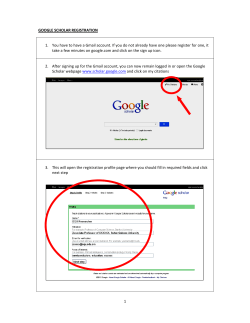
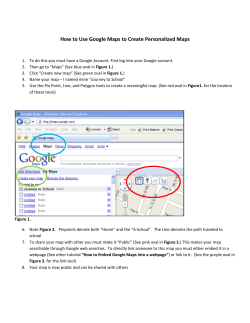
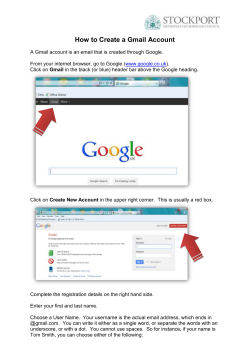
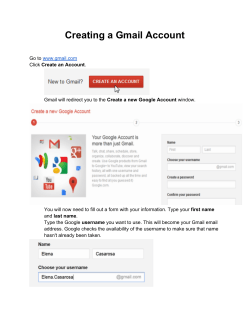
2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences
The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences 2014 the 6th International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing (ICGIP 2014) 2014 International conference on Networks and Information Security (ICNIS 2014) 2014 International Conference on Robotics and Computer Vision (ICRCV 2014) Conference Schedule Sponsored By Beijing, China October 24-26, 2014 www.icgip.org www.icnis.org www.icrcv.org The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Welcome to IACSIT Conference in Beijing October 24-26, 2014 Dear Distinguished Delegates, Welcome to the 2014 IACSIT Conference in Beijing, China. We’re confident that over the three days you’ll get the theoretical grounding, practical knowledge, and personal contacts that will help you build long-term, profitable and sustainable communication among researchers and practitioners working in a wide variety of scientific areas with a common interest in Graphic and Image Processing; Networks and Information Security and Robotics and Computer Vision. After more than half a year’s preparation, we finally will have those conferences to be held in Beijing, China during October 24-26, 2014 For the conferences of ICGIP 2014&ICNIS 2014&ICRCV 2014, we had received over 273 submissions, 89 excellent papers were accepted and published finally. Congratulations for those papers. On behalf of IACSIT organization, I would like to thank all the authors as well as the Program Committee members and reviewers. Their high competence, their enthusiasm, their time and expertise knowledge, enabled us to prepare the high-quality final program and helped to make the conference became a successful event. Once again, thanks for coming to IACSIT conferences, we are delegate to higher and better international conference experiences. We will sincerely listen to any suggestion and comment; we are looking forward to meeting you next time. Yours Sincerely, Sophie Tsang Director of Conference Department II, IACSIT The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences ANNOUNCEMENT *ICGIP 2014 conference papers will be published into the ICGIP proceedings, and will be included in the SPIE Digital Library, and provided to the Web of Science Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Science, Scopus, Ei Compendex, Inspec, Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic Search, and others, to ensure maximum awareness of the Proceedings. ICNIS 2014 conference papers will be published in the following Journals with ISSN. Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (JACN; ISSN: 1793-8244) Abstracting/Indexing: Engineering & Technology Digital Library, EBSCO, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, International Computer Science Digital Library (ICSDL), ProQuest, and Google Scholar. ICRCV 2014 conference papers will be published in one of the following Journals with ISSN. International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE; ISSN: 1793-8201) Abstracting/Indexing: Index Copernicus, Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, INSPEC, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI (INSPEC, IET). Journal of Automation and Control Engineering(JOACE; ISSN: 2301-3702) Abstracting/Indexing: Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and Electronic Journals Digital Library. *One best presentation will be selected from each session, the best one will be announced and award the certificate at the end of each session IACSIT Publication committee The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Instructions for Oral Workshop Devices Provided by the Conference Organizer: Laptops (with MS-Office & Adobe Reader) Projectors & Screen Laser Sticks Materials Provided by the Presenters: PowerPoint or PDF files Duration of each Presentation (Tentatively): Regular Oral Session: about 15 Minutes of Presentation 3 Minutes of Q&A Keynote Speech: 40 Minutes of Presentation including 5 Minutes of Q&A The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Conference Schedule Day 1, Friday, October 24, 2014 Registration: The Lobby of JIANGXI GRAND HOTEL 10:00am-12:00pm 13:30pm-17:00pm Arrival, Registration and Conference materials collection **Certificate for Participation can be collected at the registration counter** Day 2, Saturday, October 25, 2014 09:00am-09:05am Opening Remarks Keynote Speech I: 09:05am-09:50am Keynote Speech II: Morning 09:50am-10:35am Venue: Multifuncti onal Hall (1st floor) Prof. David Zhang Hong Kong Polytechnic University,Hong Kong 10:35am-10:55am Prof. Xudong Jiang Nanyang Technological University, China Coffer Break / Plenary Photo Keynote Speech III: 10:55am-11:40am Prof. Ming Yang, Southern Polytechnic University, USA 12:00pm-13:30pm Lunch State The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Afternoon 13:00pm-15:30pm Session I - Machine Vision Venue: 15:30pm-16:00pm Coffee Break Conference room 2 15:30pm-18:00pm Session II - Image processing (3rd floor) Venue: 13:00pm-15:30pm Session III - Pattern Recognition Conference 15:30pm-16:00pm Coffee Break room 3 (3rd floor) 15:30pm-18:00pm Session IV- Video processing and computer vision Venue: 13:00pm-15:30pm Session V - 3D reconstruction and visualization Conference 15:30pm-16:00pm Coffee Break room 5 (3rd floor) 16:00pm-18:00pm Session V - 3D reconstruction and visualization Dinner 18:00pm-20:30pm Day 3, Sunday, October 26, 2014 One-day Tour Set off in the hotel gate at 6:00 am The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Session I –Authors’ Oral Presentation (ICNIS 2014 & ICRCV 2014)---Machine Vision 13:00am-15:30pm, Session Chair: Dr. Weiping Zhu, University of New South Wales, Australia Opening Presentation(IS001) Network Topology Estimation using Normalized Temporal Correlation Weiping Zhu University of New South Wales, Australia IS001 Abstract—Almost all of the previous works in topology discovery use an indirect approach to estimate the topology of a network that introduce the dependency between the feature extracted from observation and the topology to be estimated. We in this paper advocate a direct approach to estimate the topology of a network that uses temporal characteristic observed by receivers to overcome the weakness of its predecessors. In addition, a number of features are proposed that can be used to identify the topology. Simulation study is carried out that confirms the direct approach can achieve the same as the indirect approach with less probes. Index Terms—Correlation, Similarity, Time Series, Topology Inference Trends & Future for Enterprise Integration Usman bin Danish Chawla and Lareb Hussain Halepoto Institute of Business Administration (IBA) – Karachi, Pakistan IS005 Abstract—this is no surprise that the businesses today depend heavily on information technology than they ever did. It is one of these technologies that have made interoperability, interconnection and knitting of applications an easier task. EAI is the combination of hardware and software to share data and process in manner undisturbed and unrestricted for those applications and data files that have been so integrated. This research report attempts to look at the evolution of EAI and the challenges that it faces presently and in future. Index Terms—Enterprise Integration, Trends, Service Bus Optimal Fault-tolerant Multi-robot Team Design using Robot Reliability GyuhoEoh, Beom H. Lee Seoul National University, South Korea CV004 Abstract—This paper presents an optimal multi-robot team design using robot reliability for satisfying desired probability of mission completion in fault system. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Previous studies in this area mainly described a quantitative analysis, but an analytic solution for optimal multi-robot team organization was not presented. The proposed method, however, suggests not only a quantitative analysis but also provides necessary information for optimal team organization. In addition, an algorithmic solution is also provided for the optimal multi-robot team design when a faulty robot occurs. Simulated experiments are presented for verifying the proposed method, which proves the efficiency of the method. Index Terms—Reliability, multi-robot, fault-tolerant system reliability function Enhanced Pose Estimation Method Using Selective Scan Data in Structured Environments Wonsok Yoo,Beom H. Lee Seoul National University, South Korea CV005 Abstract—This paper suggests enhanced robot pose estimation method by using selective scan data in structured environments. Previous pose estimation approaches, which estimate the pose by scan matching method, use scan data of constant interval. However, these approaches do not consider the property that scan matching result is affected by the scan data distribution in the overlapping areas between two consecutive scans. Our proposed method varies scan interval in order to adjust overlapping areas between current and next scans. Through the experiments, we compared our method to the previous approaches which use constant interval scans and verified improved performance of our new approach. Index Terms—Robot, pose estimation, scan matching, map building, selective data process Kalman Consensus based Multi-robot SLAM with a Rao-Blackwellized Particle Filter Seung-Hwan Lee, Beom H. Lee Seoul National University, South Korea CV007 Abstract—This paper addresses a multi-robot SLAM approach based on the Kalman consensus filter (KCF). Under the unknown initial condition, a reference robot designates the initial poses of other robots when the first rendezvous between them occurs. Accordingly, past and current poses and maps of these robots are estimated by an acausal filter and a causal filter. If initialized robots meet again, their current poses are updated using the KCF. Accordingly, their past poses and maps until the most recent rendezvous are also compensated through the acausal filter. In two simulations, the FastSLAM algorithm, which is a special case of Rao-Blackwellized particle filters, was employed for SLAM. The performance of the proposed approach was verified by comparing conventional approaches. Index Terms—Kalman Consensus Filter, Rao-Blackwellized particle filter, Multi-robot SLAM, FastSLAM The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Wheel Velocity Obstacles for Differential Drive Robot Navigation Jae D. Jeon and Beom H. Lee Seoul National University, South Korea CV008 Abstract—In this paper, we deal with the real-time navigation problem of a differential drive robot in dynamic environments. As a rule, the robot is controlled by wheel velocity commands at sampling intervals and moves along a straight line or a circular arc in accordance with those commands. Thus, we define the wheel velocity obstacle, which is a set of all the left and right wheel velocity pairs that induce collisions with obstacles within a given time horizon. Also, a navigation strategy is suggested that will allow the robot to reach its destination without colliding with obstacles. Our algorithm was found to outperform previously released collision avoidance algorithms in terms of safety through Monte Carlo simulations. Index Terms—Collision avoidance, motion planning, velocity obstacles, differential drive robot Accurate Visual Loop-Closure Detection using Bag-of-Words for Multiple Robots Jung H. Oh, Seung-Hwan Lee and Beom H. Lee Seoul National University, South Korea IV009 Abstract—We propose a method to detect loop-closures in a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) problem for multiple robots. Each robot should be able to detect other robots’ previously visited locations from camera measurements. To identify these places, our approach adapts the bag-of-words method in image recognition, and improves it by applying a Gaussian filter and a logistic function to correct the similarity scores. We can detect the robust loop-closures using only visual information of multiple robots. Experiments are performed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method in indoor environments. Index Terms—Loop-closure, mobile robots, SLAM, visual feature, bag-of-word Colored Point Cloud Registration with Improved Hue-Assisted Normal Distributions Transform Hyunki Hong and Beomhee Lee Seoul National University, South Korea Abstract—This paper describes an improved Hue-Assisted Normal Distributions Transform (HANDT), which enhances the accuracy of the registration of point clouds. In our previous work, HANDT was developed to improve the speed and accuracy of registration by utilizing the hue from the hue-saturation-value model. To improve the accuracy, the score function of HANDT is changed from the normal distribution function to the Mahalanobis distance function. In addition, the The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences CV015 functions of the hue mean and variance are modified for the circular property of the hue. The performance of normal distributions transform (NDT), HANDT, and improved HANDT are evaluated by benchmark data sets. As a result, the translation and rotation errors of improved HANDT are lower than those of NDT and HANDT. Index Terms—Hue, color, point cloud, registration, normal distributions transform (NDT) Fast Image Diffusion for Feature Detection and Description Lu Feng, Zhuangzhiwu and Xiang Long BeiHang University, China CV017 Abstract—In this paper, we introduce a new multiscale 2D feature detection and description method based on optimal O(1) bilateral filter feature (OBFF). Existing methods detect and describe features by analyzing the scale space generated by linear and nonlinear diffusion kernel function, like Gaussian scale space and anisotropic diffusion scale space. By using the anisotropic diffusion scale space, KAZE features achieve significant progress on the 2D feature detection by using the anisotropic diffusion scale space. It makes the blurring locally adaptive and retains better feature localization accuracy and distinctiveness than the SIFT method. Our method OBFF also generates the nonlinear scale space of image to detect the local feature. The optimal bilateral filter is advantage in object boundary preserving and antinoise ability and dramatically speed up feature detection in nonlinear scale space. We use the benchmark datasets to compare our method with state-of-the-art approaches. Index Terms—Bilateral filter, Nonlinear scale space, Feature detection, SIFT, Binary descriptor A Leukocyte Detection System using Scale Invariant Feature Transform Method Lina Lina, Arlends Chris, Bagus Mulyawan, and Agus Budi Dharmawan Tarumanagara University, Indonesia CV018 Abstract—Image inpainting is an important research topic in the field of image processing. The objective of inpainting is to “guess” the lost information according to surrounding image information, which can be applied in old photo restoration, object removal and demosaicing. Based on the foundation of previous literature of image inpainting and image modeling, this paper provides an overview of the state-of-art image inpainting methods. This survey first covers mathematics models of inpainting and different kinds of image impairment. Then it goes to the main components of an image, the structure and the texture, and states how these inpainting models and algorithms deal with the two separately, using PDE’s method, exemplar-based method and etc. Afterwards sparse-representation-based inpainting and related techniques are introduced. Experimental analysis will be presented to evaluate the relative merits of different algorithms, with the measure The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences of Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) as well as direct visual perception. Index Terms—Image inpainting, variational method, partial differential equation(PDE), exemplar based method, sparse representation A novel 3D camera based supervision system for safe human-robot interaction in the operating room Philip Nicolai, Jörg Raczkowsky, Heinz Wörn Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany CV020 Abstract—In anticipation of upcoming technological advances in the operating room, it is necessary to already give thought to how humans and robots can safely interact and cooperate in the operating room of the future. In this paper, we present a supervision system, consisting of seven 3D cameras, and the according shape cropping algorithm, which allows verifying the correct setup of surgical robots, detecting potential collisions between robots and their surroundings as well as monitoring the correctness of the robots’ motions. The system has already been successfully implemented, set up and evaluated. Index Terms—Robot assisted surgery, surgical robots, human-machine interaction, scene supervision Session II –Authors’ Oral Presentation (ICGIP 2014)--- Image processing 15:30pm-18:00pm, Session Chair: Dr. Hui Yu, University of Portsmouth, the United Kingdom A Multi-scale Fusion-based Dark Channel Prior Dehazing Algorithm Yujun Zeng, Xiaolin Liu College of Mechatronic Engineering and Automation, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China IP001 Abstract—During model-based image dehazing, the role of the accuracy of transmission estimation is crucial, which has a decisive effect on the final result. Considering that an ideal transmission map must be smooth, edge-preserving and free of redundant false details, a fusion-based dark channel prior (DCP) dehazing algorithm is presented in this paper. On the basis of DCP, a pixel-wise and a patch-wise transmission maps are obtained. Then an L0 smoothing filter and a large scale Gaussian filter are applied to them respectively. Finally, a much more accurate refined transmission map is attained through fusion and a haze-free image is restored using the atmosphere degradation model. Furthermore, a novel scheme for setting the lower bound of transmission adaptively is also put The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences forward. Experiments demonstrate a better and faster dehazing capability over original DCP algorithm and state-of-the-art dehazing methods, especially in suppressing halo artifacts, restoring details and coping with the haze existing in small-scale areas of depth discontinuity occluded by foreground.. Index Terms—Dehaze, dark channel prior, L0 smoothing, fusion Sparse Principle Component Analysis for Single Image Super-Resolution Qianying Zhang, Jitao Wu School of Mathematics and Systems Science, Beihang University, China IP007 Abstract—In this paper, we propose a novel image super-resolution method based on sparse principle component analysis. Various coupled sub-dictionaries are trained to represent high-resolution and low-resolution image patches. The proposed method simultaneously exploits the incoherence of the sub-dictionaries and nonlocal self-similarity existing in natural images. The purpose of introducing these two regularization terms is to design a novel dictionary learning algorithm for having good reconstruction. Furthermore, in the dictionary learning process, the algorithm can update the dictionary as a whole and reduce the computational cost significantly. Experimental results show the efficiency of the proposed method compared to the existing algorithms in terms of both PSNR and visual perception. Index Terms—Super-resolution, sub-dictionary learning, sparse representation, sparse principle component analysis Anaglyph videoanimations from oblique stereoimages Vit Vozenilek, Tomas Kralik Palacky University Olomouc, Czech Republic IP014 Abstract—The paper deals with the approach of compiling of animations from a pair of oblique stereoimages. The authors investigated as simple and cheap way as possible to develop such approach which will be available for wide scope of ordinary users with common equipment. They concentrated on three procedures of oblique stereoimage handling to compile sets of images, animations and analogue documents. After capturing construction site by a pair of web cameras the data were corrected, photogrammetrically adjusted (due to radial distortion) and exported. Firstly, a set of anaglyphic images were compiled, then they were trimmed and timeline was inserted. The final anaglyph animations are compiled in various versions. In addition, an anaglyphic book containing 150 images was created in a special way that the user can easily browse through its content. The main outputs are several unique anaglyph products, but more beneficial outputs are developed procedures of anaglyph visualization that can be applied with minor modifications to photographing of any objects. Index Terms—anaglyph image, videoanimation, geovisualization A Comparison of Image Inpainting Techniques Liu Yaojie, Shu Chang The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences School of Communication and Information Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China IP018 Abstract—Image inpainting is an important research topic in the field of image processing. The objective of inpainting is to “guess” the lost information according to surrounding image information, which can be applied in old photo restoration, object removal and demosaicing. Based on the foundation of previous literature of image inpainting and image modeling, this paper provides an overview of the state-of-art image inpainting methods. This survey first covers mathematics models of inpainting and different kinds of image impairment. Then it goes to the main components of an image, the structure and the texture, and states how these inpainting models and algorithms deal with the two separately, using PDE’s method, exemplar-based method and etc. Afterwards sparse-representation-based inpainting and related techniques are introduced. Experimental analysis will be presented to evaluate the relative merits of different algorithms, with the measure of Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) as well as direct visual perception. Index Terms—Image inpainting, variational method, partial differential equation(PDE), exemplar based method, sparse representation A Novel Color Filter Array and Demosaicking Algorithm for Hexagonal Grids Alexander Fröhlich and Andreas Unterweger Salzburg University of Applied Sciences, Austria IP023 Abstract—We propose a new color filter array for hexagonal sampling grids and a corresponding demosaicking algorithm. By exploiting properties of the human visual system in their design, we show that our proposed color filter array and its demosaicking algorithm are able to outperform the widely used Bayer pattern with state-of-the-art demosaicking algorithms in terms of both, objective and subjective image quality. Index Terms—Hexagonal Sampling, Color Filter Array, Demosaicking Effective and Fully Automatic Image Segmentation Using Quantum Entropy and Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks Songlin Du, Yaping Yan, and Yide Ma School of Information Science and Engineering, Lanzhou University, China IP040 Abstract—A novel image segmentation algorithm which uses quantum entropy and pulse-coupled neural networks (PCNN) is proposed in this paper. Optimal iteration of the PCNN is one of the key factors affecting segmentation accuracy. We borrow quantum entropy from quantum information to act as a criterion in determining optimal iteration of the PCNN. Optimal iteration is captured while total quantum entropy of the segments reaches a maximum. Moreover, compared with other PCNN-employed algorithms, the proposed algorithm works without any manual intervention, because all parameters of the PCNN are set The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences automatically. Experimental results prove that the proposed method can achieve much lower probabilities of error segmentation than other PCNN-based image segmentation algorithms, and this suggests that higher image segmentation quality is achieved by the proposed method. Index Terms—Image segmentation, pulse-coupled neural networks, quantum entropy, fully automatic An image denoising algorithm based on clustering and median filtering Wang YuLing , Li Ming, Li Li Department of Automation Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China IP059 Abstract—It is proposed of an improved median de-noising method, namely an image de-noising algorithm based on clustering and median filtering. The algorithm is a kind of image fast de-noising method based on the clustering idea, the singular point points are isolated from the image and then clustering. It is advantage to better protect the details of an image and to substantially reduce calculation. Compared with traditional median filter, mean filter and wiener filter, our approach is more adaptive and receives better results. While for images that have complex details such as texture images, the results of experiment show that the proposed algorithm works less well in the de-noising effect comparatively. Index Terms—image de-noising, clustering algorithm, median filter, PSN A Self-Adaptive Anti-Vibration Pipeline-Filtering Algorithm Houde Wu, Bin Wang, Ming Zhao , Wenhai Xu College of Information Science Technology, Dalian Maritime University, China IP070 IP080 Abstract—The mobile pipeline-filtering algorithm is a real-time algorithm that performs well in detecting small dim targets, but it is particularly sensitive to interframe vibration of sequence images. When searching for small dim targets at sea based on an infrared imaging system, irregular and random vibration of the airborne imaging platform causes huge interference problems for the mobile pipeline-filtering. This paper puts forward a pipeline-filtering algorithm that has a good performance on self-adaptive anti-vibration. In the block matching method using the normalized cross-correlations coefficient (NCC), the interframe vibration of sequence images is acquired in real time and used to correct coordinates of the single-frame detection results, and then the corrected detection results are used to complete the mobile pipeline-filtering. Experimental results show that the algorithm can overcome the problem of interframe vibration of sequence images, thus realizing accurate detection of small dim maritime targets. Index Terms—pipeline-filtering, anti-vibration, small dim target detection, infrared sequence images Image Haze Removal Algorithm for transmission lines Based on weighted Gaussian PDF WANG Wanguo , ZHANG Jingjing, LI Li, WANG Zhenli, LI Jianxiang, ZHAO The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Jinlong Electric Power Robotics Laboratory of SGCC, Shandong Electric Power Research Institute , China Abstract—Histogram specification is a useful algorithm of image enhancement field. This paper proposes an image haze removal algorithm of histogram specification based on the weighted Gaussian probability density function (Gaussian PDF). Firstly, we consider the characteristics of image histogram that captured when sunny, fogging and haze weather. Then, we solve the weak intensity of image specification through changing the variance and weighted Gaussian PDF. The performance of the algorithm could removal the effective of fog and experimental results show the superiority of the proposed algorithm compared with histogram specification. It also has much advantage in respect of low computational complexity, high efficiency, no manual intervention. Index Terms—Gaussian PDF, Histogram specification, image haze removal Sparse representation using multiple dictionaries for single image super-resolution Yih-Lon Lin, Chung-Ming Sung, and Yu-Min Chiang Department of Information Engineering, I-Shou University, Taiwan IP091 Abstract—New algorithms are proposed in this paper for single image super-resolution using multiple dictionaries based on sparse representation. In the proposed algorithms, a classifier is constructed which is based on the edge properties of image patches via the two lowest discrete cosine transformation (DCT) coefficients. The classifier partitions all training patches into three classes. Training patches from each of the three classes can then be used for the training of the corresponding dictionary via the K-SVD (singular value decomposition) algorithm. Experimental results show that the high resolution image quality using the proposed algorithms is better than that using the traditional bi-cubic interpolation and Yang’s method. Index Terms—Image super-resolution, sparse representation, image patch classification Weakly Supervised Glasses Removal Zhicheng Wang and Yisu Zhou School of Software, Tsinghua University, China IP095 Abstract—Glasses removal is an important task on face recognition, in this paper, we provide a weakly supervised method to remove eyeglasses from an input face image automatically. We choose sparse coding as face reconstruction method, and optical flow to find exact shape of glasses. We combine the two processes iteratively to remove glasses more accurately. The experimental results reveal that our method works much better than these algorithms alone, and it can remove various glasses to obtain natural looking glassless facial images. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Index Terms—Glasses removal, Sparse coding, Optical flow, Face reconstruction Pupil Segmentation Using Active Contour with Shape Prior Charles Ukpai, Satnam. S. Dlay and Wai. L. Woo University of Newcastle Upon-Tyne, United Kingdom IP110 Abstract—Segmentation is the process of defining the valid part/s of an image whi ch will be used for further processing like feature extraction, matching and decision making. Several segmentation algorithms have been developed for iris images howev er, they are mostly based on the assumption that iris boundaries has a circular shape. Here, we are interested in pupil segmentation which is a very important step in iris re cognition. In most pupil segmentation algorithms, it is often assumed that the pupil is circular in shape and few that considered non-circularity of the pupil paid little attenti on to time. These methods lead to inaccurate pupil segmentation for pupils with noncircular boundaries or a system which is too slow for real life implementation. In this paper, we propose a new pupil segmentation method based on active contour model with shape prior. Initially, the pupil’s position and radius is estimated using a statistic al procedure and circular Hough transform. Finally, the active contour model is initia lized close to the pupil’s boundary using information from the first step and segmenta tion is achieved using energy minimization based active contour. Pre-processing and post-processing were carried out to remove noise and reflections and remove occlusi ons respectively. Experimental results on CASIA V1.0 and 4.0 shows that the propos ed method is highly effective at segmenting irregular boundaries of the pupil. IndexTerms—pupil segmentation, active contour, feature extraction, biometrics, iris segmentation Session III–Authors’ Oral Presentation (ICGIP 2014)---Pattern Recognition 13:00pm-15:30pm, Session Chair: Prof. Vit Vozenilek, Palacky University, Czech Republic A Review of recent advances in 3D Face Recognition Jing Luo, Shu Ze Geng, Zhao Xia Xiao,Chun Bo Xiu Tianjin Polytechnic University, China. IP003 Abstract—Face recognition based on machine vision has achieved great advances and been widely used in the various fields. However, there are some challenges on the face recognition, such as facial pose, variations in illumination, and facial The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences expression. So, this paper gives the recent advances in 3D face recognition. 3D face recognition approaches are categorized into four groups: minutiae approach, space transform approach, geometric features approach, model approach. Several typical approaches are compared in detail, including feature extraction, recognition algorithm, and the performance of the algorithm. Finally, this paper summarized the challenge existing in 3D face recognition and the future trend. This paper aims to help the researches majoring on face recognition. Index Terms—3D face recognition, geometric features, space transform, minutiae approach Combining Appearance and Geometric Features for Facial Expression Recognition Hui Yu, Honghai Liu University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth, UK IP202 Abstract—This paper introduces a method for facial expression recognition combining appearance and geometric facial features. The proposed framework consistently combines multiple facial representations at both global and local levels. First, covariance descriptors are computed to represent regional features combining various feature information with a low dimensionality. Then geometric features are detected to provide a general facial movement description of the facial expression. These appearance and geometric features are combined to form a vector representation of the facial expression. The proposed method is tested on the CK+ database and shows encouraging performance. Index Terms—Geometric features, covariance descriptors, facial expression, facial patches Adaptive Object Tracking via both positive and negative models Matching Shaomei Li, Chao Gao,Yawen Wang Information Technology Research Center of PLA Information Engineering University, China IP039 IP044 Abstract—To improve tracking drift which often occurs in adaptive tracking, an algorithm based on the fusion of tracking and detection is proposed in this paper. Firstly, object tracking is posed as abinary classification problem and is modeled by partial least squares (PLS) analysis. Secondly, tracking object frame by frame via particle filtering. Thirdly, validating the tracking reliability based on both positive and negative models matching. Finally, relocating the object based on SIFT features matching and voting when drift occurs. Object appearance model is updated at the same time. The algorithm can not only sense tracking drift but also relocate the object whenever needed. Experimental results demonstrate that this algorithm outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms on many challenging sequences. Index Terms—object tracking; tracking drift; partial least squares analysis; positive and negative models matching A Novel Hybrid Motion Detection Algorithm Based On 2-D Histogram Xiaomeng Su, Haiying Wang China Mobile Group Design Institute Co., Ltd., China The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Abstract—This article proposes a novel hybrid motion detection algorithm based on 2-D (2-Dimensional) spatio-temporal states histogram. The new algorithm combines the idea of image change detection based on 2-D histogram and spatio-temporal entropy image segmentation. It quantifies the continuity of pixel state in time and space domain which are called TDF (Time Domain Filter) and SDF (Space Domain Filter) respectively. After this, put both channels of output data from TDF and SDF into a 2-D histogram. In the 2-D histogram, a curve division method helps to separate the foreground state points and the background ones more accurately. Innovatively, the new algorithm converts the video sequence to its histogram sequence, and transforms the difference of pixel’s value in the video sequence into the difference of pixel’s position in the 2-D histogram. Experimental results on different types of scenes added Gaussian noise shows that the proposed technique has strong ability of detecting moving objects. Index Terms—Motion detection, noise reducing, 2-D histogram, spatio-temporal property, contrast enhancement Two Dimensional Discriminant Neighborhood Preserving Embedding In Face Recognition Meng Pang, Jifeng Jiang, Chuang Lin and Binghui Wang School of Software, Dalian University of Technology, China IP057 Abstract—One of the key issues of face recognition is to extract the features of face images. In this paper, we propose a novel method, named two-dimensional discriminant neighborhood preserving embedding (2DDNPE), for image feature extraction and face recognition. 2DDNPE benefits from four techniques, i.e., neighborhood preserving embedding (NPE), locality preserving projection (LPP), image based projection and Fisher criterion. Firstly, NPE and LPP are two popular manifold learning techniques which can optimally preserve the local geometry structures of the original samples from different angles. Secondly, image based projection enables us to directly extract the optimal projection vectors from two-dimensional image matrices rather than vectors, which avoids the small sample size problem as well as reserves useful structural information embedded in the original images. Finally, the Fisher criterion applied in 2DDNPE can boost face recognition rates by minimizing the within-class distance, while maximizing the between-class distance. To evaluate the performance of 2DDNPE, several experiments are conducted on the ORL and Yale face datasets. The results corroborate that 2DDNPE outperforms the existing 1D feature extraction methods, such as NPE, LPP, LDA and PCA across all experiments with respect to recognition rate and training time. 2DDNPE also delivers consistently promising results compared with other competing 2D methods such as 2DNPP, 2DLPP, 2DLDA and 2DPCA. Index Terms—Two-dimensional projection, Fisher criterion, Feature extraction, Neighborhood preserving embedding (NPE), Locality preserving projection (LPP) The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Missile placement analysis based on improved SURF feature matching algorithm Kaida Yang, Wenjie Zhao, Dejun Li, Xiran Gong, Qian Sheng Aviation University of Air Force, China IP061 Abstract—The precious battle damage assessment by use of video images to analysis missile placement is a new study area. The article proposed an improved speeded up robust features algorithm named restricted speeded up robust features, which combined the combat application of TV-command-guided missiles and the characteristics of video image. Its restrictions mainly reflected in two aspects, one is to restrict extraction area of feature point; the second is to restrict the number of feature points. The process of missile placement analysis based on video image was designed and a video splicing process and random sample consensus purification were achieved. The RSURF algorithm is proved that has good real-time performance on the basis of guarantee the accuracy. Index Terms—missile placement analysis, speeded-up robust features, restricted speeded-up robust features, TV-command-guided missile, target damage assessment Detection and Recognition of Uneaten Fish Food Pellets in Aquaculture using Image Processing Huanyu Liu, Lihong Xu , Dawei Li College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Tongji University, China IP071 Abstract—The waste of fish food has always been a serious problem in aquaculture. On one hand, the leftover fish food spawns a big waste in the aquaculture industry because fish food accounts for a large proportion of the investment. On the other hand, the left over fish food may pollute the water and make fishes sick. In general, the reason for fish food waste is that there is no feedback about the consumption of delivered fish food after feeding. So it is extremely difficult for fish farmers to determine the amount of feedstuff that should be delivered each time and the feeding intervals. In this paper, we propose an effective method using image processing techniques to solve this problem. During feeding events, we use an underwater camera with supplementary LED lights to obtain images of uneaten fish food pellets on the tank bottom. An algorithm is then developed to figure out the number of left pellets using adaptive Otsu thresholding and a linear-time component labeling algorithm. This proposed algorithm proves to be effective in handling the non-uniform lighting and very accurate number of pellets are counted in experiments. Index Terms—Fish food pellets recognition, image processing, Otsu algorithm, connected area algorithm. Supervised Descent Method with Low rank and Sparsity Constraints for Robust Face Alignment Yubao Sun, Jiankang deng Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, China The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences IP086 Abstract—Supervised Descent Method (SDM) learns the descent directions of nonlinear least square objective in a supervised manner, which has been efficiently used for face alignment. However, SDM still may fail in the cases of partial occlusions and serious pose variations. To deal with this issue, we present a new method for robust face alignment by utilizing the low rank prior of human face and enforcing sparse structure of the descent directions. Our approach consists of low rank face frontalization and sparse descent steps. Firstly, in terms of the low rank prior of face image, we recover such a low-rank face from its deformed image and the associated deformation despite significant distortion and corruption. Alignment of the recovered frontal face image is more simple and effective. Then, we propose a sparsity regularized supervised descent model by enforcing the sparse structure of the descent directions under the l1constraint, which makes the model more effective in computation and robust to partial occlusion. Extensive results on several benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method is robust to facial occlusions and pose variations. Index Terms—Face alignment; sparse descent direction; low rank texture. A Statistical Description of 3D Lung Texture from CT Data Kraisorn Chaisaowong, Andreas Paul King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok, Thailand IP087 Abstract—A method was described to create a statistical description of 3D lung texture from CT data. The second order statistics, i.e. the gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), has been applied to characterize texture of lung by defining the joint probability distribution of pixel pairs. The required GLCM was extended to three-dimensional image regions to deal with CT volume data. For a fine-scale lung segmentation, both the 3D GLCM of lung and thorax without lung are required. Once the co-occurrence densities are measured, the 3D models of the joint probability density function for each describing direction of involving voxel pairs and for each class (lung or thorax) are estimated using mixture of Gaussians through the expectation-maximization algorithm. This leads to a feature space that describes the 3D lung texture. Index Terms—CT, lung, segmentation, pattern recognition, texture extraction, statistical models, co-occurrence matrix Saliency Region and Density Maximization for Salient Object Detection Xin He, Huiyun Jing National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team / Coordination Center of China, China IP090 Abstract—In this paper, we propose an alternative salient object detection method based on maximum saliency region and density. The proposed approach can automatically detect the salient object with a well-defined boundary. Saliency region and density maximization is used as the quality function to find the optimal window containing a salient object. And for efficiently executing window search, a The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences branch-and-bound search algorithm based on saliency region and density is proposed. Then the located window is used to initialize the GrabCut method, and the salient object with a well- defined boundary is extracted through applying GrabCut. Experimental results show that the proposed salient object detection approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Index Terms—Salient object detection, Branch-and bound search, Saliency region and density maximization Multi-lane detection based on multiple vanishing points detection Chuanxiang Li, Yiming Nie, Bin Dai, Tao Wu College of Mechatronic Engineering and Automation, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China IP107 Abstract—Lane detection plays a significant role in Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) for intelligent vehicles. In this paper we present a multi-lane detection method based on multiple vanishing points detection. A new multi-lane model assumes that a single lane, which has two approximately parallel boundaries, may not parallel to others on road plane. Non-parallel lanes associate with different vanishing points. A biological plausibility model is used to detect multiple vanishing points and fit lane model. Experimental results show that the proposed method can detect both parallel lanes and non-parallel lanes. Index Terms—Multi-lane detection, winner-take-all, inhibition of return multi-vanishing point detection, Gaze Estimation using a Hybrid Appearance and Motion Descriptor Chunshui Xiong, Lei Huang, Changping Liu Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China IP022 Abstract—It is a challenging problem to realize a robust and low cost gaze estimation system. Existing appearance-based and feature-based methods both have achieved impressive progress in the past several years, while their improvements are still limited by feature representation. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel descriptor combining eye appearance and pupil center-cornea reflections (PCCR). The hybrid gaze descriptor represents eye structure from both feature level and topology level. At the feature level, a glints-centered appearance descriptor is presented to capture intensity and contour information of eye, and a polynomial representation of normalized PCCR vector is employed to capture motion information of eyeball. At the topology level, the partial least squares is applied for feature fusion and selection. At last, sparse representation based regression is employed to map the descriptor to the point-of-gaze (PoG). Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves high accuracy and has a good tolerance to head movements. Index Terms—Gaze estimation, hybrid appearance and motion descriptor, pupil center-cornea reflections, partial least squares, sparse representation The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Session IV–Authors’ Oral Presentation (ICGIP 2014)--- Video processing and computer vision 15:30pm-18:00pm, Session Chair: Asst.Prof. Jing Luo, Tianjin Polytechnic University, China Groupwise Surface Correspondence Using Particle Filtering Guangxu Li, Hyoungseop Kim, Joo Kooi Tan and Seiji Ishikawa School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Tianjin Polytechnic University, China IP011 Abstract—To obtain an effective interpretation of organic shape using statistical shape models (SSMs), the correspondence of the landmarks through all the training samples is the most challenging part in model building. In this study, a coarse-to-fine groupwise correspondence method for 3-D polygonal surfaces is proposed. We manipulate a reference model in advance. Then all the training samples are mapped to a unified spherical parameter space. According to the positions of landmarks of the reference model, the candidate regions for correspondence are chosen. Finally we refine the perceptually correct correspondences between landmarks using particle filter algorithm, where the likelihood of local surface features are introduced as the criterion. The proposed method was performed on the correspondence of 9 cases of left lung training samples. Experimental results show the proposed method is flexible and under-constrained. Index Terms—Statistical shape model, correspondence, particle filter Image Authentication via Sparsity-Based Phase-Shifting Digital Holography Wen Chen and Xudong Chen Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore IP012 Abstract—Digital holography has been widely studied in recent years, and a number of applications have been demonstrated. In this paper, we demonstrate that sparsity-based phase-shifting digital holography can be applied for image authentication. In phase-shifting digital holography, the holograms are sequentially recorded. Only small parts of each hologram are available for numerical reconstruction. It is found that nonlinear correlation algorithm can be applied to simply authenticate the reconstructed object. The results illustrate that the recovered image can be correctly verified. In the developed system, the recorded holograms are highly compressed which can facilitate data storage or transmission, and one simple authentication strategy has been established instead of applying relatively complex algorithms (such as compressive sensing) to recover the object. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Index Terms—Image authentication, holography-based security, sparsity constraint. Fast Ellipse Detection by Elliptical Arcs Extracting and Grouping Yipeng Li, Chunhui Zhao Beijing Institute of Control Engineering, China IP030 Abstract—A novel and simple ellipse detection method is proposed in this paper. First, Canny operator is carried on the gray image to get edge image. Second, all the edge segments are obtained from edge image and output gradients of edge segments for further analysis. According to gradient direction, the edge segments are split into primitive lines and arcs. Then elliptical arcs are extracted from the results of splitting and an efficient grouping strategy is proposed to group elliptical arcs coming from the same ellipse as candidate ellipse. Finally, least-square fitting method is implemented to estimate the parameters of these candidate ellipses. Experiment results show that the proposed method is robust to noise and fast for real-time implementation. Index Terms—Ellipse detection; arc segments; gradient direction; least-square fitting method Target Confirmation and Relocation using the Correlation Filter in Mean Shift Tracking Yi Song, Shuxiao Li, Hongxing Chang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China IP031 IP054 Abstract—The accurate locating for the target is critical for robust visual tracking methods. This paper addresses the target position confirmation and relocation in mean shift tracking, and proposes a novel method to integrate a MOSSE based correlation filter into the mean shift tracker to obtain its ability of accurate locating. To confirm whether the estimated location of the target is accurate, four measures are evaluated. If the proposed conditions for relocating the target are satisfied, the estimated target position will be adjusted to be more accurate. When the target is occluded, a relocating approach is developed using the correlation filter to find the target after occlusion. The target model and the filter template are updated in each frame according to the evaluation results of the estimated target. Experimental results show the integration of the correlation filter can help the mean shift tracker locate and relocate the target well. Index Terms—object tracking, mean shift, target relocation, correlation filter Heuristic-driven GraphWavelet Modeling of Complex Terrain Teodor Cioaca, Bogdan Dumitrescu, Mihai-Sorin Stupariu, Ileana P˘atru-Stupariu, Magdalena N˘ap˘arus¸, Ioana Stoicescu, Alexander Peringer, Alexandre Buttler and Franc¸ois Golay University Politehnica of Bucharest, Romania The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Abstract—We present a novel method for building a multiresolution representation of large digital surface models. The surface points coincide with the nodes of a planar graph which can be processed using a critically sampled, invertible lifting scheme. To drive the lazy wavelet node partitioning, we employ an attribute aware cost function based on the generalized quadric error metric. The resulting algorithm can be applied to multivariate data by storing additional attributes at the graph’s nodes. We discuss how the cost computation mechanism can be coupled with the lifting scheme and examine the results by evaluating the root mean square error. The algorithm is experimentally tested using two multivariate LiDAR sets representing terrain surface and vegetation structure with different sampling densities. Index Terms—Graph wavelets, terrain modeling, multivariate heuristic cost Modeling synthetic radar image from a digital terrain model Philippe Durand, Luan Jaupi, Dariush Ghorbanzadeh and Jean Paul Rudant Conservatoire national des arts et metiers, France IP004 Abstract—In this paper we propose to simulate SAR radar images that can be acquired by aircraft or satellite. This corresponds to a real problematic, in fact, an airborne radar data acquisition campaign, was conducted in the south east of France. We want to estimate the geometric deformations that a digital terrain model can be subjected. By extrapolation, this construction should also allow to understand the image distortion if a plane is replaced by a satellite. This manipulation allow to judge the relevance of a space mission to quantify geological and geomorphological data, the radar wave is an electromagnetic wave, they have the advantage of overcoming atmospheric conditions since more wavelength is large is better crossing the cloud layer. Therefore imaging radar provides continuous monitoring Index Terms—Radar SAR images, mnt Video Object Segmentation via Adaptive Threshold based on Background Model Diversity Boubekeur Mohamed Bachir, SenLin Luo, Labidi Hocine and Benlefki Tarek School of Information and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, China IP081 Abstract—The background subtraction could be presented as classification process when investigating the upcoming frames in a video stream, taking in consideration in some cases: a temporal information, in other cases the spatial consistency, and these past years both of the considerations above. The classification often relied in most of the cases on a fixed threshold value. In this paper, a framework for background subtraction and moving object detection based on adaptive threshold measure and short/long frame differencing procedure is proposed. The presented framework explored the case of adaptive threshold using mean squared differences for a sampled background model. In addition, an intuitive update policy which is neither conservative nor blind is presented. The algorithm succeeded on extracting the moving foreground and isolating an accurate background. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Index Terms—Background Subtraction, video object segmentation, surveillance, square successive differences An Experimental Evaluation of Some Background Subtraction Algorithms Under a Variety of Video Surveillance Challenges Benlefki Tarek, Rongke Liu, Boubekeur Mohamed Bachir, Labidi Hocine School of Electronics and Information Engineering, China IP082 Abstract—This paper analyses the behavior of some existing background subtraction algorithms for possible use in automated video surveillance applications. The performance of the analyzed algorithms has been demonstrated by their authors on a selected video sequences to show the merits of their approaches. Nevertheless, choosing an adequate approach for a given application is not an easy task. In this study; by using background subtraction evaluation metrics combined with visual inspection, we asses in deep the performance of 04 algorithms under a variety of video surveillance challenges. This experimental analysis highlights the advantages and the limitations of each approach and helps in choosing the suitable method for a given video surveillance scenario. Index Terms—Video surveillance challenges, background subtraction algorithms, moving object detection. A robust Mean-shift Tracking Through Occlusion and Scale Based on Object Trajectory for Surveillance Camera Hocine Labidi, Sen-Lin Luo, Boubekeur Mohamed Bachir Department of Information and Electronic, Beijing Institute of Technology, China IP084 IP085 Abstract—Object tracking is an important part in surveillance systems, One of the algorithms used for this task is the mean-shift algorithm due to the robustness, computational efficiency and implementation ease. However the traditional mean-shift cannot effectively track the moving object when the scale changes, because of the fixed size of the tracking window, and can lose the target while an occlusion, In this study a method based on the trajectory direction of the moving object is presented to deal with the problem of scale change. Furthermore a histogram similarity metric is used to detect when target occlusion occurs, and a method based on multi kernel is proposed, to estimate which part is not in occlusion and this part will be used to extrapolate the motion of the object and gives an estimation of its position, Experimental results show that the improved methods have a good adaptability to the scale and occlusion of the target. Index Terms—Object tracking, Mean-shift, histogram similarity. target occlusion, scale changing. Real-time Video Analysis for Retail Stores Ehtesham Hassan and Avinash Kumar Maurya Department of Information and Electronic, Beijing Institute of Technology, China The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Abstract—With the advancement in video processing technologies, we can capture subtle human responses in an retail store environment which play decisive role in the store management. In this paper, we present a novel surveillance video based analytic system for retail stores targeting localized and global traffic estimate. Development of an intelligent system for human traffic estimation in real-life poses a challenging problem because of the variation and noise involved. In this direction, we begin with a novel human tracking system by an intelligent combination of motion based and image level object detection. We demonstrate the initial evaluation of this approach on available standard dataset yielding promising result. Exact traffic estimate in a retail store require correct separation of customers from service providers. We present a role based human classification framework using Gaussian mixture model for this task. A novel feature descriptor named graded colour histogram is defined for object representation. Using, our role based human classification and tracking system, we have defined a novel computationally efficient framework for two types of analytics generation i.e., region specific people count and dwell-time estimation. This system has been extensively evaluated and tested on four hours of real-life video captured from a retail store. Index Terms—Human detection and tracking, Video Analytics An Improved Bayesian Matting Method Based on Image statistic characteristics Wei Sun, Siwei Luo, Lina Wu School of Computer Science and Information Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, China IP099 Abstract—Image matting is an important task in image and video editing and has been studied for more than 30 years. In this paper we propose an improved interactive matting method. Starting from a coarse user-guided trimap, we first perform a color estimation based on texture and color information and use the result to refine the original trimap. Then with the new trimap, we apply soft matting process which is improved Bayesian matting with smoothness constraints. Experimental results on natural image show that this method is useful, especially for the images have similar texture feature in the background or the images which is hard to give a precise trimap. Index Terms—image matting, texture information, trimap Session V–Authors’ Oral Presentation (ICGIP 2014)--- 3D reconstruction and visualization 13:00pm-15:30pm,16:00pm-18:00pm Session Chair: Prof. Godfried T. Toussaint, New York University Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Opening Presentation(IP204) Measuring the Complexity of Binary Patterns: Kolmogorov Complexity versus Subsymmetries Godfried T. Toussaint New York University Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates IP204 Abstract—A simple mathematical measure of binary pattern complexity based on sub-symmetries possessed by the patterns, originally proposed by C. Alexander and S. Carey, is compared with a computationally feasible approximation of the Kolmog orov complexity proposed by F. Papentin & M. Krüger, in terms of the effectiveness with which the measures predict empirical measures and human judgments of patter ncomplexity, as well as with regards to their computational complexity. The results of experiments with binary images show that for small patterns it is difficult to explo it the hierarchy of languages proposed by Papentin & Krüger for the approximation of the Kolmogorov complexity. Furthermore, the Alexander-Carey measure exhibits higher correlation with the empirical measures and human judgments. In addition, ex perimental results show that the Alexander-Carey measure also predicts human judg ments of complexity with two data sets in the aural domain with musical rhythms, th us providing a connecting bridge between visual and auditory information processin g IndexTerms—binary patterns, visual patterns, auditory patterns, subsymmetries, Ale xander-Carey complexity, Papentin complexity, Kolmogorov complexity, image pro cessing, computer vision, computational music A New Improved Local Chan-Vese Model Wu Yiping, Shen Ming College of Mathematics and Computer Science, Fuzhou University, China IP005 IP016 Abstract—Based on the local image information, we propose a new improved local active contour model to segment inhomogeneous images. The level set evolution equation of the proposed model which is different from improved Chan-Vese (ICV) model and local Chan-Vese (LCV) model is ordinary differential equation. Without mean curvature and other complicate difference items, the implementation becomes simpler by employing a finite difference scheme, thus the efficiency of global segmentation is dramatically improved. Experimental results on synthetic images as well as real medical images are shown in the paper to demonstrate the segmentation accuracy, efficiency and robustness of the proposed method. Index Terms—Image segmentation, inhomogeneous, active contour model, ordinary differential equation Towards Relative Gradient and Its Applications Yang Wang, Hongzhi Liu, Zhonghai Wu Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Abstract—Image gradients which present directional changes of pixel values in an image are widely considered as important clues for salient features like edges. However, it is difficult to distinguish edges from details which also have large gradients merely based on gradients. In this paper, we propose a novel model called relative gradient which can overcome the problem and better distinguish edges from flat regions and details. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our model by improving some representative algorithms using the relative gradient instead of traditional gradient in contexts of edge detection and non-linear filtering. More applications can be found in image processing, analysis and related tasks. Index Terms—Relative gradient, edge detection, non-linear filtering Learning Historical Heritage with a Serious Game: A User Study of Heerlen Roman Bathhouse Wen Qi Open University Nederland, Heerlen, The Netherlands IP017 Abstract—The advances of computer games have shown their potentials for developing edutainment content and services. Current cultural heritages often make use of games in order to complement existing presentations, to create a memorable exhibition. It offers opportunities to reorganize and conceptualize historical, cultural and technological information or knowledge about the exhibits. To demonstrate the benefits of serious games in terms of facilitating the learning activities in a constructive and meaningful way, we designed a video game about the Heerlen Roman bathhouse heritage. This paper explains the design considerations of this Roman bathhouse game, with a particular focus on the link between game play and learning. In addition, we have carried out a user study to observe and measure the learning effects of this game. Both quantitative and qualitative data are collected to analyze the performance of the learners. The results have shown that this game indeed can help learners understand the important historical facts and the related knowledge of the heritage being studied. Further directions include converting the first-person game into a third-person or multiple players’ game. Index Terms—cultural heritage, Roman Bathhouse, pedagogy, serious game design Crystallization Mosaic Effects Generation via Superpixels Yuqi Xie, Pengbo Bo, Ye Yuan, Kuanquan Wang School of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, China IP021 Abstract—Art effect generation from digital images using computational tools has been a hot research topic in recent years. We propose a new method for generating crystallization mosaic effects from color images. Two key problems in generating pleasant mosaic effect are studied: grouping pixels into mosaic tiles and arrangement of mosaic tiles adapting to image features. To give visually pleasant mosaic effect, The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences we propose to create mosaic tiles by pixel clustering in feature space of color information, taking compactness of tiles into consideration as well. Moreover, we propose a method for processing feature boundaries in images which gives guidance for arranging mosaic tiles near image features. This method gives nearly uniform shape of mosaic tiles, adapting to feature lines in an esthetic way. The new approach considers both color distance and Euclidean distance of pixels, and thus is capable of giving mosaic tiles in a more pleasing manner. Some experiments are included to demonstrate the computational efficiency of the present method and its capability of generating visually pleasant mosaic tiles. Comparisons with existing approaches are also included to show the superiority of the new method. Index Terms—Mosaic effect, superpixel, image segmentation, Voronoi diagram Block-matching 3-D Transform Based Multi-focus Image Fusion Feng Zhu, Yingkun Hou, Minxian Li, Jingyu Yang School of Computer Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China IP024 Abstract—Block matching 3-D transform (BM3D) is an excellent image denoising algorithm, the success of this algorithm is that it makes full use of the image self-similarity. Profiting from the superior performance of the BM3D, this paper propose a multi-focus image fusion algorithm. A pair of the original images are both implemented BM3D respectively, averaging their low frequency coefficients can get the low frequency coefficient of the result image, the bigger high frequency coefficient in these two transforms is chosen as the high frequency coefficient of the result image; Implementing inverse 3-D transformation can obtain the fused image. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is better than the existing multi-focus image fusion algorithms on both the subjective visual and the objective evaluation. Index Terms—Image fusion, block-matching, 3-D transform Satellite Image Scene Classification Using Spatial Information Weiwei Song, Dunwei Wen,Ke Wang, Tong Liu and Mujun Zang College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China IP052 Abstract—In order to enhance the local feature’s describing capacity and improve the classification performance of high-resolution (HR) satellite images, we present an HR satellite image scene classification method that make use of spatial information of local feature. First, the spatial pyramid matching model (SPMM) is adopted to encode spatial information of local feature. Then, images are represented by the local feature descriptors and encoding information. Finally, the support vector machine (SVM) classifier is employed to classify image scenes. The experiment results on a real satellite image dataset show that our method can classify the scene classes with an 82.6% accuracy, which indicates that the method can work well on describing HR satellite images and classifying different scenes. Index Terms—Satellite image, spatial pyramid model, spatial information, support The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences vector machine Attitude measurement by using target schlieren graph and 3D digital model in wind tunnel CHENG Lei, YANG Yinong, XUE Bindang,ZHOU Fugen and BAI Xiangzhi School of Astronautics, Beihang University, China IP068 Abstract—Schlieren photography is normal device in wind tunnel. It records varying density of flow and also shows the attitude of model. In this paper, a method is proposed to estimate the model attitudes through matching the projection drawings of 3D digital model with the schlieren photography and high speed camera image. A simulation experiment is also designed to test the method. The results show that the maximum error less than 0.1°.We also use the method to deal with the wind tunnel test data, and experimental results show that the proposed system can meet the demands of the wind tunnel test. Index Terms—Attitude measurement, Schlieren graph, Image Matching, Wind tunnel 3D Reconstruction and Visualization of Plant Leaves Xiaomeng Gu, Lihong Xu,,Dawei Li, and Peng Zhang College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Tongji University, China IP072 Abstract—In this paper, a three-dimensional reconstruction method, which is based on point clouds and texture images, is used to realize the visualization of leaves of greenhouse crops. We take Epipremnum aureum as the object for study and focus on applying the triangular meshing method to organize and categorize scattered point cloud input data of leaves, and then construct a triangulated surface with interconnection topology to simulate the real surface of the object. At last we texture-map the leaf surface with real images to present a life-like 3D model which can be used to simulate the growth of greenhouse plants. Index Terms—visualization, triangulated meshing method, 3D reconstruction, greenhouse plants. Improved stereo matching applied to digitization of greenhouse plants Peng Zhang, Lihong Xu, Dawei Li, Xiaomeng Gu College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Tongji University, China IP073 Abstract—The digitization of greenhouse plants is an important aspect of digital agriculture. Its ultimate aim is to reconstruct a visible and interoperable virtual plant model on the computer by using state-of-the-art image process and computer graphics technologies. The most prominent difficulties of the digitization of greenhouse plants include how to acquire the three-dimensional shape data of greenhouse plants and how to carry out its realistic stereo reconstruction. Concerning these issues an effective method for the digitization of greenhouse plants The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences is proposed by using a binocular stereo vision system in this paper. Stereo vision is a technique aiming at inferring depth information from two or more cameras; it consists of four parts: calibration of the cameras, stereo rectification, search of stereo correspondence and triangulation. Through the final triangulation procedure, the 3D point cloud of the plant can be achieved. The proposed stereo vision system can facilitate further segmentation of plant organs such as stems and leaves; moreover, it can provide reliable digital samples for the visualization of greenhouse tomato plants. Index Terms—digitization, greenhouse plants, stereo matching, binocular stereo vision An efficient framework for modeling clouds from Landsat8 images Chunqiang Yuan Beihang University, Beijing, China IP083 Abstract—Cloud plays an important role in creating realistic outdoor scenes for video game and flight simulation applications. Classic methods have been proposed for cumulus cloud modeling. However, these methods are not flexible for modeling large cloud scenes with hundreds of clouds in that the user must repeatedly model each cloud and adjust its various properties. This paper presents a meteorologically based method to reconstruct cumulus clouds from high resolution Landsat8 satellite images. From these input satellite images, the clouds are first segmented from the background. Then, the cloud top surface is estimated from the temperature of the infrared image. After that, under a mild assumption of flat base for cumulus cloud, the base height of each cloud is computed by averaging the top height for pixels on the cloud edge. Then, the extinction is generated from the visible image. Finally, we enrich the initial shapes of clouds using a fractal method and represent the recovered clouds as a particle system. The experimental results demonstrate our method can yield realistic cloud scenes resembling those in the satellite images. Index Terms—satellite image, cumulus cloud, three-dimensional reconstruction, particle system An artificial target location method for curiosity rover LI Ying, PENG Jing, DU Ying China Academy of Space Technology, China IP092 Abstract—Template matching is a common method for object recognition and location. But the premise of template matching is the target should not change a lot in shape from the template image. When non-coplanar rotation exits, the traditional template matching method is helpless. By analyzing the artificial target of the curiosity rover, a two-step artificial target location method is proposed. Firstly, least squares ellipse fitting method is used to recognize the artificial target in the image and locate the center of each ellipse preliminary. Secondly, according to the preliminary result of ellipse fitting, the image is graph cut into pieces, and each piece only has one ellipse. Then Hough transform is used to locate the center of the artificial target precisely. Meanwhile, before edge detection, mathematical The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences morphology technology is conducted to remove the influence of the shadow in the image. Otsu algorithm is used to choose the threshold value of canny edge detector adaptively. Experiments are carried out based on artificial target images of curiosity rover, which show that the robustness of the algorithm in non-ideal illumination situation. The location accuracy is within 1 pixel. Index Terms—Hough transform, artificial target location, curiosity rover, ellipse fitting An Optimizing Processing Approach to Contrast Correction Based on Nonlinear Mapping of Windowed Tone Ming Gao, Shiyin Qin School of Automation Science and Electrical Engineering, Beihang University, China IP093 Abstract—A contrast correction method is presented based on nonlinear mapping of windowed tone. The main idea of method is to employ the local nonlinear mapping model on the small size with overlapping windows of traversal the whole image. At first, a high dynamic range (HDR) image contrast correction is introduced, and then through the formula deduction, a model for decision optimization of contrast correction is established, in which some constraints are termed as two adaptive guided images based on human visual properties so as to improve the optimal solution. Finally, the optimal contrast correction can be implemented by solving the optimizing processing problem through a linearized reduction. A series of experiments with the HDR natural images are carried out and the results of objective quality metrics have showed that the proposed method can effectively improve and optimize the contrast correction to outperform those current existing methods. Index Terms—contrast correction, nonlinear mapping, adaptive guided images, optimizing processing Learning Self-adaptive Color Harmony Model For Aesthetic Quality Classification Zhijie Kuang , Peng Lu, Xiaojie Wang Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China IP097 Abstract—Color harmony is one of the key aspects in aesthetic quality classification for photos. The existing color harmony models either are in lack of quantization schemes or can assess simple color patterns only. Therefore, these models cannot be applied to assess color harmony of photos directly. To address this problem, we proposed a simple data-based self-adaptive color harmony model. In this model, the hue distribution of a photo is fitted by mean shift based method, then features are extracted according to this distribution and finally the Gaussian mixture model is applied for learning features extracted from all the photos. The experimental results on eight categories datasets show that the proposed method outperforms the classic rule-based methods and the state-of-the-art data-based model. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Index Terms—Aesthetics, mean shift, color harmony, image quality, GMM A robust method for estimating motorbike count based on visual information learning Chi-Kien HUYNH\, THAI N. Dung, LE Thanh Sach, THOAI Nam, Kazuhiko HAMAMOTO HCMC University of Technology, Vietnam IP0103 Abstract—Estimating the number of vehicles in traffic videos is an important and challenging task in traffic surveillance, especially with a high level of occlusions between vehicles, e.g.in crowded urban area with people and/or motorbikes. In such the condition, the problem of separating individual vehicles from foreground silhouettes often requires complicated computation [1][2][3]. Thus, the counting problem is gradually shifted into drawing statistical inferences of target objects density from their shape [4], local features [5], etc. Those researches indicate a correlation between local features and the number of target objects. However, they are inadequate to construct an accurate model for vehicles density estimation. In this paper, we present a reliable method that is robust to illumination changes and partial affine transformations. It can achieve high accuracy in case of occlusions. Firstly, local features are extracted from images of the scene using Speed-Up Robust Features (SURF) method. For each image, a global feature vector is computed using a Bag-of-Words model which is constructed from the local features above. Finally, a mapping between the extracted global feature vectors and their labels (the number of motorbikes) is learned. That mapping provides us a strong prediction model for estimating the number of motorbikesin new images. The experimental results show that our proposed method can achieve a better accuracy in comparison to others. Index Terms—Crowd analysis, SURF, Bag-of-Words, motorbike counting, traffic density estimation Design of 3D Simulation Engine for Oilfield Safety Training Li Hua-Ming, Kang Bao-Sheng College of Information Science and Technology, China IP201 Abstract—Aiming at the demand for rapid custom development of 3D simulation system for oilfield safety training, this paper design and implement a 3D simulation engine based on script-driven method, multi-layer structure, pre-defined entity objects and high-level tools such as scene editor, script editor, program loader. A scripting language been defined to control the system's progress, events and operating results. Training teacher can use this engine to edit 3D virtual scenes, set the properties of entity objects, define the logic script of task, and produce a 3D simulation training system without any skills of programming. Through expanding entity class, this engine can be quickly applied to other virtual training areas. Index Terms—3D simulation engine, script-driven method, entity objects, safety training The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Poster Presentation 13:10pm-18:00pm Stereo Vision-Based Pedestrian Detection Using Dense Disparity Map- Based Detection and Segmentation Chung-Hee Lee, Dongyoung Kim Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology(DGIST), Daegu, KOREA IP035 Abstract—In this paper, we propose a stereo vision-based pedestrian detection method using a dense disparity map-based detection and segmentation algorithm. To enhance a pedestrian detection performance, we use a dense disparity map extracted from a global stereo matching algorithm. First, we extract a road feature information from the dense disparity map, which is a decision basis of presence or absence of obstacles on the road. It is very important to extract the road feature from the disparity for detecting obstacles robustly regardless of external traffic situations. The obstacle detection is performed with the road feature information to detect only obstacles from entire image. In other words, pedestrian candidates including various upright objects are detected in the obstacle detection stage. Each obstacle area tends to include multiple objects. Thus, a disparity map-based segmentation is performed to separate the obstacle area into each obstacle accurately. And then, accurate pedestrian areas are extracted from segmented obstacle areas using road contact and pedestrian height information. This stage enables to reduce false alarms and to enhance computing speed. To recognize pedestrians, classifier is performed in each verified pedestrian candidate. Finally, we perform a verification stage to examine the recognized pedestrian in detail. Our algorithms are verified by conducting experiments using ETH database. Index Terms—dense disparity map, stereo vision, pedestrian, segmentation, detection Barcode Localization With Region-Based Gradien t Statistical Analysis Zhiyuan Chen, Yuming Zhao Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China IP041 Abstract—Barcode, as a kind of data representation method, has been adopted in a wide range of areas. Especially with the rise of the smart phone and the hand-held de vice equipped with high resolution camera and great computation power, barcode tec hnique has found itself more extensive applications. In industrial field, barcode readi ng system is highly demanded to be robust to blur, illumination change, pitch, rotatio n, and scale change. This paper gives a new idea in localizing barcode under a regio The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences n-based gradient statistical analysis. Making this idea as the basis, four algorithms h ave been developed for dealing with Linear, PDF417, Stacked 1D1D and Stacked 1 D2D barcodes respectively. After being evaluated on our challenging dataset with m ore than 17000 images, the result shows that our methods can achieve an average loc alization accuracy of 82.17% with respect to 8 kinds of distortions and within an ave rage time of 12 ms. Index Terms—barcode localization, region-based gradient statistical analysis, vertices finding The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences About Keynote Speaker: Keynote Speaker I Prof. David Zhang Hong Kong Polytechnic University,Hong Kong Prof. David Zhang graduated in Computer Science from Peking University. He received his MSc in 1982 and his PhD in 1985 in Computer Science from the Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT), respectively. From 1986 to 1988 he was a Postdoctoral Fellow at Tsinghua University and then an Associate Professor at the Academia Sinica, Beijing. In 1994 he received his second PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. He is a Head, Department of Computing (2008-10) and Chair Professor since 2005 at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University where he is the Founding Director of the Biometrics Technology Centre (UGC/CRC) supported by the Hong Kong SAR Government in 1998. He also serves as Visiting Chair Professor in Tsinghua University, and Adjunct Professor in Peking University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, HIT, and the University of Waterloo. He is the Founder and Editor-in-Chief, International Journal of Image and Graphics (IJIG); Book Editor, Springer International Series on Biometrics (KISB); Organizer, the International Conference on Biometrics Authentication (ICBA); Associate Editor of more than ten international journals including IEEE Transactions and so on; and the author of more than 10 books,over 250 international journal papers and around 30 patents from USA/Japan/HK/China. According to Science Citation Index (SCI)- Expended and Google Scholar, his papers have got over 8,000 citations and 18,000 citations, respectively. Professor Zhang is recognized as a world leading expert in biometrics, specially palmprint recognition. He is a Croucher Senior Research Fellow, Distinguished Speaker of the IEEE Computer Society, and a Fellow of both IEEE and IAPR. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Keynote Speaker II Prof. Xudong Jiang Nanyang Technological University Xudong Jiang received the B.Eng. and M.Eng. degree from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China in 1983 and 1986, respectively, and received the Ph.D. degree from the Helmut Schmidt University Hamburg, Germany in 1997, all in electrical and electronic engineering. From 1986 to 1993, he worked as Lecturer at the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China where he received two Science and Technology Awards from the Ministry for Electronic Industry of China. He was a recipient of the German Konrad-Adenauer Foundation young scientist scholarship. From 1993 to 1997, he was with the Helmut Schmidt University Hamburg, Germany as scientific assistant. From 1998 to 2002, He worked with the Centre for Signal Processing (CSP), Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, first as Research Fellow and then as Senior Research Fellow, where he developed a fingerprint verification algorithm that achieved the fastest and the second most accurate fingerprint verification in the International Fingerprint Verification Competition (FVC2000). From 2002 to 2004 he worked as Lead Scientist and appointed as the Head of Biometrics Laboratory at the Institute for Infocomm Research, A*Star, Singapore. From 2002 to 2004 he was an Adjunct Assistant Professor. and joined NTU as a full time faculty member in 2004. Currently, Dr Jiang is an Associate Professor (tenured) of School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University and is appointed as Director of Centre for Information Security (CIS). Dr Jiang has published over seventy research papers in international refereed journals and conferences. He is also an inventor of one PCT patent application, three Singapore patents and three United States patents, some of which were commercialized. Dr Jiang is a senior member of IEEE and has been serving as Editorial Board Member, Guest Editor and Reviewer of multiple international journals, and serving as Program Committee member, Keynote Speaker and Session Chair of multiple international conferences. His research interest includes pattern recognition, computer vision, image and signal processing, biometrics, face recognition and fingerprint recognition. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Keynote Speaker III Prof. Ming Yang, Southern Polytechnic State University, USA Dr. Ming Yang is currently an Associate Professor with School of Computing and Software Engineering, Southern Polytechnic State University, USA. He obtained his BS and MS degrees in Electrical Engineering from Tianjin University (Tianjin, China) in 1997 and 2000 respectively, and his Ph.D. degree in Computer Science and Engineering from Wright State University (Dayton, Ohio, USA) in 2006. His research interests include Information Security, Multimedia Communication, and Mobile Security. He is the author/co-author of over fifty peer-reviewed journal, conference, and book chapter publications. His research has been supported by US National Science Foundation and Computing Research Association. He is currently serving the Co-Editor-in-Chief of International Journal of Monitoring and Surveillance Technology Research. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Conference Venue JIANGXI GRAND HOTEL http://www.bjjxhotel.com/index_en.php ADD: NO.8 Hengyitiao, Feng Tai District, Beijing , China 4 Boulevard Berthier, 17. Palais des Congrès - Batignolles, 75017 Paris TEL: 0086---10-6760 8866 FAX: 0086---10-8767 7728 The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Upcoming Conferences Information: Welcome to Our More Upcoming Conferences in 2014: DATE NAME PAPER WILL BE PUBLISHED BY Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Dec 18-20, 2014 Barcelona, Spain ICPSE 2014 2014 3rd International Conference on Power Science and Engineering http://www.icpse.org/ ICNB 2014 2014 5th International Conference on Nanotechnology and Biosensors http://www.icnb.org/ ICMPM 2014 2014 Conference Mechanical Materials International on Properties of http://www.icmpm.org/ Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. Journal of Computers (JCP, ISSN: 1796-203X, 20 Papers) ICCNE 2014 Dec 22-24, 2014 Barcelona, Spain 2014 International Conference on Communications and Network Engineering Journal of Software (JSW, ISSN: 1796-217X, 20 Papers) International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (IJFCC, ISSN: 2010-3751, 30 Papers) http://www.iccne.org/ International Journal of Computer and Communication Engineering (IJCCE, ISSN: 2010-3743, 30 Papers) ICOAI2014 2014 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence http://www.icoai.org/ Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (JACN, ISSN: 1793-8244, 20 Papers) International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing (IJMLC ISSN: 2010-3700) Abstracting/ Indexing: Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, DOAJ and EI (INSPEC, IET). The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. Journal of Computers (JCP, ISSN: 1796-203X, 20 Papers) Journal of Software (JSW, ISSN: 1796-217X, 20 Papers) Journal of Communications(JCM, 1796-2021, 20 papers) ISSN: ISSN: International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (IJFCC, ISSN: 2010-3751, 30 Papers) ICCSIT 2014 2014 7th International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology http://www.iccsit.org/ International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE, ISSN: 1793-8201, 30 Papers) International Journal of Computer and Electrical Engineering (IJCEE, ISSN: 1793-8163, 30 Papers) International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering (IJIEE, ISSN: 2010-3719, 20 Papers) International Journal of Information and Education Technology (IJIET, ISSN: 2010-3689, 20 Papers) Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (JACN, ISSN: 1793-8244, 20 Papers) Lecture Notes on Software Engineering (LNSE, ISSN: 2301-3559, Papers) Welcome to Our More Upcoming Conferences in 2015: ICSST 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Security Science and Technology http://www.icsst.org/ Jan 15-16, 2015 Portsmouth, UK ICNCS 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Network and Computer Science http://www.icncs.org/ ICK 2015 2015 International Conference on Knowledge http://www.ick.org/ All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN; 1793-8244 (Online Version); 1793-8236 (Print Version)) All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (IJFCC) (ISSN: 2010-3751) Abstracting/ Indexing: Google Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, and Crossref, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Knowledge Engineering (IJKE) The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences All accepted papers of ICMM 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). Feb 12-13, 2015 Busan, South Korea ICMM 2015 2015 6th International Conference on Mechatronics and Manufacturing http://www.icmm.org/ ICAEE 2015 2015 the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electronics Engineering http://www.icaee.org/ ICAPM 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Applied Physics and Mathematics http://www.icapm.org/ ICMLC 2015 Mar19-20, 2015 Florence, Italy 2015 7th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing http://www.icmlc.org/ ICEIT 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Educational and Information Technology http://www.iceit.org/ ICICN 2015 2015 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Networks http://www.icicn.org/ Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICAEE 2015 will be published by International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering (IJIEE) (ISSN: 2010-3719) Indexed by Google Scholar, Electronic Journals Library,Engineering & Technology Digital Library,Crossref and ProQuest, DOAJ, Ei (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICAPM 2015 will be published by International Journal of Applied Physics and Mathematics (IJAPM) (ISSN: 2010-362X) Indexed by EI (INSPEC, IET),Chemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ,Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Nanowerk Database, Crossref, Google Scholar and ProQuest. All accepted papers of ICMLC 2015 will be published by International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing (IJMLC) (ISSN: 2010-3700) Indexed by Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, DOAJ and EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICEIT 2015 will be published by Journal of Information and Education Technology (IJIET). (ISSN: 2010-3689) Indexed by EI (INSPEC, IET),Cabell's Directories, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, EBSCO, Google Scholar, Crossref and ProQuest. All accepted papers of ICICN 2015 will be published by Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (ISSN: 1793-8244) Indexed by Engineering & Technology Digital Library, EBSCO, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, International Computer Science Digital Library (ICSDL), ProQuest, and Google Scholar. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences ICTLE 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Traffic and Logistic Engineering http://www.ictle.org/ ICCEB 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Bioinformatics http://www.icceb.org/ ICFD 2015 2015 International Conference on Fluid Dynamics http://www.icfd.org/ April 6-7, 2015 Orlando, USA All accepted papers of ICTLE 2015 will be published by Journal of Traffic and Logistics Engineering (JTLE) (ISSN: 2301-3680) Indexed by Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and Electronic Journals Digital Library. All accepted papers of ICCEB 2015 will be published by International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN: 1793-8236). Indexed by Chemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, Index Copernicus, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICFD 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences All accepted papers of ICEEE 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. ICEEE 2015 2015 2nd International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering http://www.iceee.org/ International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering (ISSN: 2301-380X) Indexed by Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, etc. Journal of Automation and Control Engineering (ISSN: 2301-3702) Indexed by EI (INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. International Journal of Electrical Energy (ISSN: 2301-3656) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. All accepted papers of ICCIT 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Journal of Software (JSW, ISSN 1796-217X) April 28-29, 2015 Ankara, Turkey ICCIT 2015 2015 International Conference on Computer and Information Technology http://www.iccit.org/ International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE) (ISSN: 1793-8201) Indexed by Index Copernicus, Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI (INSPEC, IET), Cabell's Directories. International Journal of Computer and Electrical Engineering (IJCEE) (ISSN: 1793-8163) Indexed by Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Crossref, ProQuest, EI (INSPEC, IET), and Electronic Journals Library Lecture Notes on Information Theory (ISSN: 2301-3788) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences All accepted papers of IOAC 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) ICOAC 2015 2015 International Conference on Automatic Control http://www.icoac.org/ ICMML 2015 2015 6th International Conference on 2015 6th International Conference on Material and Manufacturing Technology http://www.icmml.org/ May 9-10, 2015 Bali, Indonesia ICRE 2015 2015 International Conference on Reliability Engineering http://www.icre.org/ Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICMML 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc All accepted papers of ICRE 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN: 1793-8236). Indexed by Chemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, Index Copernicus, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICLB 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). ICLB 2015 2015 International Conference on Lithium Batteries http://www.iclb.org/ Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences All accepted papers of ICCSN 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) ICCSN 2015 2015 the 7th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks http://www.iccsn.org/ Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. Journal of Communications (JCM) (ISSN: 1796-2021; DOI: 10.12720/jcm) Indexed by EI Compendex; SCOPUS; ULRICH's Periodicals Directory; Google Scholar; INSPEC; etc. All accepted papers of ICIIP 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) June 6-7, 2015 Chengdu, China ICIIP 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing http://www.iciip.org/ Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. Journal of Industrial and Intelligent Information (ISSN: 2301-3745; DOI: 10.12720/jiii) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. All accepted papers of ICWOC 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) ICWOC 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications http://www.icwoc.org/ ICDDM 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference on Database and Data Mining http://www.icddm.org/ July 2-3, 2015 Chicago, USA ICKD 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery http://www.ickd.org/ Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (ISSN: 2010-3751; DOI: 10.7763/IJFCC) Indexed by Google Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, and Crossref,DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICDDM 2015 will be published by WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. All accepted papers of ICKD 2015 will be published by International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE)(ISSN: 1793-8201) Indexed by Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, INSPEC, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI(INSPEC, IET). The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences ICOIP 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference on Optoelectronics and Image Processing http://www.icoip.org/ All accepted papers of ICDDM 2015 will be published by WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. All accepted papers of ICCSS 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering(IJEEE)(ISSN: 2301-380X) ICCSS 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Circuits, System and Simulation http://www.iccss.org/ Indexed by Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and Electronic Journals Digital Library. International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering(IJIEE)(ISSN: 2010-3719) Indexed by Google Scholar, Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Crossref and ProQuest, DOAJ, Ei (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICROM 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680) July20-21 2015 Madrid Spain ICROM 2015 ICAME 2015 The 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics http://www.icrom.org/ 2015 the 4th International Conference on Advances in Mechanics Engineering http://www.icame.org/ Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc All accepted papers of ICAME 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680) Applied Mechanics and Materials (ISSN: 1660-9336) is Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc From the next year, those conferences will be organized and assisted by American Society for Research(ASR), for more conferences and information about ASR, please visit: http://www.asr.org/ The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences Note The 2014 IACSIT Beijing Conferences
© Copyright 2025