How to develop SRM as a discipline
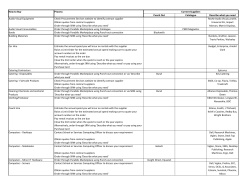
How to develop SRM as a discipline For it to work well it has to be a part of the corporate DNA A seminar on the development of SRM presented at the Premier ConfeX 2013 prepared by Adrian Bower, State of Flux Limited © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 1 The State of Flux SRM Report State of Flux has been performing Supplier Relationship research globally for the last five years. © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 2 Agenda What is SRM? How to develop SRM as a discipline: » Step 1: Understand current situation » Step 2: Create a plan » Step 3: Implementation – Key learnings » Step 4: Sustainability – What makes it last © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 3 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability What is SRM? © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 4 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Supplier relationship management in the wider context of procurement lifecycle management A discipline of working collaboratively with those suppliers that are vital to the success of the organisation, to build trust and maximise the mutual value of those relationships. Frameworks that measure and drive improved performance of contracts through the lifecycle of engagement. These can include bonuses, extensions scope expansion etc. Ensures that contracts fit the deal to mitigate risks and provide full value by improving the contracting approach which enables quick identification of contractual rights, obligations and liabilities. Establishes systems that consider causes and treatments to minimise the occurrence and outcomes of events, along with treatments to minimise the impact Reviewing a component of spend, identifying the best approach to testing and re-contracting the market ENHANCE VALUE ASSURE VALUE SECURE VALUE CAPTURE VALUE SRM PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT CONTRACT MANAGEMENT RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGIC SOURCING Pre-award © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 NEW VALUE Post-award 5 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability ‘Six pillars’ of SRM: Six key elements of best practice implementation © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 6 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Building on contract and performance management, SRM can deliver direct and indirect benefits through collaborating with key suppliers VALUE CREATION CUSTOMER OF CHOICE » Best resource » Capacity prioritisation » Preferred pricing » Responsiveness » Access to R&D » Executive focus » Account management » Contract value retained » Cost reduction/avoidance » Revenue generation » Speed to market » Risk reduction » Incremental value » Competitive edge STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT » Shared vision » Joint goals and objectives » Investment » Improved planning » Market knowledge » Vested interest in success » Win : Win INNOVATION & IMPROVEMENT » Breakthrough innovation » Guided innovation » Shared intelligence » Joint R&D » Continuous improvement » Shared road maps » Value engineering GOVERNANCE & ACCOUNTABILITY COLLABORATIVE WORKING » “One truth” » Improved decision making » Consistency » Clear RACI » Optimise time & resource » Transparency » Compliance » Decision making » Problem solving » Development » Shared risk and reward » Open book » Value chain improvement » Risk management VALUE RISK © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 © State of Flux Ltd 2013 7 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Degrees of supplier management in the context of value If applied correctly throughout the procurement lifecycle Strategic Sourcing and Contract Management will secure and protect value. Performance Management will enhance value, whilst Supplier Relationship Management has the potential to create new value. SUPPLIER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT delivers value over and Contract Value to You above scope of contract Incremental value gains over life of contract from PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT and continuous improvement Optimal Negotiated Value Robust CONTRACT MANAGEMENT retaining full contract value Contract never effectively implemented and VALUE ERODED from day one Value from Business Engagement Over zealous negotiation and continuous price squeeze is unsustainable. Net VALUE LOST as supplier is in an unsustainable position to maintain service and works to reclaim margin Historic Value Sourcing Requirements Definition Implementation © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 Time 8 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability SRM benefits reported through the 2012 global research The charts reproduced here indicate the range of benefits and value being reported by leaders and followers responding the to the 2012 survey. Level of post contract financial value being delivered directly by or enabled through SRM as reported by leaders and followers. (proportion of leaders reporting 8% + has doubled since 2011) © State of Flux Ltd 2013 Nature and range of benefits being reported by leaders and followers. Year on year trend is for a wider range of benefits to be reported. © State of Flux Ltd 2013 © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 9 How to develop SRM as a discipline Step 1: Baseline the current situation © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 10 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Capability assessment must consider all key organisational components across the major procurement functions Procurement functions need to take stock on the maturity of each element of their business and understand where SRM fits: Organisational Component • Supplier Relationship Management: Incremental value or incremental workload? People Supplier Relationship Management Process Category Management Strategy • Category Management: Proactive integration of business strategy and supplier capability or contract authoriser? Procurement Function • Governance and Strategy: Strategic Partner or Order Processor? Technology Governance and Strategy • Buying Management: ‘Amazon easy’ or bottleneck? Buying Management There is only so much change a business can consume © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 11 11 2. Baseline the current situation 1. What is SRM? 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability A ‘Voice of the Customer’ programme allows you to understand how you are perceived and provides intelligence about your customers priorities Why do we engage in a ‘Voice of the Customer’ programme? The concept of being a ‘provider of choice’ is increasingly recognised as a strategic objective. Few organisations really understand what customers genuinely think about them. Not many companies know how they are regarded in comparison to their competitors. What do we ask to achieve this? Ask challenging questions. Ask about scenarios. ‘What if?’ Ask what you can do to help. © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 12 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability The ‘Voice of the Supplier’ survey consists of questions which can be tailored according to your industry, business context and category focus. The standard State of Flux VoS survey consists of multiple choice and open-ended questions and is structured into six sections as follows: Section 1: Introduction » Key demographic information » Business unit/division interfaces » Major competitors doing business with (optional) Comparison of customer with four major competitors Growth & innovation 4.00 Section 2: Growth & innovation » Communication of business strategy, product/service roadmaps, etc » Openness to ideas/innovations » Process for evaluating ideas/innovations » Barriers to successful implementation » Functional responses to ideas/innovations Section 3: Sustainability » Communication of sustainability strategy » Impact of this strategy on supplier » Receptiveness to ideas to improve sustainability of products/services » Collaboration on sustainability initiatives 3.80 3.60 3.40 General relationship 3.20 3.00 Tendering & negotiation 2.80 2.60 Section 4: Operational » Planning and forecasting process » Ordering and receiving process » Interfaces at operational level Competitor 1 2.40 Competitor 2 Customer Section 5: Commercial » Receptiveness to proposals (e.g., reducing total cost, risk sharing) » Tendering and negotiation process » Sharing of rewards » Use of key performance indicators » Payment process Section 6: General relationship » Degree of business alignment » Experiences of dealing with customer (e.g., trust, decision making, recognition) » ‘Customer of choice’ status » Comparison with major competitors (optional) © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 Competitor 3 Competitor 4 Ordering process & forecasting Payment 13 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Levels of maturity can be benchmarked through an SRM survey Based on responses to key questions embedded in their SRM survey questionnaire State of Flux have been able to separate ‘leaders’ in the development and deployment of SRM from ‘followers’ and plot these two groups on an SRM maturity model reproduced here. OPTIMISED ESTABLISHED DEVELOPING UNDEVELOPED © State of 2013 Flux © State of Flux Ltd Pty Ltd 2013 14 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability The anatomy of SRM – talent development For learning and development investments to deliver sustainable change, they must be put into a wider context of talent development. Job design, attracting talent and setting up people to be successful... Supporting, developing and retaining top talent... Ensuring pre-requisite capabilities and operational excellence is addressed... Customer of choice is won or lost through the interpersonal skills that make the difference... © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 15 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Nine key talent development factors assess and enable the value-add that ‘People and Skills’ bring to achieving SRM benefits © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 16 How to develop SRM as a discipline Step 2: Create a plan © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 17 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability To create a plan, consideration needs to be given to each of the six elements of SRM • The 6 P’s – planning and preparation prevent………. • Considering all components will allow a holistic approach to the response and avoid areas without focus disrupting the rest • Armed and ready for supplier, team and business questions • Develop your sales pitch: 20 – 2 – 20 • Fully estimate resource, budget, time and effort……..it’s good to only ask once © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 18 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Business Drivers and Value quantify the benefit of SRM in terms the business will understand • Understand the needs of the business and their priorities • Capture the cost of supply disruptions, missed revenue opportunities, examples of value delivery • Build a business case that effectively estimates costs and benefits, providing a vehicle to measure successful implementation • Be able to communicate value in their terms not yours © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 19 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Stakeholder Engagement and Support demonstrates makes is a enterprise initiative not just a procurement one • Identify who your Executive Sponsor/s is/are • Align the SRM programme to the solving of business challenges • Canvass stakeholder/customer opinion on priorities – ‘Voice of the Customer’ • Understand your supplier priorities – Revenue growth, innovation, brand appetite © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 20 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability We explore Governance and Process to provide a robust and consistent solution • Who is already doing SRM in what part of the business – critical high value areas? • What projects are also in train? How do you align them with your programme? • Who will own the process and governance? Who will run it? • Supplier segmentation and scalable framework. Industrialise it. © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 21 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability A deep dive in to People and Skills reveals where you have effective skills that can be adopted and where there are development requirements • SRM is constantly recognised as an area that is under invested in when it comes to people development • Traditionally procurement training is targeted at commercial negotiation not collaboration • Understand and identify the ability of the team and future requirements • Develop existing capability and amend the recruitment process to attract the right new talent © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 22 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Knowing our Tools and Systems allows us to scale up to operate across the enterprise and retain knowledge within the business • Identify existing platforms, if any, within the business and understand their capability • Review against external opportunities and build into your technology roadmap • Create tools that will support the effective execution of SRM related activates and make it easy for the business to operate • Have a clear knowledge retention strategy – laptops and in peoples heads are not sustainable © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 23 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Relationship Characteristics provide the platform for the whole program. Encouraging collaboration and trust is proven to deliver benefit • From each of the other pillars understand where your business culture sits – win at all costs or collaborators • Define a set of values or align them with those of the business. Gain executive support • Be prepared to police manage behaviour – ‘call out’ behaviour that doesn’t align with the values • Share the creation of incremental value © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 24 How to develop SRM as a discipline Step 3: Implementation – key learnings © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 25 2. Baseline the current situation 1. What is SRM? 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Successful implementation is vital in achieving a successful SRM rollout There is no ‘one size fits all’ approach to SRM implementation, and the right approach must be chosen depending on your organisation’s priorities Approach Pros Run a pilot Big bang deployment » Serious issues can be contained to one business unit or area » Concentrated efforts leads to faster transition » Quick wins » Will have executive support » Opportunity to refine the implementation process » Can create a sense of urgency » Less time from implementation team can be more cost effective Cons » Takes time, which increases risks such as competing projects, project fatigue and staff changes » Learn as you go » May require temporary interfaces and bridges between systems, which can be costly » Stakeholder overload » Large amount of change at once » Risk of re-implementation © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 26 2. Baseline the current situation 1. What is SRM? 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability The journey to SRM PEOPLE PROCESS TECHNOLOGY 1 2 Respond to the need for change 3 Recognise that the current ‘As Is’ operating environment is no longer producing the required results 4 Identify 5 Design the desired ‘To Be’ outcomes a Change Management Framework and Implementation strategy 6 Implement a Change Management Framework Support the gradual Internalisation of Change COMMUNICATION with key stakeholders throughout the process Identify the business drivers and related SRM value Stakeholder engagement and support © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 Create the ‘burning platform’ • Is year on year savings a sustainable strategy? • Contract value being lost. • Risk not being managed. • Value and opportunities being missed. Define requirements People Process Technology Vision, goals and objectives Process ownership How to develop / identify best practice and use it? Develop an IT strategy to support PMO Implementation strategy Implementation support Resourcing and budget Develop a learning and development strategy 27 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Critical Success Factors » Collaborative working » Foundations » Adopt a more balanced approach » The elevator pitch » Develop more trust » Areas of good practice » Reward not reprimand » Scalable framework » Manage behaviour in the business © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 28 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Critical Success Factors » Collaborative working » Foundations » Do you have an SRM » The elevator pitch » Areas of good practice » Scalable framework © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 framework in place? » Do you have a senior SRM sponsor? 29 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Critical Success Factors » Collaborative working » Foundations » Have you defined SRM? » Do you have an SRM business case or » The elevator pitch communications pack » Areas of good practice ready to go? » Scalable framework » Does your stakeholder community understand the value of doing SRM? © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 30 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Critical Success Factors » Collaborative working » Foundations » Find the people who are already doing SRM well in » The elevator pitch » Areas of good practice » Scalable framework your organisation » Harness this good practice and share it across the organisation. © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 31 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability Critical Success Factors » Collaborative working » Foundations » The elevator pitch » One size does not fit all! » Segment your suppliers for improved performance. » Areas of good practice » Scalable framework © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 » Be clear about how you work with your suppliers. 32 How to develop SRM as a discipline Step 4: Sustainability – What makes it last? © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 33 1. What is SRM? 2. Baseline the current situation 3. Create a plan 4. Implementation 5. Sustainability How do you make it last longer than the head of SRM appointment? » Industrialise the processes, ensure their enterprise wide and make them auditable » Ensure reporting links through to the boardroom to create an ongoing business pull » Build it into job descriptions and performance objectives across the business » Add it into the induction process » Assess the benefit of delivery and report accordingly » Create external value in the creation and running of the programme » Retain the knowledge beyond the employees » Constantly evolve © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 34 ADRIAN BOWER CEO - STATE OF FLUX ANZ State of Flux Limited 50 York Street, Sydney. NSW 2000 M: +61 (0) 449840942 E: adrian.bower@stateofflux.com www.stateof-flux.com © State of Flux Pty Ltd 2013 35
© Copyright 2025