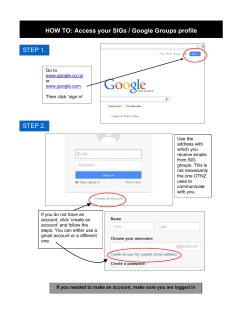
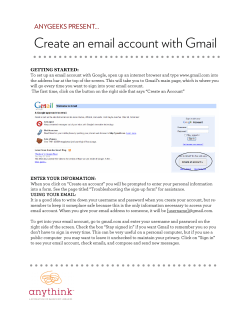
International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information
International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) 27-28 April 2015. PROCEEDINGS – Abstracts Organised by Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, RajaRajeswari College of Engineering (RRCE), Bangalore, India ABOUT ICPCIT-2015 The 1st International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) will be held at RAJARAJESWARI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (RRCE), Bangalore, India during April 27th-28th 2015. This conference is to provide an international forum for industry professionals and researchers to deliberate and state their research findings, discuss the latest advancements and explore the future directions in the emerging areas of Engineering and Technology. The conference also bring together both novice and experienced scientists and developers, to meet new colleagues, collect new ideas and establish new cooperation between research groups and provide a platform for researchers from academic and industry to present their original work and exchange ideas, information, techniques and applications in the field of Circuit, Power and Computing Technology. ABOUT RAJARAJESWARI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING: RajaRajeswari College of Engineering (RRCE), established in the year 2006 and is managed by Moogambigai Charitable and Educational Trust (MCET),Bangalore. The college is approved by All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), New Delhi, and is affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University (VTU), Belgavi, and recognised by government of Karnataka. The college is an ISO 9001-2008 certified Institution. The Institute offers 6 UG courses in engineering (Electronics & Communication, Civil, Computer Science and engineering, Information Science and engineering, Mechanical, and Electronics & Electrical Engineering) and 5 PG courses Master of Technology in Digital Electronics & Communication, Master of Technology in communication systems, Master of Business Administration & Master of Computer Applications, also 6 R&D centres. The college has well equipped laboratories, library, digital library computing and sports facilities along with other amenities and the college is located at a distance of 18kms from Bangalore City Railway Station on Mysore road. ABOUT ELECTRONICS AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT : COMMUNICATION Dept. of ECE established in 2006 with an intake of 60 and the intake has increased to 120 from the academic year 2013-14. ECE department is rich enough to organize and encourage teaching & non teaching staff by conducting various events like Workshops, Technical seminars, Expert lectures, FDPs etc. Department is well equipped with laboratories. ECE Department has qualified and dedicated faculty members with vast experience and expertise in their respective domains. In addition, the department runs Master of Technology in Digital Electronics & Communication and Master of Technology in communication systems of VTU. A.C. Shanmugam Chairman RajaRajeswari Group of Institutions, Bangalore MESSAGE I am glad to know that, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is organizing Two days “1st International Conference on Power, Circuits and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015)”, on 27 - 28th April 2015. The aim of this conference is to keep abreast of the Frontiers and Advances in Electronics and Communication Engineering field and acquiring knowledge for the promotion of human race. The impact of advanced technology along with globalization is tremendous. The Industries in our country face tough challenges and competition with the world. However, by updating the newer techniques in our industries we stand as the developed country. The discussion and deliberations that are going to take place among the delegates of the conference would enlighten and accelerate the growth and development of the industries in our nation. I wish all the best for the participants and organizers of this mega event in our campus and wish all the delegates to carry sweet memories of our institutions and the event. A. C. S. Arunkumar Vice Chairman RajaRajeswari Group of Institutions, Bangalore MESSAGE I am happy to note that the RajaRajeswari College of Engineering, Bangalore, is conducting a two days “1st International Conference on Power, Circuits and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015)”, on 27 - 28th April 2015. Such Conference provides the right forum and platform for Engineers, Technocrats and the academic faculty to present their research and interact for the benefit of society at large and technical community in Particular. I congratulate the entire community of the college in general and all the committee members in particular for their effort and wish the conference a thumping success. Dr. M. S. Bhagyashekar Principal RajaRajeswari College of Engineering, Bangalore MESSAGE I on behalf of the organizing committee am very much pleased to invite engineers, technocrats and the teaching faculty to contribute technical papers to 1st International Conference – ICPCIT-2015. It is designed to attract as many experts from the Electronics and Communication Engineering from all over the nation to showcase their research and interact for the benefit of all academicians and the industry. I hope that each participant gets individually enriched in turn enriching every other participant. This conference is being organized with the theme of sharing knowledge and exchange of ideas to bring out quality of research, presentation skills and interactions between various interrelated opportunities I believe that this conference will help us in many directions to develop our country’s research potential. Dr. P. V. Rao Professor and R & D Head, Dept of ECE Program Chair – ICPCIT 2015 MESSAGE It gives me an immense pleasure to note that RajaRajeswari college of Engineering is organizing “1st International Conference on Power, Circuits and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015)” for research scholars during 27th -28th April 2015. My congratulations on this thoughtful step, which is in tune with times. I am happy that the proposed International conference for research scholars intends to bring out the latest developments in various research activities, processes, properties and methods of characterization, which are essential for the R&D, Academia and industries. I am sure that the conference and expositions will provide an opportunity to share one’s experience and expertise with fellow participants, scientists and engineers of eminence. On behalf of management, staff and students of RRCE, I wish the conference all the success. Organizing Committee CHIEF PATRON Sri A.C. Shanmugam, Chairman, Moogambigai Charitable Educational Trust, RajaRajeswari Group of Institutions, Bengaluru PATRON Sri A.C.S. Arun Kumar, Vice Chairman, RajaRajeswari Group of Inst., Bengaluru Sri Vijayanand S. Exe. Director, RajaRajeswari Group of Institutions, Bengaluru GENERAL CHAIRS Dr. Bijay Ketan Panigrahi, IIT Delhi Dr. Dash S S, SRM University, Chennai Dr. Florian Misoc, UWM, USA PROGRAMME CHAIR Dr. M.S. Bhagyashekar, Principal, RajaRajeswari College of Engg, Bengaluru Sri S. Jeyabalan, Special Officer, RajaRajeswari Group of Inst., Bengaluru Dr. P. V Rao, Professor. and R & D Head, Dept. of ECE, RajaRajeswari College of Engineering, Bengaluru Dr. Ramazan Bayindir, Gazi University, Turkey ORGANIZING SECRETARIES Prof. Pradeep Kumar Mallick, IRD India, Bhubaneswar Dr. P. V Rao, Prof., Dept of ECE, RajaRajeswari College of Engg, Bengaluru SPECIAL SESSION CHAIRS Prof. V.Sreepathi, Prof., Dept of ECE, RajaRajeswari College of Engg, Bengaluru Dr. Balakrishna R, HOD, Dept of ISE, RajaRajeswari College of Engg, Bengaluru INTERNATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE Dr. Ganesh R Naik, FEIT-UTS, Sydney, Australia Dr. Savitri Bevinakoppa, MIT, Australia Dr. Sergey Mosin, Vladimir State University, Russia. Dr. Katina Michael, University of Wollongang, Australia. Dr. Ahmed Faheem Zobaa, BU, UK Dr. Akhtar Kalam, VU, Australia. Dr. Alfredo Vaccaro, US, Italy Dr. David YU, UWM, US Dr. Dmitri Vinnikov, TUT, Estonia Dr. Gorazd Stumberger, UM, Slovenia Dr. Jagadish Nayak, BITS pilani, Dubai Campus Dr. Lausiong Hoe, Multimedia University, Malaysia Dr. Hussain Shareef, UK, Malaysia Dr. Joseph Olorunfemi Ojo, TTU, USA Dr. Junita mohamad-Saleh, US, Malaysia Dr. Mohamed A.Zohdy, OU, MI Dr. Murad AL-Shibli, Head, EMET, Abu Dhabi Dr. Nesimi Ertugrul, UA, Australia Dr. Omar Abdel-Baqi, UWM,USA Dr. Richard Blanchard, LBU,UK Dr. Shashi Paul, DM,UK Dr. Zhao Xu, HKPU, Hong Kong Dr. Ahmed Zobaa, Brunel University, UK NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE Dr. Vivek Deshponde, MIT, Pune Dr. Awale R N VJTI, Mumbai Dr. S.Jeevananthan, Pillaichavadi, Puducherry, India Dr. Debashish Jena, NITK , India Dr. M.P Somasundaram, Anna University, Chennai, India Dr. N.K.Mohanty, Chennai Dr. K.Somashekar, Sambram Institute of Technology, Bengaluru Dr. R Shashi Kumar, EWIT, Bangalore Dr. Y R Manjunath HOD, UVCE, Bangalore Dr. C Subramani, SRM University, Kattankulathur Dr. Suresh Chandra Satapathy, ANITS, Vishakapatnam Dr. P.Sakthivel, Anna University, Chennai Dr. L Padma Suresh, NIU, Nagercoil Dr. N.P.Padhy, IIT Roorkee Dr. Patnaik S.K, Anna University Dr. Rama Reddy S, JCE Dr. Velusami.S, Annalai University Dr. G.Uma, Anna University Prof. P Bhuvaneswari, RRCE,Bangalore PROGRAM COMMITTEE MEMBER Dr. P. V Rao, Prof. and R&D Head, Dept. of ECE, RajaRajeswari College of Engg. Bengaluru -560074 Dr. Balakrishna R, Prof.& HOD Dept. of ISE, RajaRajeswari College of Engg. Bengaluru -560074 Prof. Mihir Narayan Mohanty, Department of ECE Engg., Institute of Technical Education and Research, SOA University, Bhubaneswar Dr. Rangaiah Leburu, HOD. Dept of ECE, Srinivasa Ramanujan Anantapur-515701 Inst. of Technology, Dr. Varadarajan S, Prof. Dept of ECE, SVU Engg College, Tirupathi AP Prof. (Dr.) Selvaraj Saravana Kumar, Professor, Dept of Computer Science Engineering, Panimalar Institute of Technology (Pit), Chennai, India Dr. Shashikumar R. Prof. Dept of ECE Engg, EWIT , Bengaluru Dr. S Sumathi, Prof & HOD Dept. of ECE, Adhiyaman College of Engg, Hosur, TN-635109 Dr. Y R Manjunath, Prof. & Head, Dept of EEE, UVCE, Bengaluru Dr. Cyril Raj Prasanna P, Prof. & R&D Head. Dept of ECE, M. S. Engg College, Bengaluru Dr. Sheerish S, Prof. & Head. Dept of EEE, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal Dr.Shubhransu Sekhar Dash, Prof Dept of EEE, SRM Engg College, SRM University, Chennai Dr. Vipin Tyagi, Prof. Dept of CSE, JPIT, Raghogarh Guna , M.P Dr. M.Z Kurian, Prof & Head Dept. of ECE, SSIT, Tumkur, Karnataka Dr. P. Subbaiah, Principal, Bharath College of Engg for Women, Rayachoti, Cuddapah, AP Dr. T. Srinivasa Rao, Principal, Chaithanya Technical, Institute JNTU, Hyderbad Dr. Ramesh S, Prof. Dept of ECE, Dr.AIT, Bengaluru -560072 Dr. Ramakrishna K, Prof & HOD, Dept of ISE, Velammal Institute of Technology, Ambattoor, Chennai Dr. Suresh H.N, Prof. Dept of IT, Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bengaluru 560004 Dr. S. Ravi, Prof. & Head Dept, of ECE, Dr. M.G.R University, Madhuravoyal, Chennai Dr. A. Brintha Therese, Professor, SENSE Dept, VIT University, Chennai Dr. Ramachancra A.C, Prof and Head, Dept of ECE, Alpha College of Engg, Bengaluru Mr. Rishi Kumar Verma, Scientist- D, DEBEL- DRDO, Bengaluru Table of Contents Sl. No. 01. Topic BER Analysis and MAI cancellation of Voice Signal through CDMA communication using FPGA Spartan 3E Processor - 02. 03. 04. 05. 06. 07. 08. 7 Prantik Biswas, Shahin Shabnam, Abhisek Paul, Paritosh Bhattacharya Differential Iilumination Enhancement Technique For A Night Time Video - 6 Vinothini M, Syed Ibrahim B A Cycle Detection Based Efficient Approach for Constructing Spanning Trees Directly from Non-regular Graphic Sequences - 5 Sangeetha K, Sudhakar Babu T, N.Rajasekar Design of Low Power Efficient Median Filter for Noise Reduction in Image - 4 Rajeshwari D S, P V Rao, Rajesh V Fireworks Algorithm based Maximum Power Point Tracking for uniform irradiation as well as under partial shading condition - 3 Ahmed M. Atallah, Almoataz Y. Abdelaziz, Mohamed Ali, R.K.Saket, O. P. Bharti Charge pump with improved high swing cascode current source for accurate current matching in PLL - 2 T.N.Anitha, Balakrishna .R Reliability assessment and economic evaluation of offshore wind farm using stochastic probability - 1 Manjunatha Reddy E, Nagaraj P, Siva Yellampalli Content Based Load Balancing Using Web Clusters & Service Rankings - Page No. G.Abirami, S.Padmavathi 8 09. Low Cost Appliance Control System for Home Automation and Energy Management Using Image Processing - 10. 11. 13. 18. 13 Anbarasi P N, Senthilkumar Mathi 14 K.Viswanath and R.Gunasundari 15 Ajith P, Unnikrishna Menon K A and Vrinda N Menon 16 Pranshu Agrawal, Gaurav Ojha, Mahua Bhattacharya prediction: Clustering and classification 17 Ashok M V, Apoorva A, Chethan V Cluster Based Distributed Key Architecture Scheme for MANETs - 12 Gaurav Ojha, Rakesh Singh, Anupam Shukla Placement chance approach - 11 Shukla, A generic algorithm for segmenting a specified region of interest based on Chanvese’s algorithm and active contours - 17. Anupam Simulation Framework for Modeling Magnetic Induction Based Wireless Underground Channel - 16. Ojha, VLSI implementation and analysis of Kidney Stone Detection from Ultrasound Image by Level Set Segmentation and MLP-BP ANN Classification - 15. Gaurav A Tokenized Binding Update Scheme for Next Generation Proxy IP Mobility - 14. Partho Manda, S. S. Agrawal Improved Identity Anonymization using Hashed-TOR Network - 10 Varna C Prakash, Sivraj P. and Sasi K.K. Accoustic Modeling for Development of Accented Indian English ASR - 12. Nagaraj Shet, Shreesha C, P.V. Rao, Abdullah Gubbi Communication Network of Wide Area Measurement System for Real Time Data Collection on Smart Micro Grid - 9 B.Rajanna, R.Rajeswara Rao 18 19. Design and Implementation of 270 Tap Finite Impulse Response Filter - 20. 21. Chain 21 Data Mining for Healthy Tomorrow with the implementation of Software Project Management technique 22 23. 28. 25 Chaitra N Shivayogimath, N.V.Umareddy 26 R. C. Barik, R. Mishra 27 Rahul R.Pillai, Mirav Mehta, Naveen K.A, Vishnu.Rajan and Sreedevi K.Menon Energy efficient communication in wireless sensor network for precision farming - 24 Arathi K, Anju S Pillai Planar Crossover using Microstrip Patch Antenna for Beamforming Networks - 23 Jitendra V. Tembhurne, S. R. Sathe Comparative analogy on Classification and Clustering of Genomic Signal by a novel Factor analysis and F-score method - 27. K.Venkata Rao, Balakrishna R, Aditya Pai H & Piyush Kumar Pareek Performance Analysis of a Software Defined Network Using Mininet - 26. Tausif Diwan, S. R. Sathe Low-power Home Embedded Surveillance System Using Image Processing Techniques - 25. Matrix RSA public-key Acceleration on CUDA GPU - 24. 20 Sreelakshmi S, Vandana Raj T Dynamic Programming Parallelization of Multiplication on GPU: A Comparative Study - 22. Vandana Raj T, Sreelakshmi S Implementation of 18 Bit High Speed Binary Multipliers - 19 T V Aneeth and R Jayabarathi, 28 29. Design and Evaluation of 3D NoC Routers with Quality -ofService (QoS) Mechanism for Multi-core Systems - 30. 31. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 37 Nibi K V , K A Unnikrishna Menon, Preeja Pradeep, Static noise margin Analysis of 6T SRAM CELL - 36 Anjali Arunan, Aryadevi R.D Underground Tunnel Detection Across Border Areas - 35 Prabhavathi C.N, K.M Ravikumar Design of Wireless Sensor Network for Submarine Detection - 34 S.V.Mahesh Kumar, R. Gunasundari A Fast Adaptive Kalman Filtering Algorithm for Speech Enhancement Under Stationary Noise Environment - 33 Seyed Reza Hashemi, Ata Jahangir Moshayedi Diagnosis of Corneal Arcus Using Statistical Feature Extraction and Support Vector Machine - 32 Nissy Sara Mathai, Gandhiraj R LAB View Based Smart Washing Machine Analyzer for Energy Consumption Features - 31 Yasmeen Arafath, Ranjith Kumar R Performance Improvement of Compressed Sensing Reconstruction using Modified-AMP algorithm - 30 Ria George, Sreekala.M, Deepa .K Big Data Analytics for Network Congestion Management Using Flow Based Analysis - 32. Pournamy Mohan and K. Somasundaram Single Stage Boost Rectifier for Wireless Charging of Portable Devices through Magnetic Resonant Coupling - 29 38 Abinkant A Jose, Nikhitha C Balan Topology Preserving Map Generation for Multiple Mobile Fishing Vessels Sruthi N, Divya P, Maneesha Vinodini Ramesh 39 40. Accumulator Design in Cadence 90nm Technology - 41. 44. 46. 47. 48. 46 Siva V Girish, R Prakash, A. Balaji Ganesh 47 M. Abdul Rahman Rafi, N. Albert Singh Enhancement in the performance of routing protocols for wireless communication using Clustering, Encryption and Cryptography - 45 Sunny Nandwani, Mohit Achhra, Raveena Shah, Aditi Tamrakar, K K Joshi, Sowmiya Raksha Naik Energy Conservation in Multi-Storey Buildings at Indian cities by Daylighting Control – A Study - 44 S.Kalaivani, I.Shahnaz, Shaikh Rizwana Shirin, C.Tharini Real-time remote monitoring of indoor air quality using Internet of Things (IoT) and GSM connectivity - 43 Haripriya H.Kulkarni, D.G.Bharadwaj, Dipti B. Yeolekar, Sheetal B. Mhetre Weight Based Data Center Selection Algorithm in Cloud Computing Environment - 42 Barat, Real time ECG acquisition and detection of Anomalies - 45. Subhendu Roy, Sraboni Ghosh, Aratrika Madhurima Chattopadhyay, Debjyoti Chowdhury A Real Time Intelligent Micro-controller based Harmonic Computing with Smart Phone Connectivity - 41 Vidula.S.Jape, D.G.Bharadwaj Real Time Implementation of Electromyography for Hand Gesture Detection Using Micro Accelerometer - 43. Nikhitha C Balan, Abinkant A Jose A New Approach of Object Oriented Programming Language for Remote Power Quality Monitoring & Analysis Considering Harmonics - 42. 40 Kanchan Dhote, G.M.Asutkar 48 49. Design and Implementation of MRI Brain Image using Level Set Segmentation and Classification 49 C.M.Naveen Kumar, B.Ramesh 50. Robotic imitation of human hand using RGB Colour Gradient Mapping - 51. 52. 56. Manjunath.R, S.T.Bibin 54 G.K.Venkatesh, P.V.Rao 55 Minal S.Dahake, Vivek S.Deshpande 56 Umashankar, R Gunasundari Non-Invasive EEG Feature extraction and recognition of epileptiform activity using Adaptive resonance theory - 53 Shalini, A Review on Electro diagnosis to detect Retinitis Pigmentosa - 57. R.Ranjith Kumar, S.Saranya Energy Efficient Data aggregation protocol for wireless sensor network - 52 Mangala Gowri S .G, Navya P, Cyril Prasanna Raj. P Performance Analysis of a Novel Method for Fast Handovers in TDD and FDD for Long Term Evolution - 55. Shantakumar B. Patil, Premjyoti Patil, K Prudhvi Yaswanth, R.Priyanka Design and simulation of PI Controller for Multi-lift Push Pull Switched Capacitor Main Series Elementary DC-DC Luo Converter - 54. 51 An Efficient Performance analysis for EEG signal Denoising and classification using Multiwavelets - 53. Thyagaraj T., Kumar Abhishek, Brunda N.S., Rakesh Ranjan, Nikita Kini Intelligent Business: An Auto Client Controller - 50 Aswathappa P, S.Ranjitha, H. N. Suresh 57 58. DWT-SVD Based Watermarking Scheme Using Optimization Technique - 59. 58 V. Santhi and Sarthak Nandi Recent Research and various Techniques available for Efficiency Improvement of IGCC Power Plants 59 Ruchi Pandey, V K Sethi, Mukesh Pandey, Maneesh Choubey 60. Hospital based screening for Osteoporosis in both sexes aged above 50 years using prototype US bone densitometer - 61. 62. 64. 65. 66. 65 R. Deepa,R Manicka Chezian An Enhanced RSA with Attribute Based Encryption for Securing User Log in Cloud Computing - 64 Rajesh K S , R.Balakrishna An Involuntary Data Extraction And Information Summarization Expending Ontology - 63 Saroj Pradhan, Rabindra Kumar Sahu and Sidhartha Panda Minimize the data packet dropping by malicious Nodes in MANET using FSR Algorithm - 62 A. Y. Abdelaziz, Sanjay Kumar, Biplab Bhattacharyya , M. Ezzat, W. Sameh Differential Evolution Based LFC of Two Area Interconnected Power System with SMES Units - 61 S Krishnama Raju, GN Pillai Passive and Active Methods of Islanding Detection for grid Connected PV Distributed Generators - 63. Moataz Samir, Anburajan,.M Enhancing LVRT capability of DFIG based Wind power plants by Interval Type-2 Fuzzy logic Controller - 60 S. Hemalatha, and R.Manickachezian 66 67. Design of a 16 Bit Arithmetic And Logical Unit Using Vedic Multiplication Technique - 68. 69. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. Kratika Malik, Ravikiran Pise, Warade, G.M. Gaikwad 75 S.Niraimathi Effective Cluster Key Mechanism for Integrated Internet MANETs - 74 Lucky Atkare, Sneha A Novel Fuzzy Rule Based Design Interface to Counteract Headlamp Glare Uncertainties Exhibited by Vehicles - 73 Bhaskar B, Anushree P S,Divya Shree S Detection of Vampires in Ad Hoc Sensor Networks - 72 Biswajit Mahapatra, Likan Priyadarsini Kernel Gablet based Face Recognition in Quintuple Space using fSVD - 71 ShekharShivam, Archana Chaudhari, Abhijit Pawar, JayantV. Kulkarni Study of a Grid Connected To PV System Using Different MPPT Algorithms - 70 R.Saranya and R.Dhanalakshmi. Segmentation of TOF-MRA Blood Vessels Using GMM & EM Algorithm - 69 Nivedita Bhattacharya, and Deepak Kumar Dewangan Enhanced Cost Aware Secure Routing Protocol For Lifetime Optimization And Energy Balance In Wireless Sensor Networks - 68 M.Manasa, C.Karthikeyan, and N.D.Thamarai Selvi Implementation And Assessment For Identification of Finger Knuckle Using Scale Invariant Feature Transform Technique - 70. Deepak Rao, and Anuradha S Savadi Change Detection in SAR Images Based on MRFFCM using SWT - 67 CAtheeq, MMunirAhmed Rabbani 76 77. Study on Six Sigma approach to improve the quality of process outputs in business processes in Small & Medium Level Software Firms. - 78. 85. 80 Shashibhushan G, Savita Sonoli. 81 S. A. Hariprasad, Anupama H.G., Chitkala P, Gangothri N. 83 Akash Kumar Bhoi, Pradeep Kumar Mallick, S. Saravana Kumar, Karma Sonam Sherpa Thirunarayana Jayadevappa Theerthan, 84 Vinay Kumar R, D. Hybrid Renewable Energy for Rural Electrification by Using 1 Phase Supply - 82 Amol A. Kalage, Nitin D. Ghawghawe, Pradnya D. Sonawane Valve Control Using Microcontroller - 79 Kumar Gaurav, Amit Kumar Sahoo, Sudhansu Kumar Mishra Brain Tumor Detection: A Comparative Analysis of Edge Detection Techniques - 84. Minakshi D. Gavande, Mahesh K. Penshanwar , M. F. A. R. Satarkar Optimum TMS and PS settings of Directional Overcurrent relays using Teaching Learning Based Optimization Technique - 83. 78 Early Warning System for Earthquake - 82. Gudi, Implementation of Single Phase Nine Level Inverter - 81. Krishna Nonlinear System Identification Using Functional Link Multilayer Perceptron Artificial Neural Networks - 80. R, STATCOM as a Voltage Sag Compensator - 79. K.Venkata Rao, Balakrishna Piyush Kumar Pareek 77 Swaraj Kadam, Nagesh Dudile , P. K. Katti 85 86. Big Energy Efficient and Optimal Path Selection in LEACH Algorithm - 87. 88. 90. 91. B.B.Neelakantappa, 91 Samyak Shamkuwar, Parikshit Chavan, Sujay Kakkad, Ajinkya Walimbe, Kiran Joshi, SowmiyaRaksha Naik 92 B.B.S.Kumar, P.S.Satyanarayana, Rohini G.V, Savitha N 93 P.V.Rao, K.Viswanath A Survey of Recent Data Mining Applications and Research Perspectives - 90 B.Ramesh, Design and Implementation of MRI Brain Image Enhancement and Segmentation using Xilinx System Generator - 94. M.E.Tejamorthy, N.A.Ranjan Edge Segmented Human Brain Image Denoising using Wavelets - 93. Veni devi Gopal, Nidhitha Gopinath, Resmi R Rating Based Load Balancing Algorithm in Grid Computing - 92. 89 Design and Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy and Funds Detection using Cup to Disk Ratio and Wavelets - 88 Dany Varghesea, Viju Shankar Survey On Clustering And Routing Protocols - 87 Seyed Samsamoddin Naghavi Chaleshtori, AdinathM. Funde A Novel Approach for Single Image Super Resolution using Statistical Mathematical Model - 89. Krutika Barabde, Shilpa Gite Econometric analysis of solar tracker systems in India, a Case Study - 86 M. Inbavalli , Tholkappia Arasu, C.Anitha 94 95. A Hybrid Neural Network Model for Active Noise Cancellation Using TMS320C6713 DSK - 96. 97. 99 100 99 Sumalatha U, Seema Patil Analysing Attack Pathways Through Security Metrics - 98 Anupama Sheela, Kamalanathan Kandasamy Analysis of an Improved Apriori Algorithm for Association Rule Mining - 97 Kaliprasanna Swain, Manoj Kumar Sahoo, Annapurna Swain, Lopa Nayak A Novel Hybrid SMS Spam Classification Framework for Android - 96 Tanveer Kaur Dewgun, Pushpraj Singh Chauhan FPGA Implementation of Color Space Transformation RGB to YCbCr Using XSG - 98 Shashi Kumar, Rajeswari, G. Ramanjulu, NNSSRK Prasad Enhanced Integrated Approach to Predict Web User’s Future Requests Using K-Means and FP-Growth - 95 Krishnashree Achuthan, Reshma Mohan 100 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) BER Analysis and MAI cancellation of Voice Signal through CDMA communication using FPGA Spartan 3E Processor 1 Manjunatha Reddy E, 2Nagaraj P, 3Siva Yellampalli This paper presents the bit error rate analysis with different coding rates and MAI cancellation. The main objective of this paper is to design and to implement an embedded system by using reconfigurable Micro blaze processor, which is present in Spartan 3E FPGA, for the purpose of Bit Error Rate analysis and MAI cancellation to a voice signal in CDMA communication system. Xilinx Platform Studio (XPS) is used to develop the Base System, this is the combination of the peripherals available in the Micro blaze processor. Then the software for the convolution encoding and viterbidecoding is developed, with the EDK tool in Xilinx platform studio for BER analysis and MAI cancellation. Mat lab is used for the purpose of creating the CDMA system that includes Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), Pseudo-Noise (PN) Sequence generator block, Spread spectrum, Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation and demodulation blocks. AWGN noise is considered the source of MAI in the signal and the results were measured and tabulated. It was found that the BER curve had an exponentially reducing curve with gain, and importantly it is good that the reduction of noise level in the form of error bits for every 10,000 bits as we decode using Viterbi decoder in the cumulative order. Our tested results shows that for the 1/3 code rate we are able to make down noise level up to 20.40% reduction in the form of bit error rate for the noise of -10db. 1 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Content Based Load Balancing Using Web Clusters & Service Rankings 1 T.N.Anitha, 2Balakrishna .R 1,2 Research Scholar, Dept of CSE, Rajarajeswari College of Engineering, Mysore road, Bangalore. Professor & HOD, Dept of ISE, Rajarajeswari College of Engineering, Mysore road, Bangalore. Email:1anithareddytn72@gmail.com, 2rayankibala@yahoo.com Web Servers have gained an immense popularity these days due to its nature to cater huge number of user requests were any number of users can get service from web based applications. As it comes with global accessibility, servers hosting popular website tends to get massive load which deteriorates its efficiency to provide quality service. These days most of the servers use load balancing techniques which distribute load among multiple virtual servers hosting a website. Generally these load balancing techniques concentrates on balancing user requests load on server and ignore the type of content requested. Reason behind it is overhead on dispatcher for analysing content request and assigning appropriate rank. This process consumes additional time for dispatcher to allocate server and users face little delay in viewing their site but is helpful in long run as heavy bandwidth consuming services such as multimedia requests can be catered efficiently by high priority servers only. priority of servers can be defined as per their configuration and capabilities. Through experimental results on JMeter software it is proved that this concept can be helpful in providing better Quality of Service (QoS) to the website users. 2 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Reliability assessment and economic evaluation of offshore wind farm using stochastic probability 1 Ahmed M. Atallah, 2Almoataz Y. Abdelaziz, 3Mohamed Ali, 4 R.K.Saket, 5O. P. Bharti 1,2,3 Electrical Power & Machines Department, Faculty of Engineering Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt 4,5 Electrical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) Varanasi (UP) India Email: 1atallah_eg@yahoo.com, 2almoatazabdelaziz@hotmail.com, 3 mohamed_ali_mohamed_ali86@yahoo.com, 4drrksaket@gmail.com, 5 opiitbhu@gmail.com This paper shortly introduced the electric power transmission system for offshore wind farms (OWF). The transmission system components are demonstrated. Each component cost and reliability are studied and tabulated. An evaluation of the transmission system reliability of OWF is performed to increase the dependence on the OWF as a power sources in the future. Reliability assessment is performed on a proposed site in Zafarana, Egypt and results are tabulated and simulated for different distance from the shore. The cost of the transmission system is studied using the stochastic probability method; optimization is performed on the investment cost, unavailability cost and ohmic cost losses. Optimization results on the proposed site are done using different electrical power transmission systems schemes. Losses due to the wind unavailability and ohmic losses are studied and simulated. 3 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Charge pump with improved high swing cascode current source for accurate current matching in PLL 1 Rajeshwari D S, 2P V Rao, 3Rajesh V 1 Electronics & Communication Department, 2Electronics & Communication Department 1 Jain University & SiCon Design Technologies Pvt. Ltd, Bengaluru560024, India, 2 RajaRajeshwari college of Engineering, Bengaluru-560074, India, 3 SiCon Design Technologies Pvt. Ltd, Bengaluru-560037, India. Email: 1dsrajeshwari@gmail.com, 2pachararao@rediffmail.com In loop dynamics of Charge Pump Phase Locked Loop the charge pump current plays pre dominate role to loop bandwidth. Different charge pump architectures suffer from charge sharing, clock feed-through, channel charge injection and current mismatch. Due to this Charge Pump Phase Locked Loop can have more reference spur. Improved high swing current source is proposed to obtain nearest current matching characteristics. 0.01% of current mismatch is achieved with 3.3V, 90nm CMOS technology. The circuit is verified at Process Voltage Temperature corners. 4 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Fireworks Algorithm based Maximum Power Point Tracking for uniform irradiation as well as under partial shading condition 1 Sangeetha K, 2Sudhakar Babu T, 3N.Rajasekar 1,2,3 School of Electrical Engineering, VIT University, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India. Email: 1sangukrish21@gmail.com, 2sudhakarbabu66@gmail.com, 3 natrajanrajasekar@gmail.com Harnessing of maximum power from solar PV with the aid of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) methods is of significant importance as it contributes to better utilization of the system. Amidst the conventional MPPT methods, Hill climbing and Incremental conductance methods are widely recognized but they yield maximum power only under constant irradiation and utterly fail when exposed to conditions of varying irradiation levels. Besides these, they exhibit wide power fluctuations even under steady state along with poor transient characteristics under partial shading conditions which is quite probable. Therefore, a recently developed optimization technique namely Fireworks Algorithm is utilized for Global Maximum Power Point Tracking. Extensive simulations are performed for constant irradiation as well as partial shading condition .The obtained results are compared with existing methods to highlight the superiority of the method used in this work. 5 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design of Low Power Efficient Median Filter for Noise Reduction in Image 1 Vinothini M, 2Syed Ibrahim B 1 PG Scholar, ECE Department, Chettinad College Of Engineering, Karur, India 2 Senior Assistant Professor, ECE Department, Chettinad College of Engineering, Karur, India Email: 1vinothini.1505@gmail.com; 2ibzz82@gmail.com In this paper designing of the median filter is done with help of the comparator and multiplexer. In image processing , as median filter is an important factor to reduce salt & pepper noise , it is essential to develop a new design techniques to reduce the power consumption. So, the comparator and multiplexer design used in the median filter is designed using various styles of the full adder with help of DSCH and Microwind tool. 6 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Cycle Detection Based Efficient Approach for Constructing Spanning Trees Directly from Nonregular Graphic Sequences 1 Prantik Biswas, 2Shahin Shabnam, 3Abhisek Paul, 4Paritosh Bhattacharya 1,3,4 Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Agartala, India 2 Department of Computer Science, Assam University, Silchar, India Email: pranmasterbi@gmail.com Realization of graphic sequences and finding the spanning tree of a graph are two popular problems of combinatorial optimization. A simple graph that realizes a given non-negative integer sequence is often termed as a realization of the given sequence. In this paper we have proposed a method for obtaining a spanning tree directly from a degree sequence by applying cycle detection algorithm, provided the degree sequence is graphic and non-regular. The proposed method is a two step process. First we apply an algorithm to check whether the input sequence is realizable through the construction of the adjacency matrix corresponding to the degree sequence. Then we apply the cycle detection algorithm separately to generate the spanning tree from it. 7 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Differential Iilumination Enhancement Technique For A Night Time Video 1 G.Abirami, 2S.Padmavathi 1 Student M.TECH, CSE Dept, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Amrita Nagar, Ettimadai, Coimbatore-641112 2 Assistant Professor, CSE Department, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Amrita Nagar, Ettimadai, Coimbatore-641112 Email: 1abiramigovindarajan@ymail.com, 2s_padmavathi@cb.amrita.edu Video surveillance has become a common security need in the present world scenario. The Night time video surveillance becomes more challenging due to the presence of extreme illumination conditions, which is not uniform in a frame. Pedestrian detection would be very difficult under such illumination condition. The system proposes a method to identify and segregate the differently illuminated regions with the help of day time reference image. Various enhancement techniques are applied on these regions separately and the results are combined to obtain the enhanced frame. Results of these techniques are summarized and appropriate methods are suggested for specific cases. 8 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Low Cost Appliance Control System for Home Automation and Energy Management Using Image Processing 1 Nagaraj Shet, 2Shreesha C, 3P.V. Rao, 4Abdullah Gubbi 1 1 Dept of ECE, 2Dept I& CE, 3Dept of ECE, 4Dept of ECE, VTU Belgaum, India, 2MIT Manipal, India, 3VTU Belgaum, India, 4VTU Belgaum, India Email: 1shet_nagaraj@yahoo.co.in; 2shreesha.c@manipal.edu; 3 pachararao@rediffmail.com; 4abdullahgubbi@yahoo.com In the stressful life enhancing the quality of life at home is the need of the hour. smart home automation is being incorporated with intelligent system. Existing systems are creating major challenges in terms of cost and energy management. In a home network environment keeping the sensors and devices always on consumes more electrical power and increases the cost paid for consumption of power. In proposed work, energy management has been carried out with an intelligent algorithm. Image processing has a very big potential to do virtually anything. The challenges of cost have been overcome by using image processing. Algorithm is developed for image processing based appliance control system. The method proposed in this paper reduces the cost of sensors used in home automation. With image processing based home automation there is less energy consumption, reduction in umber of sensors and also optimized maintenance cost of home automation networks. 9 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Communication Network of Wide Area Measurement System for Real Time Data Collection on Smart Micro Grid 1 Varna C Prakash, 2Sivraj P. and 3Sasi K.K. 1,2,3 Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Amrita School of Engineering Coimbatore, India Email: varna1312@gmail.com This paper deals with communication architecture employing appropriate communication technologies for distribution side Wide Area Measurement System (WAMS). The different communication technologies like WiredLAN, WLAN, ZigBee protocol are simulated in ns2 considering a five bus smart micro grid topology and the performance metrics are compared and analysed based on the standard requirements, in order to suggest the apt technology. The study shows that in comparison with a homogeneous network, a heterogeneous network provides a better result considering the operational demands at different levels of the smart distribution grid architecture. 10 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Accoustic Modeling for Development of Accented Indian English ASR 1 Partho Manda, 2Gaurav Ojha, 3Anupam Shukla, 4 S. S. Agrawal 1,2,3 Department of Information Technology, ABV-IIITM, Gwalior, India 4 KIIT Group of Colleges, Gurgaon, India This paper investigates Indian English from the point of view of a speech recognition problem. A novel approach towards building an Automated Speech Recognition System (ASR) for Indian English using Pocket Sphinx has been proposed. The system was trained with a database of English words spoken by Indians in three different accents using continuous as well as semi-continuous models. We have compared the performances in each case and the optimum case performance comes close to 98% accurate. Based on this study, we tweaked the original Pocket Sphinx Android application in order to incorporate our results and present it as an Indian English-based SMS sending application. We are working further on this approach to identify ways of successfully training a speech recognition system to recognize a much wider variety of Indian accents with much more significant accuracy. 11 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Improved Identity Anonymization using HashedTOR Network 1 Gaurav Ojha, 2Rakesh Singh, 3Anupam Shukla 1,2,3 Department of ICT, ABV-IIITM, Gwalior, INDIA Email: 1ojha.iiitm@gmail.com, 2f25527180@gmail.com, 3 dranupamshukla@gmail.com Today, the modern world has been computerized to a huge extent because of the increasing penetration of the Internet. There is a plethora of services available on the web platform these days. Services available may be either legitimate or illegitimate. International borders have been effectively eliminated with the help of the internet and so more and more companies are offering their services across the globe. The physical location of the service provider doesn‘t matter anymore. Since every request that is sent to the WWW, every message that is relayed and, in fact, every click is logged somewhere on the internet, it gives rise to a huge knowledge base of user data. This knowledge base can be manipulated and exploited in a number of ways. This poses a great threat to any individual user who wants to utilize the services available on the internet anonymously. A mechanism is required using which individuals can maintain their own privacy from global organizations such as the NSA, Google, etc. which are believed to collect huge amounts of personal user data. The TOR network goes a long way in doing that and abstracts the user from the conventional internet. But TOR itself isn‘t free from vulnerabilities. In this paper, vulnerability with the ONION routing protocol, which is the spine of the TOR network, has been presented. It has been analyzed and a technique to overcome it has also been discussed to make the TOR network safer for anonymous use on the World Wide Web. 12 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Tokenized Binding Update Scheme for Next Generation Proxy IP Mobility 1 Anbarasi P N, 2Senthilkumar Mathi 1 PG Scholar, 2Assistant Professor (Selection Grade), Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Amrita School of Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (University) Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, Email: 1anbarasipn@gmail.com, 2m_senthil@cb.amrita.edu Now-a-days the users are apparently high for wireless networks. In proxy mobile IPv6, the mobility management among the network is tedious for the location update of mobile node and the secrecy plays a tremendous role. Here, the messages are exchanged via localized mobility anchor between the communicants. Consequently, the data traffic is high due to centralized feature of local mobility anchor. Also, there is a single point of failure and increase in the network cost. Therefore, the efficacy of the network is increased by distributing the functionality of local mobility anchor among mobile access gateways present in the network. However, there are several security challenges such as denial-of-service, manin-the-middle attack etc. Thus, the network needs enhancement in prevention of threat and location update of mobile node. Hence, the present paper proposes a new tokenized binding update scheme by sharing a routing table. Here, the token of mobile node is incorporated in the routing table and shared among the mobile access gateways. In addition, the proposed scheme decreases the cost of signaling and traffic overhead by eliminating unnecessary queries for binding update and acknowledgment. The security of the scheme is validated using AVISPA - the model checker. From the security and numerical analysis, the proposed scheme shows the enhancement of security and significant reduction in the connection cost and data delivery cost when compared to the existing schemes. 13 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) VLSI implementation and analysis of Kidney Stone Detection from Ultrasound Image by Level Set Segmentation and MLP-BP ANN Classification 1 K.Viswanath and 2R.Gunasundari 1,2 Pondicherry Engineering College, Ph.D. Scholar, Department of ECE, Pondicherry Engineering College Email: 1viswa_kv@pec.edu, 2gunasundari@pec.edu The abnormalities of the kidney can be identified by ultrasound imaging. The kidney may have structural abnormalities like kidney swelling, change in its position and appearance. Kidney abnormality may also arise due to the formation of stones, cysts, cancerous cells, congenital anomalies, blockage of urine etc. For surgical operations it is very important to identify the exact and accurate location of stone in the kidney. The ultrasound images are of low contrast and contain speckle noise. This makes the detection of kidney abnormalities rather challenging task. Thus preprocessing of ultrasound images is carried out to remove speckle noise. In preprocessing, first image restoration is done to reduce speckle noise then it is applied to Gabor filter for smoothening. Next the resultant image is enhanced using histogram equalization. Level set segmentation is applied two times, first to segment kidney portion and its output is the input to second to segment stone portion, since it yields better results. In level set segmentation two terms are used in our work. First is using a momentum term and second is based on resilient propagation (Rprop). Extracted region of the kidney stone after segmentation is applied to Symlets, Biorthogonal (bio3.7, bio3.9 & bio4.4) and Daubechies lifting scheme wavelet subbands to extract energy levels. These energy level gives an indication about presence of stone, which significantly vary from that of normal energy level. These energy levels are trained by Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Back Propagation (BP) ANN to identify the type of stone with an accuracy of 98.8% and real time implementation is done using Verilog on Vertex-2Pro FPGA. 14 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Simulation Framework for Modeling Magnetic Induction Based Wireless Underground Channel 1 Ajith P, 2Unnikrishna Menon K A and 3Vrinda N Menon 1,2,3 Amrita Centre for Wireless Networks and Applications, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Amritapuri, Kollam, Kerala, India, 690525. Email: 1ajithvatsan@gmail.com, 2kaumenon@gmail.com, 3 vrindanm@gmail.com Wireless Underground Communication is a challenging task when Electro Magnetic (EM) waves are used. The communication has to face many limitations like spreading loss, fading and attenuation. The existing solution for this problem is Magnetic Induction (MI) - based communication. The performance of this method depends on many factors like the distance between the transmitter and receiver, placement of relay coils, moisture content, permeability, seasonal changes and the depth at which the system is deployed. There are no proper MI channel model which incorporates all these soil parameters and geometrical parameters for predicting the signal quality at the receiver. We propose a simulation model using MATLAB, to predict the signal quality at the receiver by optimizing the placement of relay coils, taking into consideration, the soil parameters, geometrical parameters of coils and geological parameters. 15 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A generic algorithm for segmenting a specified region of interest based on Chanvese’s algorithm and active contours 1 Pranshu Agrawal, 2Gaurav Ojha, 3Mahua Bhattacharya 1,2,3 Indian Institute of Information Technology and Management Email: 1pranshu.a.11@gmail.com, 2ojha.iiitm@gmail.com, 3mb@iiitm.ac.in Image processing and recognition is a modern field which is gaining popularity due to its capability to automate certain mundane object recognition tasks and provide unparalleled accuracy and precision. Computer graphics have evolved sufficiently so as to cater to a wide array of applications ranging from categorizing mechanical parts of a machine to identifying foreign objects/tumours inside the human body. In this particular application, we are working towards identifying cotton plants from a heap. Traditionally, this task has been performed by laborers who identify the cotton plants from a collection and classify them based on certain characteristics. This task can take anywhere from a day to a week depending upon how good the yield is. We propose that this entire task from identifying cotton to classifying it based on the prerequisite characteristics can be performed automatically. We have developed an algorithm that can provide the exact position of cotton buds from pictures of the harvested plant. From the hardware aspect, this is the scope of automating the harvesting task. We have used the techniques of image acquisition, segmentation and feature extraction. A highly modified iterative version of Chanvese‘s algorithm is utilized to chalk out a starting boundary (contour) and then work successively on it to reach at a final segment that defines the cotton buds. 16 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Placement chance prediction: Clustering and classification approach 1 Ashok M V, 2Apoorva A, 3Chethan V Educational Data Mining is an area where in a combination of techniques such as Data mining, Machine Learning and Statistics, is applied on educational data to get valuable information. The purpose of this paper is to help the prospective FAD students in selecting or choosing a right under graduate course viz., Accessory design, fashion design, textile, and Fashion communication etc., based on the entrance exam ranking for admission to UG course. A clustering and classification approach is applied to solve placement chance prediction problem. Two classification algorithms viz., Decision tree and naïve Bayes and a clustering algorithm, KMeans are applied on the same data set. Algorithms applied are compared and was found that clustering algorithm K-means predicts better in terms of precision, accuracy and true positive rate. This work will help the students in selecting a best course suitable for them which ensure best placement chance. 17 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Cluster Based Distributed Key Architecture Scheme for MANETs 1 B.Rajanna, 2R.Rajeswara Rao 1 2 Associate Professor of Compute Science& Engineering, T.S, India Associate Professor of Computer Science& Engg, JNTUK University College of Engg, Vijayanagaram, A.P., India Email: 1raj1math@yahoo.co.in,2raob4u@yahoo.com Security deployment in data communication is very vital, where authentication is most obvious pre requisite. However, similar authentication procedures are not appropriate in hierarchical mobile ad hoc networks as it is characterized by infrastructure less. We develop and evaluate security method based on multi level key distribution; called cluster based distributed Key architecture for MANETs .Which addresses two important characteristics: authentication and authorization. It considers Cluster head selection based on novel metric called ‗Optimized packet processing capacity‘ and multi level key distribution process with the help of diffie-Hellman Key distribution. We evaluated the availability of the security infrastructure, and its overhead using NS2 .Results shows that it is possible to deploy security architecture with an acceptable performance and overhead. 18 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design and Implementation of 270 Tap Finite Impulse Response Filter 1 Vandana Raj T, 2Sreelakshmi S 1,2 Electronics and Communication Department, Amrita Viswa Vidyapeedom Amrita School of Engineering, Amritapuri, Kollam, Kerala, India Email: 1vandanattt@gmail.com; 2sreelakshmi.sree001@gmail.com; Filtering is processing of a time domain signal resulting in changing the original spectral components. The change is usually reduction or filtering out some of the unwanted input spectral contents i.e., it allows certain frequencies to pass while attenuating some other frequencies. When an analog filter processes continuous signal, digital filter operates on discrete sample values. Digital filters are basically of two types: Finite impulse response (FIR) and Infinite impulse response (IIR) filters. FIR filter uses only current and past input samples and none of the filters previous output values to obtain the current output sample value. This paper is about the implementation of a 270 tap low pass FIR filter. This paper implements a direct form fir filter with given pass band, stop band specifications using MATLAB and Verilog code. Specifications of the FIR filter are: Pass band frequency=100 kHz, Stop band frequency =500 kHz, Pass band attenuation=0.01dB Stop band attenuation=120 dB, Sampling frequency=20 MHz. 19 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Implementation of 18 Bit High Speed Binary Multipliers 1 Sreelakshmi S, 2Vandana Raj T 1,2 Electronics and Communication Department, Amrita Viswa Vidyapeedom Amrita School of Engineering, Amritapuri, Kollam, Kerala, India Email: 1sreelakshmi.sree001@gmail.com; 2vandanattt@gmail.com; Multiplication is a heavily used arithmetic operation that figures prominently in signal processing and scientific applications. Multiplication is hardware intensive, and the main criteria of interest are higher speed, lower cost, and less VLSI area. Multiplication involves basically two operations, generation of the partial products and their accumulation where the partial product is shifted and added with the previous partial product. The speed of multiplication can be enhanced by reducing the number of partial products or accelerating the accumulation .Hence in this paper, the novel study of the different fast multipliers like radix-2 or booth algorithm, radix4 or modified booth algorithm is done and implementation of 18 bit multiplier is done in Verilog (Modelsim) and compared the results in MATLAB. The SNR analysis of the multiplier of finite precision product, truncation and rounding is done. Algorithms for reducing the hardware complexity in partial product sign extension is implemented for both radix-2 booth multiplication and radix-4 modified booth multiplication. The Wallace tree adder is implemented for increasing the speed of the accumulation of the partial products. 20 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Dynamic Programming Parallelization of Matrix Chain Multiplication on GPU: A Comparative Study 1 Tausif Diwan, 2S. R. Sathe 1,2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology, Nagpur, Maharahtra, India Email: 1tausifdiwan.tausif@gmail.com; 2srsathe@cse.vnit.ac.in The dynamic programming paradigm involves various important optimization problems. The set of optimization problems include optimal binary search tree, longest common subsequence, binary knapsack, matrix chain multiplication and many more. In dynamic programming problems, the Matrix Chain Multiplication (MCM) of n matrices comprises the computation of the parenthesization for an optimal matrix product, which requires the computation time of O(n3) by using O(n2) table size. We propose the MCM parallelization techniques for thread-level of multi-core CPU and group of threads on NVIDIA GPU. The prime objective of this paper is to present and analyze massively parallel implementations of MCM algorithm using OpenMP and CUDA on a parallel systems such as Intel Xeon CPU and NVIDIA GPU. The implemented parallel MCM algorithm achieved a speedup of 10x on an Intel Xeon using OpenMP and a speedup of 7x on NVIDIA Quadro FX 3800 GPU with reference to its serial implementation. So, the speedup achieved on multi-core CPU dominates the speedup achieved by the GPU. This paper also presents performance comparisons for OpenMP, when chunksize of iterations of a loop and scheduling techniques of those chunks among cores changes. 21 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Data Mining for Healthy Tomorrow with the implementation of Software Project Management technique 1 K.Venkata Rao, 2Balakrishna R, 3Aditya Pai H & 4Piyush Kumar Pareek 1 Research Scholar, Computer Science & Engineering, JAIN University, Bengaluru & Associate Professor in Dept of CSE, Kammavari Sangham Institute of Technology, Bengaluru 2 Professor and HOD Dept of Information Science and Engineering RajaRajeswari College of Engineering, Bengaluru 3 Assistant Professor in Dept of CSE, Kammavari Sangham Institute of Technology, Bengaluru 4 Assistant Professor in Dept of CSE, Kammavari Sangham Institute of Technology, Bengaluru Email: 1kothapallivenkat@yahoo.co.in, 2rayankibala@yahoo.com, 3 adityapaih2007y@gmail.com, 4piyushpareek88@gmail.com In the current scenario we find many Data Mining related projects being used. These projects are being used very widely and very effectively for the extraction of data in the organization. The usage of data mining has helped in big way in terms of getting information where the nature of the database retrieval is humongous. In the current paper we are seeing how to carry out these data mining projects by using the project management technique. The project management technique makes the project to be carried out very effectively and very efficiently by properly planning the project, organizing according to the objectives, controlling or coordinating the projects. Hence making the project reach the objectives being framed or formulized. 22 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) RSA public-key Acceleration on CUDA GPU 1 Jitendra V. Tembhurne, 2S. R. Sathe 1,2 Deparment of Computer Science and Engineering, Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India Email: 1dt11cse077@cse.vnit.ac.in; 2srsathe@cse.vnit.ac.in Cryptography is a technique of using number theoretical mathematics for the key-generation, encryption and decryption of confidential information. Cryptography has many uses in real world applications such as Digital Right Management, ECommerce, Secret Broadcasting and Financial Cryptography etc. In this paper, we mainly focus on speedup of the RSA public-key cryptosystem algorithm. We proposed the high performance parallel RSA algorithms on parallel hardware such as Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). We used NVIDIA GPU Quadro FX 3800 to exploit the many-core parallelism for the implementation of highly parallel and efficient RSA algorithm on Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA). The experiments conducted on many-core GPUs show, the enhanced speedup of proposed parallel RSA algorithms compared to single CPU RSA algorithm implementation. We observed that the speedup achieved by the GPU dominates the single CPU RSA implementation. 23 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Low-power Home Embedded Surveillance System Using Image Processing Techniques 1 Arathi K, 2Anju S Pillai 1 Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (University),India Email: aarathijayakrishnan@gmail.com; 2s_anju@cb.amrita.edu 1 The need for surveillance systems are increasing due to safety and security requirements. And there exist an ample amount of challenging work yet to be explored in this domain. The current work proposes design, development and implementation of a low power home embedded surveillance system. Such systems being operated throughout the day, consumes considerable amount of power. Power consumption being a crucial design parameter affects the utility of the system. In the proposed system to consume power, use of low power sensor groups and controlling the activation of surveillance camera is incorporated through the M-bed microcontroller. Presence of a person is detected and face recognition is carried out using various image processing techniques. 24 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Performance Analysis of a Software Defined Network Using Mininet 1 Chaitra N Shivayogimath, 2N.V.Umareddy 1 Mtech Student,AMC Engineering College, Dept of E&C, Bangalore, India. 2 Professor, AMC Engineering College, Dept of E&C, Bangalore, India Email: 1chaishivyogi@gmail.com, 2nvumareddy@gmail.com Network is growing day by day. New devices are getting added into the network making it very difficult for an IT administrator to configure the ACLs and the other network parameters in the devices. Flexibility and programmability are the key factors in the present day scenario. Software Defined Networks (SDN) is the evolving network technology which provides the two factors mentioned. The latency in the packet delivery is less compared to the legacy Hardware Defined Networks (HDN) and in turn the throughput is also high. The work done in this paper provides a proof Of Concept (POC) for the better throughput of SDN based routing. 25 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Comparative analogy on Classification and Clustering of Genomic Signal by a novel Factor analysis and F-score method 1 R. C. Barik, 2R. Mishra 1,2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Vikash Institute of Technology, Bargarh, Odisha, India Email: 1ramchbarik@gmail.com; 2rosymishra93@gmail.com Data is the centroid in any dimension of scientific research. Most of the research arena is problem specific with respect to its data. In Machine learning more and more data samples are used for training a machine for efficient cluster formation, prediction, recognition, classification. Variation between data sample to data sample and data sample from its centroid using Euclidean distance, Mahanalabolis distance for better cluster formation has better focused among computational researcher. In this paper we proposed a novel loss less feature extraction and selection using feed forward cascaded Factor Analysis and F-score method. Comparative analysis of classification and clustering after efficient feature extraction applied to life killer cancer disease. Tumor classification is based on Multilayer Perceptron and clustering is based on k-means clustering method. 26 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Planar Crossover using Microstrip Patch Antenna for Beamforming Networks 1 Rahul R.Pillai, 2Mirav Mehta, 3Naveen K.A, 4Vishnu.Rajan and 5Sreedevi K.Menon 1,2,3,4,5 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Clappana P.O, Kollam, Kerala, India -690525 Email: 1rahulrpillai93@gmail.com, 5sreedevikmenon@am.amrita.edu In this paper, a simple planar design for a symmetric four-port crossover is presented. The proposed crossover is derived from a microstrip patch antenna with a set of two orthogonal feeds. Electrical length of the microstrip patch antenna is increased by incorporating slots achieving a frequency shift to lower side. The slot in the patch antenna is derived from fractal geometry, which allows three stages of iteration. Isolation better than -15 dB and transmission ~0 dB is observed in the frequency range of interest. The proposed crossover is a potential candidate for Butler Matrix in Beamforming applications. 27 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Energy efficient communication in wireless sensor network for precision farming 1 T V Aneeth and 2R Jayabarathi, 1,2 Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Amrita School of Engineering Coimbatore, India Email: 1aneethvasu@gmail.com, 2r_jayabarathi@cb.amrita.edu Wireless sensor network is a modern technology used for remotely monitoring the agricultural farms. Sensor network with sensor such as moisture sensor, temperature sensor, and humidity sensor can be used for control of the farm‘s moisture, temperature, humidity either manually or automatically. In this paper simulation is performed by placing the sensor nodes at various locations in the square shaped one hectare area. Simulation is performed on four different topologies namely random, cluster, star with gateway inside, star with gateway outside and the performance of the system is compared for all the four topologies and suitable topologies are proposed for the system. In the selected topology a communication technique is proposed for irrigation application showing the energy efficiency of sensor network. In this application, wireless sensor network uses IEEE 802.15.4/Zigbee communication standard for the topology study. In the selected topology, adhoc on demand distance vector and dynamic source routing protocol are implemented in star topology with gateway at center to determine the energy efficient network. 28 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design and Evaluation of 3D NoC Routers with Quality -of-Service (QoS) Mechanism for Multicore Systems 1 Pournamy Mohan and 2K. Somasundaram 1 Department of ECE 2Department of Mathematics Amrita School of Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Coimbatore-641 112, India. Email: 1pournamy2124@gmail.com, 2s_sundaram@cb.amrita.edu The advent of deep sub-micron technology has recently highlighted the criticality of the on-chip interconnects. As diminishing feature sizes have led to increases in global wiring delays, Network-on-Chip architectures are viewed as a possible solution to the wiring challenge and have recently crystallized into a significant research thrust. The communication on NoC is carried out in specific topologies by means of routers. In this paper, Partial Mesh of Grid topology (PMG) is considered. We use the Quality of Service (QoS) mechanism to minimize the area and power. PMG based NoC will give minimum area and power and it reduces the high chances of redundant connections. Throughput and latency are analyzed along with other parameters like packet loss ratio and jitter using network simulator NS-2. Area and power analysis is done using Synopsys Design Compiler and PrimeTime PX tool. Our experimental results show that the architecture with QoS mechanism gives a significant reduction in area and power when compared to Region based Routing (RBR) mechanism. Moreover, the Partial Mesh of Grid topology gives minimal latency and high throughput when compared to Mesh of Grid topology. 29 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Single Stage Boost Rectifier for Wireless Charging of Portable Devices through Magnetic Resonant Coupling 1 Ria George, 2Sreekala.M, 3Deepa .K Student1, Assistant Professor2,3 ,Dept. of EEE, , Amrita VishwaVidyapeetham University, Amrita school of engineering, Bangalore, India Email: 1riajoy1991@rediffmail.com; 2 m_sreekala@blr.amrita.edu; 3 deepa.kaliyaperumal@rediffmail.com Advancements in power electronics have aided in the development of inductive power transfer technologies by providing transmitter coil drivers and converters for conditioning the power received at the receiver coil. But the use of traditional two stage circuit with half wave or full wave rectifiers and boost converter at the receiver side may be inefficient, as it reduces the total power delivered to the load. As an alternative, single stage boost rectifier can be used, which is compact and more efficient. This paper introduces an efficient wireless charging system based on resonant magnetic coupling that contains single stage boost rectifier at receiver. Single stage rectification and boosting is made possible by the bidirectional conduction capability of MOSFETs. The system is designed and simulated in PSIM software. The overall power transfer efficiency of the system is analyzed for different coupling factors of the inductive links, and for different loads. 30 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Big Data Analytics for Network Congestion Management Using Flow Based Analysis 1 Yasmeen Arafath, 2Ranjith Kumar R 1-2 Department of ECE, AMC Engineering College, 18th, KM Bannerghatta Road, Kalkere, Bangalore-560083, India. Email: 1 yasmeenshaan@gmail.com , 2ranjithocet@gmail.com Due to explosive growth of traffic volume, it‘s hard to accumulate Internet traffic on a single machine. In this paper a Hadoop-based traffic analysis system which accepts input from multiple data traces. Hadoop facilitates scalable data processing and storage services on a distributed computing system. This system accepts input of large scale of trace file generated from traffic measurement tool like Wireshark, identifies flows running on the network from this trace file. Characteristics of flow describe the pattern of network traffic, it helps network operator understand network capacity planning, traffic engineering and fault handling. The main objective to design and implement a Traffic flow identification system using Hadoop. The traffic flow identification system will be very useful for network administrator to monitor faults and also to plan for the future. 31 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Performance Improvement of Compressed Sensing Reconstruction using Modified-AMP algorithm 1 Nissy Sara Mathai, 2Gandhiraj R 1,2 Department of Electronics and Communication, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham,Coimbatore, India Email: 1nissysara@gmail.com, 2r_gandhiraj@cb.amrita.edu Compressed sensing (CS) is an emerging field which enables the under sampling of sparse signals rather than at the Nyquist rate. But the main computational challenge involved is in the reconstruction process as it is nonlinear in nature and the solution is obtained by solving a set of under determined linear equations. Greedy algorithms offer the solution to these kind of problems with less computational complexity than the convex relaxations or linear programming methods. The approximate message passing algorithm offers accurate reconstruction of even the approximately sparse signals with reasonable computational intensity. In this paper we have implemented a modified version of AMP algorithm and obtained a 50% reduction in mean squared error and an improvement in signal to noise ratio. 32 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) LAB View Based Smart Washing Machine Analyzer for Energy Consumption Features 1 Seyed Reza Hashemi, 2Ata Jahangir Moshayedi 1 R&D, Entekhab Industrial Group, Morchekhort Industrial Zone Isfahan, Iran 2 Dept. of Electronic Science, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, India Email: 1rezahashemi383@gmail.com, 2 MOSHAYEDI@electronics.unipune.ernet.in Nowadays, to indicate the quality of washing machines including the calculation of the energy consumption grade and performance investigation of some main parts of washing machine, a number of price energy consumption analyzers are being used in most areas. This article proposes an alternative of such equipment called a Smart Recording Washing Machine Analyzer (SRWMA) using a combination of Labview algorithms and a cost effective data acquisition (DAQ) device. The newly proposed set of equipment not only has high accuracy, but also has some advanced features which support future-to-come washing machines. The proposed SRWMA is capable of simultaneous monitoring/recording both numerical data and waveforms in normal system operating conditions. In this paper, the SRWMA hardware configurations and LabVIEW algorithms will be thoroughly elaborated. The performance verification process has been strictly done under various controllable conditions by comparing the results of the SRWMA with the standard measuring units. Experimental results in the laboratory illustrate that the proposed SRWMA is comparable in accuracy and far superior to several references in terms of Functionalities and flexibilities. Experimental results from a washing machine demonstrates that the proposed SRWMA is highly efficient and reliable compared to the factory-installed measuring units. 33 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Diagnosis of Corneal Arcus Using Statistical Feature Extraction and Support Vector Machine 1 S.V.Mahesh Kumar, 2 R. Gunasundari 1 Research Scholar- Department of ECE, Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducherry, India. 2 Associate Professor- Department of ECE, Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducherry, India. Email : 1svmaheshkumar@pec.edu Corneal Arcus is a white ring or arc deposited in the corneal region of the human eye. This corneal abnormality is significantly associated with the lipid disorders and atherosclerosis. In this paper, we proposed a computer aided diagnosis system to detect the corneal arcus. The proposed method detects the corneal arcus using the statistical features extracted from the iris region of the eye image. The iris region is segmented from the other regions of the eye image using Circular Hough Transform (CHT). In order to achieve the better classification results, a morphological operation based specular reflection removal and colour transformation based enhancement methods are also developed in this paper. Our method was implemented and evaluated using the abnormal eye images from our database and normal eye images collected from UBIRIS.v1 database. Our database contains the eye images with different grades of corneal arcus abnormality. The performance of our method was evaluated using the confusion matrix based metrics. In the training phase, our method achieved 100 % classification accuracy. In the testing phase, our method achieved a classification accuracy of 96% with a positive predictive value 97.91%, negative predictive value 94.23%. 34 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Fast Adaptive Kalman Filtering Algorithm for Speech Enhancement Under Stationary Noise Environment 1 1 Prabhavathi C.N, 2K.M Ravikumar Research Scholar, Jain University. Bangalore. (Asst. Professor, RNSIT, Bangalore), 2 Prof and Head, SJCIT, Chickballapur. Email : 1prabhacngowda@gmail.com; 2kmravikumar@rediffmail.com Kalman Filtering is one of the time domain speech enhancement techniques. The conventional Kalman filtering technique involves more number of matrix operations. The complexity of matrix operations is reduced by fast adaptive Kalman Filtering technique. The proposed method of fast adaptive filtering technique is simple and gives best results for stationary noises. From the simulation results it is seen that the proposed method of Kalman filering is more effective in obtaining the clean speech signal. The performance of this filter is compared with the conventional method with respect to the signal to noise ratio and the execution time. 35 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design of Wireless Sensor Network for Submarine Detection 1 Anjali Arunan, 2Aryadevi R.D 1 Amrita Center for Wireless Networks and Applications Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Kollam, Kerala, India Email: 1anjali.a27@gmail.com, 2aryadevird@am.amrita.edu 2 The coastline of India extends up-to nearly 12 Nautical miles which increase the possibility of intruders into the coastline of country. This work looks into the intrusion of the other submarine to coastline of the country. Most of the existing submarine intrusion detection systems use sonar based technologies. As submarine hulls can absorb the sonar waves, it can effectively hide from the detection system. The proposed submarine detection system described in this paper helps to avoid this issue. The proposed system uses a wireless sensor network which provides an effective submarine detection and localization. In this work a new MAC protocol and Routing Protocol is proposed for efficient working of the system. 36 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Underground Tunnel Detection Across Border Areas 1 Nibi K V , 2K A Unnikrishna Menon, 3Preeja Pradeep, 1,2,3 Amrita Center for Wireless Networks and Applications Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Amritapuri, Kollam, 690525, India Email: 1nibikv@gmail.com, 2kaumenon@amritapuri.amrita.edu, 3 preejapradeep@am.amrita.edu. Tunnels are considered as an oldest method of passageway. Underground tunnels are popular from olden eras for connecting places, travelling, and aid for various surface threats. They are also used for illegal activities like smuggling of unlicensed drugs, weapons, currency, gold, explosives and even human trafficking is being done through these tunnels. These immoral activities are concentrated in national border areas in order to escape from the border security measures. Hence the detection processes of such tunnels in the national security border areas are necessary in order to protect our homeland security systems. The geology plays an important role in the detection of the underground tunnel system procedures. There is no perfect system for the tunnel detection and localization and even today the tunnels revealed in coincidence. The basic principle to find the hollow space (tunnel) is, by sending an ultrasonic frequency signal into the ground, and study the reflected beam from the tunnel or the hollow space. By analyzing the reflected signal characteristics, preliminary detection of a tunnel/void is possible. Basic idea of the detection is to perform the Range Estimation Algorithm (REA) by pulse echo method. From these we can estimate the depth of the tunnel. The characteristics of the signal at the soiltunnel (air) reflection interface are to be investigated. 37 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Static noise margin Analysis of 6T SRAM CELL 1 Abinkant A Jose, 2Nikhitha C Balan 1,2 Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Amritapuri, Kollam, 690525, India Email: 1abin.kant @gmail.com, 2nikhithacbalan34@gmail.com This report describes the SNM Calculation and analysis of SRAM cell which are obtained from simulations performed in Cadence Virtuoso 90nm technology. The SRAM cell structure is implemented with a compact structure of 6 transistors. Static noise margin is found from the butterfly curve obtained for read, write and hold modes of operation. 38 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Topology Preserving Map Generation for Multiple Mobile Fishing Vessels 1 Sruthi N, 2Divya P, 3Maneesha Vinodini Ramesh 1,2,3Amrita Center for Wireless Networks and Applications Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Kollam, Kerala, India Email: 1sruthinnampoothiri@gmail.com, 2divyap@am.amrita.edu, 3 maneesha@am.amrita.edu In Indian coastal zone, real-time tracking of fishing vessels are non-existing. This leads to numerous challenges in search and rescue operation, communicating emergency messages etc. A quick solution for this is to install GPS devices, but costly. In our research work, we designed and developed a low cost hybrid solution with minimum number of location aware nodes. Real-time relative location information of mobile sensor nodes was developed by integrating mobility management, Virtual Coordinate System (VCS) and Topology Preserving Map (TPM). The architecture is implemented in MATLAB and is tested with a rectangular network scenario with up to five mobile nodes and is able to track the relative location trace of mobile nodes at a particular interval of time. The effect of various simulation parameters such as communication range, node placement, number of mobile nodes and sampling rate selection in tracking the mobile nodes with our system is also performed. 39 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Accumulator Design in Cadence 90nm Technology 1 Nikhitha C Balan, 2Abinkant A Jose 1,2 Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Amritapuri, Kollam, 690525, India Email: 1nikhithacbalan34@gmail.com, 2abin.kant @gmail.com This paper describes the characteristics and analysis of accumulator which are obtained from simulations performed in Cadence (Virtuoso) and done the layout. The sizing strategy used for sizing the standard cell blocks used to build the accumulator result in a minimum propagation delay between input and output. 40 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A New Approach of Object Oriented Programming Language for Remote Power Quality Monitoring & Analysis Considering Harmonics 1 Vidula.S.Jape, 2D.G.Bharadwaj 1,2 BVDUCOE,Pune, Maharashtra, India. Email: Jape_swati@yahoo.co.in Use of micro processed technology enhance the power system operation and control tasks but at the same time resulting into Power Quality problems for utility as well as consumers. One of the major issues Power Quality is harmonics in power system. Through mandatory regulations harmonics in the power system must be prevented to ensure good Power Quality. This paper presents a new approach of object oriented programming for remote Power Quality monitoring and analysis with harmonic considerations. The real time monitoring and analysis of power systems parameters is inherently complex due to large data handling process. Object oriented programming tool has been used as computational tool which performs monitoring and analysis in substation related to power quality and gives subsequent analysis for the residual life assessment of substation equipment due to Power Quality. A GUI is created in java to create user friendly environment. Data can be transmitted from remote station to the central server and authority sharing has been developed as per the process. This is an innovative approach in electrical field in terms of substation monitoring thereby improves Power Quality. A case study of distribution network supplying linear and nonlinear loads is presented which encompasses the effects of harmonics on substation equipments to find out the solution to be implemented. 41 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Real Time Implementation of Electromyography for Hand Gesture Detection Using Micro Accelerometer 1 Subhendu Roy, 2Sraboni Ghosh, 3Aratrika Barat, 4Madhurima Chattopadhyay, 5Debjyoti Chowdhury 1,2,3,4,5 Applied Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Dept, Heritage Institute of Technology, Kolkata-107, India Email: 1subhenduroy4@gmail.com; 2srabonighosh26@gmail.com; 3 barataratrika5@gmail.com; 4 madhurima.chattopadhyay@heritageit.edu, 5 djbabai.debjyoti@gmail.com This paper focuses on development of a novel approach for identification of various hand movements in a person that involve actions like first opening, closing and arm roll. The system consists of an electromyogram (EMG) sensor coupled with a digital MEMS accelerometer (full scale range of ±2g, ±4g, ±8g and ±16g) for detection of hand gestures; this system is mounted over a strip strapped on the limb of its user. Based on the analysis of the EMG signals that are coupled with the MEMS accelerometer data from the limb, an innumerous of hand gestures is identified. Six point based calibration of the accelerometer data is done to eliminate mounting errors. The hand movements involving roll are better identified using this sensor topology which is based on EMG sensor coupled with MEMS accelerometer than a system which just uses an EMG sensor to find out hand gestures because the accelerometer data gives precise information about the orientation of the limb in three dimensional spaces. 42 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Real Time Intelligent Micro-controller based Harmonic Computing with Smart Phone Connectivity 1 Haripriya H.Kulkarni, 2D.G.Bharadwaj, 3Dipti B. Yeolekar, 4 Sheetal B. Mhetre 1,2,3,4 J.M.Road,Shivajinagar,Pune, Maharashtra India Email: 1electricalmcoe@yahoo.com, 3yeole.sachin9@gmail.com Increased use of nonlinear loads injects current harmonics in Electrical Distribution Networks and creates new problems of Power Quality in the power system. In today‘s competitive electrical market, Electric utilities strive to supply consumers with reliable & pure sinusoidal electric power that does not represent a damaging threat to their equipment. In the restructured power system, prices of the power are associated to Power Quality. Hence it is very important to monitor and ensure Power Quality. This paper presents an innovative way of real time harmonic computing using intelligent micro-controller and its assessment with automatic meter reading (AMR) on smart phone. During preparation of this paper fifty site visits are done covering the non-linear loads like IT Industries, Steel Industries, Paper Industries, workshops etc. It is observed that the current harmonics generated are beyond the tolerable limits. Readings are taken at consumer end with the help of standard power analyzer for a period of 24 hrs. It is also observed that a good number of researchers have worked on harmonic studies in the power system network; however, their work does not fit in, into the framework of the standards applicable. The developed solution has capacity to identify the normal & abnormal presence of harmonics with colour code. Through this colour coding technique an unskilled worker can easily identify the objectionable presence of harmonics. The computing results are observed to be satisfactory and promising. It creates the awareness in the utility for measurement and control of harmonics which in turn helps to improve the power quality. 43 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Real time ECG acquisition and detection of Anomalies 1 S.Kalaivani, 2I.Shahnaz, 3Shaikh Rizwana Shirin, 4C.Tharini 1,2,3,4 Dept. of ECE, B S Abdur Rahman University, Chennai, India ECG signals occupy a vital role in the diagnosis of cardiac abnormalities. These abnormalities can be detected by the variation in the ECG parameters. This paper deals with the implementation of real time acquisition, conditioning and feature extraction of the ECG signal so as to monitor and detect various cardiac abnormalities.NI Educational Laboratory Virtual Instrumentation Suite (NI ELVIS) is used for interfacing the acquired signal with LabVIEW. Further LabVIEW based virtual system is designed to create modules for conditioning and feature extraction. The detection of cardiovascular abnormalities like bradycardia and tachycardia is based on the calculation of heart rate from extracted ECG features. Other abnormalities are detected by determining the deviation of the extracted features like duration and amplitude, from their standard values. 44 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Weight Based Data Center Selection Algorithm in Cloud Computing Environment 1 Sunny Nandwani, 2Mohit Achhra, 3Raveena Shah, 4Aditi Tamrakar, 5K K Joshi, 6Sowmiya Raksha Naik 1,2,3,4,5,6 Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute,H.R.Mahajani Marg,Matunga, Mumbai 400 019 Cloud computing is Internet-based computing, whereby shared resources, software and information are provided to computers and other devices on-demand. It involves provision of dynamically scalable and virtualized resources. Perhaps with such high provisioning of scalability and on demand resource availability and high computational facilities cloud also faces many issues. Service Availability on demand, Unpredictability of performance, on time availability of resources, data confidentiality, security and privacy are the common issues faced by the cloud computing environment. Different simulation tools have are available to test the execution of algorithm. Cloud Analyst is one of the useful tools to model and analyze cloud computing environment before the actual deployment. Cloud Application Service broker is the one which decides that which Data Center should service the request from each user base. Service proximity based routing selects that path to the data center from a user base which has lowest network latency or minimum transmission delay. If there are more than one data centers in a particular region then the data center is selected at random. The other factors such as cost, workload, number of Virtual Machines, processing time etc. are not taken into consideration. Randomly selected data center gives undesirable results in terms of response time, data processing time, cost and other parameters. In this paper we propose a Weight based data center algorithm which proves to be better in terms of processing time i.e., Performance and costs as compared to the random selection algorithm. 45 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Real-time remote monitoring of indoor air quality using Internet of Things (IoT) and GSM connectivity 1 Siva V Girish, 2R Prakash, 3A. Balaji Ganesh 1,2,3 Electronic System Design Laboratory, TIFAC-CORE, Velammal Engineering College, Chennai-600066, India Email: 1Sivagirish1@gmail.com, 2prakash.rama121@gmail.com, 3 abganesh@live.in The paper presents an Indoor air quality monitoring system which comprises of real-time sensing unit that enables remote monitoring of environmental carbon-di-oxide, temperature and relative humidity. The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) based remote monitoring system employs an Internet of Things (IoT) signal processor (CC3100) interfaced on top of a low power microcontroller (MSP430F5529). The system is also packed with a short messaging service (SMS) based emergency alerting mechanism on the mobile network through SIM900 GSM module. The whole system when integrated with precalibrated non-dispersive infrared (COZIR) sensing unit showed good response in communicating the alert messages and E-mail. The information from sensing unit can be analyzed and logged for any period of time. 46 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Energy Conservation in Multi-Storey Buildings at Indian cities by Daylighting Control – A Study 1 M. Abdul Rahman Rafi, 2N. Albert Singh 1,2 Research Scholar,Noorul Islam University, India Email: 1rafi@bsnl.co.in, 2albertsingh@rediffmail.com This is a study on the scope of energy conservation in Multistoried buildings across Indian cities by employing Daylighting control for the illumination needs of the building. In this study the possibility of energy savings in a 11 storey building in various Indian cities under various conditions such as different illumination levels, different building orientations and have been estimated and analyzed using Energyplus simulation software. It is found that 50% to 60% of energy expenditure towards building lighting can be saved by adopting proper daylighting control techniques right from the time of building design to maintenance of the control system. 47 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Enhancement in the performance of routing protocols for wireless communication using Clustering, Encryption and Cryptography 1 Kanchan Dhote, 2G.M.Asutkar 1 Assistant Professor & Head Electronics Engg. T.G.P.C.E.T, Nagpur, MH, India 2 Principal, PIGCE, Nagpur, MH, India Email: 1hod.etrx@tgpcet.com; 2g_asutkar@yahoo.com; The field of wireless communication networks has thus been a keen area of research in the last decade. One of the crucial parameter for efficient operation of any wireless network is the routing algorithm. Advances in electronics and telecommunication industry in the last few decades have tremendously increased the use of wireless communication systems. However the choice of the routing algorithm depends not only on the physical topology and geography of the network but also on the application. This paper presents performance analysis of various routing protocols namely AODV, AOMDV, DSDV & DSR. These protocols are analyzed on four network parameters: Throughput, Jitter, Delay and Energy consumption. The results are shown in this paper after the analysis for four parameters. Further cluster head selection, Encryption, Compression is applied to improve the performance of protocols and the results are shown with the help of graphs. 48 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design and Implementation of MRI Brain Image using Level Set Segmentation and Classification 1 C.M.Naveen Kumar, 2B.Ramesh 1 Dept of ECE, Malnad College of Engineering, Hassan-600056, India Email: 1cmnk.it@gmail.com, 2sanchara@gmail.com Now a day‘s according to the fact that excess Brain Segmentation is one of the most prevalent diseases of human Brain body system. Further determination of the exact location of Brain Segmentation in the body is a big challenge. As of now, there seems to be no scientific tool which precisely determines the presence of Brain Segmentation. However, Mammography has drawbacks which yields 34% false negative rate which is too high. This has been overcome by digital mammography but has limitations regarding the x-ray exposure. Moreover, Image cannot be altered and film processing is slow. CAD based techniques provides increase in Brain Segmentation detection rate by 7.62%. Nevertheless, image segmentation in CAD based technique has advantage over spatial intensity but estimating the proper prior distribution remains a challenge. There are many Methods of medical imaging viz., magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), x-ray computed tomography (CT), ultrasound imaging (US) etc that can examine different parameters of human body. The detection of Brain Segmentation is crucial for the doctor to determine the status of the Brain Segmentations and also to visualize any abnormalities present in the Brain Segmentation. The detection of abnormalities of Brain Segmentation inside the body is a main field of study in medical research using bio-medical image processing. Due to some abnormalities (speckle noise) in ultrasound or MRI images or US or CT and artefacts, wrong diagnosis may happen by analysing the scanned image. Therefore in this proposed work the main focus is to design the algorithm based on level set segmentation, wavelets filters and artificial neural network (ANN) architecture for detection of Brain Segmentation in real time using biomedical images with the help of MATLAB with maximum accuracy of 94.8%. 49 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Robotic imitation of human hand using RGB Colour Gradient Mapping 1 Thyagaraj T., 2Kumar Abhishek, 3Brunda N.S., 4 Rakesh Ranjan, 5Nikita Kini 1 Assistant Professor Department of Electronics and Communication, B.M.S. Institute of Technology and Management, Bengaluru, India 2,3,4,5 Department of Electronics and Communication B.M.S. Institute of Technology And Management, Bengaluru, India The state-of-art developments in robotics reveal a scenario that human motion imitation has been developed through advancements in features and performance of sensors. Most of such robots uses flex sensors to acquire the information about the orientation of the body being imitated. However these are slow and are highly vulnerable to damages and physical changes. There are image processing algorithms that are focused on a robots learning through ANN and are not into imitation without memory. This paper presents an overview of research attempts to use a robotic assembly to imitate a real object using image processing. The paper describes results in force, tactile and visual sensing, sensor-based control and the configuration of a test based robot integrated system for imitation of a human hand, using vision through image processing using RGB scheme and one on one mapping for the acquisition of the current position of a body and orientation of the various parts of the robot in same fashion. This research has resulted in the development of a prototype capable of imitation. It‘s application are in the areas of Medicine, defense, safety and explorations for both research and commercial applications. 50 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Intelligent Business: An Auto Client Controller 1 Shantakumar B. Patil, 2Premjyoti Patil, 3K Prudhvi Yaswanth, 4 R.Priyanka 1 Professor and HOD, 2Professor 3, 4 Students of 8th Semester Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Nagarjuna College of Engineering & Technology, Bengaluru, Visveswaraya Technological University Email: shantakumar.p@gmail.com Abstract— In today‘s world there is a huge competition in the business. Suppliers are supplying their products to the seller on sell and pay basis. This method suffers from a big drawback that is sellers may make delay in the payment, even though they sell the products. In business money is very important. Even one day of delay in payment also makes a lot of difference to the suppliers. It is a huge loss to the suppliers. To overcome this we are proposing a method called Intelligent Business. In this method as soon as any product is scanned for the billing by the seller, immediately the supplier‘s amount is transferred to his bank account. In this technique the supplier maintains a unique database for each seller. After every delivery made to the seller the database of that particular seller is updated by the supplier and same is authenticated by the seller. 51 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) An Efficient Performance analysis for EEG signal Denoising and classification using Multiwavelets 1 Mangala Gowri S .G, 2Navya P, 3Cyril Prasanna Raj. P 1 Assistant Professor , MSEC, VTU, Bangalore, India, 2M.Tech, MSEC, VTU, Bangalore, India, 3Dean of R & D, MSEC, VTU Bangalore. Email: 1 mangalag21@gmail.com; 2navyap.91gmail.com; 3Cyril@msec.ac.in Abstract. Electroencephalography (EEG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity of the human brain. Electrical impulses generated by the nerve firings in the brain can be measured by placing the electrode on the scalp. EEG gives coarse view of neural activity and has been used non-invasively physiology of the brain. Multiwavelets have been applied for removing noise from the surface EEG. Gaussianity tests are conducted to understand changes in frequency bands and to quantify the effectiveness of the noise removal process. Wavelets are functions that satisfy certain mathematical requirements and are used in representing data or other functions. In this paper we analyze the performance of multi level DWT for EEG signal Denoising and compare the results considering mean square error (MSE).The Denoising analysis concludes using bior multi level wavelet and the mean was optimal in nature for different global threshold. 52 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design and simulation of PI Controller for Multilift Push Pull Switched Capacitor Main Series Elementary DC-DC Luo Converter 1 R.Ranjith Kumar, 2Manjunath.R, 3S.T.Bibin Shalini, 4 S.Saranya 1-4 Department of ECE, AMC Engineering College, 18th,KM Bannerghatta Road, Kalkere, Bangalore-560083, India. Email: 1ranjithocet@gmail.com, 2manjunath.iyer@wipro.com, 3 stbibinshalini@gmail.com, 4saranyasubburam@gmail.com Abstract. DC-DC Converter is a combination of passive components like inductors and capacitors such as Buck Boost converter, Boost converter, Buck Converter and Luo Converter. All Classical converters are having low power density and large in size. To increase the power density, micropower consumption technique is required. Voltage lift technique is popular method for electronic circuit design. Switched capacitor can be incorporate into power IC, compact size, having high efficiency, high voltage transfer gain, high power density and low EMI. The main objective is simulation of PI controller for the chosen converter to track rejection of supply and load disturbances using Matlab/Simulink. 53 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Performance Analysis of a Novel Method for Fast Handovers in TDD and FDD for Long Term Evolution 1 G.K.Venkatesh, 2P.V.Rao Asst. Prof, Dept. of Electronics Engg, Jain University, Banglaore, India Prof., Dept. of Electronics Engg, Rajarajeshwari College of Engineering, Bangalore, India Email: 1gkvlshiv@gmail.com; 2pachararao@rediffmail.com Abstract- In Long Term Evolution Advanced Technology Handovers are the basic criteria of mobility of the user in cellular networks by using Time Division Duplex and Frequency Division Duplex. Handover is one of the essential component that can affect the Quality of Service (QoS) and Capacity of mobile in Mobile Broadband Networks. In the cellular network communication systems, a limited shared resource like spectrum needs to be shared with all users so full duplex communication is essential. In this paper by studying the different Hand over delay parameters and also focusing on reducing Hard Handover delay by reducing interruption time, activation time, wireless channel access time and the wireless link transmission delay. An efficient handover algorithm is developed to reduce the handover delay time in network such as Time Division Duplex and it also reduces the wireless channel access time and link transmission delay. By developing a novel handover algorithm which would reduce the handover delay time and access time in mobile network environment. The future work on hard handover may be by applying different handover strategies to get better performance and Quality of service in Time Division Duplex mobile network. 54 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Energy Efficient Data aggregation protocol for wireless sensor network 1 Minal S.Dahake, 2Vivek S.Deshpande 1 Department of Information Technology, MITCOE, Kothrud, Pune, India, 2 Savitribai Phule Pune University 1 Email: mpjungare@gmail.com; 2vsd.despande@gmail.com Wireless Sensor Networks consists of a large number of sensor nodes, which are operated by a small battery. Many routing protocols have been proposed to maximize the network lifetime and decrease the consumption energy. To overcome this problem we propose data aggregation algorithm for WSNs. In this algorithm clusters are formed of the sensor networks. The Cluster Head (CH) selection phase of a random cluster based wireless sensor network (WSN) has been assumed as an insignificant factor in the previous research works. We propose a scheme based on the counting technique to deal with the over counting problem and selection of CH based on energy, distance, rssi and power ratio. These schemes process aggregates by statically and dynamically, respectively, allocating space for the use of the counting technique. In this paper, data aggregation is observed by different parameters like energy consumed, delay, control overhead, packet delivery ratio, packet loss ratio and throughput against node density. 55 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Review on Electro diagnosis to detect Retinitis Pigmentosa 1 Umashankar, 2R Gunasundari 1,2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducherry-605014, India Email: 1umashankar_ara@yahoo.co.in, 2gunasundari@pec.edu Abstract. The term ―retinitis pigmentosa‖ refers to a group of eye conditions that affect the retina, or the layer of nerve cells at the back of the eye. There are two main cell types within the retina: rods and cones. In retinitis pigmentosa, the rod cells and eventually the cone cells stop working, causing vision loss. Thus early detection of retinitis pigmentosais very essential to prevent vision loss. 56 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Non-Invasive EEG Feature extraction and recognition of epileptiform activity using Adaptive resonance theory 1 Aswathappa P, 2S.Ranjitha, 3H. N. Suresh 1 Research scholar, Dept. Of ECE,Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamil nadu,, India. 2 Final BE (ECE),Bangalore Institute of Technology, vvpuram,Bangalore-04 3 Professor, Bangalore Institute of Technology, Dept. of Electronics and Instrumentation Engg., Bangalore–04,Karnataka, Email : 1paswathappa@yahoo.com, 2hn.suresh@rediffmail.com Abstract: The recent researches in artificial neural networks (ANN) have provided us many information about a natural learning strategy. Artificial neural network consists of densely interconnected simple neuron like elements. Information is represented in the strengths of the connections (synapses) between elements and is processed in parallel. Different neural network models are specified by the topology of connections, characteristics of processing elements and training rules. The aim of this study is to develop a simple model for characterization of Epileptical seizure. Emerging Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART2 Neural Network) are used in this study to detect and generate epileptical seizure. 57 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) DWT-SVD Based Watermarking Scheme Using Optimization Technique 1 V. Santhi and 2Sarthak Nandi 1,2 SCSE, VIT University Vellore - 632014, India Email: 1vsanthinathan@gmail.com; 2sarthakn@gmail.com Abstract. In this paper a watermarking scheme has been proposed for embedding a digital watermark in images. The process of inserting a watermark is carried out in invisible mode. The proposed watermarking algorithm utilizes particle swarm optimization technique to obtain the scaling and embedding factors which are required to carry out watermarking process, thus the proposed methodology is adaptive. The embedding and extraction processes are carried out using discrete wavelet transform and singular value decomposition techniques. The proposed scheme finds application in curbing copyright infringement of images by inserting an invisible watermark in the image which can becolour or grayscale. The watermarked images are tested with various attacks in order to ensure the robustness of the proposed technique. The results obtained have been tabulated to verify and prove the efficiency of the proposed technique. 58 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Recent Research and various Techniques available for Efficiency Improvement of IGCC Power Plants 1 1 Ruchi Pandey, 2V K Sethi, 3Mukesh Pandey, 4Maneesh Choubey Research Scholar, School of Energy &Environment Management, RGPV, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India 2 Vice Chancellor RKDF University, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India 3 Head-School of Energy & Environment Management, RGPV, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India 4 Group Director, Gyan Ganga Group, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India Email: ruchipandey@ggits.org Abstract — This paper mainly focuses on the various technological improvements that need to be made for the current Integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) based power plants such that in the near future, efficiency of above 50% would be achievable. Also this paper elaborates about the working and the parts of an Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) based power plant. A discussion on the premier technologies that make IGCC the foremost prominent and promising technology for power generation today and tomorrow has been done, such as the advanced turbine technology, hot gas clean up technology and the efficiency enhancement of the process, while taking into account the various aspects of each of these. If all of these novel technologies are adopted, then not only will this make the process very efficient, but also will be a promising solution for the years to come. 59 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Hospital based screening for Osteoporosis in both sexes aged above 50 years using prototype US bone densitometer 1 Moataz Samir, 2Anburajan,.M 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering (BME), SRM University, Kattankulathur, Chennai- 603203,Tamil Nadu, India. Email: 1Moatazsamir1010@hotmail.com, 2hod.biomedi@ktr.srmuniv.ac.in Abstract: ‗Osteoporosis‘ is the cause for bone mineral loss. The aim of this study was to screen subjects of both sexes, aged 50 years and above using a low-cost, portable constructed prototype of QUS bones densitometer. A total number of 98 women, and men, were screened in a hospital. In each subject, the ulna aBMD was estimated with good accuracy. In the total women screened, (n=49), it was found that 57.1%, 20.4% , and 22.4% were found to be having osteoporosis, osteopenia, and normal respectively. Also, it was observed that, in osteoporotic women, the percentage difference in the mean value of estimated BMD (g cm-2) compared to normal was greater (71.8%), when compared to men counterpart (59.1%). The designed prototype US bone densitometer can be used to screen an individual who are at risk for future osteoporosis, with good accuracy. 60 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Enhancing LVRT capability of DFIG based Wind power plants by Interval Type-2 Fuzzy logic Controller 1 S Krishnama Raju, 2GN Pillai 1,2 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Roorkee, Roorkee-247667, India Email: 1skrajuap@gmail.com; 2gopinath.pillai@gmail.com Abstract: This paper presents a new control strategy using Interval type-2 fuzzy sets (IT-2 FSs) to enhance the low voltage ride-through (LVRT) capability of doubly fed Induction generator (DFIG) based wind turbine. The existing control schemes with conventional PID and Type-1 fuzzy sets are not effective in conforming to the modern grid code regulations. The proposed strategy with IT-2 Fuzzy sets is an advanced control scheme, to model and handle the uncertainties in the system parameters that arise during network faults. The presence of third dimension in the membership function, gives an additional degree of freedom in the design of the controller to counter the effects of low voltage during fault conditions. The performance of the proposed strategy is compared with Type-1 fuzzy logic controller (FLC) for various operating conditions, when the system is subjected to a single phase to ground short circuit fault. A case study is carried out on a grid connected DFIG using simulations and the results are presented to validate the proposed strategy . Keywords: DFIG, Grid integration, Interval Type-2 Fuzzy logic Control, LVRT, Type-1 FLC 61 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Passive and Active Methods of Islanding Detection for grid Connected PV Distributed Generators 1 A. Y. Abdelaziz, 2Sanjay Kumar, 3Biplab Bhattacharyya , 4M. Ezzat, 5 W. Sameh 1,4,5 Electrical Power and Machines Department, Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt 2,3 Dept of Electrical Engineering, Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad, India, Email: sanjayism2012@gmail.com Abstract: This study proposes a comparison between two islanding detection methods (IDMs) for grid-interconnected distributed generators (DG). The first method is a passive technique based on monitoring the frequency of the system and the rate of change of frequency (ROCOF) at the point of common coupling (PCC).The second method is an active technique based on the injection of a current waveform distortion to the original reference current of the inverter, to force a frequency drift in case of islanding operation. The test results show that there is a difference between the two techniques. Islanding detection methods are investigated, simulated and evaluated in MATLAB / SIMULINK. Key-Words: Islanding detection, Distributed generator, Rate of change of frequency, Single phase system, PV 62 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Differential Evolution Based LFC of Two Area Interconnected Power System with SMES Units 1 Saroj Pradhan, 2Rabindra Kumar Sahu and 3Sidhartha Panda 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Parala Maharaja Engineering College, Berhampur 2&3 Department of Electrical Engineering, Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology, Burla, Odisha, India Email: 1callsaroj201@rediffmail.com, 2 rksahu123@gmail.com, 3 panda_sidhartha@rediffmail.com Abstract. In the present work, Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm optimized Proportional-Integral (PI) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers is studied for Load Frequency Control (LFC) of an interconnected two area thermal system with non-reheat turbine considering Generation Rate Constraint (GRC) and including Superconducting Magnetic Energy Storage (SMES) units in each area. The gains of PI and PID controller are tuned by DE algorithm based on an Integral of Time multiplied Absolute value of Error (ITAE) as objective function. It is seen from the simulation result that the system performance improves when SMES units are included in each area. The simulation result also reveals that the performance of PID controller with SMES is robust and satisfactory regardless of location of load perturbation and minimizes the effect of perturbation. Keywords: Load Frequency Control (LFC); Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm; Generation Rate Constraint (GRC); Superconducting Magnetic Energy Storage (SMES). 63 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Minimize the data packet dropping by malicious Nodes in MANET using FSR Algorithm 1 Rajesh K S , 2R.Balakrishna 1 Dept of CSE, Rajarajeswari College of Engineering, Bangalore, India. Dept of ISE, Rajarajeswari College of Engineering Bangalore, India. Email: 1rayankibala@yahoo.com, 2rajeshks_hrr@yahoo.com 2 Abstract: Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) is infrastructure less and dynamically forming a temporary network without the use of any preexisting network infrastructure. The MANET has two type of attack are active attacks and passive attacks. The proposed scheme deals with minimizing passive attacks known as black hole attack which causes dropping of data packets by malicious nodes and provides a solution to minimize the number of malicious nodes in the path to destination and hence minimizes number of data packet dropping by these malicious nodes hence, it secures the fisheye state routing algorithm against the black hole attack. 64 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) An Involuntary Data Extraction And Information Summarization Expending Ontology 1 R. Deepa,2R Manicka Chezian 1,2 NGM College Pollachi, Coimbatore, India Email: deepaharini2015@gmail.com, 2Chezian_r@yahoo.co.in 1 Abstract: The World Wide Web is the repository for huge data that are the web pages. The web pages are got using a Query given by the user. The web Pages may sometimes be unstructured and unequal. The Main objective of the study is information extraction and summarization using Ontology. The System proposes a new method named as SSDO (Structural Semantic Domain Ontology) to effective information retrieval. The proposed system automatically extracted the information‘s from unstructured and stored in the Search Buffer. The information Extraction will be performed using domain ontology. There are various algorithms which are used for the information extraction from the unstructured data failed to obtain data alignment and summarization. The current proposal overcomes the above problem by adopting the technologies which are named as pair alignment, top down alignment and loop structure algorithms. The main disadvantage of the existing system is that the information which is extracted from the various sources will not be aligned properly. The system may fail to known where the exact information is located on the website. The system which is proposed in this research will eliminate a lot of things such as if the user need to know any data, then the user will type the detail known as a label. Then the web page will extract the information with a proper description and further details. The experiments and results show the proposed system outperforms for information extraction and summarization. 65 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) An Enhanced RSA with Attribute Based Encryption for Securing User Log in Cloud Computing 1 S. Hemalatha, and 2R.Manickachezian 1,2 Department of Computer Science, N.G.M College, Pollachi1 Abstract: A storage server in the cloud storage system is used to store large number of data. The cloud system does not provide data privacy because it makes hackers stole data easily. The problem of outsourcing data is that the data owner loss their novel data and it becomes an important barrier to the broad implementation of cloud services. The 1024 bit RSA keys has been cracked and for providing more security for the cloud user, the RSA is combined with Attribute Based Encryption(ABE) for user log in data encryption whoever stores their file in cloud. To make sure the security of outsourced data, this work encrypts the user attributes with the keys generated by Attribute Based Encryption (ABE) and Improved RSA. The main aim of this work is to increase the security strength of encrypted data irrespective of time and cost at the both of encryption and decryption processes. The number of key generation exponents has been increased in comparison to the original RSA in the proposed work. Also, the security and performance matrices between ABE-RSA and original RSA have been compared. For this reason, Key Generation, Encryption and Decryption time in novel RSA and ABE-RSA have been evaluated according to the different Key sizes. Keywords: Data Security, Cloud Computing, Homomorphic Encryption, RSA algorithm, Attribute based encryption. 66 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design of a 16 Bit Arithmetic And Logical Unit Using Vedic Multiplication Technique 1 Deepak Rao, and 2Anuradha S Savadi 1,2 Department of ECE, VLSI Design & Embedded System, Appa Institute of Engineering &Technology, Gulbarga Abstract : This project is related to the designing of a high speed arithmetic logical unit. As we know that ALU is a module which can perform arithmetic and logic operations. The reason behind choosing this topic is that, ALU is the key element of digital processors such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, central processing unit etc. Every digital domain based technology is depending upon the operations performed by the ALU either whole or partially. That‘s why it is required to designing high speed ALU, which can enhance the efficiency of those modules which rely upon the operations, performs by ALU. The speed of ALU basically depends upon the speed of multiplier. Hence it is considered to design a high speed multiplier using vedic technique. Keywords: Vedic Urdhva Triyambakam multiplication algorithm, Arithmetic Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit, Addition tree structure. 67 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Change Detection in SAR Images Based on MRFFCM using SWT 1 M.Manasa, 2C.Karthikeyan, and 3N.D.Thamarai Selvi 1,2,3 Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Easwari Engineering College, Bharathi Salai, Ramapuram, Chennai-600083, India. Email: 1 manasaa.m93@gmail.com, 2karthi28121993@gmail.com, 3 thamarai.nd@gmail.com Abstract. This paper presents a change detection approach for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images based on image fusion strategy and novel fuzzy clustering algorithm. The image fusion technique is introduced to generate a difference image. In order to restrain the background information and enhance the information of changed regions in fused difference image, wavelet fusion i.e., Stationary Wavelet Transformation (SWT) is used. Fuzzy C-Means clustering algorithm is proposed for classifying changed and unchanged regions in fused difference image. To remove speckle noise in SAR we use Modified MRF and modified energy value with FCM . It incorporates the information about spatial context in a novel fuzzy way for the purpose of enhancing the changed information and reducing the effect of speckle noise. Experiments on real SAR images show that image fusion strategy integrates the advantages of log-ratio operator and mean-ratio operator and gains better performance that exhibits lower error than its pre-existences. 68 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Implementation And Assessment For Identification of Finger Knuckle Using Scale Invariant Feature Transform Technique 1 1,2 Nivedita Bhattacharya, and 2Deepak Kumar Dewangan Dept of Computer Science & Engineering, ITM University, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India Email: 1niveditabhattacharya.6580@gmail.com, 2 deepakdewangan27@gmail.com Abstract: This paper brings a novel approach for recognizing finger knuckle print (FKP). In this paper SIFT algorithm is used for implementation and assessment of finger knuckle images. Due to some of the limitations of gabor feature and MMDA, SIFT algorithm is proposed in this approach. As compared with image based recognition methods, the computational cost of gabor feature for calculation and recognition for representation are high. In MMDA method, the data sampled from multiple manifolds of different dimensionality fail to uncover the geometrical structure because the corresponding manifolds of different classes may not have same intrinsic dimensionality. As a result of implementing SIFT algorithm, outputs some parameters like pyramid level, key points, magnitude and key point descriptor with a range of values. The database is collected from Hong Kong Polytechnic University containing 7920 samples collected from 660 individuals. 69 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Enhanced Cost Aware Secure Routing Protocol For Lifetime Optimization And Energy Balance In Wireless Sensor Networks 1 R.Saranya and 2R.Dhanalakshmi. 1,2 Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, KCG College of Technology, Chennai, India. Abstract. A Wireless sensor network of globally distributed autonomous sensors to monitor physical or environmental conditions such as temperature, noise, pressure etc. and to cooperatively pass their data through the network to the main location. CASER protocols are used to increase the lifetime of the network. Energy consumption and security are the two conflicting issues are in WSN. To overcome those problem some parameters are used Energy balance control using PSO (Particle swarm optimization), and TORA (Temporally ordered Routing Algorithm) are used for route maintenance in the network for security Probabilistic random walking. The proposed protocol can achieve a high message delivery ratio while prevent routing from polluting attacks. Keywords: CASER, Energy Consumption, security, Lifetime optimization, TORA 70 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Segmentation of TOF-MRA Blood Vessels Using GMM & EM Algorithm 1 ShekharShivam, 2Archana Chaudhari, 3Abhijit Pawar, 4 JayantV. Kulkarni 1, 2, 4 Department of Instrumentation Engg., Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune, India 3 Department of Radiology, S. K. Navale Medical College, Pune, India Email : 1shekhar.shivam13@vit.edu, 2 archana.chaudhari@vit.edu, 3 abhijitpawar.rad@gmail.com, 4jayant.kulkarni@vit.edu Abstract: The use of expectation maximization (EM) algorithm is present adhere to extract the blood vessels from Time of Flight (TOF) Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) images. The Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) is applied to fit the middle and high intensity area of the intensity histogram of the MRA image sequence. The cerebral vascular structure and the other low intensity tissues are removed. To estimate the parameters of the GMM, EM algorithm is proposed. The estimated model parameters are then used to statistically segment the blood vessels from the other brain tissue classes. 71 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Study of a Grid Connected To PV System Using Different MPPT Algorithms 1 Biswajit Mahapatra, 2Likan Priyadarsini 1,2 Dept of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Centurion University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India Email: 1biswajitmohapatra@cutm.ac.in, 2 linkan.priyadarsini@cutm.ac.in Abstract: Sun is the ultimate source of all energy. These forms of energy are utilized by human beings from ancient times by using conventional to modern technologies. The modern method which is used to generate electricity from solar radiation is photovoltaic using semiconductor. This type of energy conversion is the cleanest form of energy conversion and has no bad impact on the environment. Maximum power point tracking is the technique which is been applied to PV panels to produce maximum power by reducing the number of PV panels. This paper demonstrates the application of different MPPT techniques to the grid connected PV system. This paper also illustrates modeling of PV cell and its simulation when connected to a grid. Keywords: MPPT, Perturb and Observe algorithm, incremental conductance algorithm, fuzzy logic control 72 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Kernel Gablet based Face Recognition in Quintuple Space using fSVD 1 Bhaskar B, 2Anushree P S, 3Divya Shree S 1,2,3 Department of Electronics and Communication, SJB Institute of Technology, Bangalore, Karnataka-India Email: 1bhaskar.brv@gmail.com, 2anushreeps91@gmail.com, 3 divyashravani92@gmail.com Abstract: Face recognition is a technology of using software to fetch face images which are akin to a specific target face image in a large face dataset. We have invoked quintuple color space to examine the robustness of our algorithm on two different globally accepted databases. A new face image is de-rived by using fSVD, which focus at reducing the illumination problem. Wavelet is used to decompose the original image into wavelet sub bands each with different co-efficient. Further to achieve two fold dimensionality mitigations of data, linear subspace method PCA is espoused. In our method, the required facial traits can be extracted by the application of Kernel Gablets wherein input image is mapped into high dimensional feature space. Experimental consequences on Dr. Libor Spacek, Caltech segmented database manifests that our propound model can attain efficient success rates for the faces fluctuating in pose, illumination, expressions, orientations, and skin color. Diverse similarity measures have been incorporated for classification purpose. 73 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Detection of Vampires in Ad Hoc Sensor Networks 1 Kratika Malik, 2Ravikiran Pise, 3Lucky Atkare, 4 Sneha Warade, 5G.M. Gaikwad 1,2,3,4,5 Dept of Information Technology, Sinhgad Institute of Technology, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune. Email : 1kratika.malik@yahoo.com, 2ravikiran.pise@hotmail.com, 3 lucky2oct@gmail.com Abstract: An ad hoc network is a local area network that is dynamically built when the devices connect with each other. This connection is pre nominal between computers and devices used for specific purposes. An ad hoc network refers to a network connection established for a single session and does not require a router or a wireless base station. Vampire Attacks are resource depletion attacks, which permanently incapacitate networks by draining nodes‘ battery power. They are not protocol specific but depend on characteristics of most of the popular classes of protocol. A vampire in a network can raise the energy usage across the network by O(n), n being the number of nodes in the network. This paper aims at detecting the vampires in the network and guarantee secures transmission of packets from source to destination. We infer through this paper that the malicious node in the network could be detected without causing much harm to the contingency of the network. Key Words: Ad Hoc Networks, duplication, test packets, malicious node. 74 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Novel Fuzzy Rule Based Design Interface to Counteract Headlamp Glare Uncertainties Exhibited by Vehicles S.Niraimathi P.G. Department of Computer Applications, N G M College, Pollachi642001, Tamil Nadu, India Email: niraisenthil@hotmail.com Abstract : Headlamp glare has been identified as the major risk factor for the growing number of traffic injuries and deaths due to accidents. Driving on the roadways at night is inherently a critical task than the daylight hours. Driving is mainly a visual task, and there are certain situations at night in which vision and safety might be compromised. This paper proposes hardware and a software interface for reducing the effects of Headlight glare. It proposes a Fuzzy Sensor and a Fuzzy Controller that uses fuzzy rule based design approach to reduce the Headlight glare emitted by the oncoming vehicles during night on the Highways. Fuzzy logic has been used as it resembles human decision making with its ability to work with approximate data and to uncover precise solution. The PIC microcontroller has been used which reduces the intensity of light if it goes beyond tolerable limits, affecting the driver‘s vision. The concept of Fuzziness has been applied to the sensor and the Controller. The light intensity of the oncoming vehicle is received by the Fuzzy sensor. This input light intensity is fuzzified and checked for the tolerance limit. If this does not lie within the tolerance limit, the sensor passes it to the Fuzzy controller which converts it to an ambient light source and then on defuzzifying the output. The software has been developed using MATLAB. The headlight of the vehicle is controlled without the intervention of the driver which reduces accidents and the driver can pay more attention to steering control without dipping at critical vehicle junction. Glare at night can be mitigated by prudent design of the roadway, the automobile, and vehicle lighting systems. Keywords : Glare, Fuzzy logic, Fuzzy Sensor, Fuzzy controller, Fuzzification , Fuzzy inference, Defuzzification, PIC microcontroller 75 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Effective Cluster Key Mechanism for Integrated Internet MANETs 1 CAtheeq, 2MMunirAhmed Rabbani, 1,2 B.S AbdurRahman University. Email: atheeq.prof@gmail.com, 2marabbani@bsauniv.ac.in. 1 Abstract: The integration of internet and MANETs gives rise to heterogeneous network where effective communication between a fix ednodeinan internet and a mobile node in a MANETs is a challenging task. However gateways are used for communication between them. The data traveling in heterogeneous network must be protected from the attackers. In order to provide security we propose a method based on multilevel key distribution: one key is between fixed node and gate way, and second key used between gate way and mobile nodes. Our work is on the top of existing Diffie Helman algorithm. Proposed work addresses important characteristic of security: authentication. Simulation results show that our work is better than existing SEGK in terms of security deployment. Keywords: MANETs, Multilevelkey Security, 76 Integration, Gateway, International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Study on Six Sigma approach to improve the quality of process outputs in business processes in Small & Medium Level Software Firms. 1 K.Venkata Rao, 2Balakrishna R, 3Krishna Gudi, 4 Piyush Kumar Pareek 1 2 Computer Science & Engineering, JAIN University, Bengaluru Dept of Information Science and Engineering Raja Rajeswari College of Engineering, Bengaluru. 3,4 Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Kammavari Sangham Institute of Technology, Bengaluru Email: 1kothapallivenkat@yahoo.co.in , 2rayankibala@yahoo.com, 3 Krishna.gudi@gmail.com, 4piyushpareek88@gmail.com Abstract: Six Sigma is a mantra that many of the most successful organizations in the world swear by and the trend is getting hotter by the day. So much so that corporations like GE insist that every project be a Six Sigma project. The Six Sigma methodology has indeed made a tangible difference to the bottom lines of many corporations and they have the numbers to prove it because Six Sigma requires constant and consistent measurement. Six Sigma emphasizes quality from the beginning. Most often conventional Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) methodologies introduce the quality processes towards the end of the project cycle, just before implementation. Some commonly used terms are unit testing, system testing, integration testing, etc. In This Paper we are targeting small and medium level firms in Bangalore and study the effects of six sigma in improving Quality and productivity of the firm Keywords: Six Sigma, SDLC, Project Cycle. 77 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) STATCOM as a Voltage Sag Compensator 1 Minakshi D. Gavande, 2Mahesh K. Penshanwar , 3M. F. A. R. Satarkar Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, Maharashtra, India-402103. Email: 1 minakshi.gavande@rediffmail.com, 2mpenshanwar@gmail.com, 3 satarkar_fr@yahoo.com Abstract: STATCOM (Static Synchronous Compensator) is a shunt connected VSC (Voltage Source Converter) whose output voltage when varied provides reactive power compensation. Increase in power demand the system is incapable to supply or absorb reactive power. Therefore, the problem of voltage instability occurs in the system. FACTS are the new technology which can be used for many different problems in the system, among which voltage instability is one of them. In this paper the effect of STATCOM is presented. The behavior of STATCOM is studied under reactive loading condition. Comparison of simulation results are presented with and without compensation. 78 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Nonlinear System Identification Using Functional Link Multilayer Perceptron Artificial Neural Networks 1 Kumar Gaurav, 2Amit Kumar Sahoo, 3Sudhansu Kumar Mishra 1,3 Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, India Centurion Institute of Technology, Bhubneshwar, India Email: 1gaurav8131@gmail.com, 2amitkumar2687@gmail.com, 3 sudhansu.nit@gmail.com 2 Abstract. In this paper we have proposed a novel Functional Link Multilayer Perceptron (FLMLP) network for nonlinear system identification. The identification of nonlinear dynamic system finds wide application in stability analysis, controller design, analysis of power systems, modeling of multipath communication channels etc. The proposed model takes the advantage of nonlinearity in MLP due to multilayer and functional expansion of FLANN model. We have also proposed an efficient optimization technique named as Cat Swarm Optimization (CSO) algorithm to update the weights of FLMLP network. Identification of bench mark nonlinear dynamic system is carried out through simulation study to validate the proposed model. The simulation study reveals the proposed model provides superior identification compared to individual performance of MLP and FLANN based models 79 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Implementation of Single Phase Nine Level Inverter 1 Shashibhushan G, 2Savita Sonoli. 1 2 Department of ECE, Sir MVIT, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India Department of ECE, RYM Engineering College, Ballari, Karnataka, India Email: 1Shashigadigi1234@gmail.com; 2savitachitriki@gmail.com Abstract: This paper proposes a single phase nine level inverter capable of producing nine levels of output voltages from the dc supply voltage. The paper focuses on modified H-Bridge inverter for reducing the power circuit complexity. Model is implemented using MATLAB/SIMULINK with Sim Power system block set to design, analyze and evaluate the different levels of multilevel inverters. The metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) is used as switching device. A novel Pulse width modulation (PWM) technique is used to control the closing and opening of switches, to decrease the Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in the load. PWM is a way of digitally encoding the analog signal levels. The paper analyzes the switching pattern of nine level inverters to determine the pulse width and the pulse delay of switches to trigger the switches. It is seen that, as levels are increased the THD decreases in the output waveform. 80 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Early Warning System for Earthquake 1 S. A. Hariprasad, 2Anupama H.G., 3Chitkala P, 4Gangothri N. 1,2,3,4 Department of Electronics and Communication, BMS Institute of Technology and Management, Bangalore -560064, India. Email: 1harivat2002@yahoo.co.in, 2hganupama@gmail.com, 3 chitkalaprasannakumar@gmail.com, 4gangothrigv@gmail.com Abstract: An early warning of earthquake, even seconds before, play a crucial role in damage control and saving lives. Sensing the P- waves as soon as it arrives is very important to warn the approaching S-waves. Any kink in seismic vibrations cannot be considered as a P-wave. A kink in seismic vibrations can be considered as a P-wave only if it is followed by an S- wave. The arrival of S-waves cause destruction and prediction at such a point of time becomes moot. The current works take only P and S waves into account in order to give warning, but they do not take any precursors into account, which actually increases the accuracy in prediction. In this paper, we have used temperature, which is one of the precursors along with P and S waves. This will enhance the accuracy along with the early warning when compared with earlier techniques. 81 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Optimum TMS and PS settings of Directional Overcurrent relays using Teaching Learning Based Optimization Technique 1 Amol A. Kalage, 2Nitin D. Ghawghawe, 3Pradnya D. Sonawane 1,3 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Sinhgad Institute of Technology Lonavala (MS) India, 2 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Government college of Engg, Amravati (MS) India, Email: 1amolkalage@rediffmail.com, 2g_nit@rediffmail.com, 3 pradnya2904@rediffmail.com Abstract: Over current relays particularly DOCR (Directional Over current Relays) are the most indispensible protection device in the distribution system. During faulty condition the directional over current relays should only segregate the faulty part of the power system from the healthy system. To reduce power disruption, mal-operation of back up relays should be avoided therefore coordination of primary and back up relays is done by selecting the optimum values of TMS (Time Multiplier Setting) & PS (Plug Setting). In this paper a relay coordination problem is formulated as a constrained nonlinear optimization problem to minimize the operating time of all primary relays to its near end fault. A Teaching-Learning Based Optimization technique (TLBO) is used to obtain optimum values of TMS & PS. 82 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Brain Tumor Detection: A Comparative Analysis of Edge Detection Techniques 1 Akash Kumar Bhoi, 2Pradeep Kumar Mallick, 3S. Saravana Kumar, 4 Karma Sonam Sherpa 1 Dept. of AE & IE, SMIT , Sikkim, India Dept of CSE ,St. Peter‘s University, Avadi, Chennai . 3 Dept of CSE, Panimalar Institute of Technology, Poonamallee, Chennai . 4 Department Electrical & Electronics Engineering, SMIT , Sikkim, India Email: 1akash730@gmail.com, 2pradeepmallick84@gmail.com, 3 saravanakumars81@gmail.com, 4karmasherpa23@gmail.com 2 Abstract: For many human experts, manual segmentation is a difficult and time consuming task, which makes an automated brain tumor segmentation method desirable. Brain tumor area estimation is an important procedure for early tumor diagnosis and radiotherapy planning. The automatic segmentation has great potential in clinical medicine by freeing physicians from the burden of manual labelling; whereas only a quantitative measurement allows to track and modelling precisely the disease. This paper proposed six different edge detection based techniques (i.e. Roberts, Sobel, Prewitt, LoG, Zerocross and Canny operators) for brain tumor segmentation which are validated with MRI brain images. Before edge detection the pre-processing step has been implemented, this includes Otsu‘s method with global thresholding, area opening and connected component establishment. The computational results are comparatively analyzed and tumor area also estimated. As canny edge detector uses the method of optimal edge detection, the result of this operator is significantly better as compared to other operators and the distance transform result also implicates the same. Keywords: Brain tumor, MRI brain image, Otsu‘s method, Roberts, Sobel, Prewitt, LoG, Zerocross, Canny, distance transform. 83 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Valve Control Using Microcontroller 1 Thirunarayana Theerthan, 2Vinay Kumar R, 3D. Jayadevappa 1,2,3 Dept. of Instrumentation Technology, J.S.S.A.T.E. Benguluru, VTU, Karnataka, India Email: 1theerthan91@gmail.com, 2vinay.sin19@gmail.com, 3 devappa22@gmail.com Abstract: The advancement in modern Instrumentation techniques gives rise to innovative ideas which makes day to day life easier. One such product is the Valve control device, it offers easy access to control a valve in remote areas and provide many beneficiary characteristics. It can be controlled using various devices, starting from a simple key to a Smartphone. For example, controlling the valves of all the water tanks in a city by sitting in one place Or automatic shutdown of water supply to a particular room of a hotel when the key card is removed from the socket (likewise shutdown of power). And many industrial applications where the valves are inaccessible by human beings or when a valve has to be open for a particular duration of time and/or particular amount of liquid to be drained. Keywords: Solenoid Valve, PIC Microcontroller, SIMCOM 300. 84 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Hybrid Renewable Energy for Rural Electrification by Using 1 Phase Supply 1 Swaraj Kadam, 2Nagesh Dudile , 3P. K. Katti 1,2,3 Department of Electrical Engineering, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, India - 402103. Email: 1sskadam221@gmail.com, 2ns.dudile@gmail.com, 3 p_kati2003@yahoo.com Abstract: Large portion of world Population lives in a remote areas that are geographically isolated or grid supply sparely available. Also consumer expects a mobile form of energy for their daily need. These demands are for professional need or rural electrification. Due to limited reserve of conventional energy sources i.e. fossil fuels and global environment concern. For the use and generation of electric power it is necessary to use Renewable Energy sources (RES). Hybrid renewable energy system (HRES) with conventional energy sources is the ideal system for rural electrification and to provide reliable for of energy to consumer. This paper discussed the Hybrid renewable energy system for rural electrification where the electricity supply is not available and advantages of Renewable energy system. Keywords: Renewable energy system, Hybrid renewable energy system, Rural electrification, PV. 85 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Big Energy Efficient and Optimal Path Selection in LEACH Algorithm 1 Krutika Barabde, 2Shilpa Gite 1,2 Computer Science Department, Symbiosis Institute of Technology (SIT), Symbiosis International University (SIU), Gram-Lavale, Tal-Mulshi, Pune, 412115, Maharashtra, INDIA. Email: 1krutika.barabde@sitpune.edu.in, 2shilpa.gite@sitpune.edu.in Abstract: In the last few years, wireless sensor network has been highlighting spot in research and development. Wireless sensor network is class of interactive network containing small, cheap and smart sensors for collecting the information from different sensors and transfer to base-station. Limited battery life, processing power and limited resources are decisive issues of the wireless sensor network. To maximize lifespan of network the path for data transfer is selected in such a way that the total energy consumed along the path is minimized. In this paper, data transfer done by selecting shortest path between source and destination using Dijkstra‘s Algorithm. Also proposed concept called Shifting cluster head which is based on residual energy of cluster head. The proposed concept was evaluated by applying LEACH algorithm. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed mechanism improved the performance of LEACH algorithm considerably in terms of shortest path for data transfer and shifting cluster head. Keywords: Wireless sensor network, Energy clustering, LEACH Algorithm, Dijkstra‘s Algorithm 86 efficient International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Econometric analysis of solar tracker systems in India, a Case Study 1 Seyed Samsamoddin Naghavi Chaleshtori, 2AdinathM. Funde 1,2 School of Energy Studies, Savitribai Phule Pune University Ganeshkhind, Pune – 411007. India Email: 1samsam.naghavi@gmail.com, 2adinath@unipune.ac.in Abstract: Energy generation typically requires an investment in a technology that assures supply over many years. This paper deals with techno-economical study of solar tracker system employed in Photovoltaic (PV) energy conversion. The proposed single axis solar tracker device ensures the optimization of the conversion of solar energy into electricity by properly orienting the PV panel in accordance with actual position of the sun. Solar tracking system is one of the most direct approaches adopted to harvest more solar energy from PV system compared to static solar PV arrays. Hence, with the use of tracking system, the PV panels are able to receive maximum sunlight and thus generate more energy. 87 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Novel Approach for Single Image Super Resolution using Statistical Mathematical Model 1 Dany Varghesea, 2Viju Shankar 1,2 Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Jyothi Engineering College, Thrissur, Kerala, India Abstract: Images with high resolution are always a necessity in almost all image processing applications. .Super Resolution is a method in image processing to create High Resolution image from several or single low resolution image so that high spatial frequency information can be recovered. SR methods are applied on LR images in order to increase spatial resolution for a new image. The super resolution processing includes two main tasks: up-sampling of the image, removing degradations that arise during the image capture. In effect, the superresolution process tries to generate the missing high frequency components. Applications may include HDTV, biological imaging etc. In this work we deal the problem of producing a HR image from a single low-resolution image using some statistical mathematical model. Performance of this algorithm was checked by using objective image quality criteria PSNR, MSSIM and compared with other existing methods. Keywords: Super Resolution, Low Resolution, PSNR, MSSIM, statistical . 88 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Survey On Clustering And Routing Protocols 1 Veni devi Gopal, 2Nidhitha Gopinath, 3Resmi R Department of Information Technology, KCG College of Technology, Chennai, India. Email: venidevig@gmail.com Abstract: Wireless Sensor Networks has recently gained much concentration of the researchers as it has a wide scope for improvement. The sensors can be arranged and communicate using either hierarchical model or layered model. The sensors are grouped to form clusters. Intra-cluster routing and intercluster routing has gained more importance in the recent days. This paper focuses on the types of clustering, the parameters related to clustering and various challenges in clustering. This paper also focuses on routing protocols available and their related issues. 89 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design and Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy and Funds Detection using Cup to Disk Ratio and Wavelets 1 M.E.Tejamorthy, 2B.B.Neelakantappa, 3B.Ramesh, 4 N.A.Ranjan 1.4 2,3 EE Department, Malnad College of Engineering, Hassan, India. CSE Department, Malnad College of Engineering, Hassan. India Email: 1tejamurthy@gmail.com, 2bbn@mcehassan.ac.in, 3 sanchara@gmail.com, 4ranjanmce@gmail.com. Abstract: Glaucoma is an eye disease which damages the optic nerve of the eye and becomes severe over time. It is caused due to buildup of pressure inside the eye. Glaucoma tends to be inherited and may not show up until later in life. The detection of glaucomatous progression is one of the most important and most challenging aspects of primary open angle glaucoma (OAG) management. The early detection of glaucoma is important in order to enable appropriate monitoring, treatment and to minimize the risk of irreversible visual field loss. Although advances in ocular imaging offer the potential for earlier diagnosis, the best method is to involve a combination of information from structural and functional tests. In this proposed method both structural and energy features are considered then analyzed to classify as glaucomatous image. Energy distribution over cup to disk ration were applied to find these important texture energy features. Finally extracted energy features are applied to Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Back Propagation (BP) neural network for effective classification by considering normal subject‘s extracted energy features. Naive Bayes classifies the images in the database with the accuracy of 89.6%. MLP-BP Artificial Neural Network (ANN) algorithm classifies the images in the database with the accuracy of 90.6%. Keywords: Z-score normalization, Cup-to-Disc, Symlets, Biorthogonal (bio3.7, bio4.2 & bio4.7) and Daubechies wavelets, MLP-BP ANN 90 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Rating Based Load Balancing Algorithm in Grid Computing 1 Samyak Shamkuwar, 2Parikshit Chavan, 3Sujay Kakkad, Ajinkya Walimbe, 5Kiran Joshi,6SowmiyaRaksha Naik 4 1,2,3,4,5,6 Dept. of Computer Technology and IT, Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute, Mumbai, India Email: 1samyakshamkuwar@live.com, 2parikshitschavan@gmail.com, 3 sujay.kakkad@gmail.com, 4ajinkyawalimbe@gmail.com, 5 kkjoshi@vjti.org.in, 6sraksha@vjti.org.in Abstract: Grid computing is a form of Parallel and Distributed computing and is an emerging area of use for a wide range of applications. The high computing requirements exert high task loads on the grid resources which may be spread in a geographically dispersed area. Certain software intervention is required when the tasks allocated to the grid resources are unequally distributed and create burden only a part of the system. This paper proposes such a load balancing algorithm, to re-distribute allocated tasks and compensate the imbalance on the system as a whole, which uses MIPS rating of machines and task lengths to make decisions. 91 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Edge Segmented Human Brain Image Denoising using Wavelets 1 B.B.S.Kumar, 2P.S.Satyanarayana, 3Rohini G.V, 4Savitha N 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Jain University, Bengaluru, India. Dept of ECE, Don Bosco Institute of Technology, Bengaluru, India. 3,4 Dept of ECE, RajaRajeswari College of Engineering, Bengaluru, India. Email: 1bbskumarindia@gmail.com, 2pssvittala@gmail.com, 3 rohinigv92@gmail.com, 4savitha.sav28@gmail.com 2 Abstract: This paper approaches on Edge Segmentation technique to find out the exact edges in the human brain. The experimental results are carried out on simulation using jpeg human brain image format. Segmentation provides the better analysis to identify the particular region and filtering unwanted data which is not relevant. The segmented outline original image is examined on using different wavelets with adding a noise and denoising to obtain better results and finding out the measure of quality of image by PSNR & MSE. 92 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Design and Implementation of MRI Brain Image Enhancement and Segmentation using Xilinx System Generator 1 P.V.Rao, 2K.Viswanath 1 Dept ECE, RajaRajeswari College Engg, Bangalore 2 R.L.Jalappa Institute of Technology, Bangalore Abstract: This paper presents a novel method for enhancing and segmenting MRI of the human brain. The MRI brain image enhancement and segmentation is done using Xilinx System Generator (XSG), which is a digital signal processing tool from XINLINX Corporation. This architecture has a Graphical User Interface (GUI) that groups MATLAB Simulink and XSG to provide a proper hardware implementation. By enhancing the image resolution and quality of image will improve. The performance of the image is implemented in FPGA XC5VLX50T is presented. Keywords: Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), Digital Signal Processing (DSP), MATLAB, Xilinx System Generator (XSG) 93 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Survey of Recent Data Mining Applications and Research Perspectives 1 M. Inbavalli , 2Tholkappia Arasu, 3C.Anitha 1 MCA, Er. Perumal Manimekalai College of Engineering, Hosur, Tamilnadu, India 2 AVS Engineering College, Salem, Tamilnadu, India 3 Sr.Technical Lead ,HCL, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India Email: 1 inbavelu@yahoo.com, 2tholsg@gmail.com, 3anithacj@hcl.in Abstract: Abundant research have been carried out in Data mining with various applications. In this paper we have focused on current applications of data mining for knowledge discovery and efficient implementation for decision making. In this competitive globalised environment huge data‘s from tera to peta bytes are generated and available for assessment and finding dynamic and competent solutions for the business environment and it constructs many challenges in science and technology. The objective of this paper is to identify various applications in diverse areas by applying various data mining technologies. The review specifies that the knowledge discovered from this survey can be utilized for accumulate knowledge on data mining and its research perspective. Keywords: Data mining, Knowledge discovery, Data mining Technologies, Data mining Applications, Data mining Research perspectives. 94 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Hybrid Neural Network Model for Active Noise Cancellation Using TMS320C6713 DSK 1 Shashi Kumar, 2Rajeswari, 3G. Ramanjulu, 4NNSSRK Prasad 1,2 Department of ECE, Acharya Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India Aeronautical Defense Agency (Ministry of Defense), Bangalore, India Email: n.shashi.kumara@gmail.com 3,4 Abstract: This paper discusses the implementation and performance analysis of varied neural network algorithms for Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) using TMS320C6713 processor. A hybrid neural network model exploring the feedforward and feedback neural network models has been proposed. The proposed system is suitable for high frequency noise signal with lower SNR levels like cockpit noise embedded low frequency audio signals. The experimental results indicate that the proposed hybrid model provides a better and stable control signal, with an improvement in SNR for Active Noise Cancellation when compare to feed-forward and feedback neural models. Keywords: Neural network algorithm, SNR, Hybrid, Fx-LMS. 95 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Enhanced Integrated Approach to Predict Web User’s Future Requests Using K-Means and FPGrowth 1 Tanveer Kaur Dewgun, 2Pushpraj Singh Chauhan 1,2 Bansal Institute of Science and Technology, Bhopal, India Email: 1tanveer.devgan16@gmail.com Abstract: The tremendous growth in the World Wide Web has led to the user perceived latency when requesting for resources from the web servers. Millions of users are connected to the web server for different needs. To improve the performance of the servers, caching is used where the frequently accessed pages are stored in proxy server caches. Pre-fetching of web pages is the new research area which when used with caching greatly increases the performance. In this paper, we have proposed a better algorithm for predicting the web pages. We have clustered web users according to their location using KMeans clustering and then each cluster is mined using FPGrowth algorithm to find the association rules and predict the pages to be pre-fetched for storing in cache. Keywords: Web Usage Mining, Apriori, FP-Growth algorithm, K-Means clustering 96 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) FPGA Implementation of Color Space Transformation RGB to YCbCr Using XSG 1 Kaliprasanna Swain, 2Manoj Kumar Sahoo, 3Annapurna Swain, 4Lopa Nayak 1,2,3,4 Dept. of ECE, GITA, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India Email: 1kaliprasanna_ece@gita.edu.in, 2mksahoo@hotmail.com, 3 swain121annapurna@gmail.com, 428lopa.nayak@gmail.com Abstract: The benefit of fast prototyping tools such as Xilinx System Generator (XSG) and Matlab-Simulink becomes progressively significant because of design time compulsion. This paper illustrates a perspective for especially DSP applications using XSG on a reconfigurable logic platform. This technique intent to escalate the design verification efficiency for such convoluted system. It outlines a framework for color space conversion RGB to YCbCr using XSG in the field of video processing. The mention model explains a reconfiguration design approach, where the design is implemented in the MATLAB environment, then analyzed with fix point architecture using XSG with Xilinx blockset, then corresponding RTL-HDL code is generated. This code is used to describe the conversion equations and synthesize to a target to the FPGA. The obtained results are analyzed and confronted with architecture, producing no visually perceptual errors in the out-turn image. Keywords: RGB, YCbCr, FPGA, Xilinx System Generator 97 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) A Novel Hybrid SMS Spam Classification Framework for Android 1 Anupama Sheela, 2Kamalanathan Kandasamy 1,2 Amrita Center for Cyber Security Systems and Networks,Amrita University, Kollam Kerala, India Email: 1anu109.indeevaram@gmail.com, 2kamalanathan@am.amrita.edu Abstract : With developments in the mobile technology over recent years, SMS texting has become more popular than before. This has led to increase in the number of spam messages communicated via mobile phones. Even though email was the main source for spam in earlier days, SMS service is not far behind in contributing to spam messages these days. But nobody wants their mobile phones to get filled with spam texts. Various strategies have been developed to detect and reduce spam messages and researches are still going on regarding this topic. In this paper, a hybrid framework to detect mobile spams is proposed. Our approach is a combination of different techniques like detection based on blacklisted phone numbers and urls, machine learning approach, text based filtering and detection based on challenge response. Performance of the proposed system was evaluated at the end and we observed that a combination of different methods is more effective rather than using a single method. The proposed methodology was first experimented as a web application. Later it was also implemented in Android platform and tested using Android Virtual Device (AVD). Keywords: Spam, Ham, Blacklist, Machine learning, Support vector machine, Challenge response, Text based filtering, Confusion matrix, Precision rate, Recall rate. 98 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Analysis of an Improved Apriori Algorithm for Association Rule Mining 1 Sumalatha U, 2Seema Patil 1,2 Department of computer Science and Engineering, The Oxford College of Engineering Bangalore, India. Abstract: Association Rule Mining is the main technique to determine the frequent item sets from large data repositories. Apriori and FP Growth are the two base frequent pattern mining algorithms. Both of these algorithms suffer time and space complexities. An effort to optimize the execution time and search space of the base Apriori is carried out by eliminating the unnecessary multiple transaction scans. Efficiency of any mining algorithm depends upon the minimum support threshold, the type of the dataset and density of items in dataset used for mining. A comparative analysis and experimental results show the behavior of the Improved Apriori and Apriori algorithms on mushroom dataset. The Improved Apriori consumes less execution time and minimizes the search space in comparison with the Apriori, thereby increasing the efficiency of the base Apriori algorithm. Keywords: Data Mining, Association Rule Mining, Support, Confidence, Apriori , FP-Growth, Frequent item sets. 99 International Conference on Power, Circuit and Information Technologies (ICPCIT-2015) Analysing Attack Pathways Through Security Metrics 1 Krishnashree Achuthan, 2Reshma Mohan 1,2 Amrita Center for Cybersecurity Systems & Networks,Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham,Kollam-690525,India Email: 1krishna@amrita.edu, 2reshmamohan0706@gmail.com Abstract: Organizational networks with connected machines and a large number of users are often vulnerable to cyber attacks. The types of vulnerabilities and attack pathways are proportional to the size, architecture and in built security policies. This work involves understanding and developing a framework to analyze vulnerabilities in organizational networks. The main focus of this work includes analyzing hospital networks. Building attack trees for possible attack scenarios and consequently computing the probabilities of attack will provide directives on how to prevent potential network compromise. By computing static phase and dynamic phase probabilities, a metric representing the security posture of a network is derived based on an information theoretic approach. The work is based on predictability of an attack and behavior of an attacker. Outcome of this work include impact of time constraints in an attack. Keywords: Attack tree, Security Metric, Entropy, Vulnerability Indicator 100
© Copyright 2025