General Travel Recommendations Personal Safety
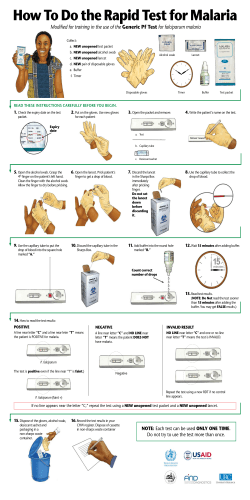
General Travel Recommendations Personal Safety Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings. Undertake pre-travel research using reputable guide books and web resources to determine threats Arrange insurance that is appropriate for the destination and anticipated activities; include medical evacuation insurance Keep family and friends informed of your itinerary, and communicate regularly throughout the trip—for example, with a travel blog Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) at http://travel.state.gov/ Accidents and Injuries Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries. Avoid using scooters or motorcycles and wear helmets if you do so Wear seatbelts in motor vehicles and on public transport if available Avoid travel at night and in bad weather conditions Avoid unsafe travel, such as a quad bike, on the back of a truck, or on the roof of a bus If planning sport or adventure activities, ensure safety equipment is provided and bring appropriate and well fitting clothing, footwear, and protective eye wear Undertake adventure sports with a companion or in a small group, with an experienced guide if your experience is limited Seek local advice on environmental hazards and weather conditions if planning outdoor pursuits, and carry a mobile phone if possible Know the depth of water and any underwater hazards before diving; diving feet first is advised. Do not dive into shallow water. Pay attention to signs and surf conditions when swimming or undertaking water sports, and use flotation devices or life jackets where necessary Do not consume alcohol before swimming, cycling, or using a watercraft Remain in vehicles when travelling through wildlife reserves Violence and Theft Avoid travel to areas of conflict or political unrest; avoid participating in local demonstrations Travel with a companion or group Stay in secure accommodation and use a safety deposit box Use only official taxi services Carry minimal amounts of money; a hidden money belt may be useful for holding passports and larger amounts of money Do not wear expensive watches or jewelry Dress appropriately with respect to local culture Avoid illicit drug use and excessive use of alcohol because of the increased risk of violent attacks and theft Never accept food or drink from strangers, and do not leave drinks unattended because of the risk of “spiking” Ensure that hired cars are roadworthy and can be locked securely Upload important documents onto a secure website before travel in case of theft Environmental Related Illnesses Seek local advice on environmental hazards, including flora, fauna, and weather conditions Wear protective clothing, high factor sunscreen (reapplied regularly), and insect repellent (also reapplied as directed) Carry a first aid kit and know how to use it Carry an adequate supply of water and high energy snacks Carry a flashlight for walking at night Check shoes and clothes carefully for spiders, scorpions, and so on Wear a stinger suit when swimming in areas with jellyfish Altitude illness usually occurs at about >9000 feet (2700 meters). Symptoms can include headache, lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, loss of appetite; more serious symptoms include breathlessness and confusion. When ascending to high altitude, adjust ascent to 300 m a day if possible; prophylactic medication, such as acetazolamide, should not replace gradual ascent. o Acetazolamide (500mg once daily or 250mg twice daily): start 24 hours before ascent and continue daily for two or more days. May cause increased urination and numbness in extremities. Contraindicated with sulfa allergy. Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor. Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick. To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste. Risk Factors for Accidents and Disease Studies have shown that students traveling abroad may adopt higher risk behaviors, such as excessive alcohol use, drug use, and unsafe casual sex Such activities are associated with increased incidence of accidents, violence and sexually transmitted illnesses, which can have lifelong consequences o Use latex condoms correctly and with all sexual activity o Do not inject/use drugs. o Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated. o Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture. Food and Water Illnesses Eat and drink safely. Unclean food and water can cause travelers' diarrhea as well as other diseases such as hepatitis A, typhoid, and polio. Wash your hands often, especially before eating. If soap and water aren’t available, use hand sanitizer. Eat Food that is cooked and served hot Hard-cooked eggs Fruits and vegetables you have washed in clean water or peeled yourself Pasteurized dairy products 2 Don't Eat Food served at room temperature Food from street vendors Raw or soft-cooked (runny) eggs Raw or undercooked (rare) meat or fish Unwashed or unpeeled raw fruits and vegetables, including salsas and chutneys Unpasteurized dairy products “Bushmeat” (monkeys, bats, or other wild game) Drink Bottled water that is sealed Water that has been disinfected Ice made with bottled or disinfected water Carbonated drinks Hot coffee or tea Pasteurized milk Don’t Drink Tap or well water Ice made with tap or well water Drinks made with tap or well water (such as reconstituted juice) Unpasteurized milk Travelers’ Diarrhea Prevention: Pepto-Bismol: 2 chewable tablets 4 times per day. Side effects: blackening of tongue and stool; may cause nausea, constipation, and rarely tinnitus (ringing in the ears). Contraindicated with aspirin allergy and in some medical conditions. Treatment: Early self-treatment with antibiotics can limit the duration of illness to 6–24 hours in most cases. Ciprofloxacin: One 500 mg tablet twice daily for 1-3 days. Azithromycin: 1000 mg (four 250 mg tablets once) for one day (this regimen may cause nausea) or two 250mg tabs once a day for 1-3 days (less risk of nausea) Imodium can be used with antibiotic therapy to shorten illness duration, but should not be used on its own, as it may prolong symptoms Rehydrate with bottled water and electrolytes (such as a pinch of salt) Insect Borne Diseases Bugs (including mosquitoes, ticks, and some flies) can spread diseases such as malaria, yellow fever, dengue fever, and Japanese encephalitis, to name only a few. Many of these insect borne diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites. Malaria: If the CDC considers malaria a risk at your destination, it is always important to take malaria prophylaxis and avoid bug bites. Locals or other travelers may minimize the risk of malaria based on anecdotal information and not recommend medication. However, the risk varies from region to region and from traveler to traveler, within the same country. Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. Malaria Prophylactic Medications: (check with pharmacy for cost with your insurance) Chloroquine: One 500mg tablet once a week; start one week before travel to region with malaria, take every week while at risk, and for four weeks after leaving at risk area. o o Side effects uncommon (usually not serious enough to stop med): Nausea/vomiting, headache, dizziness, blurred vision and itching, may worsen psoriasis. Out of pocket cost: ~$28.30 for 7 day trip to region + $3.03 for each additional week of travel. May not be covered by all insurance. 3 Malarone: One tablet once daily; start one to two days before travel to region with malaria, every day while in at risk area, and for seven days after leaving at risk area. o o Doxycycline: One 100mg once daily; start one to two days before travel to region with malaria, every day while in at risk area, and for 28 days after leaving at risk area. o o Side effects uncommon (usually not serious enough to stop med): abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and headache. Do not take if pregnant, severe kidney disease, or allergic. Out of pocket cost: $106.10 for 7 day trip to region + ~$6.20 for each additional day of travel. Not covered by Aetna Student Health. May not be covered by insurance. Side effects: Sunburn (wear sunscreen), nausea/stomach pain if taken on empty stomach, pill can get lodged in esophagus (take with full glass of water and don’t lie down within 1 hour), vaginal yeast infection (bring over-the-counter yeast med). Don’t take if pregnant or allergic. Out of pocket cost: $192.10 for 7 day trip to region + $5.00 for each additional day of travel (current shortage). May be covered by most insurance. Malaria medications should be purchased before travel. Drugs purchased overseas may not be effective, and could be counterfeit as well as dangerous. Seek immediate healthcare if you develop a fever or flu-like illness while traveling or for up to one year after returning home. Inform healthcare provider of malaria risk history Avoid Bug Bites An insect repellent with at least 20% DEET can protect against mosquitoes and ticks. Insect repellents with the following active ingredients protect against mosquitoes only (but not ticks): Picaridin, Oil of lemon eucalyptus or PMD, IR3525. Make sure to read directions and reapply as directed to maintain effectiveness. Repellents containing a higher percentage of the active ingredient typically provide longer-lasting protection. Regardless of what product you use, if you start to get mosquito bites, reapply the repellent according to the label instructions. When using sunscreen, apply sunscreen first and insect repellent second. Consider using permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents); you can buy items already treated or can treat them yourself. Do not use permethrin directly on skin. Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats. Stay and sleep in screened or air-conditioned rooms. Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors. To prevent tick bites, tuck in shirts, tuck pants into socks, and wear closed shoes instead of sandals. Keep Away from Animals Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies. Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know. Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth. Avoid rodents and their urine and feces. If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Rabies vaccine may still be required after a possible rabies exposure, regardless of previous rabies shots. Seek medical evaluation as soon as possible. The risk of bird flu to travelers is extremely low. People who come in contact with live poultry may be at higher risk. Avoid live bird or poultry markets. Updated August 19, 2013 4
© Copyright 2025