Review problems
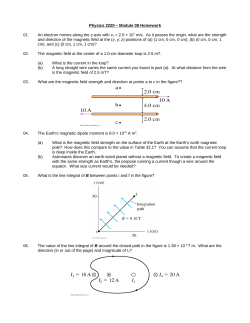
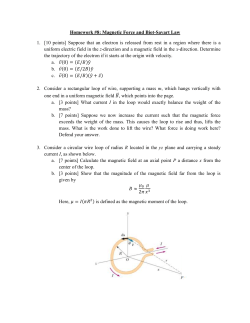
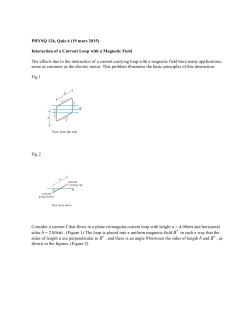
Name: ___________________________________ Date: ______________ AP Physics - Review problems for test on DC Circuits and Magnetism 1. For copper, ρ = 8.93 g/cm3 and M = 63.5 g/mol. Assuming one free electron per copper atom, what is the drift velocity of electrons in a copper wire of radius 0.435 mm carrying a current of 5 A? A) 5.43 × 10– 4 m/s B) 2.11 × 10– 4 m/s C) 4.67 × 10– 4 m/s D) 6.21 × 10– 4 m/s E) 8.37 × 10– 4 m/s 2. In a certain particle accelerator, a current of 800 µA is carried by a 6.00-MeV proton beam that has a radius of 1.50 mm. The mass of a proton is 1.67 × 10–27 kg. If the beam hits a target, how many protons hit the target in 5 s? A) 2.50 × 101 6 B) 6.78 × 101 6 C) 5.68 × 101 6 D) 1.37 × 101 6 E) 3.71 × 101 6 3. A potential difference V = 25 V is applied across a wire of length L = 10.0 m and uniform diameter. The electric field throughout the wire is A) 250 V/m B) 2.5 V/m C) 0.4 V/m D) 0.25 V/m E) zero 4. Wire A, which is of the same length and material as wire B, has twice the diameter of wire B. If the resistance of wire B is R, what is the resistance of wire A? A) R B) 2R C) R/2 D) 4R E) R/4 Page 1 5. A heating element made of nichrome wire (temperature coefficient of resistivity, α = 0.400 × 10– 3 K– 1) is connected to a source. When it has just been turned on and its temperature is 20°C, it dissipates 960 W of power. What power is dissipated when its temperature has risen to 300°C? A) 1.1 × 103 W B) 9.6 × 102 W C) 8.6 × 102 W D) 8.6 × 103 W E) 1.1 × 102 W 6. A comparison of the power losses (P1 , P2 , or P3 ) in the resistors of the circuit in the diagram shows that, if R1 = R2 = R3 , A) B) C) D) E) 4P1 = P2 = P3 P1 = 2P2 + 2P3 P1 = P2 = P3 P1 = (1/2)P2 = (1/2)P3 P1 = P2 + P3 7. In the circuit element shown, the current through the 6-Ω resistor is approximately A) B) C) D) E) 1.0 A 2.0 A 0.40 A 0.67 A 1.3 A Page 2 8. The power dissipated in the 21-Ω resistor in this circuit is A) B) C) D) E) 14 W 68 W 43 W 13 W None of these is correct. 9. In this circuit, the batteries have negligible internal resistance and the ammeter has negligible resistance. The current through the ammeter is A) B) C) D) E) 0.30 A 0.69 A 2.1 A 4.2 A 3.6 A 10. A 20.0-µF capacitor is charged to 200 V and is then connected across a 1000-Ω resistor. What is the initial current just after the capacitor is connected to the resistor? A) 100 mA B) 200 mA C) 150 mA D) 300 mA E) 50 mA Page 3 11. A 20-µF capacitor is charged to 200 V and is then connected across a 1000-Ω resistor. The time constant for this circuit is approximately A) 20 ms B) 40 ms C) 10 ms D) 30 ms E) 15 ms 12. A 20-µF capacitor is charged to 200 V and is then connected across a 1000-Ω resistor. The amount of charge on the capacitor after 10 ms is approximately A) 14 mC B) 2.4 mC C) 0.80 mC D) 1.6 mC E) 3.2 mC Use the following to answer questions 13-14. 13. The switch S is initially at position a for a long time. It is then switched to position b. Describe what happens to the light bulb as a function of time when the switch is flipped from a to b? A) The light bulb was on but goes off immediately. B) The light bulb was off and stays off. C) The light bulb was on but its brightness decreases with time and eventually goes off. D) The light bulb was on and stays on. E) The light bulb was off. It then lights up but the brightness decreases with time and eventually goes off. Page 4 14. The switch S is initially at position b for a long time. It is then switched to position a. Describe what happens to the light bulb as a function of time when the switch is flipped from b to a? A) The light bulb was on but goes off immediately. B) The light bulb was off and stays off. C) The light bulb was on but its brightness decreases with time and eventually goes off. D) The light bulb was on and stays on. E) The light bulb was off. It then lights up but the brightness decreases with time and eventually goes off. 15. An electron (q = –1.6 × 10–19 C) is traveling east with an instantaneous velocity of 2.5 × 105 m/s when it enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.45 T that points 35° north of east. What are the magnitude and direction of the force on the electron? A) 1.8 × 10–14 N up B) 1.5 × 10–14 N down C) 1.5 × 10–14 N up D) 1.0 × 10–14 N down E) 1.0 × 10–14 N up 16. A wire 30 cm long with an east–west orientation carries a current of 3.0 A eastward. There is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to this wire. If the force on the wire is 0.18 N upward, what are the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field? A) 0.20 T up B) 0.20 T north C) 0.20 T south D) 2.0 × 10– 3 T north E) 2.0 × 10– 3 T up 17. A long straight wire parallel to the y axis carries a current of 6.3 A in the positive y direction. There is a uniform magnetic field = 1.5 T . The force per unit length on the wire is approximately A) 6.3 N/m B) –9.5 N/m C) –6.3 N/m D) 9.5 N/m E) 1.5 N/m Page 5 18. An electric field and a magnetic field are at right angles to each other and to the direction of a beam of electrons. There is no deflection of the beam when the magnitudes of the fields are 30 × 104 V/m and 2.0 × 10– 3 T, respectively. The velocity of the electrons must be approximately A) 0.60 km/s B) 6.7 × 10– 8 m/s C) 2.3 × 101 6 m/s D) 1.5 × 108 m/s E) 1.5 × 10– 8 m/s 19. The radius of the orbit of an electron moving with a speed of 108 m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of 5.0 × 10– 3 T is approximately A) 1.1 m B) 0.11 m C) 0.34 m D) 0.011 m E) 8.9 m 20. A circular, 20-turn coil of radius 5.0 cm is oriented in such a way that its axis makes a 30° angle with a uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. What is the torque on the coil when it carries a current of 2.5 A? A) 1.5 × 10– 3 N m B) 9.4 × 10– 3 N m C) 2.9 × 10– 2 N m D) 5.1 × 10– 2 N m E) 0.59 N m Page 6 Use the following to answer questions 21-22. 21. A circular current loop lies in the xy plane and has radius R = 10 cm. The loop has 20 turns and carries a current I = 4 A. The magnetic dipole of the loop is A) B) C) D) E) 22. A circular current loop lies in the xy plane and has radius R = 10 cm. The loop has 20 turns and carries a current I = 4 A. A magnetic field of strength 0.3 T is applied at an angle of θ = 30° to the loop. The potential energy of the magnetic dipole is A) 0.163 J B) 0.544 J C) 0.314 J D) 0.653 J E) 0.377 J Page 7 Answer Key - ch 25 and 26 review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. D A B E C B D E B B A B E E D B B D B C A E Page 8
© Copyright 2025