Resumes & CVs Department of Mechanical Engineering
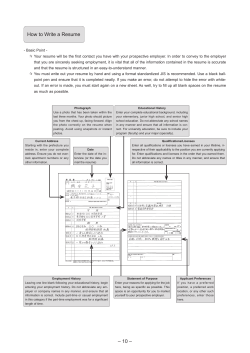
Resumes & CVs Department of Mechanical Engineering Agenda Resumes vs CVs Purpose of a Resume Purpose of a CV Resume Formats & Content CV Formats & Content Differences Between a CV and a Resume Resume/CV Dos and Don’ts Cover Letters Research Statements Resumes vs Curriculum Vitae (CVs) Resumes are required for an Industry Job Search Process Resumes are the written inventory of your work experience and accomplishments, skill set, career and educational highlights CVs are required by environments that demand doctoral degrees – SAM communities CVs are a chronological representation of credentials - “the course of one’s life” A Resume and its Purpose Marketing Tool Key component in the job search process To get you an interview Resumes are as unique and individual as the individuals they represent Tailored to the specific job A CV and its Purpose Important piece of documentation Key component in the search for scientific, academic, or medical positions Usually accompanied by a cover letter and a research statement To highlight your credentials CV follows a specific structure Only one version of a CV is enough Resume Formats Reverse Chronological – Lists your experiences in reverse chronological order, beginning with most recent position Functional – Combination – Promotes and headlines skills and accomplishments, without emphasizing where or when you developed those skills Utilizes reverse chronological order as well as organizes experiences in order of importance The Four Ws of a Resume? What opportunity are you seeking? What is your specific background that relates to this opportunity? What are the roles, relevant work experiences and education that provided you with this experience? What are your unique accomplishments? Resume Guidelines/Length Easy to read – Resume should be in a Easy to find out what you are good at – consistent format and the reader should have a clear understanding of who you are effective formatting, clear articulate language and pertinent information will enable the reader to access what is important Length of Resume – Keep your resume concise – make every word count – 2 page optimum Resume Headings Contact Information Profile Summary Skill Set vs. Objective Work Experience Education Professional Associations and Membership Use Words Carefully Avoid use of confusing terms or acronyms Avoid use of long sentences or paragraphs Focus on concise factual statements Emphasize hard skills, e.g. computer software applications Focus on specific action verbs Resume Content Show a progressive history of success (increased responsibilities, promotions, etc) Address specific accomplishments – PAR statements Identify your unique achievements within organizations Provide metrics that support these accomplishments PAR – Example Project: Recognized a need for an interactive videodisc/computer database for students and faculty Action: Analyzed database and procedural requirements and designed an interactive tool Result: Installed in MIT Libraries Putting it all together: Identified the need for and led the design and delivery of a database project which resulted in easier access of information for faculty, students and staff through MIT Libraries PAR Statement Practice 1. Think about an accomplishment or project 2. Write down the following: that you wish to include in your resume. With a partner, describe the issue or challenges that you addressed (P) (A) (R) What was the issue and subsequent project What actions you took using action verbs The result or impact of the project CV Formats Academic CV Executive CV International CV CV Guidelines/Length Easy to Read – line item presentation of your credentials and academic history Must haves Professional Address Educational History Honors and Awards Publications References Length of CVs – no restrictions; 5 - 10 pages is optimum CV Headings Contact Information Education/Doctoral Dissertation Medical or Academic Posts Research – with mentors and institutions Publications Presentations Teaching Honors and Awards Appointments Committees Other activities References – Resume vs CV Not included or required in a Resume – can be an addendum Typically required and listed in a CV – very important piece of information in academic searches Consistent list between CV and applications for academic positions Up to 5 reference letters are required in academic searches Post Doc mentor and Ph. D. mentor come first – most important Differences – Resume vs CV Category Curriculum Vitae Resume Essence A full list of your professional and educational history A summary of your experience and skills that are most pertinent to the job Length Not restricted; 5 - 10 – optimum for a seasoned academic 1 to 2 pages Usage SAM/Science – Academia - Medical positions Every other type of job outside of academia and research science Publications Yes – full list Rarely Style and Format Not important; content matters Very important/Make it easy to read and follow Number of versions One is enough/minor modifications are OK Many version/Tailor to each job of interest References Yes No Do Not's of Resumes & CVs Do not include personal information in resume or academic CV Do not send a photograph Do not embellish your resume/CV with false statements Do not use full sentences or pronouns Do not use abbreviations or acronyms Don’t be Shy to Share Obtain an objective review of your resume/CV Share your resume/CV with a colleague in the specific department that you are targeting for a job Keep updating resume and CV Be true to the facts Cover Letters – Industry Job Search Cover Letter + Resume = Industry Job Search Paragraph 1 – Express interest in opportunity + How you found out about it Paragraph 2 – What you have to offer to the potential employer; specific matches between your qualifications and the job Paragraph 3 – Follow up and Next Steps Cover Letters –Academic Job Search Cover Letter + CV = Academic Job Search Paragraph 1 – Express interest in opportunity + funding situation Paragraphs 2/3 – Work/mentors as a Post Doc + work/mentors as a Ph.D. Paragraph 4 – Future research focus Paragraph 5 – Follow up and Next Steps Research Statements – Academic Job Search Research Summary Graduate Research (mentor + lab) Post Doctoral Research (mentor + lab) Future Research Plans (may include abstracts) Optimum is 3-5 pages; may be more if abstracts are included Educational Plan/Teaching Plan may also be required Questions • Follow up: Bori Stoyanova bori@mit.edu Lynette Jones ljones@MIT.EDU
© Copyright 2025