Design
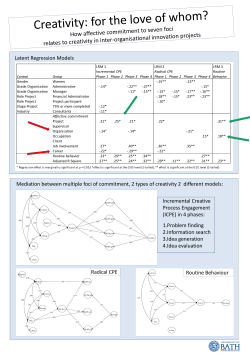
Design Design Design Design is an important aspect of the world in which we live and our everyday lives. Design focuses on the generation of ideas and their realisation. All constructed or created objects, places, events, systems and visual or sound communications involve aspects of design. Design is evident in the way different elements are selected, constructed and/or created to achieve particular expressive, aesthetic and/or functional purposes. The selection and arrangement of design elements in any object, place, event, system visual or sound communication will influence how it looks, sounds, feels, smells, tastes and works. Design Design Why do we design? To create a functional product, for example: • a building to live in • a piece of furniture built to store something • a set of instructions to use a piece of equipment. To express and communicate ideas, for example: • a presentation to explain a concept • an artwork or piece of writing that expresses a feeling • a map that describes the physical features of a place. To fulfil an aesthetic or sensual purpose, for example: • a comfortable chair • an elegant mathematical solution • a piece of music for listening pleasure. Design Background Design in the AusVELS Effective Design Design Background Design Awareness in Schools is intended to support all teachers in developing their own, and their students’, understanding of design elements and principles and how these can be applied across the curriculum. The Victorian Government is committed to building Victoria’s design capability through a series of initiatives that will enhance design production, promotion and education. Design Background Using this resource in the classroom Design Awareness in Schools is both a teacher reference and a classroom teaching tool. It can be used to stimulate classroom discussion and learning activities about design. For example, this resource can be used with students to: • foster deep learning about the place of design in the world • explore the notion of design • demonstrate the design process • enhance the presentation of ideas • illustrate the application of design elements and principles • explore careers in design. Design Design in the Standards In curriculum programs developed from the AusVELS, learning opportunities must be provided for students to: • develop an awareness of design • understand design elements and principles • apply design skills across the curriculum. An awareness of design can stimulate creativity and innovation, and enhance the presentation of work that demonstrates students’ understanding in all areas of learning. Design Design in the Standards Design Awareness in Schools illustrates how understanding of design can be developed through the three strands of the AusVELS; Physical, Personal and Social, Disciplinebased, and Interdisciplinary. This resource provides a range of student activities which focus on: • design elements and principles • the design process • design in ICT • careers in design. Design Design in the Standards Schools will continue to teach design in specialist subjects that draw specifically on the Design, Creativity and Technology, Information and Communications Technology and The Arts domains. This resource is not intended to make all teachers design specialists, but rather to demonstrate ways in which design can be effectively incorporated into student learning. Design Effective design Effective design arises from vibrant environments that celebrate: • creativity • aesthetics • critical thinking • diversity. Effective designs are sensitive to human needs. Design Effective design Creativity Creativity involves: • generating new ideas • solving problems • developing products in a unique and original manner. Creativity can be the result of: • imagination • intuition • step-by-step thinking • knowledge application. Design Effective design Creativity and innovation result in new products or ideas. Creativity requires: • an openness to possibilities or the unknown and unexpected (what if …?) • making connections between apparently unconnected ideas and forms • integrating different ways of knowing, for example physical, emotional, kinaesthetic. Creativity is aided by: • being able to give and receive constructive feedback • interpersonal and personal awareness • lateral thinking or viewing issues from different perspectives • risk-taking. Design Effective design Aesthetics Aesthetic appreciation involves perspectives that are: • cultural • social • historical. Aesthetics may be applied to: • perceptions • products • performances which are judged to have significance or appeal. Design Effective design Aesthetic judgments are often made routinely and almost unconsciously. We might, for example, have a preference for a colour or the way stripes run. There is nothing inherently superior in the object, idea or performance being judged. Other areas associated with making judgments about aesthetic qualities are knowledge and familiarity. Design Effective design Critical thinking Design thinking involves: • seeking multiple solutions to problems • innovation • imagination • judgment to create new images, products and outcomes. The design process involves: • thinking coherently and strategically • responding to challenges by producing solutions • problem-posing • reasoning • a willingness to admit errors and seek explanations • articulating processes and techniques using appropriate vocabulary.
© Copyright 2025