Document 37717
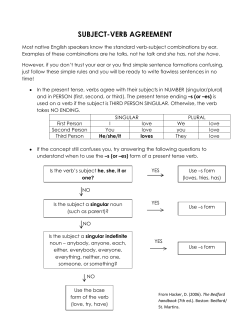
Subject-Verb Agreement 1 Number Number – the form a word takes to indicate whether the word is singluar or plural. A word that refers to one person, place, thing, or idea is singular in number. A word that refers to more than one is plural in number. 2 Subject-Verb Agreement A verb should agree in number with its subject. Singular subjects take singular verbs. ◦ Ex) He washes the dishes. [The singular verb washes agrees with the singular subject He.] A girl in my neighborhood plays in the band. [The singular subject girl takes the singular verb plays.] 3 Subject-Verb Agreement Plural subjects take plural verbs. ◦ Ex) They wash the dishes. Several girls in my neighborhood play in the band. Generally, nouns ending in –s are plural (friends, girls), but verbs ending in –s are generally singular (sees, hears). 4 Subject-Verb Agreement The following indefinite pronouns are singular: ◦ anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, neither, nobody, no one, nothing, one, somebody, someone, and something ◦ Ex) Each of the athletes runs effortlessly. Neither of the women is ready to start. Someone was waving a large flag. Does everyone who signed up enjoy playing tennis? 5 Subject-Verb Agreement The following indefinite pronouns are plural: ◦ both, few, many, and several ◦ Ex) Were both of the games postponed? Few that I know of have qualified. Several of the runners are exercising. 6 Subject-Verb Agreement The following indefinite pronouns may be singular or plural, depending on their meaning in a sentence: ◦ all, any, more, most, none, and some ◦ Ex) Some of the test is hard. [Some refers to the singular noun test.] Some of the questions are easy. [Some refers to the plural noun questions.] All of the exhibit is open to the public. All of the paintings are on display. 7 Subject-Verb Agreement At Home Practice ◦ In your notes, underline the correct form of the verb in the sentences on the following slide. 8 Class Practice: Subject-Verb Agreement Each of the comedians (tries, try) to outdo the other. 2. Somebody on the bus (was, were) whistling. 3. (Is, Are) all of the apples spoiled? 4. Neither of these books (has, have) an index. 5. (Do, Does) everybody in the class have a pencil? 6. Few of these jobs (sounds, sound) challenging. 7. (Is, Are) more of the vendors in the market? 8. She said that no one in the office (leaves, leave) early. 9. Both of her parents (has, have) offered us a ride. 10. (Do, Does) most of those CDs belong to her? 1. 9 Subject-Verb Agreement Subjects joined by and generally take a plural verb. ◦ Ex) George Lucas and Steven Spielberg make movies. [Two persons make movies.] Rhyme, rhythm, and imagery help poets express their feelings. [Three things help.] Compound subjects that name only one person, place, thing, or idea take a singular verb. ◦ Ex) My pen pal and best friend is my cousin. [One person is my best friend and pen pal.] Broccoli and melted cheese makes a tasty dish. [The one combination makes a dish.] 10 Subject-Verb Agreement Singular subjects joined by or or nor take a singular verb. Plural subjects joined by or or nor take a plural verb. ◦ Ex) After dinner, either Anne or Tony loads the dishwasher. [Anne loads the dishwasher or Tony loads the dishwasher.] Neither the coach nor the principal is happy with the team’s performance. [Neither one is happy.] Either the boys or their sisters take the garbage out. Neither the dogs nor the cats come when we call them. 11 Subject-Verb Agreement When a singular subject and a plural subject are joined by or or nor, the verb agrees with the subject nearer the verb. ◦ Ex) Neither the children nor their mother was ready for the trip. Neither the mother nor her children were ready for the trip. 12 Subject-Verb Agreement The contractions don’t and doesn’t should agree with their subjects. ◦ The word don’t is the contraction of do not. Use don’t with all plural subjects and with the pronouns I and you. ◦ Ex) I don’t know. They don’t give up. You don’t say. Don’t these shrink? We don’t want to. These people don’t care. 13 Subject-Verb Agreement The word doesn’t is the contraction of does not. Use doesn’t with all singular subjects except the pronouns I and you. ◦ Ex) He doesn’t know. She doesn’t say. It doesn’t want to. One doesn’t give up. This doesn’t shrink. Doesn’t Donna care? 14 Subject-Verb Agreement A collective noun may be either singular or plural, depending on its meaning in a sentence. ◦ A collective noun is a noun that names a group of persons or things. Examples: ◦ army, assembly, audience, class, club, committee, family, fleet, flock, group, herd, jury, public, swarm, team 15 Subject-Verb Agreement Use a plural verb with a collective noun when the noun refers to the individual parts or members of the group. Use a singular verb when the noun refers to the group as a unit. ◦ Ex) The class have completed their projects. [Class is thought of as individuals.] The class has elected its officers. [Class is thought of as a unit.] 16 Subject-Verb Agreement A verb agrees with its subject, but not necessarily with a predicate nominative. ◦ Ex) S V PN The marching bands are the main attraction. S V PN The main attraction is the marching band. 17 Subject-Verb Agreement When the subject follows the verb, find the subject and make sure that the verb agrees with it. (The subject generally follows the verb in questions and in sentences that begin with here and there.) ◦ Ex) Here is a list of addresses. Here are two lists of addresses. There is my notebook. There are my notebooks. Where is Heather? Where is Chris? Where are Heather and Chris? 18 Subject-Verb Agreement Contractions such as here’s, where’s, how’s, and what’s include the singular verb is. Use these contractions only with singular subjects. ◦ Ex) Incorrect: There’s some facts on that topic. Correct: There are some facts on that topic. Correct: There’s a fact on that topic. 19 Subject-Verb Agreement An expression of an amount (a measurement, a percentage, or a fraction, for example) may be singular or plural, depending on how it is used. A word or phrase stating an amount is singular when the amount is thought of as a unit. ◦ Ex) Thirty dollars is too much for a ticket. Two hours is a long time to wait. 20 Subject-Verb Agreement Sometimes, however, the amount is thought of as individual pieces or parts. If so, a plural verb is used. ◦ Ex) Five dollars were scattered on the desk. Two hours – one before school and one after – are all I have for practice. 21 Subject-Verb Agreement A fraction or a percentage is singular when it refers to a singular word and plural when it refers to a plural word. ◦ Ex) Three fourths of the pizza is gone. Of these songs, three fourths are new. 22 Subject-Verb Agreement Some nouns that are plural in form take singular verbs. ◦ Ex) Politics is a controversial subject. The news of the nominee was a surprise. Rickets is a serious health problem in some countries. 23 Subject-Verb Agreement Some nouns that end in –s take a plural verb even when they refer to a single item. ◦ Ex) The scissors need to be sharpened. Were these pants on sale? The Olympics are on television. 24 Subject-Verb Agreement Even when plural in form, the title of a creative work (such as a book, song, film, or painting), the name of an organization, or the name of a country or city generally takes a singular verb. ◦ Ex) The Souls of Black Folk is often cited as a classic of African American literature. [one book] “Greensleeves” is an old English folk song. [one piece of music] The United Nations was founded in 1945. [one organization] White Plains is home to several colleges. [one city] 25 Subject-Verb Agreement Subjects preceded by every or many a take singular verbs. ◦ Ex) Every homeowner and storekeeper has joined the cleanup drive sponsored by the town council. Many a litterbug was surprised by the stiff fines. 26 Subject-Verb Agreement When the relative pronoun that, which or who is the subject of an adjective clause, the verb in the adjective clause agrees with the word to which the relative pronoun refers. ◦ Ex) This is the store that has the discount sale. [That refers to the singular noun store.] London, which is the capital of England, is the largest city in Europe. [Which refers to the singular noun London.] The Garcias, who live next door, are going with us to the lake. [Who refers to the plural noun Garcias.] 27 Subject-Verb Agreement At Home Practice ◦ Underline the correct form of the verb in the sentences on the following slide. 28 Class Practice: Subject-Verb Agreement 1. Mumps (is, are) are common childhood disease that causes swelling in glands in the neck. 2. Politics (is, are) always a popular subject both to debate and to study at college. 3. Not one of the ushers (know, knows) where the lounge is. 4. The team (is, are) on a winning streak. 5. Carol, as well as Inés, (write, writes) a weekly column for the East High Record. 6. “Beauty and the Beast” (is, are) a folk tale that exists in many different cultures. 7. Ten pounds (is, are) to much weight for a young child to carry in a backpack. 8. It is difficult to concentrate when there (is, are) radios and stereos blasting away. 9. (Has, Have) either of you read the book or seen the movie version of To Kill a Mockingbird? 10. In most situation comedies, there (is, are) a very wise character, a very foolish character, and a very lovable character. 29
© Copyright 2025