pre-Existing Condition: A condition, whether physical or mental, regardless of the cause of the condition, for which medical advice, diagnosis, care, or treatment was recommended or received within the six-month period ending on the first day of coverage, or if there is an Eligibility Waiting Period, the first day of such Waiting Period. A Pre-Existing Condition does not include a Pregnancy when coverage is subject to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. Pregnancy: Includes obstetrics, abortions, threatened abortions, miscarriages, premature deliveries, ectopic pregnancies, or other conditions or complications caused by Pregnancy. A complication caused by Pregnancy is a condition that occurs prior to the end of the Pregnancy, distinct from the Pregnancy, but caused or adversely affected by it. Postpartum depression and similar diagnoses are not considered complications of Pregnancy as that terminology is used in the Contract. Principal Diagnosis: The condition which is determined to be the primary reason for treatment. Principal Procedure: The procedure performed for definitive treatment, rather than for diagnostic or exploratory purposes, or to resolve a complication. More than one procedure may meet this definition and may be listed on the claim. RBRVS (Resource Based Relative Value Scale): RBRVS system assigns a value of each medical procedure or service based on the resources the Physician or Provider used including physical or procedural resources, educational, mental or cognitive, and financial resources. RBRVS was based 239 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents on a study developed at Harvard University. An advisory committee provided by the American Medical Association made contributions through the length of the study. Remittance Advice (RA): The BCBSNE claim payment report for participating Hospitals, Physicians and other providers of health care services. The RA is a record of how payment was made: Total Charges, Covered Person’s Liability, Provider Liability, and BCBSNE Payment. Respite Care: Short-term Inpatient care which is necessary for the Covered Person in order to give temporary relief to the person who regularly assists with the care at home. Respite Care may be provided in the Hospice program’s designated Inpatient unit that is affiliated with the Hospice that is providing services to the Covered Person, in an acute care setting in a Hospital or in a skilled nursing facility. RX Nebraska Information Network: This audio response system verifies a patient’s prescription drug card eligibility copay amounts and effective dates. Scientifically Validated: A technology, a drug, biological product, device, diagnostic, treatment or procedure is Scientifically Validated if it meets all of the factors set forth below: • Technologies, drugs, biological products, devices and diagnostics must have final approval from the appropriate government regulatory bodies. A drug or biological product must have final approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). A device must have final approval from FDA for those specific indications and methods of use that is being evaluated. FDA or other governmental approval is only one of the factors necessary to determine Scientific Validity. • The Scientific Evidence must permit conclusions concerning the effect of the technology on health outcomes. The evidence should consist of well-designed and well-conducted investigations published in peer-reviewed journals. The quality of the body of studies and the consistency of the results are considered in evaluating the evidence. • The evidence should demonstrate that the technology can measure or alter the physiological changes related to a disease, injury, illness or condition. In addition there should be evidence based on established medical facts that such measurement or alteration improves the health outcomes. • Opinions and evaluations by national medical associations, consensus panels or other technology evaluation bodies are evaluated according to the scientific quality of the supporting evidence and rationale. Our evidence includes, but is not limited to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Technology Evaluation Center technology evaluations; Hayes Directory of New Medical Technologies' Status; Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Technology Assessments, and United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals. • The technology must improve the net health outcome. 240 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents • The technology must improve the net health outcome as much as or more than established alternatives. • The improvement must be attainable outside the investigational settings. BCBSNE, or applicable Blue Plan, will determine whether a technology is not Scientifically Validated or Investigative. BCBSNE shall post those technologies that it has previously determined to be not Scientifically Validated or Investigative and shall make such determinations available on its website. The absence of a medical policy or particular matter shall not prohibit BCBSNE or the applicable Blue Plan from concluding that a matter is or is not Scientifically Validated or Investigative. Single Membership: Membership option providing benefits for Covered Services provided to the Member only. Single Parent Membership: Membership option providing benefits for Covered Services provided to the Member and his or her eligible dependent children, but not to a spouse. Skilled Nursing Care Or Service: Medically Necessary Inpatient Skilled Nursing services for the treatment of an Illness or Injury that must be ordered by a Physician, and performed under the supervision of a Registered Nurse (R.N.) or a Licensed Practical Nurse (L.P.N.). The classification of a particular service as skilled is based on the technical or professional health training required to effectively perform the service. Services by other licensed professional providers within their scope of practice, and ordered by a Physician, are considered to be included in Skilled Nursing Care. A nursing service is not considered skilled merely because it is performed by a R.N. or a L.P.N. The service cannot be regarded as Skilled Nursing when it can be safely and effectively performed by the average nonmedical person (or self-administered) without the direct supervision of a Licensed nurse. Subrogation: Subrogation is our right to recover benefits paid for Covered Services as the result of an Injury or Illness which was caused by a third party. We also assert a contractual right of recovery to collect proceeds recovered from a third party. Subrogation and the contractual right of recovery are prior liens against any proceeds recovered by the Covered Person. Claims will be paid according to the Covered Person’s Contract, then BCBSNE will seek reimbursement from the other party. The recovery amount will not exceed the amount we paid in benefits. Substance Abuse: For purposes of the Contract, this term is limited to alcoholism and drug abuse. (See Mental Illness). Supervision: The ready availability of the Physician for consultation and direction of the activities of another provider who is providing health care services within his or her defined scope of practice. 241 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Tax Identification Number (TIN): The TIN is the number you use to file income tax with the IRS. Third-Party Payer: A company, organization, insurer or government agency which makes payment for health care services received by a patient. Blue Shield Plans, commercial insurance companies, Medicare, Medicaid, HMOs and PPOs. The patient and the provider of service are the first two parties to the delivery of health care services; the insurer becomes the third party. Traditional Coverage: Traditional coverage is a health benefit plan that provides basic and/or supplemental hospital and medical/surgical benefits (e.g., basic, major medical and add-on riders) designed to cover various services. Such products generally include cost sharing features, such as deductibles, coinsurance or copayments. Transfer Per Diem: When a patient is transferred between two or more Hospitals, and a Transfer Per Diem has been set for the applicable DRG, the transferring Hospital will be reimbursed an all-inclusive Contracted Amount for each Medically Necessary inpatient day. UB04: The Uniform Bill UB04 is intended to be used by the major Third Party Payors, most Hospitals and nursing homes. The data elements and design of the form are determined by the National Uniform Billing Committee. The MUBC has developed uniform definitions and procedures for completing the form. The procedural guidelines are designed to provide actual completion instructions for each payor. Utilization Review: The evaluation by BCBSNE or persons designated by BCBSNE, of the use of a medical, diagnostic or surgical procedure or service, the utilization of medical supplies, drugs, or home medical equipment or the treatment of Mental Illness, Alcoholism and Drug Abuse compared with established criteria in order to determine benefits. Benefits may be excluded for services, procedures, supplies, drugs or home medical equipment found to be not Medically Necessary. Waiting Period: The period of time during which no benefit payment will be made for services provided to a covered person for a Pre-Existing Condition. Work-Hardening: Physical therapy or similar services provided primarily for strengthening an individual for purposes of his or her employment. Workers’ Compensation: The Nebraska Workers’ Compensation laws are designed to provide certain benefits to employees who: 1. 2. 3. Sustain injury or contract occupational disease, Arising out of an in the course of their employment, and Are not willfully negligent at the time of their injury. The Nebraska Workers’ Compensation Act (NWCA) applied to most employers in Nebraska; however, some exceptions include employers of farm or ranch laborers and domestic workers, independent contracts and non-incorporated business owners. 242 Return to Start of Section Proceed to Next Section Go to Table of Contents Section 19 How to Contact Us Online E-mail Inquiry Go to www.nebraskablue.com and click on “Contact Us”. For questions about: Call or email: Busy Signals: If you get a busy signal, please stay on the line. The system will try to connect you to a representative. If we are unable to connect you, a voice prompt will inform you that we are unable to connect your call and you will be asked to try your call later. Please have the following information ready when you call: To verify your patient’s BCBSNE eligibility, or the status of a BCBSNE or BlueCard claim. GABBI: 800-635-0579 Monday - Friday: 7 a.m. to Midnight (CST) Saturday: 7 a.m. to 1 p.m. • • • • The provider’s NPI number. Cardholder’s ID number Cardholder’s name Patient date of birth Note: We encourage you to verify member eligibility and benefits, and claim status, on our provider portal at www.navinet.net To verify Federal Employee Program (FEP) eligibility and benefits or to inquire about a claim. FEP members can be identified by the number on the ID card which begins with the single alpha character “R.” Note: FEP eligibility, benefits, and claim status information is available on our provider portal at www.navinet.net BlueCard member Eligibility and Benefits. FEP Program Service at: 402-390-1879 800-223-5584 Monday - Wednesday, Friday: 8 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. (CST) Thursday - 9 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. 800-676-BLUE (2583) Note: You can obtain eligibility and benefits information for a BlueCard member through our provider portal on www.navinet.net 243 Return to Start of Section Go to Table of Contents Your BCBSNE provider agreement. Reimbursement issues. Interpretation and development of billing and medical policies. Your Health Network Consultant at: 800-821-4787, Option 4 A change in location, tax ID number. Electronic Funds Transfer enrollment. To request a Provider Agreement. Health Network Administration at: 800-821-4787, Option 4 ProviderSolutions@nebraskablue.com Credentialing or the status of an application. Credentialing at: 800-821-4787, Option 4 credentialingrequests@nebraskablue.com Provider newsletters and manuals. The Provider section of BCBSNE’s website. Kimberly Vavra 402-982-8816 kimberly.vavra@nebraskablue.com Precertification (BCBSNE and FEP Members only) Medical/Surgical Inpatient Admissions, Skilled Nursing Facility, Rehab Facility, and Home Health Skilled Nursing Visits: 402-390-1870 or 800-247-1103 Behavioral Health Inpatient Admissions: 402-343-3426 or 888-233-8210 Coordination of Benefits 402-390-1840 800-462-2924 Refunds 402-398-3653 800-562-3381 Subrogation 402-390-1847 800-662-3554 Worker’s Compensation 402-398-3615 800-821-4786 Pharmaceuticals – Coverage or Claim Information Online: www.primetherapeutics.com Phone: 800-821-4795 Email: pharmacy@primetherapeutics.com Online Access to Drug Pricing and Formulary: www.myprime.com 244 Return to Start of Section
© Copyright 2025