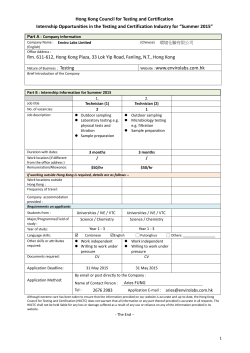
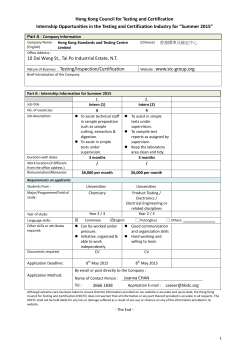
Case Report - Gigantism Diagnosed in a Grown-Up Male
BAOJ Medical and Nursing BAOJ Med Nursing 003 Vol: 1, Issue: 1 Case Report - Gigantism Diagnosed in a Grown-Up Male Cheung K K, Ma RC, So W Y, Kong A P, Chow F C. Departments of Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong. Case Report Gigantism is a rare disorder due to growth hormone (GH) excess that occurs before fusion of the epiphyseal growth plates, therefore, this condition is usually only seen in growing children.If the condition is not recognized before adulthood, a diagnosis could still be made in a grown-up based on clinical, biochemical, and histological characteristics. A 28 yr-old Chinese man, who had recently immigrated to Hong Kong from Mainland China, presented with a 6-month history of progressive worsening of vision and headache. He was noted to A B C D E F have tall stature, large hands and feet, coarsening of facial features with enlargement of the nose and frontal bossing, and widening of interdental spaces (figure A-D). An urgent CT brain showed a pituitary macroadenoma which was confirmed on a MRI pituitary to be 5x4∙7x5cmin size with compression onto the optic chiasm (figureE). Investigations revealed excessive insulin-like-growth-factor-1 650ng/mL (age-specific reference range [RR] 63-373ng/mL), elevated prolactin 788mIU/l (RR<324mIU/l), secondary hypothyroidism (free-thyroxine10∙2pmol/l [RR 12∙0-22∙0pmol/l], thyroid-stimulating-hormone 1∙9mIU/l [RR 0∙27-4∙20mIU/l]), and secondary hypogonadism (testosterone 0∙7nmol/L [RR 9-34∙7nmol/l], lutenizing-hormone 1∙5IU/l [RR 1∙7-8∙6IU/l], follicle-stimulating-hormone 1∙8IU/l [RR1∙5-12∙4IU/l]). Examination by an ophthalmologist confirmed bitemporal hemianopia (figureF). The mild elevation of prolactin illustrated the phenomenon of “pseudoprolactinoma”; an elevation of prolactin due to mass effect from a pituitary adenoma on the pituitary stalk resulting in interference of the passage of dopamine, a prolactin inhibitor, from hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary. In view of the mass effect, our patient was sent for an emergency transsphenoidal surgery with excision of the macroadenoma under hydrocortisone cover. Immunohistology showed positive staining for GH only. Post-operatively, he was noted to have excessive urine output while biochemistry results confirmed diabetes insipidus. Therefore, desmopressin was initiated. Upon discharge, the patient was on desmopressin, hydrocortisone, and thyroxine. He would be considered for testosterone replacement at a later stage at his follow-up. *Corresponding Author: Cheung K K, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong,Prince of Wales Hospital, New Territories, Hong Kong, Tel: 852-26323129 Fax: 85226358902; Email: kittyktcheung@cuhk.edu.hk Article Type: Case Report Sub Date: 4 May, 2015 Acc Date: 14 May, 2015 Pub Date: 19 May, 2015 Clinical photos and radiological image of an adult suffering from gigantism (A) Coarsening of facial features with enlargement of the nose and frontal bossing, and widening of interdental spaces. (B) Tall stature. (C) Enlarged hands. (D) Enlarged feet. (E) MRI pituitary image showing pituitarymacroadenoma with optic chiasm compression. (F) Bitemporal hemianopia on visual confrontation test. Citation: Cheung K K, Ma RC, So W Y, Kong A P, Chow F C (2015) Case Report-Gigantism Diagnosed in a Grown-Up Male. BAOJ Med Nursing 003 Vol: 1, Issue: 1. Copyright: © 2015 Cheung K K, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Citation: Cheung K K, Ma RC, So W Y, Kong A P, Chow F C (2015) Case Report-Gigantism Diagnosed in a Grown-Up Male. BAOJ Med Nursing 003 1 Vol: 1, Issue: 1.
© Copyright 2025