Document
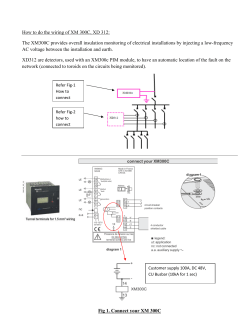
Best Practices for Achieving Low PIM Performance in DAS Networks Slide 1 Agenda What is Passive Intermodulation (PIM) Sources of PIM in a DAS environment Reasons why PIM is particularly problematic in DAS How a PIM tester works Best practices for mitigating PIM Anritsu MW82119A product features Slide 2 Passive Intermodulation (PIM) TX Signals at site Passive Intermodulation (PIM) F1 F2 2*F1–1*F2 Passive Intermodulation (PIM) 2*F2–1*F1 3*F1–2*F2 3*F2–2*F1 4*F1–3*F2 4*F2–3*F1 5*F2–4*F1 5*F1–4*F2 IM 9 IM 7 IM 5 IM 3 IM 3 IM 5 IM 7 IM 9 PIM = interference PIM = new frequencies generated by TX Signals at a cell site when they encounter non-linear junctions or materials in the RF path PIM falling in an operator’s uplink can elevate the noise floor: ▪ Dropped calls ▪ Access failures Slide 3 ▪ Slower data rates What does PIM look like at the site? PIM Mobile uplink signal Slide 4 What does PIM look like to the operator? QUIET BUSY QUIET High average noise level BUSY PIM Repair Lower average noise level Slide 5 What is a non-linear junction? Linear junctions Current Current increases linearly with applied voltage High pressure, metal-to-metal contacts Welded or soldered connections Voltage Non-linear junctions Current does not increase linearly with voltage. Low pressure, metal-to-metal contacts Current Oxide layers on metal surfaces Arcing across small air gaps or cracks Voltage What is non-linear in a DAS? Damaged / poorly made components Broken cracked solder joints Loose internal fasteners Braided cables with crimp connectors Nickel plating Shipping damage Slide 7 What is non-linear in a DAS? BTS #1 Input Out Out BTS #2 Input Slide 8 High power RF terminations Notorious for poor PIM Impact depends on frequencies being combined What is non-linear in a DAS? Metal flakes inside RF connectors Worse when touching inner or outer conductor Slide 9 What is non-linear a DAS? Poor cable termination Loose metal flakes Rough / irregular metal edges Slide 10 What is non-linear a DAS? Metal flakes inside cables Plenum rated cables have no foam to prevent metal flakes from falling inside Slide 11 What is non-linear in a DAS? Loose RF connectors Must be torqued with a torque wrench Slide 12 What is non-linear in a DAS? Type-N connectors Easy to damage contacting surfaces if over torqued Tend to loosen over time 7/16 DIN connectors better 4.1/9.5 or 4.3/10 “mini DIN” connectors also better Slide 13 What is non-linear in a DAS? External PIM Sources Fire suppression pipes Antennas flush mounted to ceiling Air handling ductwork Metal hangers Lighting fixtures Ceiling tile frames Etc., etc., etc. Slide 14 And… there are many opportunities for PIM! Floor 3 Radio 1 Radio 2 Floor 2 Floor 1 In this simple example: 63 RF connections 14 power dividers 31 cable assemblies 1 hybrid combiner 15 antennas 1 RF termination Slide 15 Where does PIM occur? F1 F2 2*F1–1*F2 2*F2–1*F1 3*F1–2*F2 3*F2–2*F1 4*F2–3*F1 4*F1–3*F2 5*F2–4*F1 5*F1–4*F2 IM 9 IM 7 IM 5 IM 3 IM 3 BTS Uplink IM 5 BTS Downlink PIM occurs at mathematical combinations of the Tx frequencies F1 = 1930 MHz F2 = 1945 MHz • IM3 = (2*1930) – (1*1945) = 1915 MHz IM3 = (2*1945) – (1*1930) = 1960 MHz • IM5 = (3*1930) – (2*1945) = 1900 MHz IM5 = (3*1945) – (2*1930) = 1975 MHz • IM7 = (4*1930) – (3*1945) = 1885 MHz IM7 = (4*1945) – (3*1930) = 1990 MHz • IM9 = (5*1930) – (4*1945) = 1870 MHz IM9 = (5*1945) – (4*1930) = 2005 MHz Slide 16 IM 7 IM 9 Where does PIM occur? (the easy way) F1 F2 15 MHz 15 MHz 15 MHz 15 MHz 15 MHz 15 MHz 15 MHz 15 MHz 15 MHz IM 9 IM 7 IM 5 BTS Uplink IM 3 IM 3 BTS Downlink Slide 17 IM 5 IM 7 IM 9 Where does PIM occur? (the easy way) F2 F1 30 MHz 30 MHz 30 MHz 30 MHz IM 5 30 MHz IM 3 BTS Uplink IM 3 BTS Downlink Wide frequency spacing moves IM products farther apart Increases probability that low order IM product will fall in uplink band Slide 18 IM 5 Neutral Host Systems Increase Probability that IM Products Will Fall in Rx Band Single PCS operator: FCC did a good job! IM 11 first product that falls in A-block uplink Multiple operators / bands: Different story! IM 3 falls in E / F block uplink IM 5 falls in A-block Slide 19 What is the bandwidth of PIM signals? F1 F2 200 KHz 200 KHz 600 KHz 600 KHz 1 MHz 1 MHz 1.4 MHz 1.4 MHz 1.8 MHz 1.8 MHz IM 9 IM 7 IM 5 BTS Uplink IM 3 IM 3 IM 5 BTS Downlink PIM bandwidth increases as carrier bandwidth increases PIM bandwidth increase with PIM order Slide 20 IM 7 IM 9 Can one wide band carrier generate PIM? 5 MHz 5 MHz 5 MHz 5 MHz 5 MHz 5 MHz 5 MHz 5 MHz IM 3 IM 5 IM 7 IM 9 BTS Uplink BTS Downlink YES ! Signal is composed of individual sub-carrier frequencies Slide 21 5 MHz What is the solution? LTE Eliminate non-linearity so that multiple frequencies can peacefully co-exist! CDMA Slide 22 How do we measure linearity? F1, F2 Load Test lead IM products PIM PIM tester PIM With a PIM tester! Inject two CW test signals at a known magnitude Measure 3rd order intermodulation product (IM3) IM3 “characterizes” the linearity of the system If IM3 is low = linearity is good If IM3 is high = linearity is poor Slide 23 Reducing IM3 Reduces all IM Products F1 F2 IM 3 IM 3 A IM 11 Noise Floor A IM 9 IM 7 IM 5 IM 5 BTS Uplink (Rx) BTS Downlink (Tx) Low IM3 = good linearity Low IM3 drives higher order products below the noise floor Slide 24 IM 7 Best Practices for Achieving Low PIM performance in a DAS Slide 25 1) Start with high quality components Only use RF components that: Are designed for low PIM performance Proper material selection No loose metal-to-metal junctions IEC-62037-1 provides more extensive list of design guidelines From companies that: Own PIM test equipment Have their manufacturing processes under control 100% test to verify performance (-150dBc with 2x 20W test tones ) Slide 26 2) Use crews that are PIM certified Understand the importance of cleanliness Use alcohol swabs to clean mated pairs of connectors Vacuum end of cables before attaching connectors Understand the importance of proper cable preparation Cut plenum rated cables with razor blade cutter (not saw) Use sharp cutting tools Use the correct tools for the type of cable in use Understand the importance of tight connections Always use a torque wrench (DIN) Do not over/under tighten (Type-N) Have experience operating PIM test equipment Slide 27 Radio 2 Radio 1 3) PIM test as you build Antenna location tests Sector test Branch test System test Floor test Slide 28 3) PIM test as you build (con’t) Problems are identified and corrected before being replicated throughout the DAS Faster to locate PIM sources when testing smaller sections Easier access to antennas / splitters to troubleshoot and correct problems Tools, materials, man-lifts, still on hand Reduced re-work at antenna locations (when antenna locations are pretested) Slide 29 Antenna Location Testing Place antenna as close to design location as possible using low PIM pole Perform PIM test Low test power (15 - 30 dBm typical) Lowest frequency only (700 or 850 MHz) Pass/Fail limit (depends on test power) Find passing location within 1 m of design location Small movements = big changes in PIM! PIM tester Slide 30 Things to Avoid Around Antennas: For every rule there is an exception This is why it is important to test! Try to avoid placing antennas within 1m of: Metal seams (ductwork, etc.) Concrete with obvious signs of rust Lighting fixtures Electronic devices Products containing RF ID tags Slide 31 PIM Master MW82119A Features Slide 32 Key Specifications / Capabilities for DAS Parameter Specification Small size 350 x 314 x 152mm (13.8 x 12.4 x 6.0in) Light weight 9 kg to 12 kg * (20 lb to 27 lb) Battery operation > 3.0 hours Wide power range 25dBm to 46dBm (0.3W to 39.8W) Low residual PIM -117 dBm @ 2x 43dBm Distance-to-PIM™ YES PIM vs. Time YES Remote Control YES * - Weight varies by frequency option Slide 33 Battery Operation = Enhanced Portability Slide 34 PIM vs. Time Capability PIM magnitude vs. time Tapping on RF connections Limit Line Tap on all RF connections while performing the PIM test Visual indication of PIM stability Peak PIM held for Pass/Fail Slide 35 Distance-to-PIM (DTP) Capability The fastest way to locate PIM PIM magnitude vs. distance Eliminates guess-work Able to see PIM beyond antenna 6 markers + marker table to identify multiple sources Slide 36 Wide Range of Test Accessories 2000-1745-R - Backpack Accessory Kit 760-259-R – Transit case (Holds MW82119A only) 760-265-R – Transit case (Holds MW82119A plus accessories) (accessories not included) 2000-1746-R - Hard Case Accessory Kit Slide 37 Conclusion PIM is a challenge in DAS environments Many potential sources More harmful frequency combinations Best practices for mitigating PIM include: Using high quality components Using trained installation crews PIM testing as you build (starting with antenna locations) Anritsu PIM Master is well suited for PIM testing in a DAS environments Exceptional portability Fully integrated, Distance-to-PIM (DTP) technology Slide 38
© Copyright 2025